
Potential health hazards of fast food

The Dangerous Effects of Fast Food: Why You Should Think Twice Before Eating It
In today's fast-paced world, fast food has become a staple for many people due to its convenience, affordability, and quick service. However, what many people fail to realize is that frequent consumption of fast food can have serious consequences on our health. From weight gain to heart disease, the dangers of fast food are numerous and should not be ignored.
In this article, we’ll dive deep into the harmful effects of eating fast food regularly and how it can impact your overall health in the long run.
1. Weight Gain and Obesity

One of the most immediate consequences of eating fast food is weight gain. Fast food is typically high in calories, fats, and sugars while offering little nutritional value. Consuming fast food frequently leads to an excess of calories, which are stored as fat in the body, resulting in weight gain and potentially obesity.
Fast food often contains large portion sizes, which can cause individuals to consume more than their daily recommended intake of calories in a single meal. Over time, this can lead to significant weight gain and increase the risk of developing obesity-related health conditions, including type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, and heart disease.
2. Increased Risk of Heart Disease
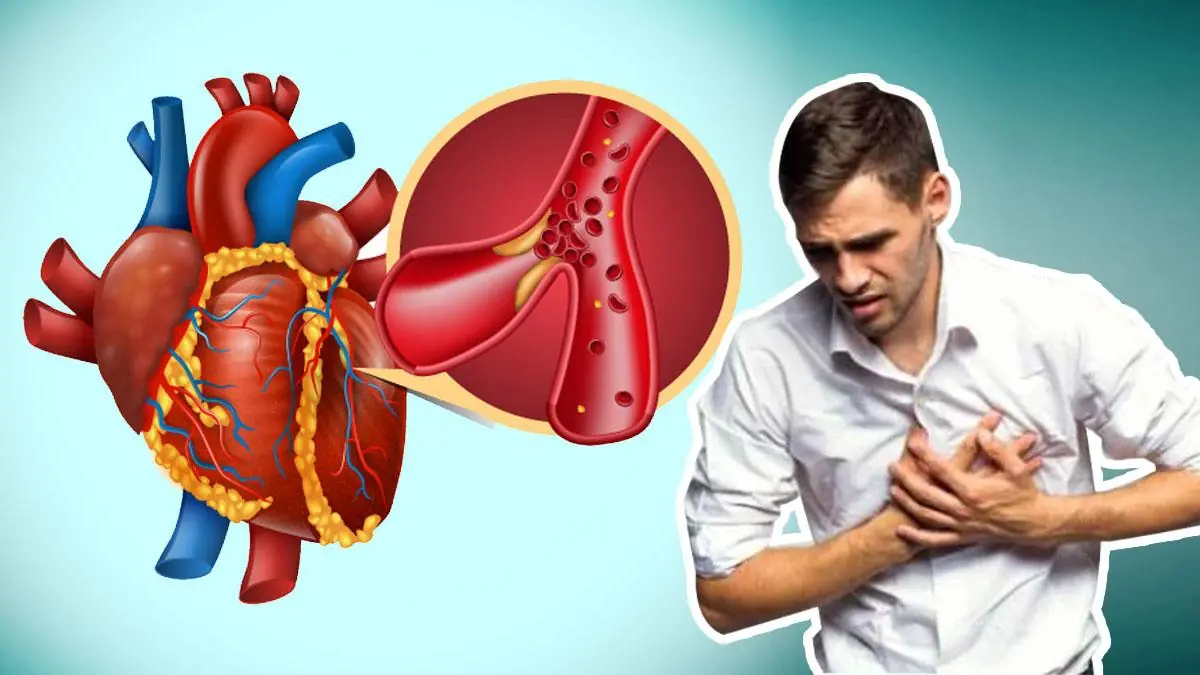
Many fast food items are high in unhealthy fats, such as trans fats and saturated fats, which can significantly increase the risk of heart disease. These fats can raise bad cholesterol (LDL) levels while lowering good cholesterol (HDL), which leads to the buildup of plaque in the arteries. Over time, this can result in atherosclerosis, a condition where the arteries become narrow and blocked, increasing the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
Additionally, fast food often contains high amounts of sodium, which can raise blood pressure and further strain the heart. Consistently consuming foods that are high in fats, sodium, and cholesterol is a major contributor to the development of heart disease.
3. Poor Digestive Health
Fast food is often made with low-quality ingredients and is rich in artificial preservatives and additives. These can have a negative impact on your digestive system. High-fat foods can be difficult to digest, leading to gas, bloating, acid reflux, and other gastrointestinal issues.
Furthermore, fast food lacks essential fiber, which is necessary for healthy digestion and regular bowel movements. A low-fiber diet can lead to constipation, digestive discomfort, and increase the risk of colon cancer over time.
4. Increased Risk of Type 2 Diabetes
Fast food is often loaded with simple carbohydrates and refined sugars, which can cause blood sugar spikes and insulin resistance. Over time, this leads to type 2 diabetes, a condition where the body no longer responds properly to insulin, resulting in high blood sugar levels.
The high glycemic index of fast food can cause blood sugar levels to rise quickly, and repeated consumption of these foods can overwhelm the body’s ability to regulate glucose. Insulin resistance, combined with other risk factors such as obesity and high blood pressure, significantly increases the likelihood of developing type 2 diabetes.
5. Mental Health Issues
The impact of fast food on mental health is often overlooked, but recent studies have shown a connection between poor dietary habits and mental health disorders. Fast food is high in unhealthy fats and sugars, which can affect the brain’s chemistry and lead to mood swings, irritability, and depression.
There is growing evidence to suggest that a diet rich in processed foods and low in essential nutrients can negatively affect brain function, leading to conditions such as anxiety, depression, and even cognitive decline. Consuming fast food regularly can lead to imbalanced blood sugar levels, which in turn can cause energy crashes and mood swings throughout the day.
6. Liver Damage
Many fast food items are high in fructose (often in the form of high-fructose corn syrup), which has been linked to fatty liver disease. This excess sugar can be stored as fat in the liver, leading to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). NAFLD can lead to inflammation and scarring of the liver, impairing its ability to function properly.
Over time, consuming large amounts of sugar and unhealthy fats can damage the liver, increasing the risk of cirrhosis and liver failure.
7. Weakened Immune System
Fast food is often low in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that are essential for a healthy immune system. The lack of nutrient-dense foods in a typical fast food meal can weaken the immune system, making the body more susceptible to infections, illnesses, and even chronic diseases.
In addition, high sugar and fat intake from fast food can increase inflammation, which is linked to a weakened immune response. A poor diet weakens the body’s natural defenses, leaving it more vulnerable to common illnesses like the flu or colds.
8. Poor Skin Health
Eating fast food regularly can also have a significant impact on your skin health. The high levels of saturated fats and refined sugars in fast food can lead to inflammation in the body, which manifests as acne, eczema, and other skin issues. Moreover, a lack of nutrients in fast food can deprive the skin of the vitamins and minerals needed to maintain a healthy complexion.
Fast food’s effect on blood sugar can also lead to insulin spikes, which can trigger the production of excess sebum (skin oil), leading to clogged pores and acne outbreaks. Over time, this can result in premature skin aging and the development of wrinkles and blemishes.
Conclusion: The Dangers of Fast Food
Fast food may be convenient and tasty, but it comes with significant risks that can negatively affect your overall health. From weight gain and obesity to heart disease, digestive issues, and mental health problems, the harmful effects of consuming fast food regularly should not be ignored.
To improve your health and well-being, it’s essential to limit fast food consumption and focus on a balanced, nutritious diet rich in whole foods, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Making small changes to your eating habits can lead to long-term health benefits, giving you the energy and vitality you need to live a happy and healthy life.
News in the same category

Keep Your Kid.neys Healthy with These Simple, Natural Choices

Experts Say These Four Foods Could Be Part of the Reason. Smart People Have Already Given Them Up

3 Danger.ous Ways Eating Red Dates Could Ha.rm Your Health

5 Natural Drinks to Keep Your Li.ver Healthy and Detoxified

This ‘Super Fruit’ Could Be the Secret to Health, Beauty, and Youth

Can.cer Will Be Defeated If You Adopt These 11 Powerful Habits!
Frequent Drooling During Sleep? It Could Be a Sign of These Six Health Issues

5 Natural Bloo.d Cleansing Drinks to Detoxify and Boost Circulation

Doctors warn: three distinct hand signs may indicate li.ver failure. If you notice any of them, don’t delay seeing a doctor.

Food groups good for bright and healthy eyes

Is Broccoli Better Than Cauliflower? The Real Truth About Cancer Risk, Heart Health and More

What Are Eye Floaters? Here What To Do If you Start Seeing Them, According to an Eye Doctor
Everything you need to know about chronic constipation: A hidden threat to your digestive health
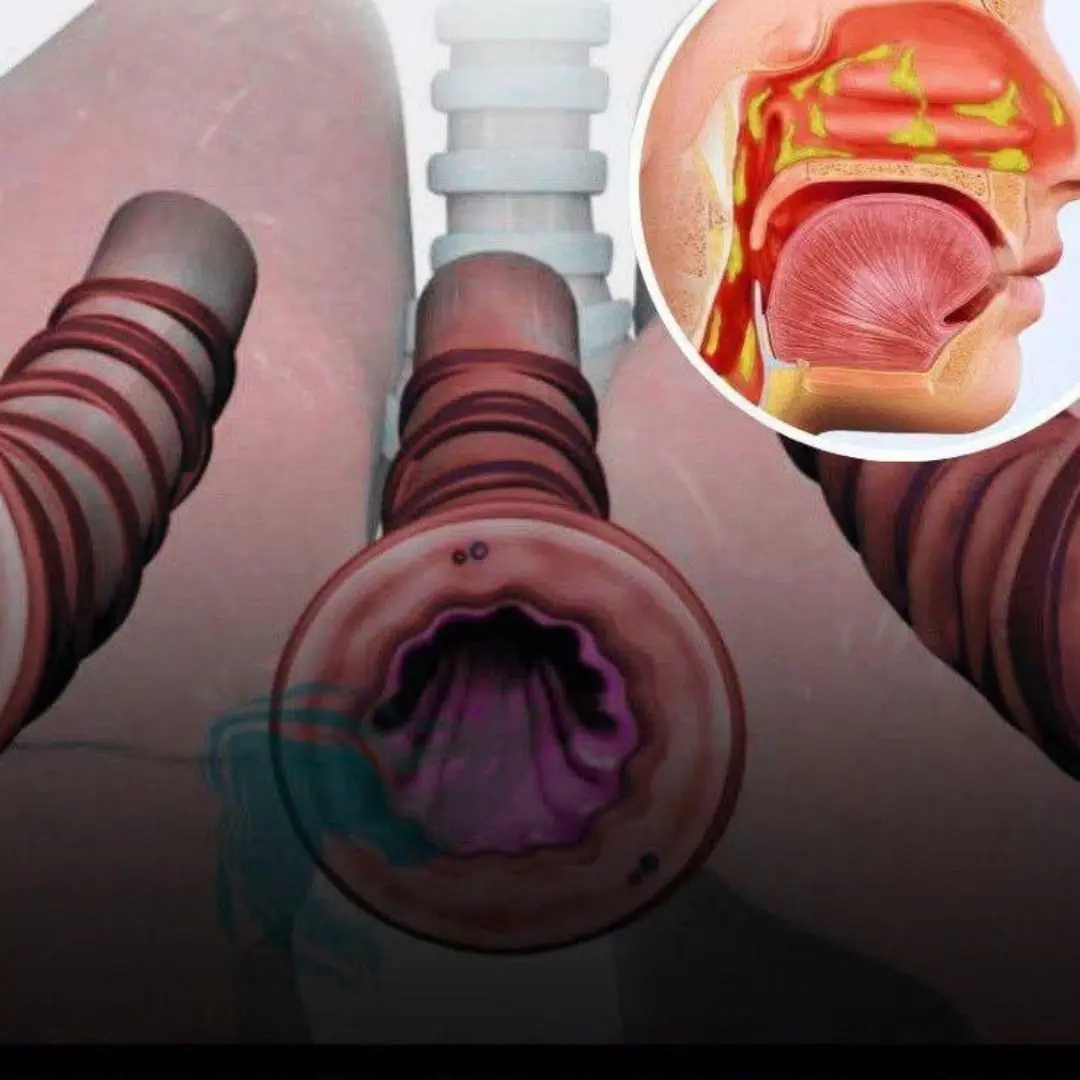
How to get rid of phlegm and mucus in your chest and throat

Doctor Shares What It Means If You Always Need To Poo Immediately After You Eat

The Reason You May Get Random Stabbing Pains in Your Chest Explained
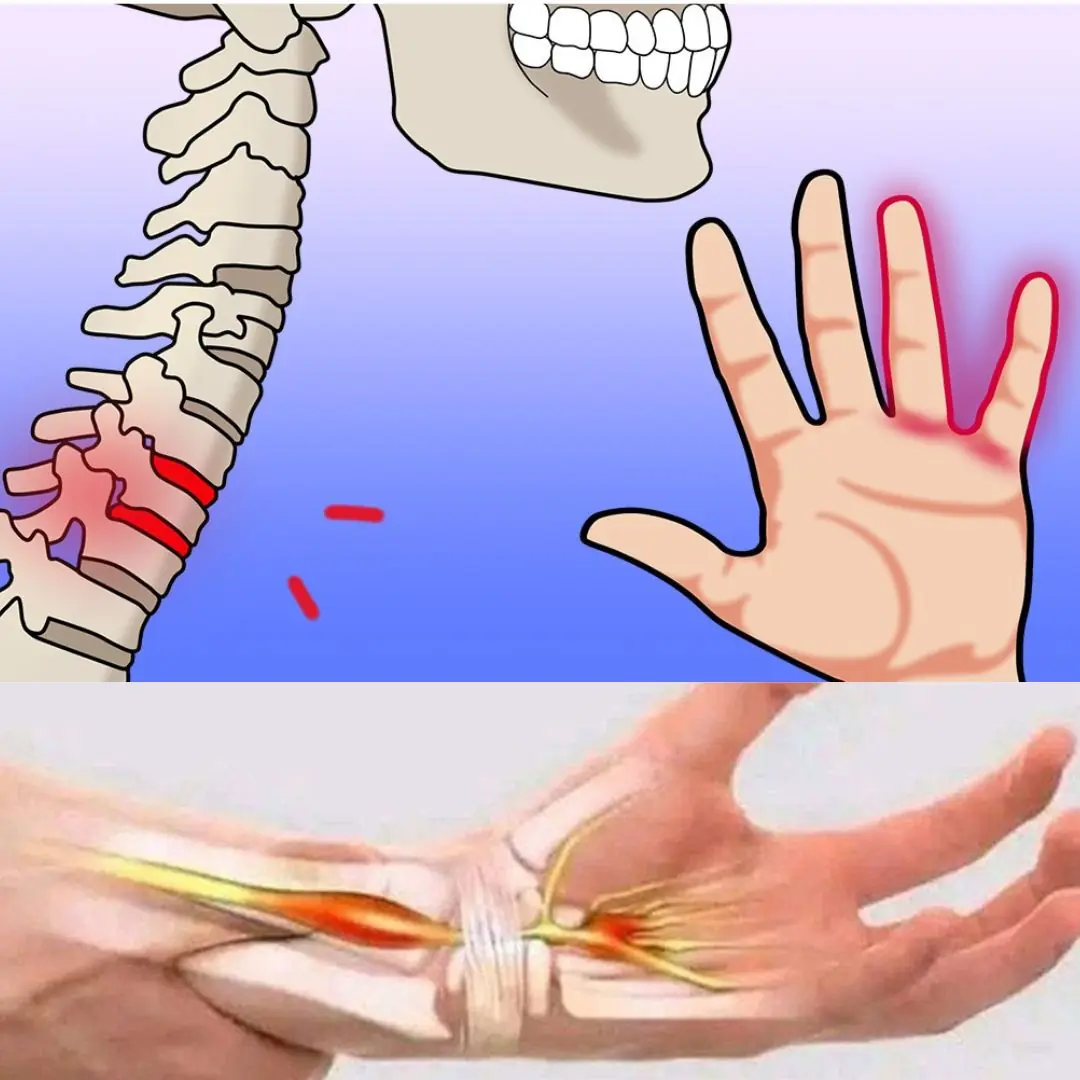
Numbness or tingling sensations in your hands
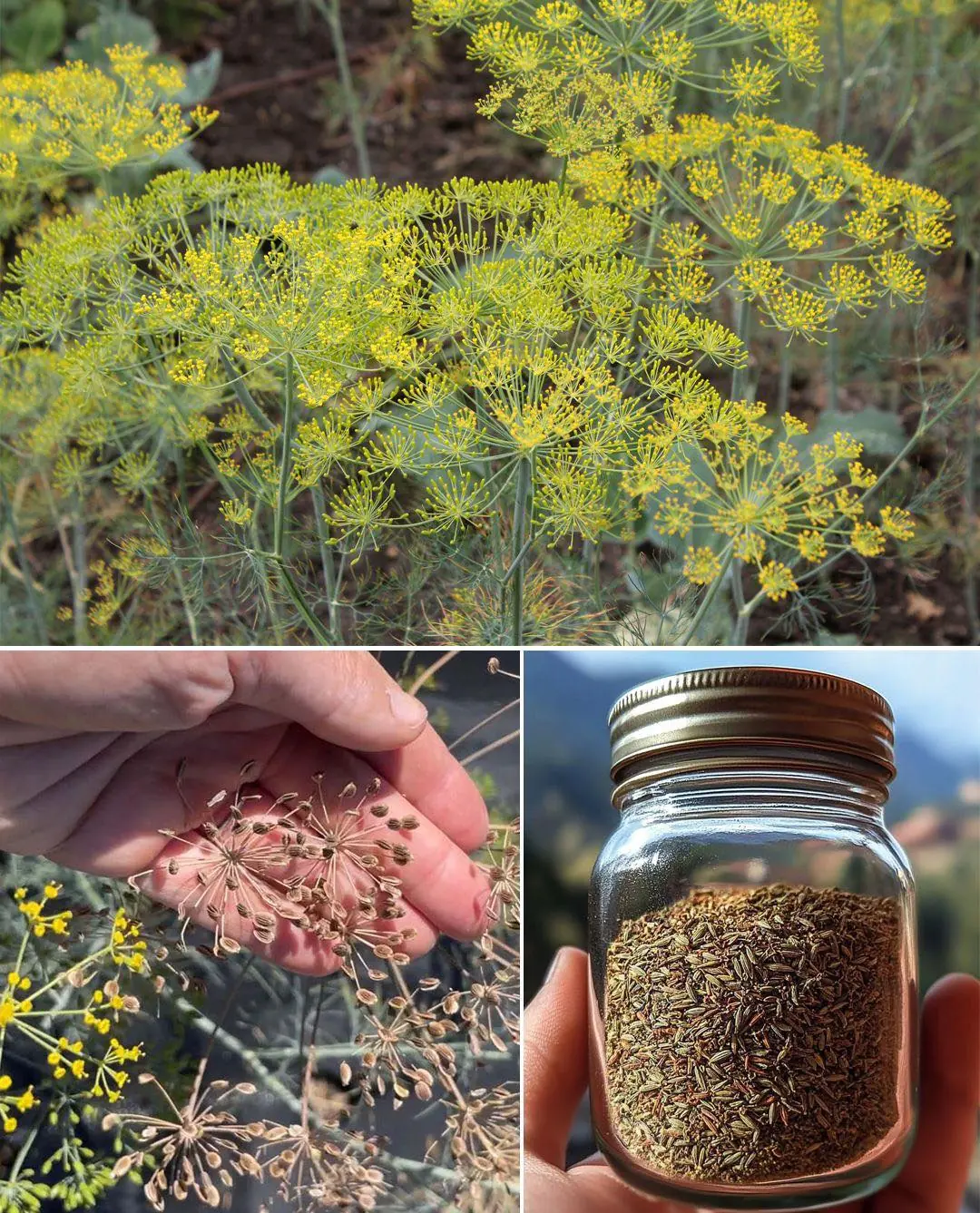

Dill Seeds: A Forgotten Treasure for Digestion, Hormones, and Restful Sleep
News Post

Take Charge of Your Health – Exercise Your Way to a Can.cer-Free Future!

Discover the Secret Omega-3 Nut That Can Naturally Lower Bloo.d Lipids & Improve Heart Health

The Power of Walnuts: A Superfood for Kid.ney Health and Brain Function

Keep Your Kid.neys Healthy with These Simple, Natural Choices

Reduce Your Can.cer Risk with These Simple Food Choices

Experts Say These Four Foods Could Be Part of the Reason. Smart People Have Already Given Them Up

3 Danger.ous Ways Eating Red Dates Could Ha.rm Your Health
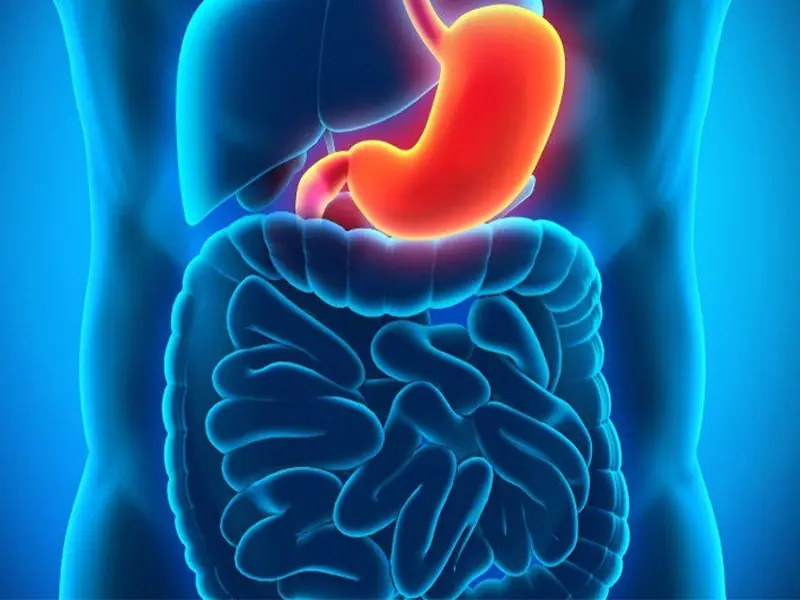
Stop Eating These 3 Foods That Are Secretly Des.troying Your Sto.mach Health

5 Natural Drinks to Keep Your Li.ver Healthy and Detoxified

This ‘Super Fruit’ Could Be the Secret to Health, Beauty, and Youth

How Eating Yogurt Before Bed Can Transform Your Health

Can.cer Will Be Defeated If You Adopt These 11 Powerful Habits!

Frequent Drooling During Sleep? It Could Be a Sign of These Six Health Issues

5 Natural Bloo.d Cleansing Drinks to Detoxify and Boost Circulation

Doctors warn: three distinct hand signs may indicate li.ver failure. If you notice any of them, don’t delay seeing a doctor.

Is Broccoli Better Than Cauliflower? The Real Truth About Cancer Risk, Heart Health and More

What Are Eye Floaters? Here What To Do If you Start Seeing Them, According to an Eye Doctor

Everything you need to know about chronic constipation: A hidden threat to your digestive health

How to get rid of phlegm and mucus in your chest and throat
