5 groups of people advised not to consume bread
Bread is one of the most widely consumed foods in the world. For many people, it’s a quick breakfast, a convenient snack, or a comforting addition to meals. While bread can offer nutrients like carbohydrates, fiber, and essential vitamins, it is not suitable for everyone. In fact, for certain groups of people, eating bread may trigger harmful reactions, worsen existing health conditions, or interfere with metabolic balance.
Understanding who should avoid bread - and who can safely enjoy it - is essential for making healthier food choices. Below are the five groups of people who should stay away from bread, along with a section explaining which individuals benefit from including bread in their diet and why.

I. 5 Groups of People Who Should Avoid Eating Bread
1. People With Gluten Intolerance or Celiac Disease
Bread, especially wheat-based bread, contains gluten, a protein that can cause serious health issues in certain individuals.
Why they should avoid bread:
• Celiac disease: Even tiny amounts of gluten can damage the small intestine, leading to nutrient malabsorption, fatigue, digestive problems, anemia, and long-term complications.
• Non-celiac gluten sensitivity: Causes bloating, abdominal pain, headaches, brain fog, skin rashes, and fatigue.
Symptoms triggered by bread consumption:
• Severe bloating
• Diarrhea or constipation
• Joint pain
• Skin irritation
• Chronic fatigue
For these individuals, all traditional bread products should be avoided, and gluten-free alternatives must be used instead.
2. People With Wheat Allergy
Wheat allergy is different from gluten intolerance and can cause immediate allergic reactions.
Possible symptoms:
• Hives, itching, or swelling
• Difficulty breathing
• Nausea or vomiting
• Anaphylaxis (in severe cases)
Anyone with a confirmed wheat allergy should avoid bread and all products containing wheat flour.
3. Individuals With Diabetes or Blo.od Sugar Instability
Most bread - especially white bread - has a high glycemic index (GI), which means it causes blood sugar levels to rise quickly.
Why this is harmful:
• Causes glucose spikes
• Increases insulin resistance
• Leads to cravings and overeating
• Raises the risk of complications
Even whole-wheat bread can cause sharp blood sugar increases in some individuals.
Recommended alternatives:
• Low-carb bread (almond flour, coconut flour)
• High-fiber breads made from seeds
• Limited portions with balanced protein and fat
People with diabetes should monitor bread consumption carefully or avoid it altogether.
4. People Trying to Lose Weight or Reduce Belly Fat
Bread is calorie-dense and easy to overeat. Many types contain refined flour, sugar, oils, and additives that contribute to weight gain.
How bread affects weight loss:
• Encourages fat storage due to insulin spikes
• Provides quick energy followed by hunger shortly after
• Contains “empty calories” with few nutrients
• Triggers cravings for more carbs
People aiming for fat loss often benefit from reducing or avoiding bread and choosing whole, minimally processed foods instead.
5. Individuals With Digestive Disorders
Certain digestive conditions can worsen with bread consumption, especially wheat-based bread.
These conditions include:
• IBS (Irritable Bowel Syndrome)
• GERD / Acid reflux
• Chronic bloating
• FODMAP sensitivity
• Chronic constipation
Bread contains fructans, a type of FODMAP that can ferment in the gut and cause gas, cramps, and digestive discomfort.
Common symptoms after eating bread:
• Bloating
• Stomach cramps
• Excess gas
• Diarrhea or constipation
For people with sensitive digestive systems, reducing bread intake can significantly improve comfort and gut health.
:quality(75)/2024_4_23_638495083979668260_banh-mi-de-duoc-bao-lau.jpg)
II. Who Should Eat Bread - and Why It Can Be Beneficial
Not all bread is bad. For many people, bread can be part of a healthy and balanced diet — especially when choosing the right type.
1. People With High Energy Needs
Bread is a fast and reliable source of carbohydrates, making it useful for:
• Athletes
• Students
• Manual laborers
• People with fast metabolisms
Whole-grain bread provides long-lasting fuel and supports high physical and mental performance.
2. Individuals Needing More Fiber in Their Diet
High-quality whole-grain bread contains soluble and insoluble fiber, which helps:
• Improve digestion
• Prevent constipation
• Support gut microbiome
• Lower cholesterol
• Stabilize blood sugar
People who struggle to meet daily fiber requirements through vegetables and fruits can benefit from fiber-rich bread options.
3. People Looking for Convenient, Nutritious Meals
For those with busy schedules, bread can be a practical choice when paired with healthy ingredients.
Examples of balanced meals:
• Whole-grain bread + avocado + egg
• Rye bread + smoked salmon + greens
• Seeded bread + hummus + vegetables
Bread can help create quick, nutrient-dense meals without requiring extensive cooking.
4. Individuals With Low Blood Sugar or Weak Appetite
Bread - especially when combined with protein - can help stabilize blood sugar and provide easy-to-digest calories for:
• Elderly individuals
• People recovering from illness
• Those experiencing appetite loss
Choosing whole-grain or sourdough bread ensures better nutrient density.
5. People Who Need Healthy Prebiotics
Fermented breads like sourdough contain prebiotics that support gut health and help nourish good bacteria.
Benefits of sourdough bread:
• Easier to digest
• Lower glycemic index
• Rich in minerals and beneficial acids
• Supports gut health
Sourdough is often tolerated even by those with mild digestive sensitivity.
Bread can be part of a healthy lifestyle, but it is not suitable for everyone. People with gluten intolerance, wheat allergies, digestive disorders, diabetes, or weight-loss goals may need to avoid it or consume it only in moderation.
On the other hand, individuals who need energy, fiber, gut-friendly prebiotics, or quick nutritious meals may benefit from including the right kinds of bread in their diets.
The key is choosing high-quality bread and understanding your body’s individual needs.
News in the same category


Heart Surgeon Reveals: Eating Eggs Every Day May Help You Live Longer

The Surprising Benefits of Eating Boiled Sweet Potatoes for Breakfast: How Your Body Can Change Over Time
29-year-old girl hospitalized for bleeding duodenal ulcer: Doctor warns of 2 harmful habits
DANGEROUS COMPLICATIONS OF PULPITIS

Butter Steak Bites with Mashed Potatoes & Glazed Carrots – A Comfort Plate With Serious Flavor
What causes black thorn disease?
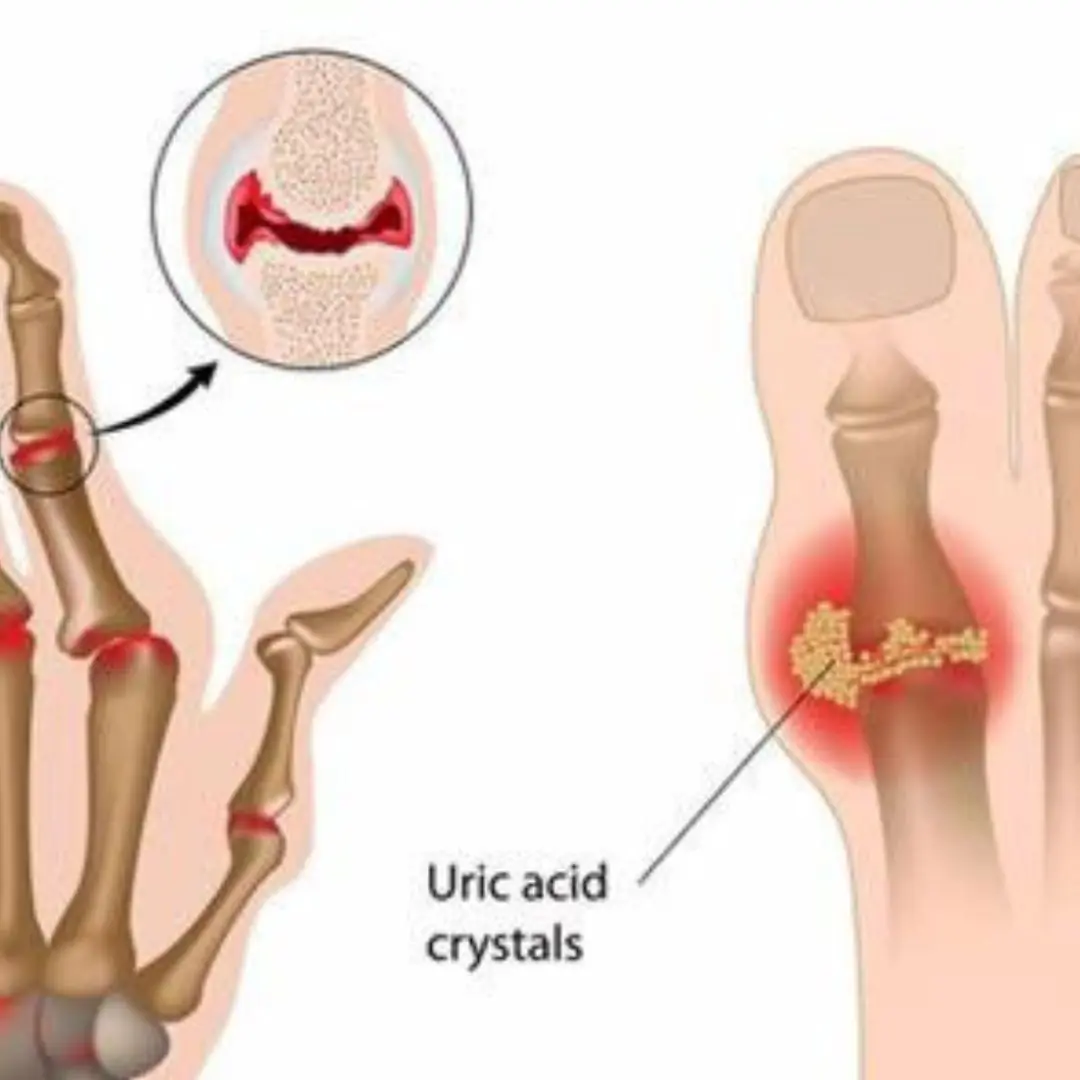
The #1 Drink to Reverse High Uric Acid and Gout — Backed by Science

If You Wake Up With These 4 Morning Symptoms, Sorry — Your Kid.neys May Be in Trouble
Drinking Coffee at the Wrong Time May Harm Your Heart:
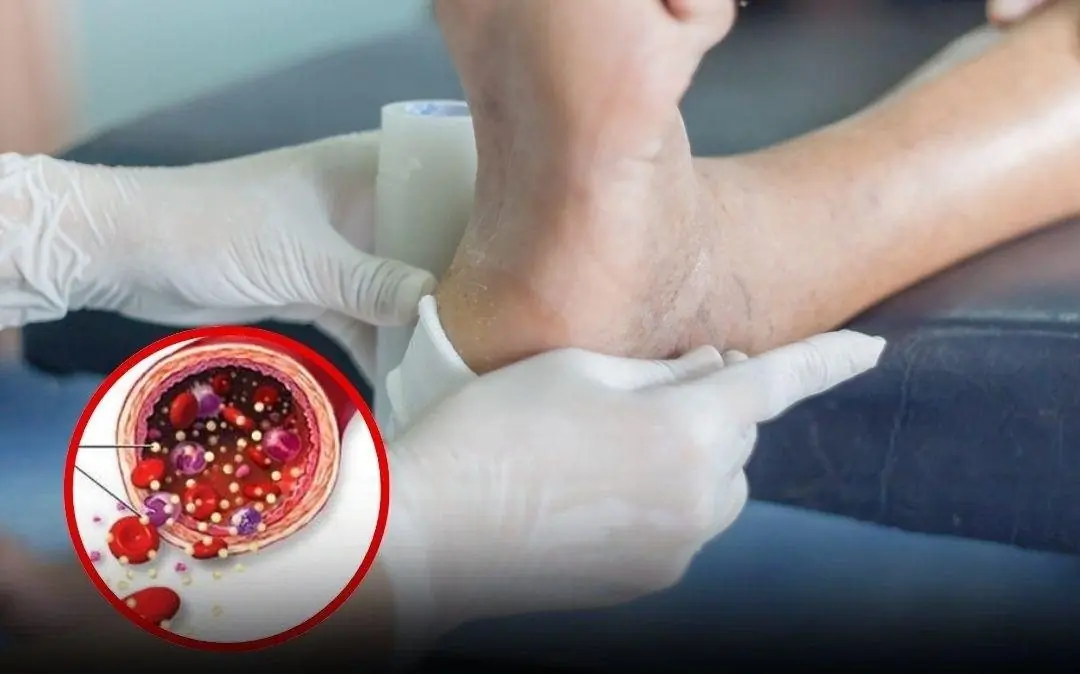
Your feet can reveal important warning signs about circulation and nerve health

Are kidney cysts really benign? Experts warn of signs that should never be ignored
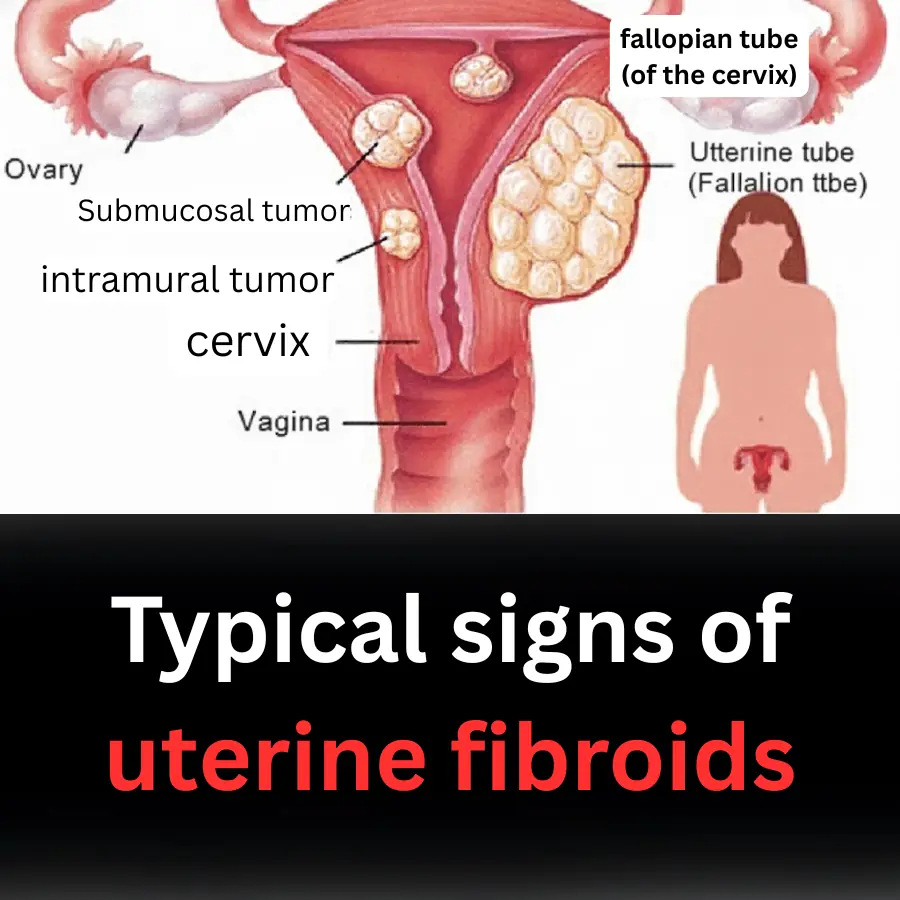
Typical signs of uterine fibroids

The More You Eat This Vegetable, the Cleaner Your Arteries Become: A Stroke-Prevention Secret Many People Overlook!
Age Spots and Selenium: How This Powerful Mineral Can Help Fight Sun Damage Naturally
A 12-year-old boy loses 12 teeth at once due to a common habit among children
Warning: A Common Daily Habit May Be “Inviting” Liver Can.cer — Many People Know It, Yet Still Do It

6 foods that clean the intestines naturally when eaten on an empty stomach
Poucas pessoas reconhecem os sinais de alerta de problemas de circulação que podem surgir nos pés e nas pernas durante a noite
News Post

To Prevent Colon Can.cer, This Is the First Thing You Need to Do

Shrimp & Pork Ball Bowl with Shimeji Mushrooms

Heart Surgeon Reveals: Eating Eggs Every Day May Help You Live Longer

The Surprising Benefits of Eating Boiled Sweet Potatoes for Breakfast: How Your Body Can Change Over Time

29-year-old girl hospitalized for bleeding duodenal ulcer: Doctor warns of 2 harmful habits

Hair loss: Doctor points out 3 mistakes when washing and drying hair and 4 ways to fix them

The truth about hotel mirrors, check now to ensure safety

To clean pig intestines, you only need to use one cheap thing, clean quickly, and have no fishy smell

Reasons why you shouldn't open your bedroom door at night

DANGEROUS COMPLICATIONS OF PULPITIS

Butter Steak Bites with Mashed Potatoes & Glazed Carrots – A Comfort Plate With Serious Flavor

What causes black thorn disease?

Baked Sweet Potatoes with Garlic Butter.

The #1 Drink to Reverse High Uric Acid and Gout — Backed by Science

If You Wake Up With These 4 Morning Symptoms, Sorry — Your Kid.neys May Be in Trouble

Drinking Coffee at the Wrong Time May Harm Your Heart:

Cardiologist reveals 3 drinks that help control blo.od pressure

A single ingredient to combat bone pain, diabetes, anxiety, depression, and constipation
