
5 reasons you should not eat tilapia

Tilapia has long been touted as a mild, versatile, and affordable fish, making it a favorite in many households. Its light taste makes it ideal for a variety of dishes, from grilled fillets to fish tacos. However, despite its popularity, nutritionists and health experts have raised concerns about tilapia’s potential impact on health. Here are five reasons why you might want to think twice before adding this fish to your regular diet.
1. High in Omega-6 Fatty Acids, Low in Omega-3s
Tilapia contains a high proportion of omega-6 fatty acids compared to omega-3s. While omega-6 fatty acids are essential, an imbalance in favor of omega-6 over omega-3 can promote inflammation in the body. Chronic inflammation is linked to a variety of health problems, including heart disease, obesity, diabetes, and autoimmune disorders. Unlike fatty fish like salmon or sardines, which are rich in anti-inflammatory omega-3s, tilapia does not provide the same cardiovascular or brain health benefits.
2. Potential Contaminants from Farmed Tilapia
Most tilapia sold in supermarkets is farmed rather than wild-caught. While aquaculture can help meet global seafood demand, farmed tilapia has been found in some studies to contain traces of contaminants, such as antibiotics, pesticides, or heavy metals. Poor farming practices, overcrowded tanks, and substandard water quality can increase the risk of harmful substances accumulating in the fish. Consuming contaminated fish over time may pose risks to liver and kidney health, as well as increase the burden of toxins on your body.
3. Low Nutritional Value Compared to Other Fish
While tilapia is a source of protein, it falls short in other essential nutrients compared to other fish. Its levels of vitamins D and B12, iodine, and essential fatty acids are relatively low. For individuals who rely on fish as a major source of nutrients, regularly choosing tilapia over nutrient-dense fish could result in missing out on key health benefits that support immunity, bone health, and brain function.
4. Risk of Promoting Inflammation and Weight Gain
Due to the high omega-6 content and low omega-3s, tilapia may contribute to an inflammatory state in the body when consumed in excess. Inflammation is not only a risk factor for chronic disease but may also make it harder for your body to regulate weight effectively. Diets with a high omega-6 to omega-3 ratio have been linked to metabolic imbalances and increased risk of obesity. For people trying to maintain a healthy weight or reduce inflammation, tilapia may not be the optimal fish choice.
5. Environmental Concerns of Tilapia Farming
Beyond health, the way tilapia is farmed can impact the environment. Intensive tilapia farming can lead to water pollution, depletion of local resources, and destruction of natural habitats. The feed used for tilapia often includes other fish species or soy products, contributing to overfishing or deforestation. Choosing alternative fish from sustainable sources can help reduce your environmental footprint while supporting healthier ecosystems.
Conclusion
While tilapia is inexpensive and easy to cook, its nutritional profile and potential health risks suggest it should be consumed with caution. The high omega-6 content, possible contaminants, low nutritional value, potential to promote inflammation, and environmental concerns make it less ideal compared to other fish. For a healthier choice, consider alternatives such as salmon, mackerel, sardines, or trout, which offer higher omega-3 content, essential nutrients, and greater health benefits overall.
News in the same category

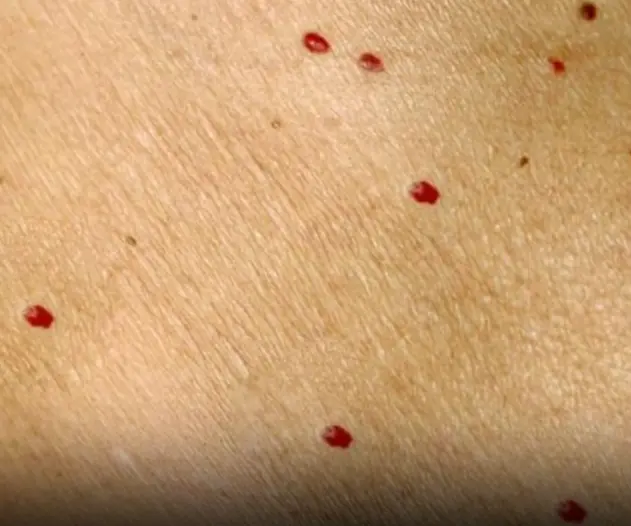
Red dots on your skin: Causes and what they could mean
Top 10 foods that improve blo.od circulation in legs
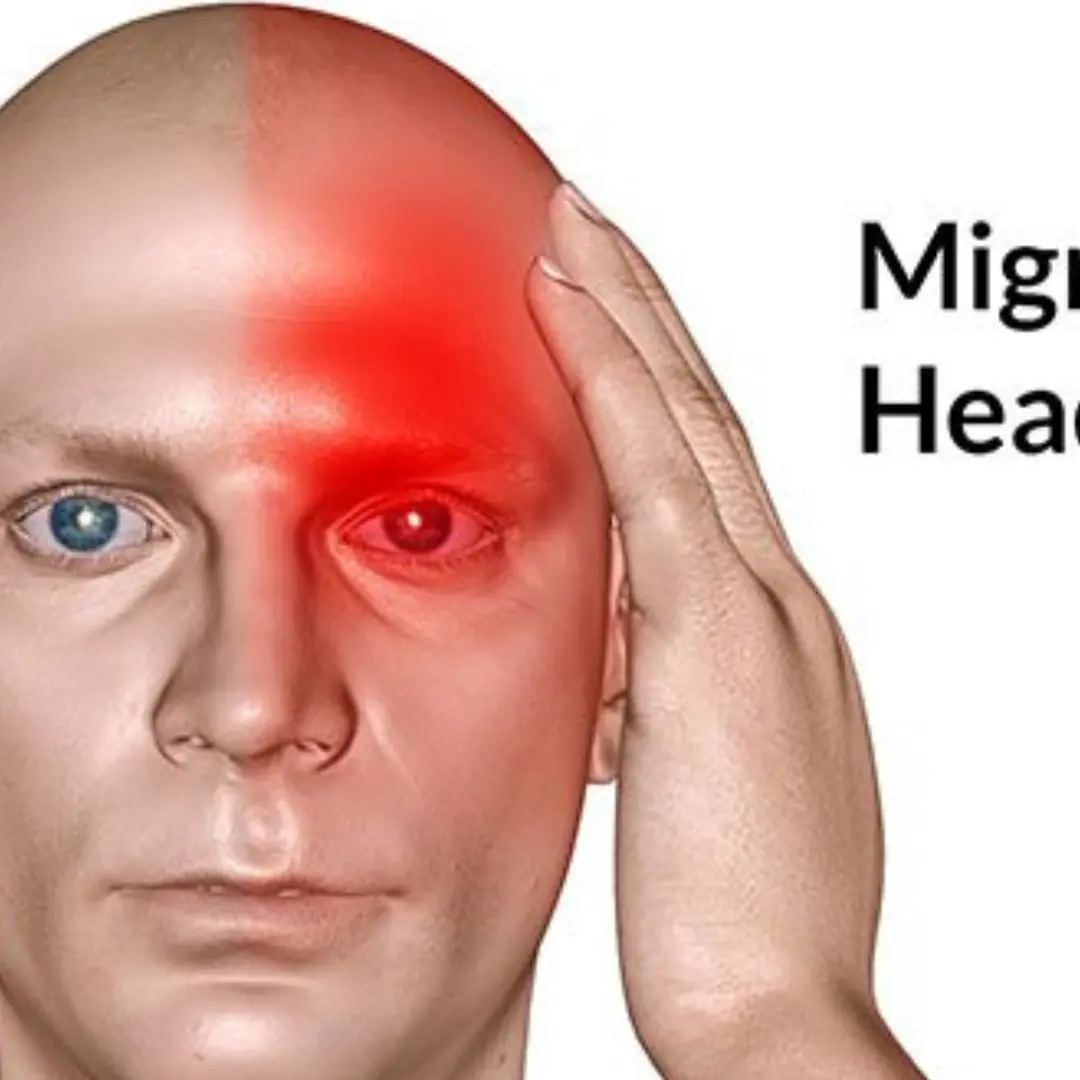
War:ning: Frequent recurring posterior migraines may be a sign of a medical condition
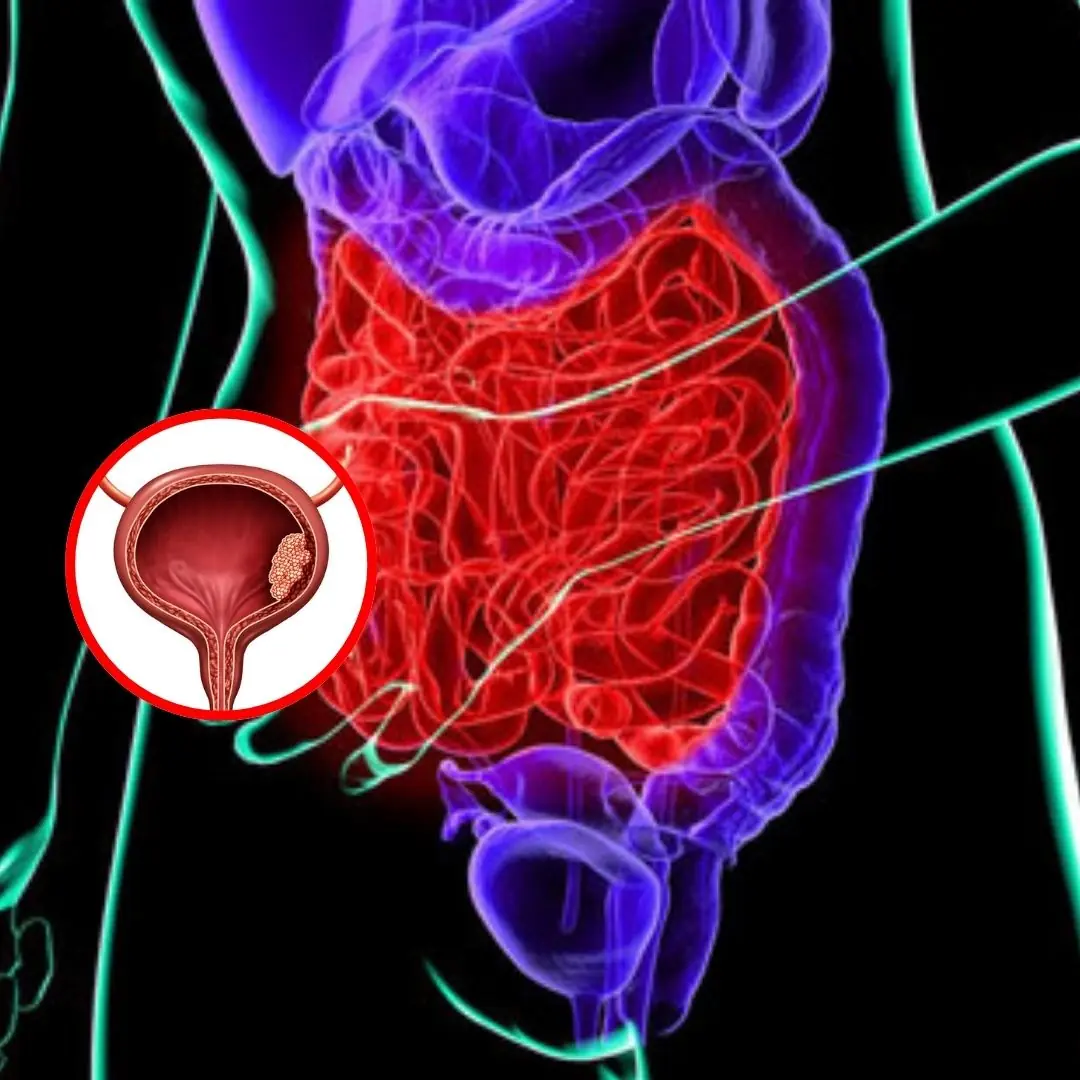
Bladder C.a.ncer: 5 Subtle Early Symptoms to Watch Out For
Doctor Shakes Head: 4 Popular Foods Were the Culprits

Keep your liver healthy: 4 vegetables and 2 fruits you should eat daily
5 Silent Habits That Put Your Kidney Health at R.i.s.k

Experts Sound Alarm: 18-Year-Old Paralyzed From Late-Night Screen Use, Don’t Let It Happen to You
Bone Cancer: 5 Red-Flag Symptoms Doctors Warn About
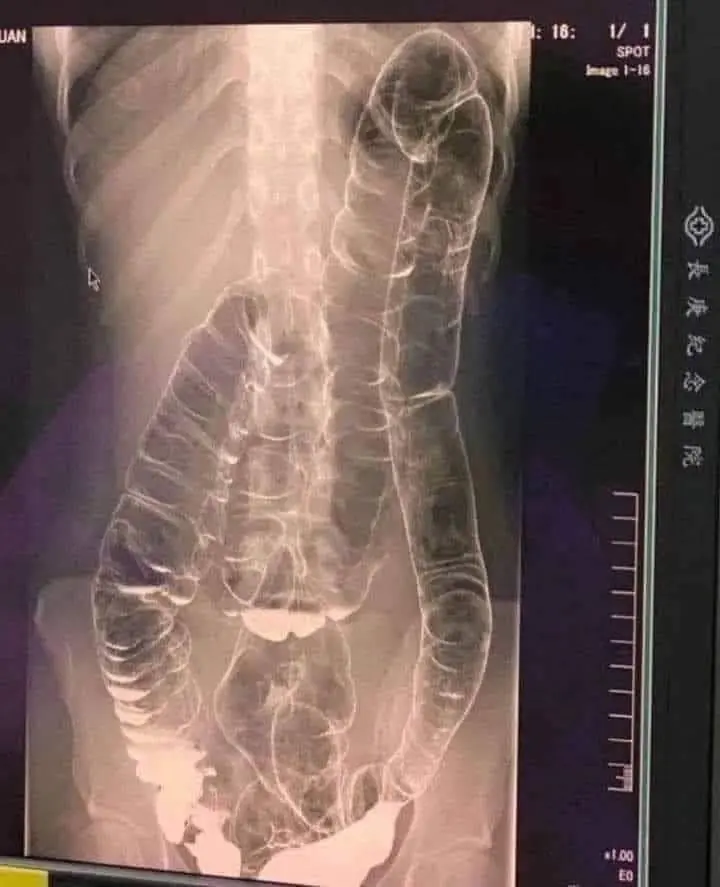
Ch.ronic constipation - A silent thr.eat to your digestive health

5 groups of people should not eat okra
After 30 years of one common mistake, a 56-year-old man paid the price with a heart attack

Che.ap dried root is considered a 'longevity elixir': Good for the kidneys, stabilizes bl.o.o.d sugar

Eating eggs regularly can be harmful for these 5 groups of people

A “small but mighty” flower that helps prevent stro.kes and supports can.cer treatment

I regularly eat these 2 fruits to keep my spleen and sto.mach clean and healthy
13-y.ear-old g.i.r.l with kidney failure, warning about high - ri.s.k drinks

4 types of sweating that can be the body's "cry for help"
News Post

5 food groups that shorten life expectancy and silently feed cancer cells are favorite dishes of many people.
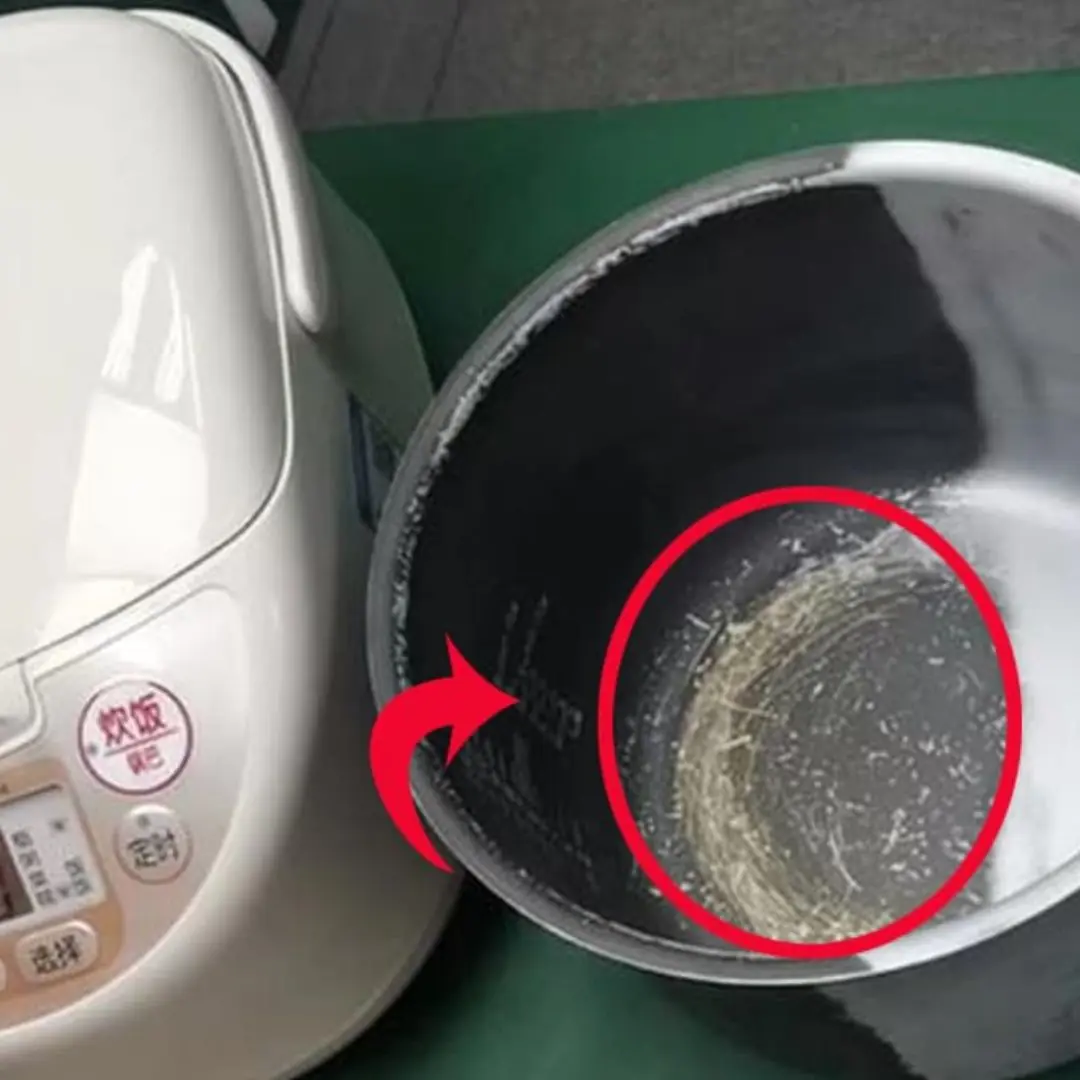

Does a scratched non-stick coating on a rice cooker cause can.cer? Expert answers

Red dots on your skin: Causes and what they could mean

Top 10 foods that improve blo.od circulation in legs

War:ning: Frequent recurring posterior migraines may be a sign of a medical condition

Bladder C.a.ncer: 5 Subtle Early Symptoms to Watch Out For

When Choosing Bananas, Pay Attention to This to Get the Best Bunch

Doctor Shakes Head: 4 Popular Foods Were the Culprits

Custard Apple: Delicious and Nutritious, But Strictly Unsuitable for These People
What to do immediately after a snake bi.te

Keep your liver healthy: 4 vegetables and 2 fruits you should eat daily

5 Silent Habits That Put Your Kidney Health at R.i.s.k

Experts Sound Alarm: 18-Year-Old Paralyzed From Late-Night Screen Use, Don’t Let It Happen to You

Bone Cancer: 5 Red-Flag Symptoms Doctors Warn About

Beef Hung High vs. Beef Laid on the Table – Food Experts Can Tell Which to Buy in Just 1 Second!

6 DON’Ts When Using Nonstick Pans to Avoid Health Risks

Smart and Natural Ways to Keep Birds Away from Rooftop Gardens

Ch.ronic constipation - A silent thr.eat to your digestive health
