
90% of Cerebral Infarction Patients Did These 3 Things in the 3 Days Before a Stroke — Chances Are You’re Doing the Second One Right Now
90% of Cerebral Infarction Patients Did These 3 Things in the 3 Days Before a Stroke — Chances Are You’re Doing the Second One Right Now
They are not dramatic warning signs, but everyday habits so familiar that they are easily overlooked.
Many people believe that a cerebral infarction (ischemic stroke) strikes suddenly, without warning. In reality, according to neurologists, most strokes caused by blocked brain arteries are “set up” in advance through long-term internal disorders and unhealthy lifestyle patterns.
Notably, in the days immediately before the event, many patients share strikingly similar behaviors and symptoms. These are not intense or alarming signals, but ordinary habits that often go unnoticed.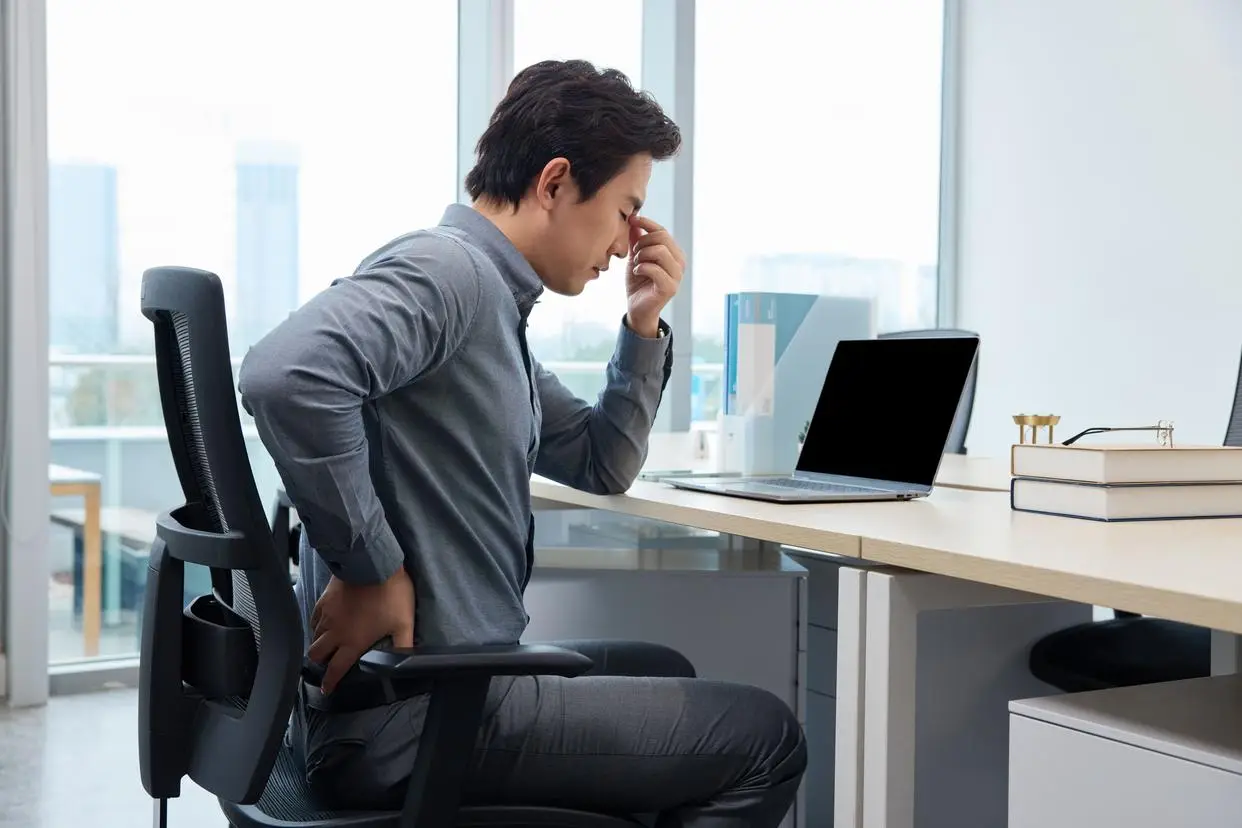
Staying up late repeatedly: When the body clock is thrown off
Staying up late for work, entertainment, or lifestyle habits has become common. However, chronic sleep deprivation over several consecutive days has clear negative effects on the cardiovascular system and cerebral blood vessels.
When the biological rhythm is disrupted, the sympathetic nervous system becomes overactive, causing blood pressure to rise, blood vessels to constrict, and blood to become thicker. Under these conditions, the risk of blood clot formation increases — especially at night or in the early morning, when blood circulation naturally slows.
Many cerebral infarctions occur while patients are asleep or just waking up, even though they previously believed they were not at risk of stroke.
Prolonged sitting and lack of movement: A common but dangerous habit
Sitting for hours in front of a computer, scrolling on a phone, or watching television without changing posture is a familiar image of modern life. However, remaining still for too long slows blood circulation, particularly in the lower limbs, increasing the risk of clot formation.
In addition, a sedentary lifestyle damages the inner lining of blood vessels, promotes inflammation, and accelerates atherosclerosis — all direct contributors to cerebral artery blockage.
Importantly, this risk is not limited to older adults. Younger people who are overweight, have abnormal blood lipids, high blood pressure, or prolonged stress are also vulnerable.
Emotional stress and sudden outbursts: The “last straw” for brain blood vessels
Emotional instability, chronic stress, or intense anger can act as triggers for stroke. When the body enters a highly agitated state, stress hormones such as adrenaline are released in large amounts, causing sudden spikes in blood pressure, irregular heart rhythms, and strong vasoconstriction.
If blood vessels already contain atherosclerotic plaques, a sudden surge in pressure can cause these plaques to rupture, leading to clot formation and cerebral artery blockage. Clinically, many patients suffer cerebral infarction shortly after a major argument or a period of severe psychological stress.
Early warning signs that are often ignored
Before a stroke occurs, the body often sends out warning signals, most commonly transient ischemic attacks (TIAs). Symptoms may include sudden numbness or weakness on one side of the body, slurred or difficult speech, blurred vision, or sudden dizziness.
Because these symptoms often last only a short time and then disappear on their own, many people dismiss them as temporary fatigue. In medical terms, however, they are considered serious warnings of an impending stroke.
The consequences go far beyond the stroke itself
Even with timely emergency treatment, cerebral infarction can leave severe long-term complications, such as paralysis on one side of the body, speech disorders, memory impairment, and reduced ability to care for oneself. These outcomes significantly affect quality of life and place a heavy burden on families.
Prevention starts with small changes
Experts emphasize that stroke is not an unavoidable fate. Most cases can be prevented by adjusting daily habits. Getting enough sleep, avoiding staying up late, exercising regularly, managing emotions, and monitoring key health indicators such as blood pressure, blood lipids, and blood sugar are crucial steps in protecting brain blood vessels.
A stroke does not happen in a single moment — it is the result of habits repeated day after day. Staying up late, sitting too long, and prolonged stress, if not corrected in time, can become the “final trigger” that leads to cerebral infarction.
News in the same category


No one would dare reheat cold rice to eat if they knew this terrible truth

A cup of hot water can cure 6 common dis.eases, simple but few people pay attention
Most stomach can.cers are detected late: Doctors say there are 5 symptoms after meals so you should have an early endoscopy

Grape Hyacinth (Muscari): A Tiny Spring Wonder with Surprising Benefits and Uses
Two itchy body parts may signal liver can.cer - Many people mistakenly think it is an allergy
If you wake up in the morning and see your body has these 2 characteristics, be careful, your liver is on the "brink" of failure: You should go see a doctor soon!
6 foods that silently drain calcium from the body, the more you eat, the weaker your bones become
Top Hospitals Issue Stark Warning: This Common Meat May Be “Feeding” Can.cer — Just 50 Grams a Day Raises De.ath Risk by 18%

Black Beans and Black Sesame: The Ancient Pair That “Cleans by Day, Restores by Night” — Yet Most People Use It Wrong
The Real Causes of Constant Phlegm and Mucus in Throat — And How to Get Rid of It

3 Signs Your Parent May Be Nearing the End of Life — How to Prepare for What’s Ahead
Why you keep waking up with dry mouth—and what it may be telling you

If You Keep Waking Up at 3AM, The Universe Might Be Trying to Tell You Something

These sudden purple patches on my arms won’t stop appearing, and my doctor is booked until January. What’s happening?

The Hidden Meaning Behind Thumb Rings for Women vs. Men
The Best Foods to Cleanse and Prevent Clogged Arteries

The Ultimate Guide to Cloves: Benefits, Uses, and How They Work

Top 10 Foods to Control Diabetes
News Post

The risk of liver fluke infection from eating habits that many people have

Snakes are af.raid of these 5 plants - Plant them around your house to repel snakes and protect your family

No one would dare reheat cold rice to eat if they knew this terrible truth

What Happens to Your Body If You Eat 1 Clove of Garlic Every Day?

A cup of hot water can cure 6 common dis.eases, simple but few people pay attention

Fresh Spicy Napa Cabbage Kimchi (Quick Kimchi)

Most stomach can.cers are detected late: Doctors say there are 5 symptoms after meals so you should have an early endoscopy

Grape Hyacinth (Muscari): A Tiny Spring Wonder with Surprising Benefits and Uses

Two itchy body parts may signal liver can.cer - Many people mistakenly think it is an allergy

If you wake up in the morning and see your body has these 2 characteristics, be careful, your liver is on the "brink" of failure: You should go see a doctor soon!

6 foods that silently drain calcium from the body, the more you eat, the weaker your bones become

90% of women don’t know this trick: Add this one thing to the pan and you can fry “everything” without worrying about oil splattering!

Top Hospitals Issue Stark Warning: This Common Meat May Be “Feeding” Can.cer — Just 50 Grams a Day Raises De.ath Risk by 18%

Black Beans and Black Sesame: The Ancient Pair That “Cleans by Day, Restores by Night” — Yet Most People Use It Wrong

When Buying Bananas, Just Say These 3 Words — Sellers Will Think You’re an Expert and Won’t Dare to Cheat You

The Real Causes of Constant Phlegm and Mucus in Throat — And How to Get Rid of It

3 Signs Your Parent May Be Nearing the End of Life — How to Prepare for What’s Ahead

Why you keep waking up with dry mouth—and what it may be telling you

So this is what it does, here is the answer
