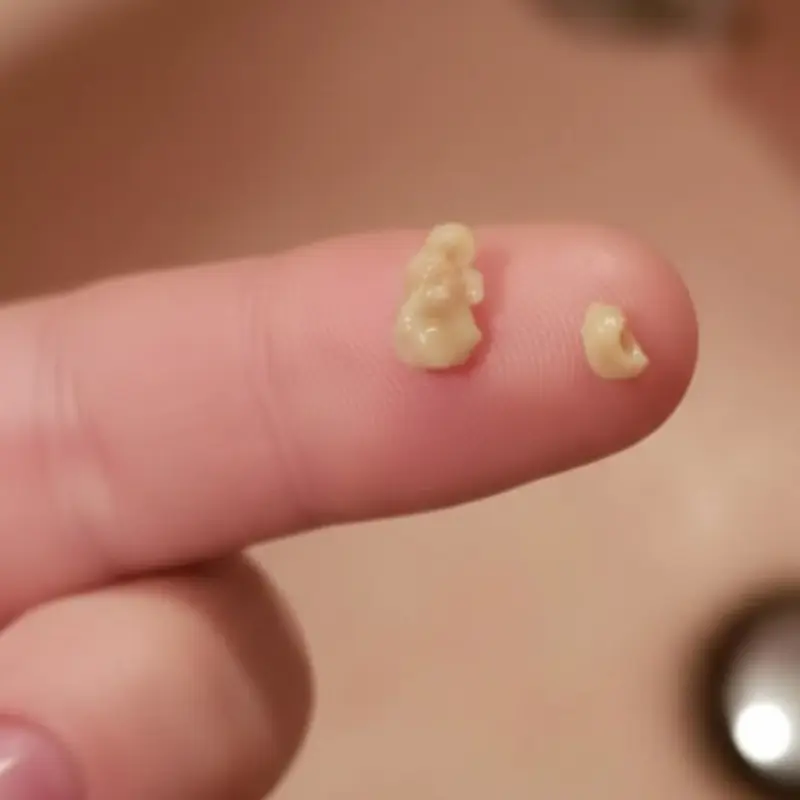
When Small Yellow Lumps Appear in Your Mouth: A Warning Sign You Shouldn’t Ignore
Small yellow lumps in the mouth may signal hidden oral health issues.
Can You Eat Meat If You Have High Uric Acid? 3 Types of Meat That Are Safe and How to Consume Them Wisely
Many people with high uric acid levels wonder whether they should completely avoid meat. In this article, doctors clarify this concern and provide guidance on which meats to eat, how much, and the best ways to prepare them.

Meat contains higher levels of uric acid compared to vegetables, grains, and other foods. Uric acid in the body is closely related to purines, as uric acid is the final metabolic product of purines. While it’s commonly advised to avoid high-purine foods, not all purines in the body come from food.
In fact, about 80% of purines are naturally produced by the body, while only 20% come from dietary sources. If you are on gout medication or not experiencing an acute gout attack, eating a small portion of meat is generally safe.
Seafood (fish, shrimp, crab) and organ meats contain the highest purine levels, whereas poultry and livestock meats contain relatively lower amounts. If you have high uric acid, you can eat lean meats from livestock in moderation but should limit seafood and organ meats.
Daily meat intake should ideally be around 45-70g (about the size of a palm). If your uric acid is under control, you may also consume some seafood with lower purine content, such as jellyfish and sea cucumbers.
Certain fish, like salmon, tuna, and eel, contain moderate purine levels (100 mg/100 g) and can be eaten in moderation. Fish like cod, swordfish, and abalone contain higher purine levels (150 mg/100 g) and should be consumed sparingly. Avoid fish with very high purine content, such as sardines, mackerel, anchovies, dried fish, and shellfish.
Processed meats, such as bacon, sausages, and canned meats, should also be avoided due to their high salt and preservative content. When cooking meat, opt for steaming, boiling, or stewing instead of frying or grilling, which can increase purine concentration.
Since meat provides essential nutrients that are difficult to replace, completely avoiding it is unrealistic. Instead, limit total daily meat intake to 200g, and strictly avoid organ meats and high-purine seafood to prevent worsening your condition.
By making smart dietary choices and managing your purine intake, you can still enjoy meat while keeping your uric acid levels in check.

Small yellow lumps in the mouth may signal hidden oral health issues.
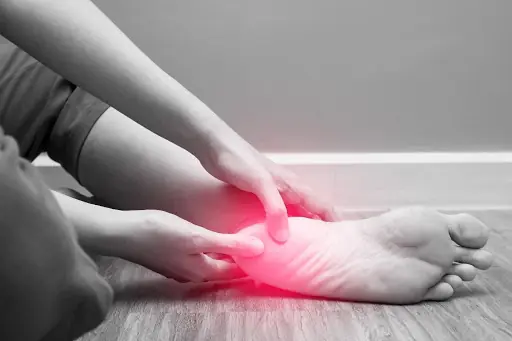
Heel pain when you wake up? Your body may be warning you about this condition

Why Do Your Legs Cramp at Night? Here’s What’s Really Happening — And How to Stop It
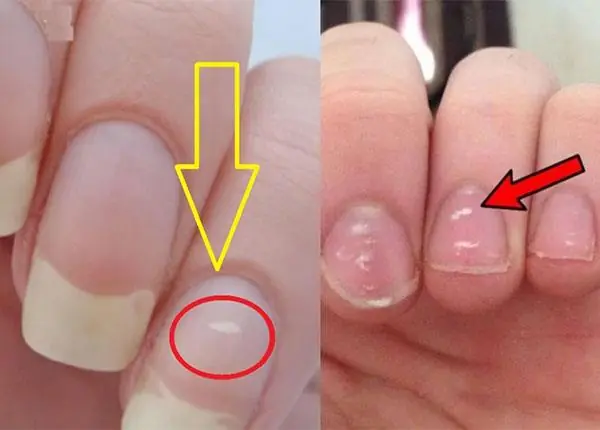
Pay Attention to Your Nails: These 3 Changes Could Be a Warning Sign

Experts reveal what really happens when you eat bananas in the morning
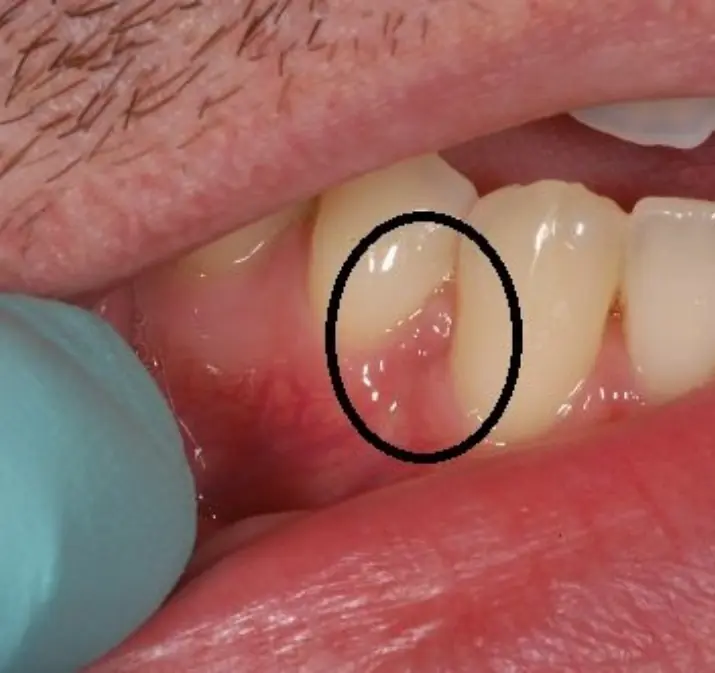
Early gum changes may reveal important clues about your health.
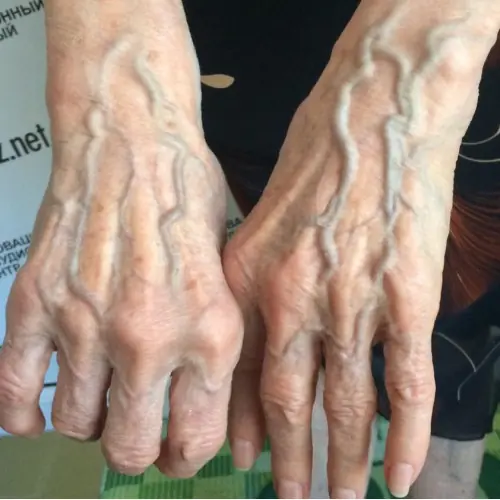
If you come across someone with bulging veins, you should definitely tell them this

Why Do You Often Wake Up Between 3 and 4 AM? 4 Possible Health Reasons

Nighttime symptoms may quietly signal early warning signs of diabetes.

Nighttime Leg Cramps Could Be a Sign Your Body Needs Attention
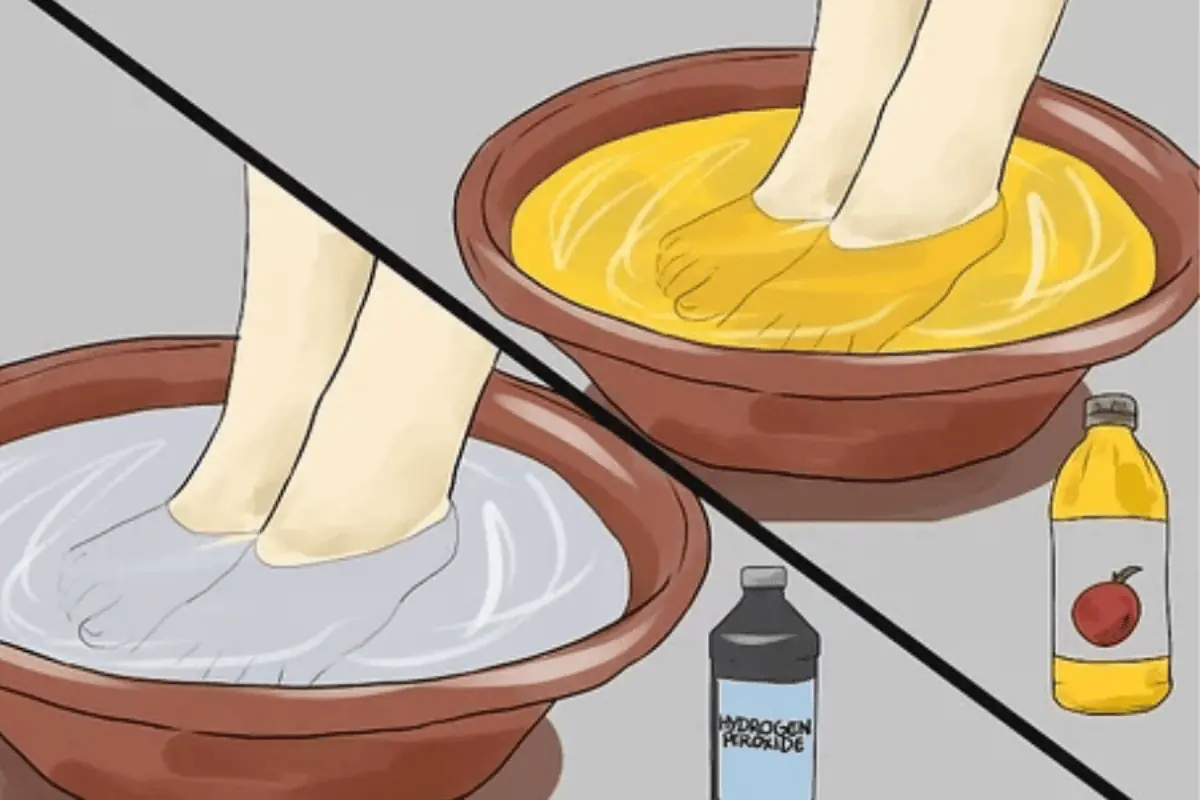
Apple cider vinegar has long been used as a natural home remedy for many everyday health concerns. Recently, one simple wellness habit has gained attention online: soaking your feet in apple cider vinegar.

Doctors reveal surprising effects of eating hard-boiled eggs regularly
8 Early Warning Signs Of Ovarian Can:cer You Shouldn’t Ignore..
Woman with Stage - Four Colon Can:cer Reveals 5 Symptoms She Overlooked
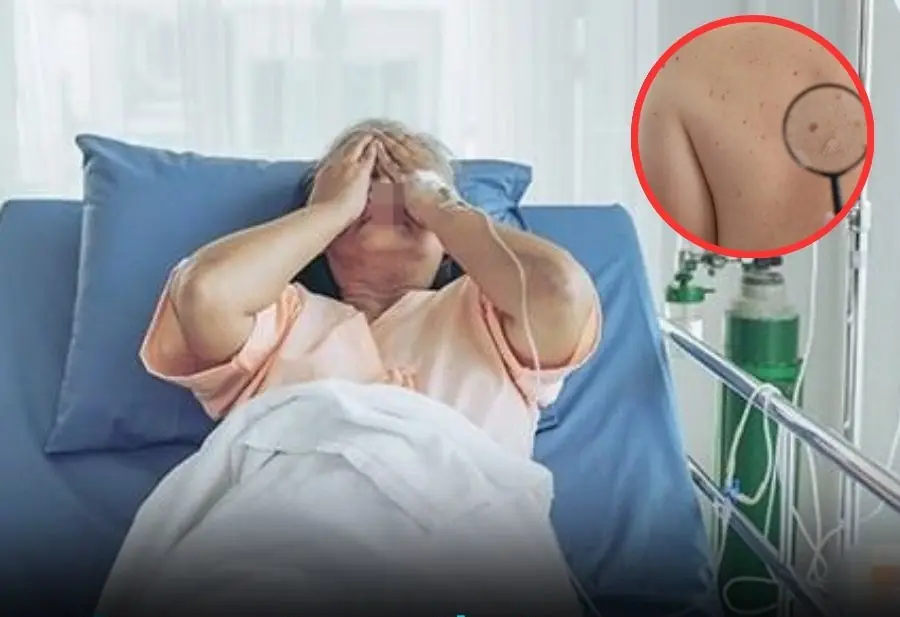
These 6 warning signs often appear late
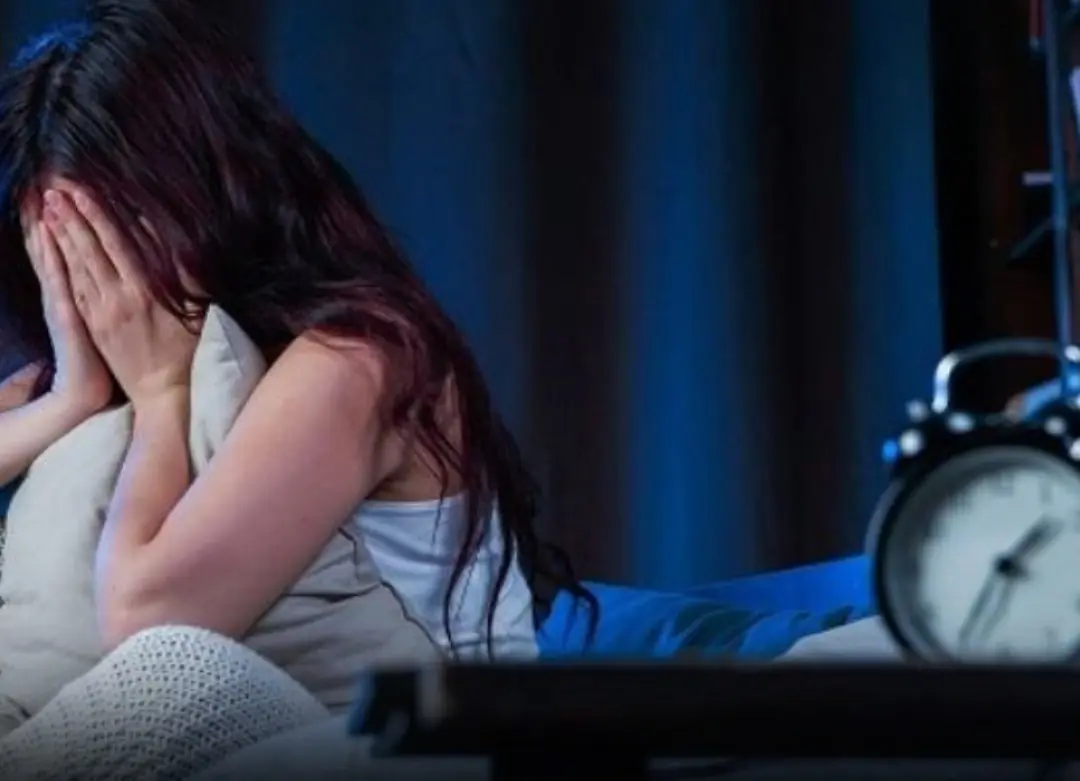

Frequently waking up at 3 or 4 a.m. can be linked to underlying health or lifestyle factors
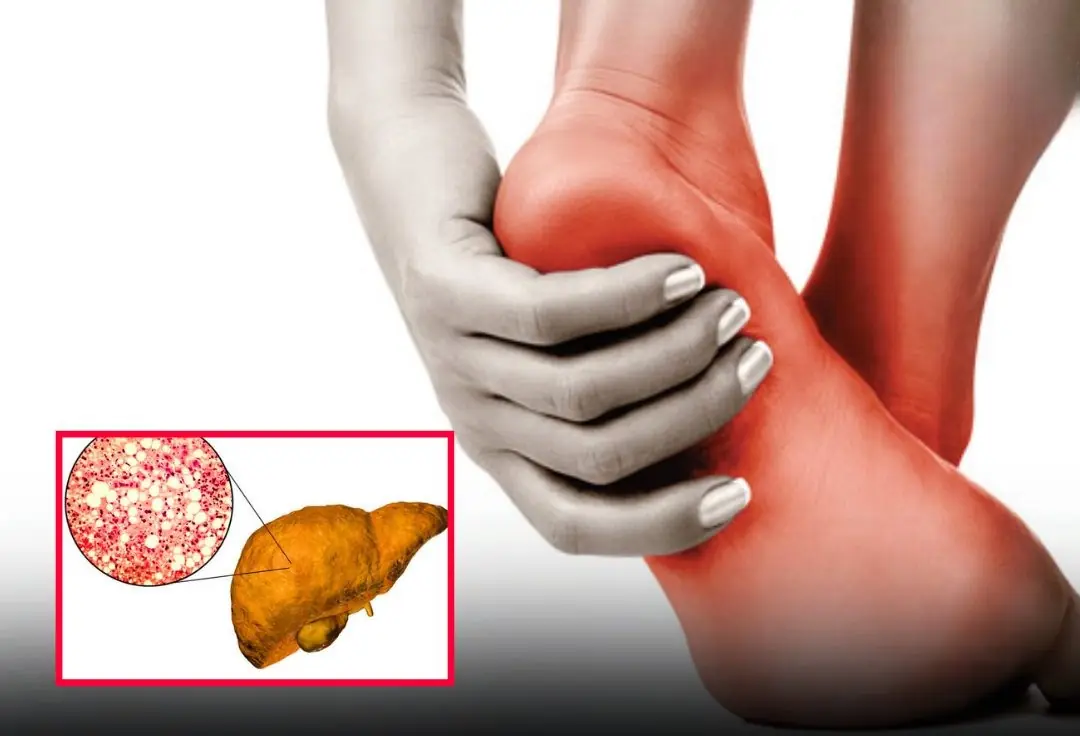
A change in your feet may signal severe fatty liver disease — don’t ignore it
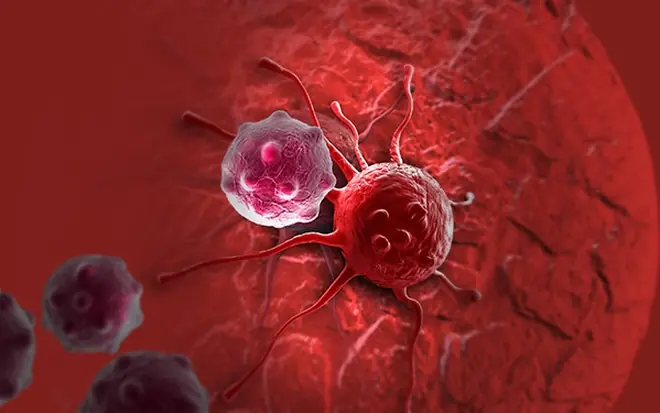
Why Can.cer Rates May Be Rising and 6 Vegetables That Contain Natural To.xins?
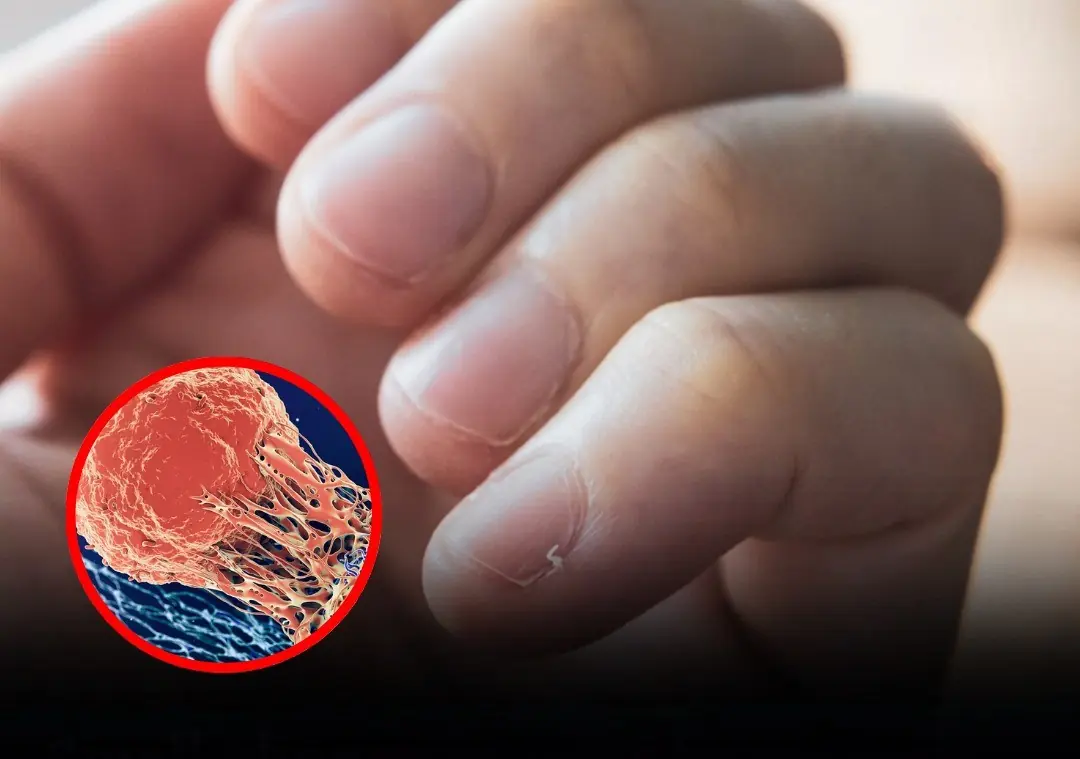
Here’s a quick test you can do yourself
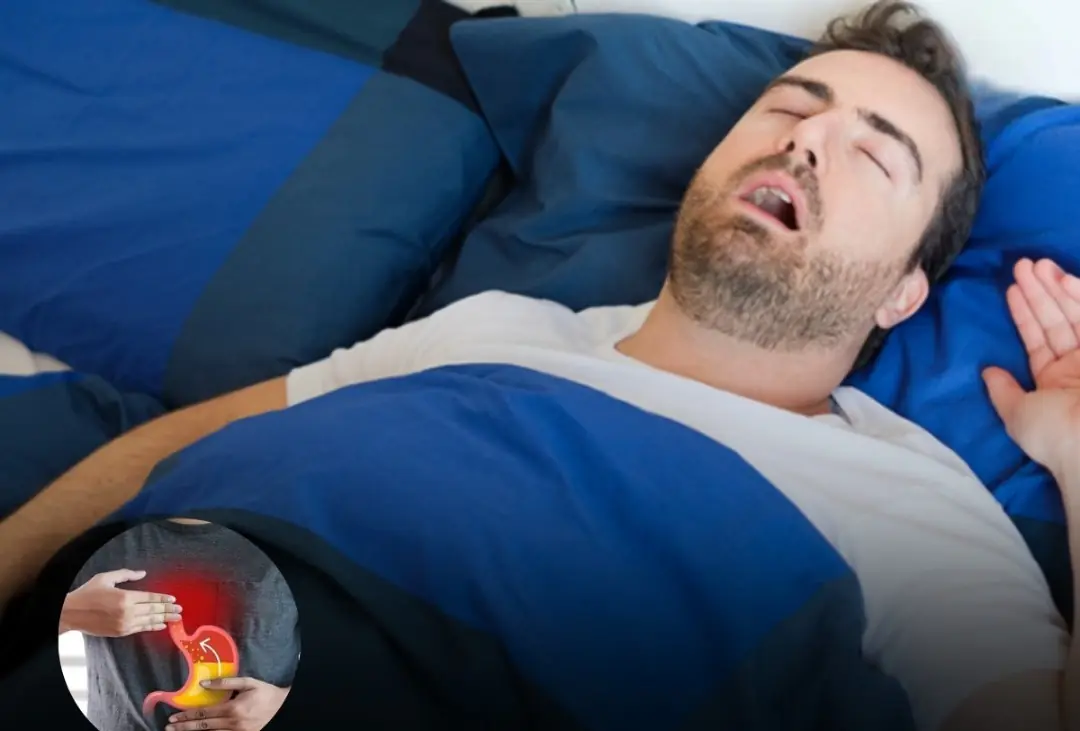

Waking Up With a Dry Mouth at Night? Here Are 8 Possible Reasons
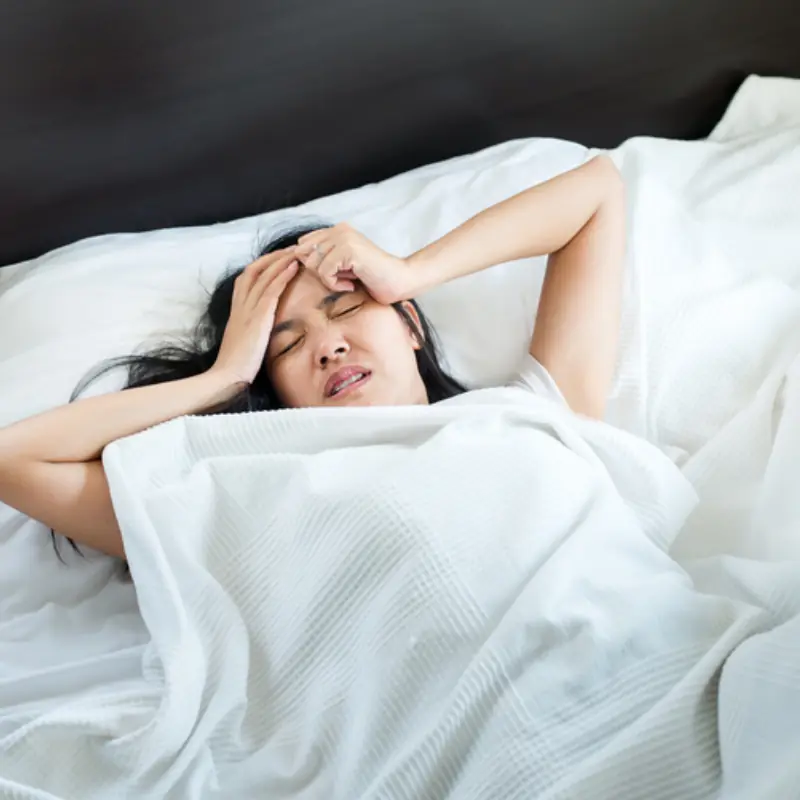

Sudden body jerks while falling asleep are common and usually harmless.

Small yellow lumps in the mouth may signal hidden oral health issues.

Heel pain when you wake up? Your body may be warning you about this condition

Why Do Your Legs Cramp at Night? Here’s What’s Really Happening — And How to Stop It

Pay Attention to Your Nails: These 3 Changes Could Be a Warning Sign

Experts reveal what really happens when you eat bananas in the morning

Early gum changes may reveal important clues about your health.
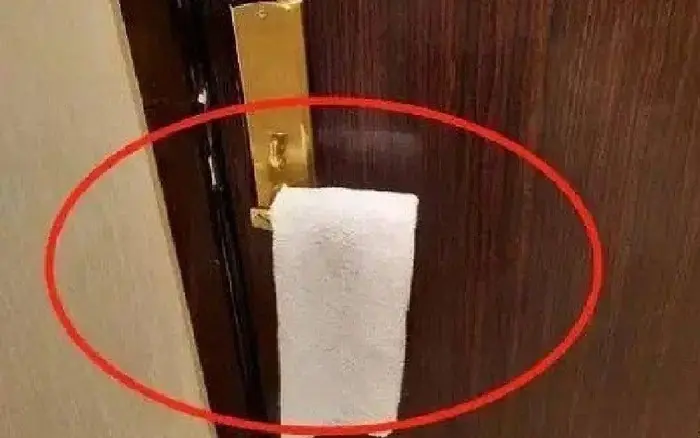

A Simple Nighttime Trick: Hanging a Towel on the Door Handle and Why It Helps

If you come across someone with bulging veins, you should definitely tell them this

Why Do You Often Wake Up Between 3 and 4 AM? 4 Possible Health Reasons

Nighttime symptoms may quietly signal early warning signs of diabetes.
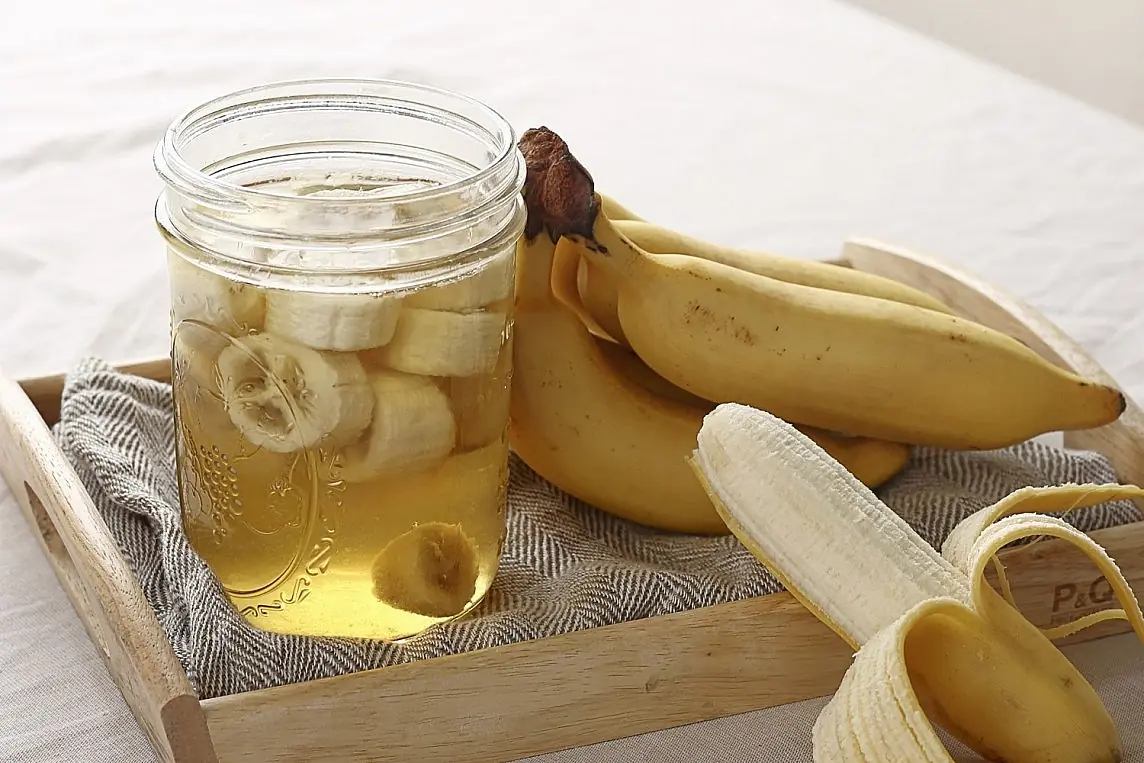

Just 4 ingredients — and you can make banana vinegar at home

Nighttime Leg Cramps Could Be a Sign Your Body Needs Attention

Apple cider vinegar has long been used as a natural home remedy for many everyday health concerns. Recently, one simple wellness habit has gained attention online: soaking your feet in apple cider vinegar.
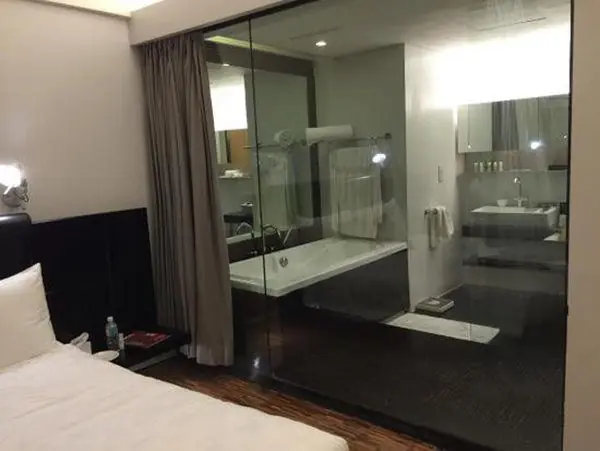

The Reason Some Hotels Use Transparent Glass Doors for Bathrooms
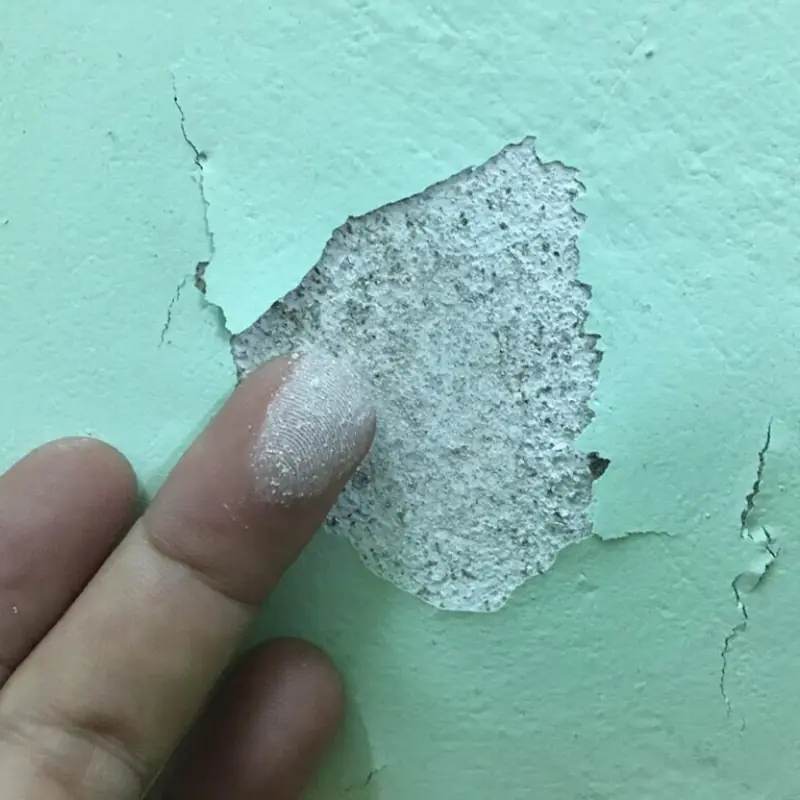

Simple DIY trick helps fix moldy or peeling walls quickly at home.

Doctors reveal surprising effects of eating hard-boiled eggs regularly

8 Early Warning Signs Of Ovarian Can:cer You Shouldn’t Ignore..
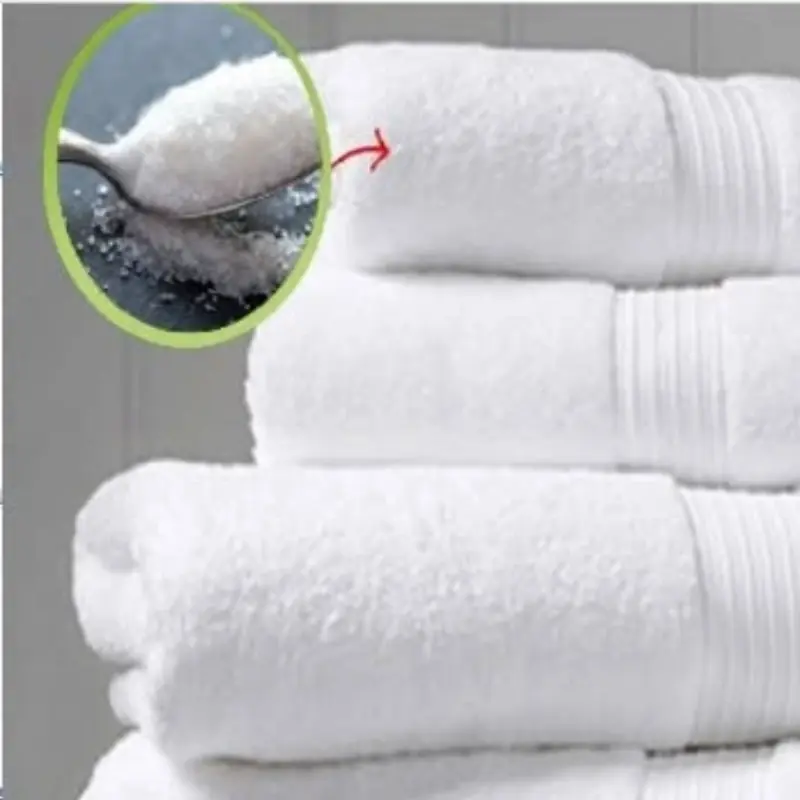

A simple natural trick can make laundry brighter and cleaner.

Woman with Stage - Four Colon Can:cer Reveals 5 Symptoms She Overlooked