Excessive Saliva Production in the Mouth: A Warning Sign of Health Issues You Shouldn’t Ignore
Excessive Saliva Production in the Mouth: A Warning Sign of Health Issues You Shouldn’t Ignore
Excessive saliva production, also known as sialorrhea or hypersalivation, can be more than just an annoying condition. While salivation is a normal process, too much saliva can signal underlying health problems that should be addressed promptly. Here’s what you need to know:
What is Excessive Saliva Production?
Excessive saliva production refers to the increased production of saliva, which may lead to drooling or difficulty swallowing. Normally, the body produces around 0.5 to 1.5 liters of saliva a day, but when this amount increases, it can affect daily activities and social interactions.
Potential Causes of Excessive Saliva Production
-
Oral Health Issues:
-
Dental infections: Gum disease, tooth decay, or mouth infections can cause inflammation, leading to excessive salivation.
-
Oral irritation: Certain oral conditions like canker sores or teething in children can trigger an increase in saliva production.
-
-
Neurological Conditions:
-
Parkinson’s disease: People with Parkinson’s often experience difficulty swallowing, leading to the accumulation of saliva in the mouth.
-
Stroke: A stroke can affect the nerves that control swallowing, leading to drooling.
-
Cerebral palsy: Children with cerebral palsy may have difficulty swallowing saliva, causing it to accumulate.
-
Multiple sclerosis (MS): This autoimmune disease can impact the nervous system and cause problems with swallowing.
-
-
Medications:
-
Certain medications, such as antipsychotics, anticonvulsants, and anticholinergics, can lead to increased saliva production as a side effect.
-
-
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD):
-
GERD, or acid reflux, can irritate the esophagus and cause an increase in saliva production as the body tries to neutralize stomach acids.
-
-
Infections:
-
Mumps and other viral or bacterial infections can cause swelling in the salivary glands, leading to excessive saliva production.
-
-
Pregnancy:
-
Hormonal changes during pregnancy, especially in the early stages, can lead to increased saliva production, often referred to as ptyalism.
-
-
Toxin Exposure:
-
Certain toxins or poisons, such as those from pesticides or heavy metals, can affect the body’s salivation process and cause excessive drooling.
-
-
Allergic Reactions:
-
Allergies to foods, medications, or environmental triggers can lead to increased salivation.
-
When Should You See a Doctor?
Excessive saliva production may seem like a mild nuisance, but if it persists or is accompanied by other symptoms such as difficulty swallowing, unexplained weight loss, or pain in the mouth, it’s important to seek medical attention.
Treatment Options
-
Oral care: Improving oral hygiene and treating dental infections can help reduce salivation.
-
Medications: If medications are causing the issue, your doctor may adjust the dosage or prescribe alternatives.
-
Botox injections: In severe cases, Botox injections into the salivary glands can reduce saliva production.
-
Surgical treatment: For conditions like salivary gland tumors, surgical intervention may be required.
-
Physical therapy: For those with neurological conditions, physical therapy may help with swallowing issues.
Conclusion
While excess saliva production might seem trivial, it can sometimes be a symptom of a more serious health problem. Don’t ignore it, especially if it’s persistent or associated with other symptoms. Early diagnosis and treatment can improve your quality of life and help manage any underlying conditions effectively.
Would you like to know more about specific treatments or conditions related to excessive salivation?

News in the same category

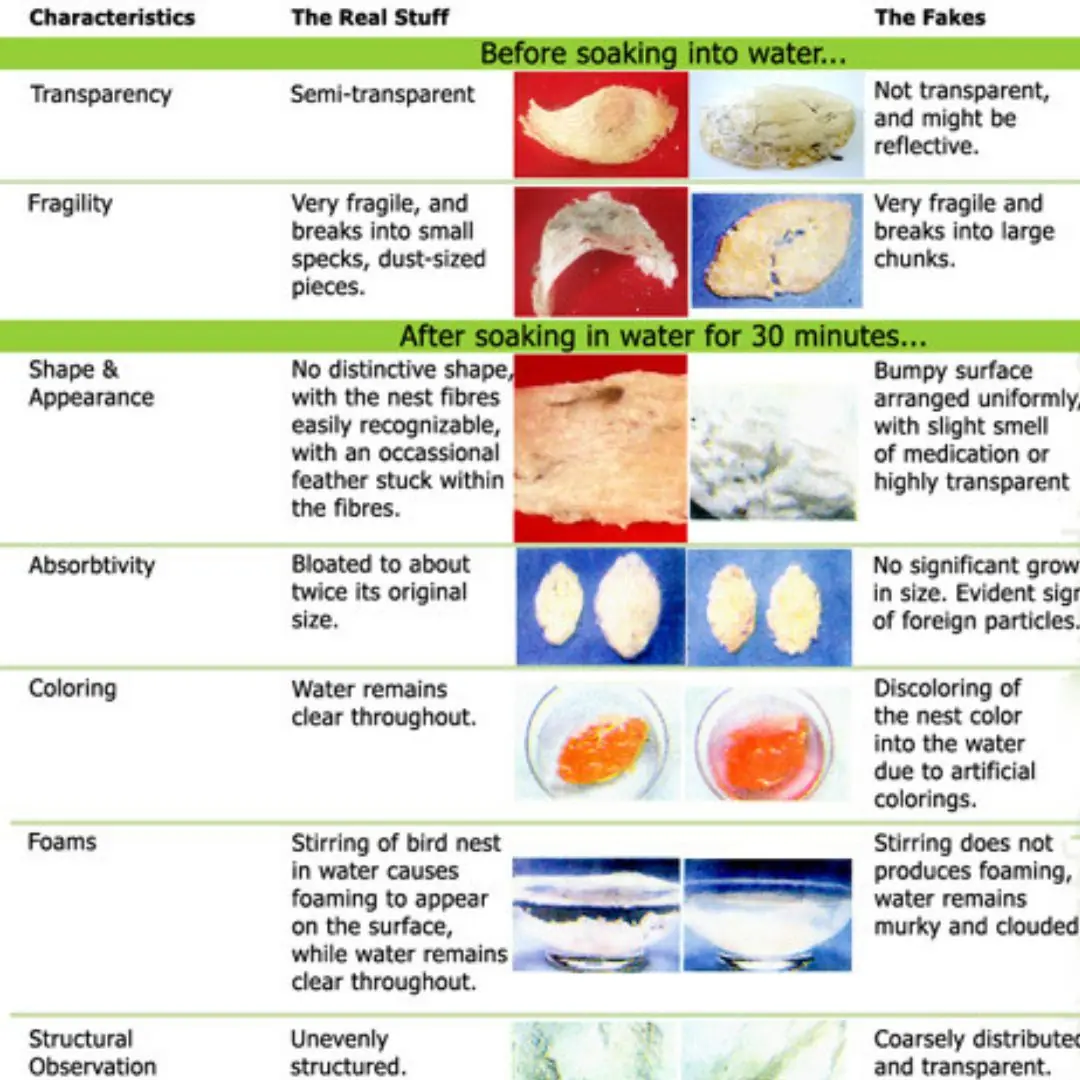
7 Ways to Differentiate Between Pure Bird Nest and Fake Bird Nest
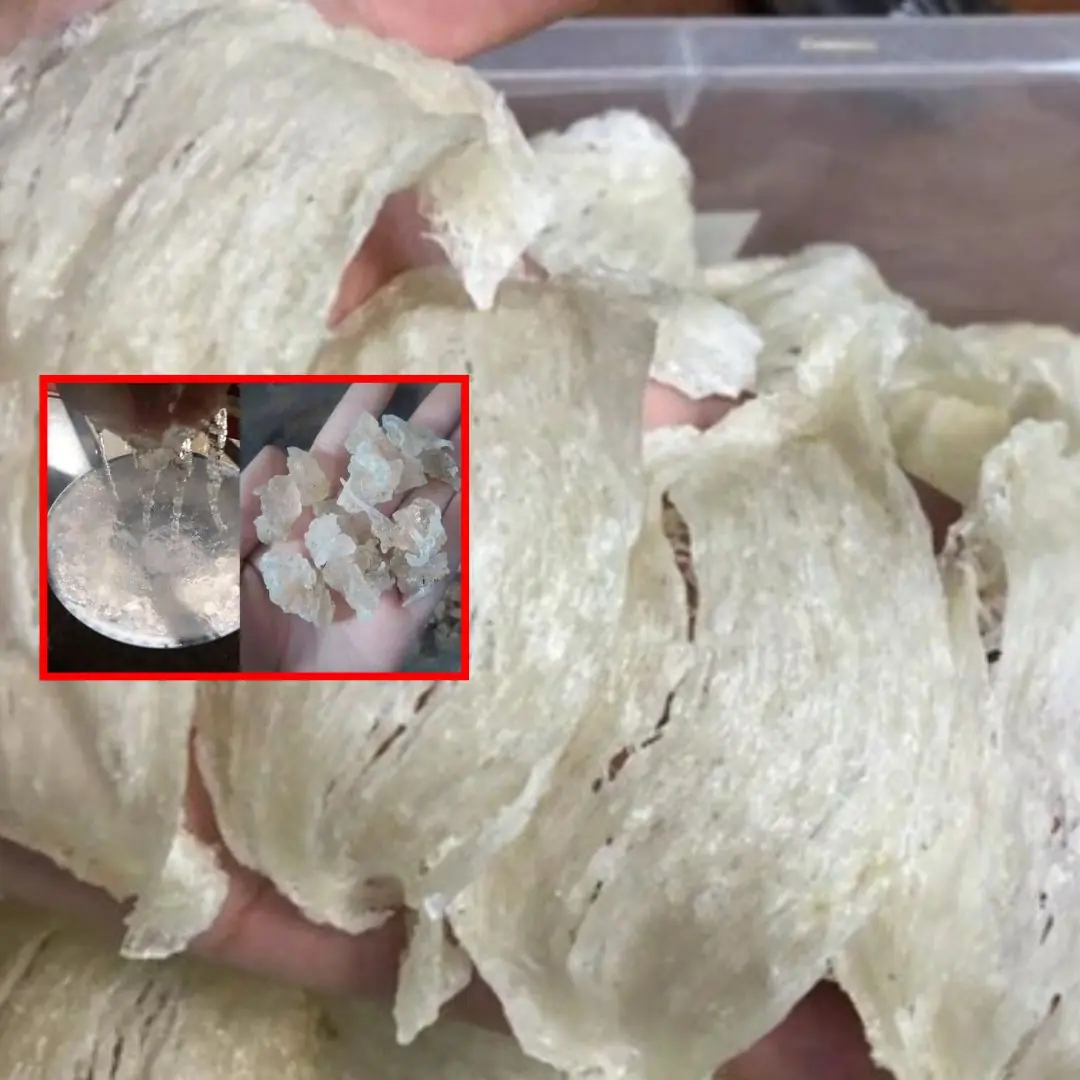

Doctor shows how to identify real and fake bird's nest
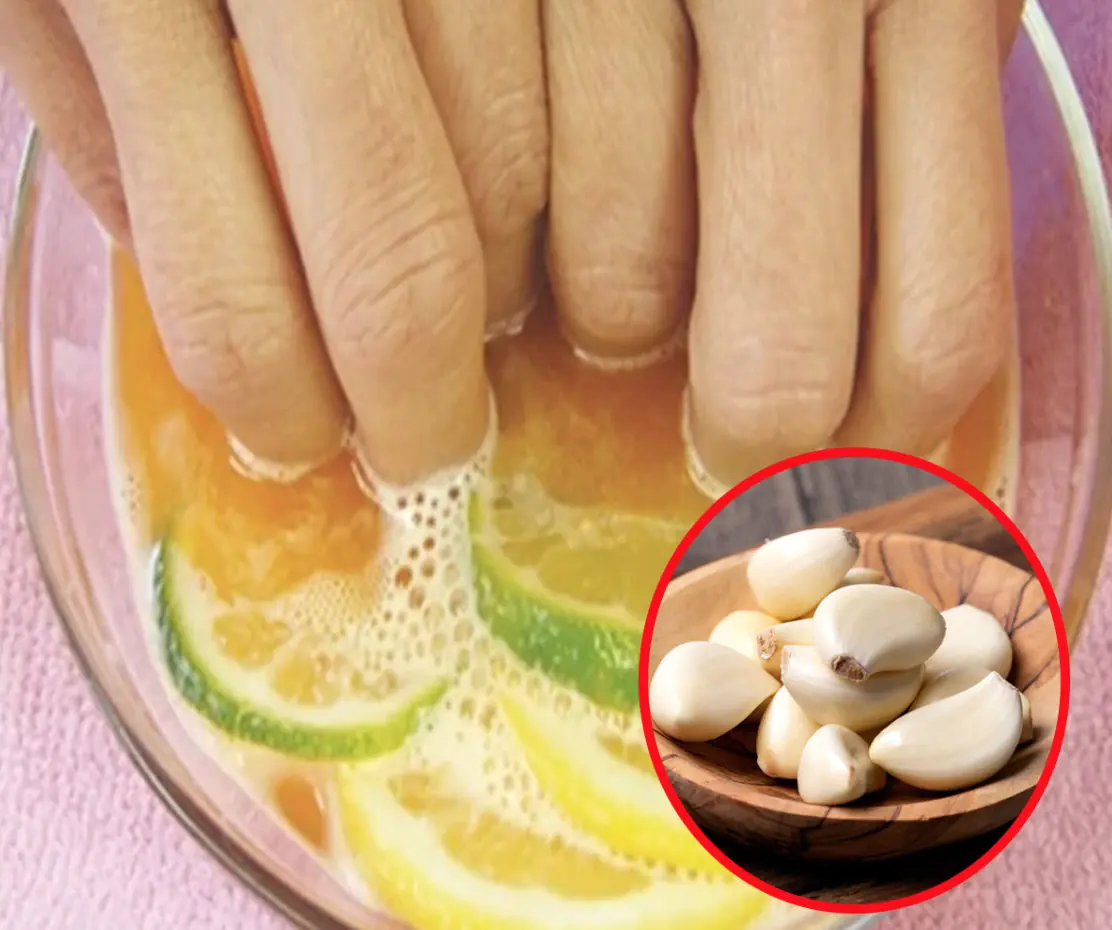

Tips to remove garlic smell from hands when cooking

Many doctors recommend using two pillows when sleeping for better sleep health!
Eat 4 foods on an empty stomach in the morning to help clean the intestines, improve digestion, and prevent canc.er

Walking around the market, a smart person can immediately see that these 5 types of vegetables are "soaked in chemicals", especially number 4
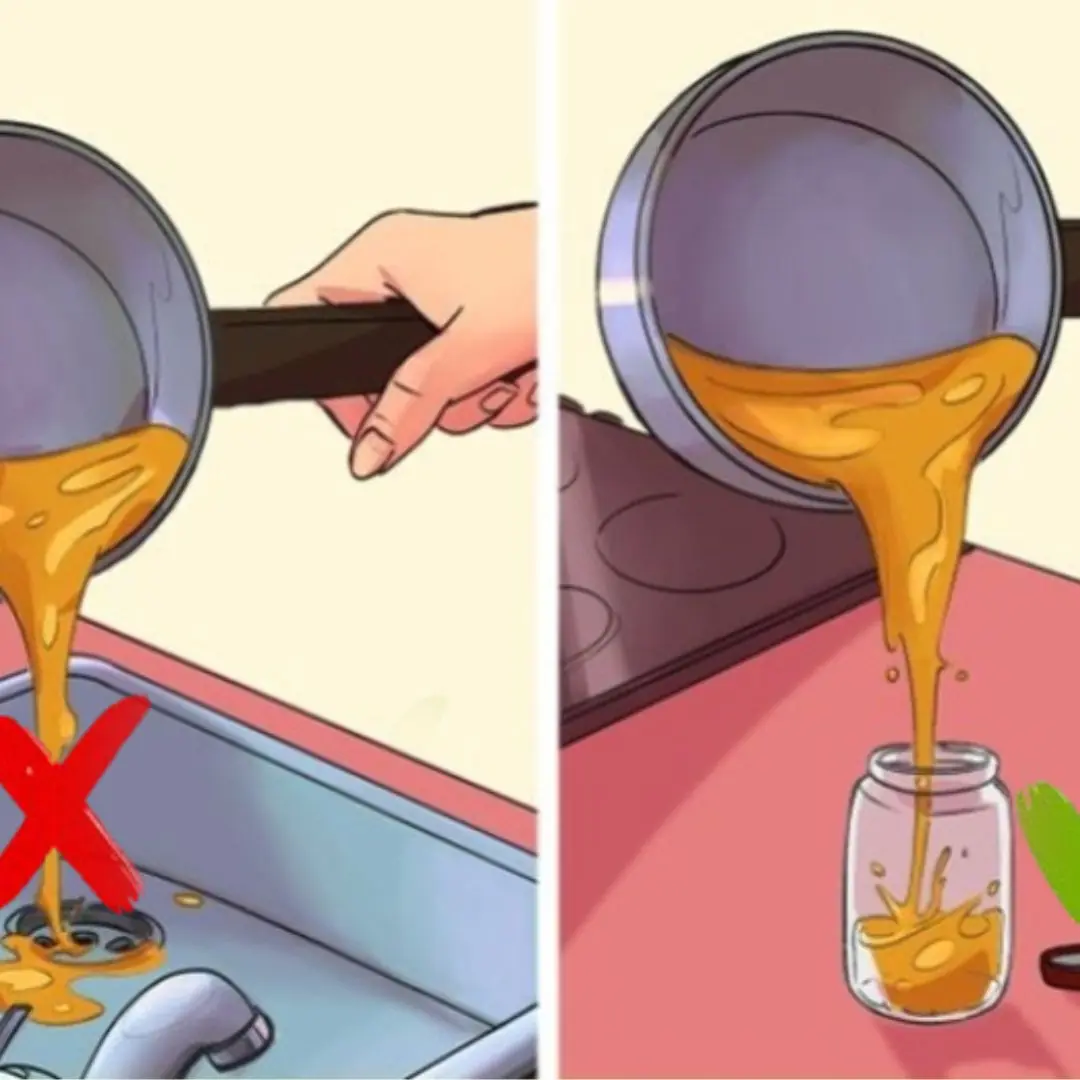
6 effective and safe ways to handle leftover cooking oil you should know

How to clean your TV screen safely without causing damage

Tips with salt and beer

Pay attention to these types of garlic when going to the market

Don’t Throw Away Leftover Lemon Peels — Keep Them for These 5 Amazing Uses

Many people do not know: Don't be foolish to combine these things with beef!

5 mistakes when washing dishes that cause cancer in the whole family, many people do them every day without knowing, especially number 3

Doctor reveals the 'often overlooked' body part you MUST clean every day, or it could be life-threatening

There Are 4 "Electricity-Guzzling Monsters" in the House—Here's How I Finally "Tamed" Them!

Why Do Towels Turn Yellow and Stiff Over Time? Add This Simple Ingredient to Restore Them Instantly

4 things you SHOULD NOT put in the refrigerator: The longer you leave them, the more they will spoil, completely counterproductive!

This wild vegetable "pumps" natural retinol, and is also super rich in vitamin C. Eat it regularly to keep your skin plump with collagen

These 7 vegetables turn out to be super "oil absorbers", be careful because the more you eat, the fatter you get
News Post

Master the Art of Growing Orchids: Expert Tips for Lush, Long-Lasting Blooms
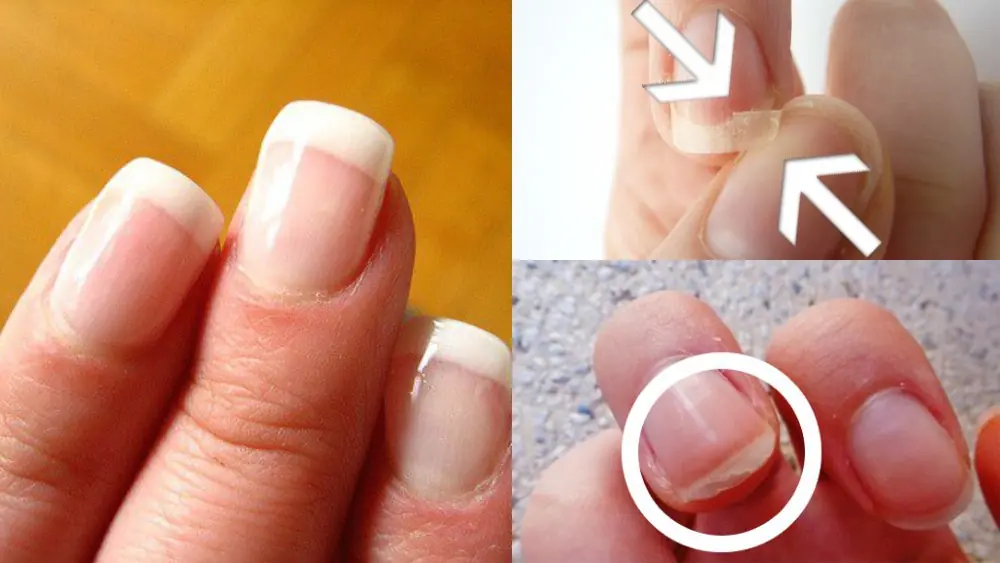
Look at your nails to detect health problems

Plant Tomatoes Like a Pro: 8 Ingredients for Super-Sonic Growth
What happens if you hold in your fart?

The Romance of a Busy Broker

The Lumber Room

How to Propagate Sweet Potatoes to Grow New Slips

How to Plant Houseplants in a Pot Without Drainage Holes

The Other Wise Man

How to remove to.xins in bean sprouts

7 Ways to Differentiate Between Pure Bird Nest and Fake Bird Nest

Doctor shows how to identify real and fake bird's nest

Growing loofah gourds: Learn how to grow your own loofah sponges

Tips to remove garlic smell from hands when cooking

Have you ever wondered why when you wake up, mysterious bruises appear on your body?

The Gospel According To Joan

Are These Mutant Eggs Safe to Eat? The Truth About Double Yolks and Rainbow Shells

Growing hydrangeas from cuttings

One Thing Most Stro.ke Victims Have in Common: Are You Living at Risk of Cerebral Infarction?
