
The amazing health benefits of potatoes

General Overview of Potatoes
Potatoes are tubers that grow underground on the roots of the potato plant, scientifically known as Solanum tuberosum. This plant belongs to the nightshade family, related to tomatoes and tobacco.
Originating in South America, potatoes were introduced to Europe in the 16th century and are now grown in numerous varieties worldwide.
Potatoes are versatile tubers that are relatively inexpensive, easy to grow and care for, and rich in nutrients. Therefore, many households in Vietnam have chosen potatoes as a staple food in their daily meals.
Potatoes can be prepared in various ways, including boiling, frying, baking, and are commonly enjoyed as popular snacks.
Nutritional Composition of Potatoes
Potatoes are a healthy food option, but the benefits depend on cooking methods, food combinations, and storage. Raw potatoes are relatively low in calories. They also provide essential nutrients such as vitamin C, vitamin B6, and minerals.
A 100-gram serving of potatoes contains approximately:
-
94 calories
-
0.15 grams of fat
-
0 grams of cholesterol
-
21.08 grams of carbohydrates
-
2.1 grams of fiber
-
2.10 grams of protein
-
10 milligrams of calcium
-
0.64 milligrams of iron
-
27 milligrams of magnesium
-
75 milligrams of phosphorus
-
544 milligrams of potassium
-
12.6 milligrams of vitamin C
-
0.211 milligrams of vitamin B6
-
38 micrograms of folate
Additionally, potatoes supply niacin, choline, and zinc.
Raw potatoes contain very little sodium - only 10 mg per 100 grams. However, this contrasts with processed potato products such as French fries, which have significantly higher sodium content.
Potatoes also contain alpha-lipoic acid (ALA), a compound that helps the body convert glucose into energy. Some evidence suggests that ALA may help control blood sugar levels, improve vasodilation, protect against diabetic retinopathy, and preserve brain and nerve tissue.
Quercetin, a flavonoid found in potato skins, has anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects, protecting cells from damage caused by free radicals. Vitamin C in potatoes acts as an antioxidant that may help prevent cell damage and cancer, while also supporting healthy digestion and cardiovascular function. The fiber content in potatoes contributes to digestive and circulatory health.
Health Benefits of Potatoes
1. Cardiovascular Health
Potatoes provide fiber, potassium, vitamin C, and vitamin B6 while containing no cholesterol, all of which support heart health. Fiber helps reduce total blood cholesterol, lowering the risk of heart disease. Research based on NHANES data found a link between higher potassium intake and lower sodium intake with reduced risk of heart disease mortality.
2. Blo.od Pressure
Low sodium intake is essential for maintaining healthy blo.od pressure, but increasing potassium intake is equally important. Potassium helps dilate blood vessels.
According to the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), fewer than 2% of American adults meet the recommended daily intake of 4,700 milligrams of potassium.
Additionally, minerals such as potassium, calcium, and magnesium in potatoes have been shown to naturally reduce blood pressure.
3. Bone Health
Minerals including iron, phosphorus, calcium, magnesium, and zinc in potatoes help build and maintain bone structure and strength. Iron and zinc play important roles in collagen production and maturation.
Phosphorus and calcium are vital for bone structure, but balancing these minerals is critical for proper bone mineralization. Excess phosphorus and low calcium can lead to bone loss and contribute to osteoporosis.
4. Digestive Health
The fiber content in potatoes helps prevent constipation and promotes regularity for a healthy digestive system.
5. Weight Management and Satiety
Fiber is widely recognized as important for weight management and appetite control. It expands in the digestive tract, increasing feelings of fullness and reducing hunger. Eating potatoes can help you feel satiated longer and decrease the likelihood of overeating.
6. Metabolism
Potatoes are an excellent source of vitamin B6, which plays a key role in energy metabolism by breaking down carbohydrates and proteins into glucose and amino acids—simple compounds the body easily uses for energy production.
7. Immune Support
Some studies have found that vitamin C can reduce the severity and duration of colds. Potatoes are a rich dietary source of vitamin C.
Important Notes When Consuming Potatoes
-
Do Not Peel the Skin: It is a common misconception that all the nutrients in potatoes are in the skin. While the skin contains about half of the fiber, most nutrients (>50%) are found inside the potato itself.
-
Cooking Methods Affect Nutrients: Like many vegetables, cooking affects the nutrient content, especially water-soluble vitamins and minerals. To preserve most nutrients in cooked potatoes, steaming or microwave cooking is recommended.
-
Proper Storage Temperature: Storing potatoes at temperatures that are too cold can cause them to turn black or gray when cooked. To prevent this, store potatoes between 7.2°C and 10°C (45°F to 55°F). Avoid eating sprouted potatoes, as they can cause poisoning and lower blood pressure.

News in the same category


These 5 groups of people shouldn’t eat watermelon
Can one kidney survive? Detailed answers from experts
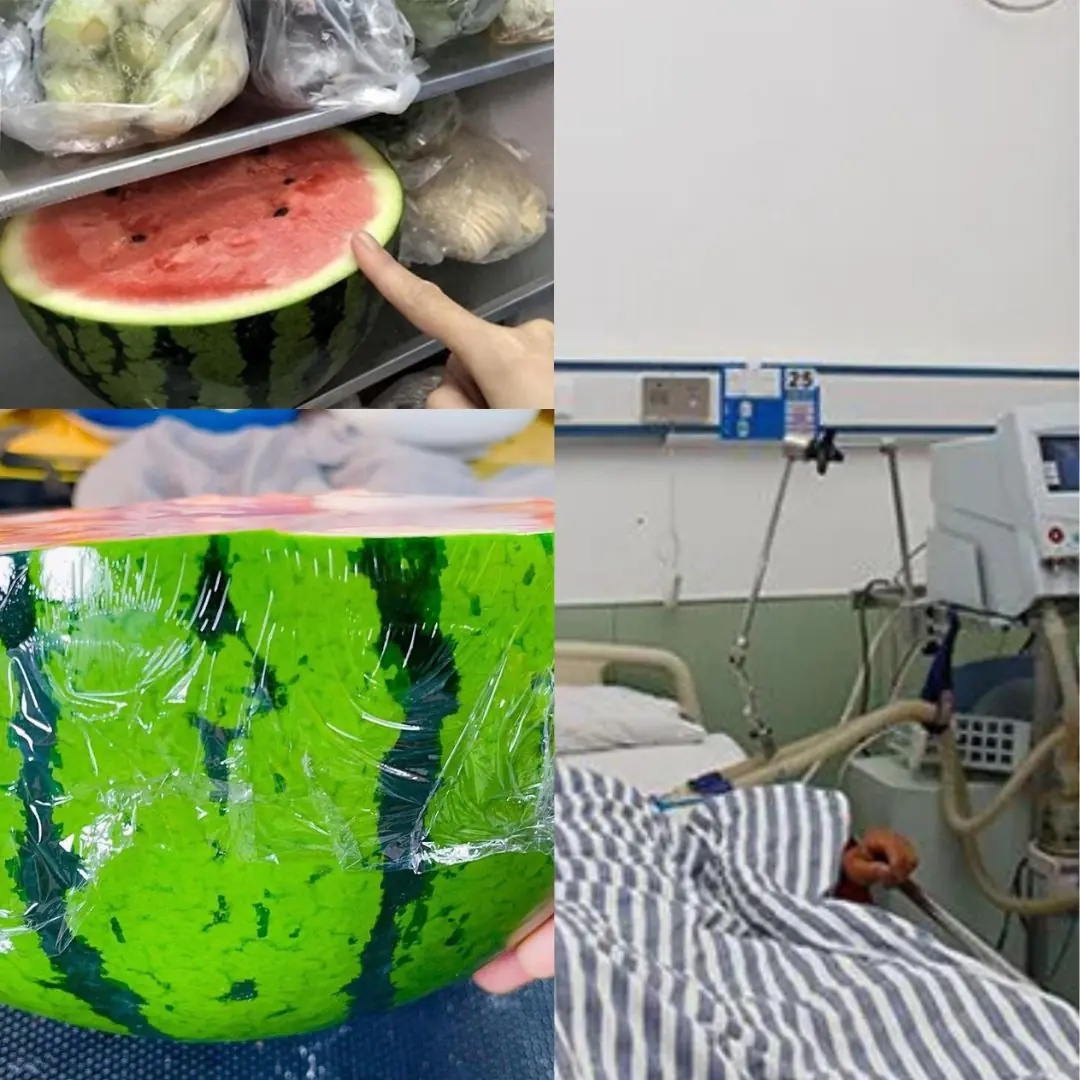
Whole family hospitalized after eating watermelon left overnight in the refrigerator: Mistakes in preserving watermelon that many people do
The disease quickly turns into cancer, changing lifestyle can 'treat' it but many people are still indifferent

Don’t Cook These Without Blanching First: 7 Common Foods That Could Accumulate Hidden To.xins in Your Body

Acute kidney injury is one of the dangerous diseases, seriously threatening the patient's health
New COVID-19 Variant Shows Unusual Behavior: Doctors Warn of Early Silent Symptoms That Are Often Overlooked
Warning signs you may have a brain hemorrhage, don't ignore them or you'll regret it too late

Seemingly harmless natural foods can affect hormones in the body!
6 Things That Will Happen When You Start Drinking Coke Every Day

8 Early Signs of Arthritis You Should Never Ignore

5 Common Mistakes When Drinking Honey That Can Harm Your Li.ver and Kid.neys — Especially #2

Sweet but Risky: 7 Types of People Who Should Avoid Ripe Mangoes

5 warning signs of vitamin E deficiency
5 morning habits that are as harmful to the liver as drinking alcohol

Excessive Yawning: A Sign of Many Dangerous Diseases
Warning signs of acute kidney injury should not be ignored

Warning: 3 Cooking Oils You Should Avoid Due to Cancer Risk — Don’t Sacrifice Your Family’s Health for Savings
News Post

The “Ginseng of the Water”: A Nutrient-Rich Fish That’s Shockingly Affordable

Signs of Omega-3 deficiency you should not ignore
Looking at the phone too much, the young man could not lift his head.

How to properly preserve onions

These 5 groups of people shouldn’t eat watermelon

DIY Garden Sprinkler: Easy and Affordable Watering Solution Using Plastic Bottles

Tips to keep ripe avocados fresh longer

Baking Soda is a Gardener’s Best Friend: 10 Clever Uses in the Garden

Tips to help you save on your electricity bill

What is strange?

A Christmas Dream, and How It Came to Be True

Can one kidney survive? Detailed answers from experts

Pay attention to these signs of your husband

Learn How To Grow Cucumbers This Summer

13 Best Tips for Planting and Growing Great Tomatoes

The Storyteller

You should consider carefully

The Open Window
