
These 10 symptoms indicate latent diabetes
Diabetes is one of the most prevalent chronic health conditions worldwide. While Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes are commonly diagnosed, latent diabetes - or what is sometimes called prediabetes - can often go unnoticed. Latent diabetes occurs when blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not yet high enough to be classified as Type 2 diabetes. If left unchecked, latent diabetes can progress into full-blown Type 2 diabetes, which can lead to serious health complications such as heart disease, kidney failure, nerve damage, and even blindness.
The good news is that latent diabetes can often be reversed or managed with lifestyle changes if detected early. Being aware of the early warning signs and symptoms is essential in preventing the condition from developing further. In this article, we’ll explore 10 symptoms that might indicate latent diabetes, so you can take the necessary precautions and prevent long-term health problems.
1. Frequent Urination (Polyuria)
What to Look For:
-
You may find yourself needing to urinate more frequently, particularly during the night (nocturia).
Why It’s Concerning:
-
The kidneys work overtime to filter excess sugar from the bloodstream, which can result in increased urination. If you are experiencing frequent urination without other obvious causes like increased fluid intake, this could be an early sign of diabetes.
What to Do:
-
Monitor your urination frequency. If it is excessive, especially at night, consider consulting your healthcare provider for a blood sugar test.
2. Unexplained Thirst (Polydipsia)
What to Look For:
-
Feeling excessively thirsty despite drinking plenty of fluids.
Why It’s Concerning:
-
Increased urination can lead to dehydration, which triggers intense thirst. This is a common symptom of latent diabetes, as the body tries to compensate for lost fluids.
What to Do:
-
Pay attention to your thirst levels. If you find yourself drinking large amounts of water constantly, it’s worth discussing this with your doctor.
3. Fatigue and Weakness
What to Look For:
-
Feeling unusually tired or weak, even after a full night's rest.
Why It’s Concerning:
-
When the body’s cells are not receiving enough glucose due to insulin resistance, you may feel drained of energy. Fatigue is one of the most common early warning signs of latent diabetes.
What to Do:
-
If you’re constantly feeling tired and don’t have an obvious reason (like lack of sleep or physical exhaustion), it's a good idea to get your blood sugar levels checked.
4. Blurred Vision
What to Look For:
-
Experiencing blurry vision, especially after eating or drinking.
Why It’s Concerning:
-
High blood sugar levels can lead to fluid changes in the eyes, affecting your ability to focus. Persistent blurred vision can be a sign that your blood sugar levels are not well controlled.
What to Do:
-
If you are experiencing blurry vision without any changes in your environment, it’s crucial to get your blood sugar checked as this could be an early indicator of latent diabetes.
5. Slow Healing of Cuts and Wounds
What to Look For:
-
You may notice that small cuts, bruises, or wounds take longer to heal than usual.
Why It’s Concerning:
-
Elevated blood sugar levels can affect your immune system and reduce the body’s ability to heal itself. Slow wound healing can be a subtle sign of latent diabetes.
What to Do:
-
Pay attention to how quickly your body heals. If you notice a delay in healing or recurring infections, it’s important to check your blood sugar levels.
6. Increased Hunger (Polyphagia)
What to Look For:
-
Feeling hungrier than usual, even after eating.
Why It’s Concerning:
-
In latent diabetes, the body becomes resistant to insulin, causing a shortage of glucose in the cells. This can trigger increased hunger as the body tries to compensate for the lack of energy.
What to Do:
-
If you are constantly hungry, despite eating regular meals, consider discussing your symptoms with a healthcare professional.
7. Tingling or Numbness in Hands or Feet
What to Look For:
-
A sensation of tingling, burning, or numbness in your hands, fingers, feet, or toes.
Why It’s Concerning:
-
High blood sugar can cause nerve damage, a condition known as diabetic neuropathy. Early-stage neuropathy can cause tingling or numbness in the extremities.
What to Do:
-
If you experience persistent tingling or numbness, especially in your hands or feet, it’s essential to consult a healthcare provider, as this could be a sign of latent diabetes affecting your nerves.
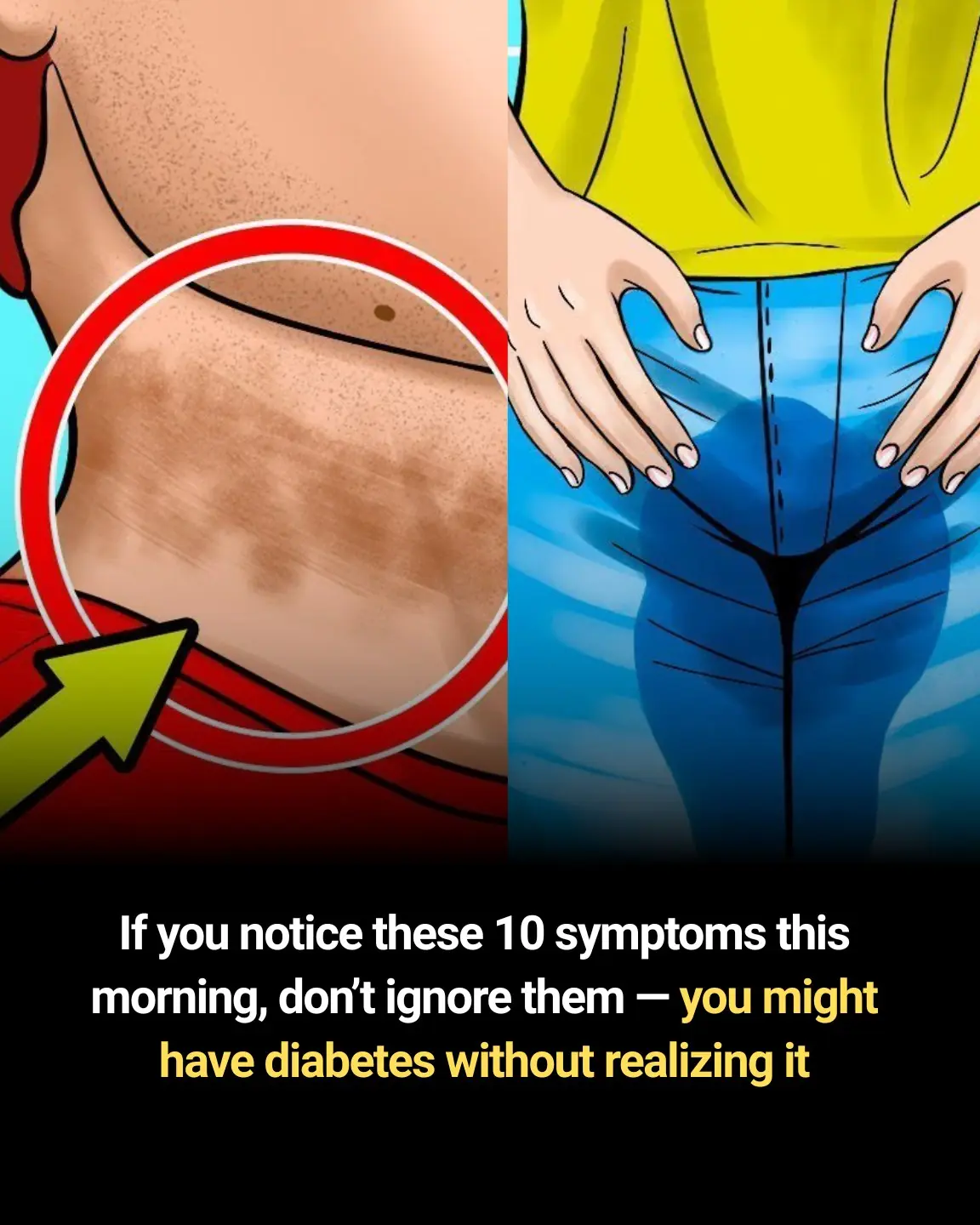
8. Darkened Skin in Certain Areas (Acanthosis Nigricans)
What to Look For:
-
Dark, velvety patches of skin, often in areas like the neck, armpits, or groin.
Why It’s Concerning:
-
Acanthosis nigricans is a skin condition commonly associated with insulin resistance. It occurs when excess insulin in the blood causes the skin to darken and thicken.
What to Do:
-
If you notice any unusual dark patches of skin, especially in the areas mentioned, it’s important to consult with a doctor for further evaluation of your blood sugar levels.
9. Frequent Infections
What to Look For:
-
Recurrent infections, such as urinary tract infections (UTIs), yeast infections, or skin infections.
Why It’s Concerning:
-
High blood sugar levels weaken the immune system, making it easier for infections to develop. This is common in people with latent diabetes, as their immune system struggles to fight off infections.
What to Do:
-
If you experience frequent infections or persistent skin issues, seek medical attention to rule out latent diabetes or other underlying conditions.
10. Unexplained Weight Gain or Loss
What to Look For:
-
Sudden weight changes without a clear cause, such as gaining weight despite not overeating or losing weight without trying.
Why It’s Concerning:
-
Unexplained weight gain can be caused by high insulin levels, while sudden weight loss may occur when the body starts using muscle mass and fat for energy due to an inability to use glucose properly.
What to Do:
-
If you notice any unexpected weight changes, track your diet and exercise habits, and consult with your healthcare provider to check your blood sugar levels.
How to Prevent Latent Diabetes: Precautionary Measures
Preventing latent diabetes, or prediabetes, involves adopting lifestyle changes that can help regulate blood sugar levels and improve overall health. If detected early, latent diabetes can often be reversed or managed effectively with a few proactive steps. Here are key precautionary measures to reduce the risk of latent diabetes and maintain optimal health:
1. Maintain a Healthy, Balanced Diet
Why It’s Important:
Diet plays a crucial role in regulating blood sugar levels. A poor diet, high in processed foods, sugary snacks, and unhealthy fats, can contribute to insulin resistance, which is a precursor to diabetes.
Prevention Tips:
-
Eat more whole foods: Focus on a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
-
Limit refined sugars and processed foods: Avoid sugary drinks, pastries, and processed snacks that cause spikes in blood sugar levels.
-
Choose complex carbohydrates: Incorporate fiber-rich foods such as oats, quinoa, and brown rice into your meals to help stabilize blood sugar levels.
-
Control portion sizes: Eating balanced portions will prevent overeating and manage blood sugar better.
2. Engage in Regular Physical Activity
Why It’s Important:
Exercise is one of the most effective ways to manage blood sugar levels. Physical activity helps improve insulin sensitivity, meaning your body can better use the insulin it produces to process sugar in the bloodstream.
Prevention Tips:
-
Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week: Activities such as brisk walking, cycling, swimming, or dancing can help maintain a healthy weight and improve insulin response.
-
Incorporate strength training: Adding muscle-building exercises, like weightlifting or resistance training, can help increase muscle mass, which in turn helps to regulate blood sugar levels.
-
Stay active throughout the day: Avoid long periods of sitting by taking short breaks to walk or stretch every hour.
3. Maintain a Healthy Weight
Why It’s Important:
Carrying excess weight, especially around the abdominal area, can increase the risk of developing insulin resistance. Even modest weight loss (5-10% of your body weight) can significantly improve blood sugar control.
Prevention Tips:
-
Set realistic goals: Aim for slow, gradual weight loss by making small, sustainable changes to your diet and exercise routine.
-
Monitor your weight: Regularly track your weight and body measurements to keep an eye on potential changes.
-
Focus on overall wellness: Rather than focusing solely on weight loss, prioritize a healthier lifestyle that includes nutritious eating and regular physical activity.
4. Monitor Blood Sugar Levels
Why It’s Important:
For individuals with a family history of diabetes or those experiencing risk factors (such as being overweight or having a sedentary lifestyle), regular blood sugar monitoring is essential to catch any irregularities early.
Prevention Tips:
-
Get regular check-ups: If you are at risk for diabetes, get regular blood sugar tests from your doctor to check for any signs of insulin resistance.
-
Track your diet and activity: Keeping a food and exercise journal can help you understand how your lifestyle choices impact your blood sugar levels.
-
Know your numbers: If your blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not yet high enough for a diabetes diagnosis, follow up with your doctor to monitor your health more closely.
5. Reduce Stress Levels
Why It’s Important:
Chronic stress can increase the production of cortisol, a hormone that, when elevated over time, can interfere with insulin function and lead to higher blood sugar levels.
Prevention Tips:
-
Practice mindfulness and relaxation: Incorporate stress-reduction techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, or yoga into your daily routine.
-
Take regular breaks: Break up your day with short moments of relaxation to help manage stress and avoid burnout.
-
Prioritize self-care: Make time for activities that you enjoy and that help you unwind, such as reading, spending time with loved ones, or engaging in hobbies.
6. Get Sufficient Sleep
Why It’s Important:
Poor sleep quality and insufficient sleep have been linked to an increased risk of developing Type 2 diabetes. Inadequate rest can affect your body’s ability to process glucose and regulate hormones involved in hunger and metabolism.
Prevention Tips:
-
Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep per night: Ensure you get enough rest to help your body function optimally.
-
Stick to a regular sleep schedule: Going to bed and waking up at the same time each day helps regulate your body’s internal clock and improve sleep quality.
-
Create a restful environment: Keep your bedroom cool, dark, and quiet to promote better sleep. Avoid screens and heavy meals before bed.
7. Quit Smoking and Limit Alcohol Consumption
Why It’s Important:
Tobacco use and excessive alcohol consumption both contribute to insulin resistance, which is a key factor in the development of latent diabetes and Type 2 diabetes.
Prevention Tips:
-
Quit smoking: If you smoke, seek professional help or support groups to quit. Quitting smoking can dramatically reduce your risk of diabetes and improve overall health.
-
Limit alcohol: If you drink alcohol, do so in moderation. The American Heart Association recommends no more than one drink per day for women and two drinks per day for men.
8. Stay Hydrated
Why It’s Important:
Drinking enough water is crucial for maintaining blood sugar balance and supporting kidney function. Staying hydrated can help your kidneys flush out excess sugar through urine.
Prevention Tips:
-
Drink water throughout the day: Aim for at least 8 cups (2 liters) of water per day to stay hydrated and support your body’s natural processes.
-
Limit sugary drinks: Avoid sugary beverages such as soda, sweetened coffee, and energy drinks, as they can cause spikes in blood sugar.
Conclusion: Prevention is Key
Latent diabetes is a serious condition that can lead to Type 2 diabetes if left untreated. The good news is that it is often preventable or manageable with lifestyle changes. By adopting healthy habits like eating a balanced diet, staying active, managing stress, getting enough sleep, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol, you can reduce your risk of developing latent diabetes and improve your overall health.
Regular check-ups and monitoring your blood sugar levels are essential in catching early signs of insulin resistance. If you notice any symptoms or risk factors, don’t wait - take action now to prevent the progression of latent diabetes into Type 2 diabetes.
Takeaway: The key to preventing latent diabetes lies in being proactive with your health. By following these preventative measures, you can ensure that you stay healthy, avoid serious complications, and enjoy a vibrant, active life.
News in the same category


The Part of the Pig Often Dismissed as “Dirty” and Thrown Away: Turns Out It’s a “Miracle Food” with 10 Times More Iron Than Meat

An 8-Year-Old Girl Complained of “Sto.mach Pain” Every Friday Afternoon

Eating Eggs Can Be Harmful for These 5 Groups of People: Better Stay Away!
Early detection colon polyps: The key to effective can.cer prevention

Think it’s harmless? The risks of wearing bras to sleep might surprise you
What dise:ase is gr.oin pa.in a symptom of?

What sleeping on the left side does for our brain, stomach and lymphatic health

Eating yogurt with these 5 mistakes can bring more dis.eases into your body
8 foot massage points that help relieve issues
7 subtle symptoms that could signal serious health problems
The 5 ‘silent’ can:cer signs you might miss on your nails
Warning about the habit of "welcoming" can:cer into the body, many people know but still do it

4 Types of Plants That Snakes Are Crazy About

Boiling Eggs with Just Water is Not Enough

Discover the Power of Rosemary: Nature’s Potent Pain Reliever & Healing Herb
Doctors Urge: Stop Eating These 6 Foods That Fuel Cancer Growth
10 Warning Signs of Stroke One Month Before - Unbelievable Signs... Revealed!

Over 200 People Are Killed By The “World’s Deadliest Food” Every Year
News Post

4 Vegetables Easily “Treated” with Chemicals

The Part of the Pig Often Dismissed as “Dirty” and Thrown Away: Turns Out It’s a “Miracle Food” with 10 Times More Iron Than Meat

An 8-Year-Old Girl Complained of “Sto.mach Pain” Every Friday Afternoon

Eating Eggs Can Be Harmful for These 5 Groups of People: Better Stay Away!

Early detection colon polyps: The key to effective can.cer prevention

Think it’s harmless? The risks of wearing bras to sleep might surprise you

What dise:ase is gr.oin pa.in a symptom of?

What sleeping on the left side does for our brain, stomach and lymphatic health

Eating yogurt with these 5 mistakes can bring more dis.eases into your body

8 foot massage points that help relieve issues

7 subtle symptoms that could signal serious health problems

Struggling with garlic or onion smell on your hands? Try this simple trick—1 minute and it’s gone!

Tightly Wrapped or Loose Cabbage – Which Tastes Better?

The 5 ‘silent’ can:cer signs you might miss on your nails

Warning about the habit of "welcoming" can:cer into the body, many people know but still do it

4 Types of Plants That Snakes Are Crazy About

Boiling Eggs with Just Water is Not Enough

Discover the Power of Rosemary: Nature’s Potent Pain Reliever & Healing Herb
