Deadly Nightshade (Atropa belladonna): A Beautiful but Lethal Plant
Deadly nightshade, or Atropa belladonna, is one of the most poisonous plants known to humankind. Its dark history spans medicine, folklore, and even assassination attempts. Native to Europe, North Africa, and parts of Asia, this perennial herb remains both fascinating and deadly.

Recognizing Deadly Nightshade
- Flowers: Bell-shaped, purple-brown with a greenish hue, blooming from midsummer to autumn.
- Fruits: Glossy black berries resembling cherries—deceptively appealing but highly toxic.
- Leaves: Dark green, oval, and pointed, often growing in pairs.
- Height: Ranges from 2 to 4 feet with branching stems.
Toxic Components
Deadly nightshade contains powerful alkaloids that interfere with the nervous system:
- Atropine
- Scopolamine
- Hyoscyamine
These compounds block acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter essential for bodily functions, leading to severe poisoning symptoms.
Symptoms of Deadly Nightshade Poisoning
- Dry mouth and difficulty swallowing
- Blurred vision and dilated pupils
- Hallucinations, confusion, and agitation
- Rapid heartbeat (tachycardia)
- High fever and flushed skin
- Seizures and paralysis
• • Respiratory failure, coma, or death in severe cases

The Danger to Humans and Animals
- Humans: Just 2–5 berries can be fatal for a child, while 10–20 berries can kill an adult. Leaves and roots are equally dangerous.
- Pets and Livestock: Dogs, cats, and grazing animals can suffer poisoning, showing symptoms like excessive drooling, dilated pupils, restlessness, and convulsions.
Safety Tips to Avoid Poisoning
- Never touch the plant without protection – Its toxins can be absorbed through the skin or mucous membranes.
- Educate children and keep pets away – Teach them to avoid unknown berries and plants.
- Identify and remove safely – If found near homes, remove it using gloves and dispose of it properly.
- Avoid burning the plant – The smoke from burning Atropa belladonna can carry toxic compounds that are harmful if inhaled.
Interesting Facts About Deadly Nightshade
- Name Origin: “Belladonna” means “beautiful lady” in Italian, as women once used its extracts to dilate their pupils for a more striking appearance.
- Symbolism: Represents danger, mystery, and death in folklore and literature.
- Medical Use: Despite its toxicity, atropine is used in modern medicine to treat certain heart conditions and poisoning from nerve agents.
Deadly nightshade is a mesmerizing yet hazardous plant. While it has played a significant role in history and medicine, its dangers far outweigh its beauty. Always handle with extreme caution—or better yet, admire it from a safe distance!
News in the same category

The daily drink that helps clear blocked arteries naturally

This food is considered the most dangerous in the world it cla.ims over 200 lives each year, yet millions still consume it
Early warning signs of diabetes that most doctors don't even know

Signs of calcium deficiency that you may not be aware of

Dry mouth during sleep is not normal — 8 reasons most people overlook
Woman diagnosed with stage four colon can.cer w.arns people about 5 symptoms she ignored

The health benefits of eating ginger first thing in the morning for m.e.n

The Iris Flower: A Timeless Symbol of Beauty, Healing, and Hidden Power

Don’t throw them away – The incredible health perks of papaya seeds you need to know

Frequent Night Leg Cramps? This Could Be a Hidden Health Signal
8 signs of kidney failure that if ignored may require lifelong dialysis
7 Warnings Your Body Gives You When You're Too Stressed
Remember the early signs of nasopharyngeal c.a.ncer, the chance of survival is up to 72%

3 Signs Your Parent May Be Nearing the End of Life — How to Prepare for What’s Ahead

A Doctor On TikTok Explains The Risks Of Kissing Dying People
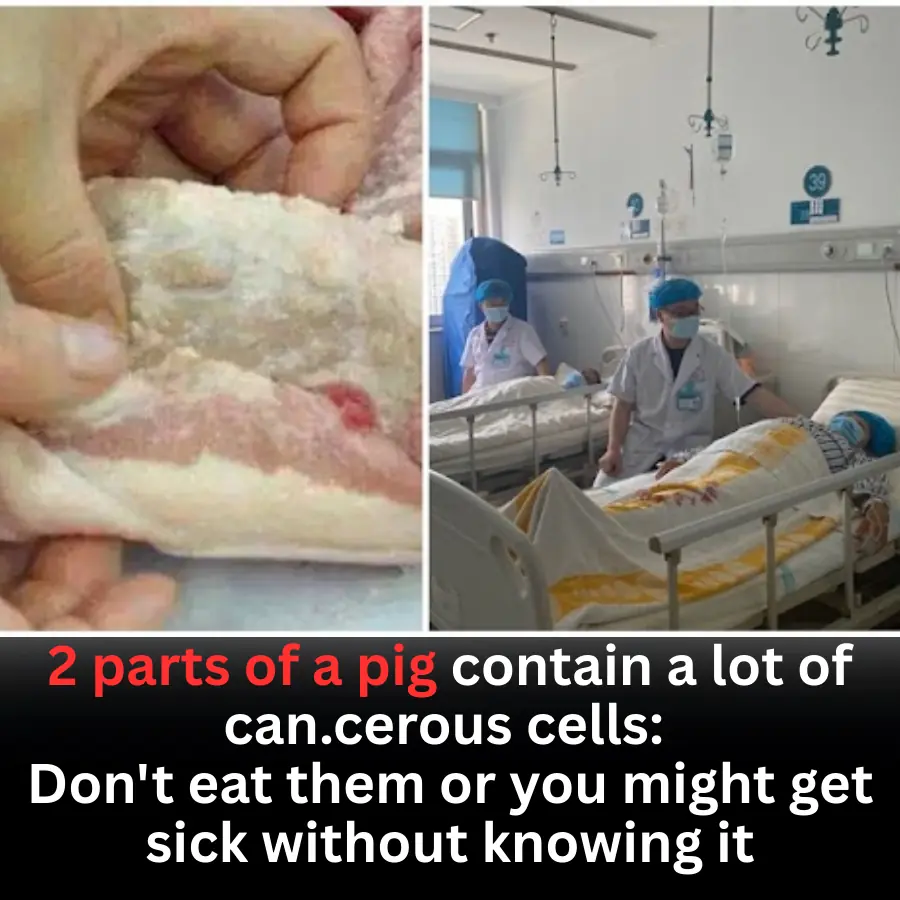
Two Parts of Pork You Should Avoid: Potential Health Risks Many People Overlook
9 Silent Signs of a Brain Blood Clot That May Appear Weeks Before a Stroke

Regular Yogurt Consumption Linked to Reduced Chronic Inflammation
High-Dose Nattokinase Reduces Carotid Plaque Size and Arterial Thickness in 12-Month Clinical Study
News Post

Top 10 Symptoms of LOW Potassium You May Be Ignoring

The daily drink that helps clear blocked arteries naturally

Housewives should pay close attention to these common supermarket items

Have you ever wondered why people pour hot water into the drain?

This food is considered the most dangerous in the world it cla.ims over 200 lives each year, yet millions still consume it

Early warning signs of diabetes that most doctors don't even know

Signs of calcium deficiency that you may not be aware of

How to drive away an entire rat colony using simple household ingredient

Dry mouth during sleep is not normal — 8 reasons most people overlook

Is Your Phone Overheating and Draining Battery Too Fast? Here’s How to Fix It and Restore Performance

Woman diagnosed with stage four colon can.cer w.arns people about 5 symptoms she ignored

The health benefits of eating ginger first thing in the morning for m.e.n

The Iris Flower: A Timeless Symbol of Beauty, Healing, and Hidden Power

Don’t throw them away – The incredible health perks of papaya seeds you need to know

Boil eggshells and say goodbye to waste: The surprising uses you need to know

Frequent Night Leg Cramps? This Could Be a Hidden Health Signal

Doctors Speak Frankly: Four Types of People Should Avoid Onions

8 signs of kidney failure that if ignored may require lifelong dialysis

7 Warnings Your Body Gives You When You're Too Stressed
