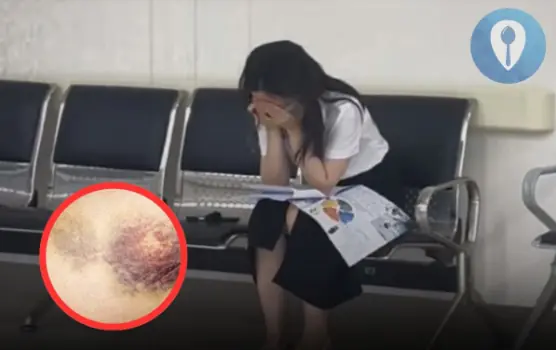
Despite the support from those around her, she remained quiet.
The Heartbreaking Moment a 23-Year-Old Girl Diagnosed with Leukemia Cries Alone in a Hospital Hallway: Don’t Ignore the Signs
Bananas are often considered one of the healthiest and most convenient snacks available. Rich in potassium, fiber, and essential vitamins, they are widely recommended as part of a balanced diet. However, some health experts suggest that eating bananas right before bedtime may have unexpected effects — depending on your body and overall health.
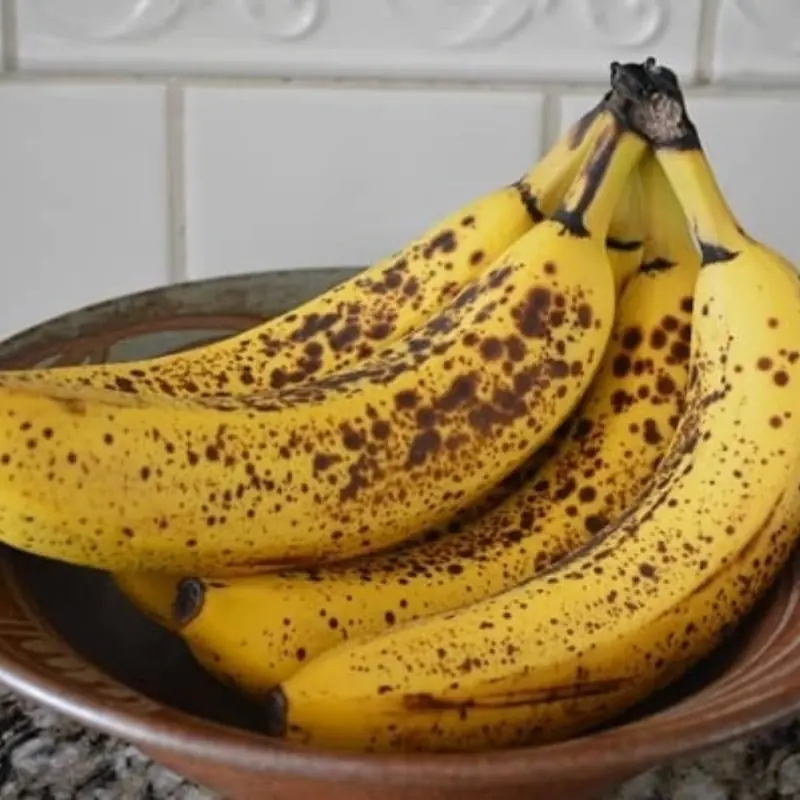
The image above shows a bowl of ripe bananas covered with brown speckles, a sign that the fruit is sweet and ready to eat. While many people enjoy a banana as a nighttime snack, it’s worth understanding how this fruit may influence sleep, digestion, and metabolism.

Bananas contain several nutrients linked to better sleep. They are a natural source of magnesium and potassium, two minerals that help relax muscles. Bananas also contain tryptophan, an amino acid that the body converts into serotonin and melatonin — hormones involved in regulating mood and sleep cycles.
For some individuals, eating a banana before bed may promote relaxation and make it easier to fall asleep. This is one reason bananas are often recommended as a light, calming evening snack.
However, not everyone reacts the same way. Because bananas contain natural sugars and carbohydrates, they may provide a small energy boost. In sensitive individuals, this could lead to increased alertness rather than drowsiness.
Ripe bananas, especially those with brown spots like the ones in the image, contain higher levels of natural sugars compared to less ripe bananas. While these sugars are natural, they can still affect blood glucose levels.
For people with diabetes or insulin resistance, eating a banana before bed may cause fluctuations in blood sugar overnight. A spike followed by a drop in blood sugar could potentially disturb sleep.
Pairing a banana with a source of protein, such as a small amount of peanut butter or yogurt, may help slow sugar absorption and reduce sudden changes in blood glucose levels.
Bananas are generally easy to digest, but eating any food right before lying down can sometimes cause discomfort. For individuals prone to acid reflux or indigestion, a bedtime snack — even a healthy one — may trigger symptoms.
Although bananas are not highly acidic, the act of eating close to bedtime increases stomach activity. When you lie down shortly after eating, stomach acid may move upward more easily, potentially leading to heartburn.
Experts often recommend finishing meals and snacks at least two to three hours before sleep to allow proper digestion.
Another factor to consider is total daily calorie intake. While a single banana contains roughly 90 to 120 calories, consistently adding extra nighttime snacks without adjusting overall intake may contribute to gradual weight gain.
Late-night eating is sometimes linked to mindless snacking rather than genuine hunger. If a banana replaces less healthy desserts, it may actually be a smart choice. But if it is an additional snack on top of an already sufficient diet, it may increase calorie consumption unnecessarily.
The speckled bananas shown in the image are fully ripe. As bananas ripen, their starch converts into simple sugars, making them sweeter and softer. Riper bananas are easier to digest but have a higher glycemic index.
Less ripe bananas contain more resistant starch, which digests more slowly and may have a smaller impact on blood sugar. Choosing a slightly less ripe banana may help reduce rapid glucose spikes at night.
While bananas are safe for most healthy individuals, certain groups may need to be more mindful:
People with diabetes or blood sugar concerns
Individuals with acid reflux or GERD
Those trying to manage weight through calorie control
Anyone sensitive to carbohydrate intake before bed
For these individuals, monitoring how the body responds to a nighttime banana can help determine whether it’s a suitable choice.
It’s important not to overstate the risks. Bananas remain a nutritious fruit packed with fiber, vitamin B6, vitamin C, and potassium. For many people, a banana before bed may actually support better sleep and muscle relaxation.
The key lies in moderation and timing. Eating a banana occasionally before bed is unlikely to cause harm in healthy individuals. Paying attention to portion size, ripeness, and overall diet makes a difference.
The warning that “eating bananas before bedtime may have unexpected effects” does not mean bananas are dangerous. Rather, it highlights that even healthy foods can affect people differently. Sleep quality, digestion, blood sugar, and personal health conditions all play a role.

The Heartbreaking Moment a 23-Year-Old Girl Diagnosed with Leukemia Cries Alone in a Hospital Hallway: Don’t Ignore the Signs
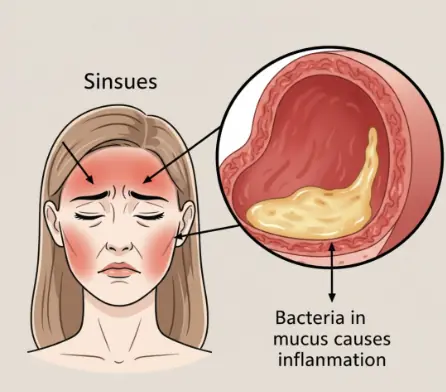
I was talking to my friend the other day, who complained of yet another sinus infection.
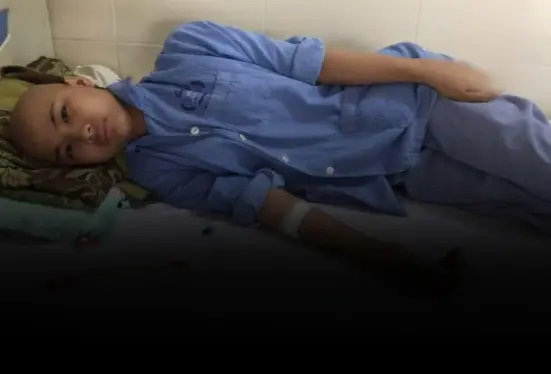
At just 28 years old, a young woman was diagnosed with stage 4 cancer—a diagnosis that shocked not only her but also those around her.

Doctors Warn: This Common Way of Eating Boiled Eggs Can Clog Your Arteries — Yet Many Still Do It Daily Without Realizing the Risk
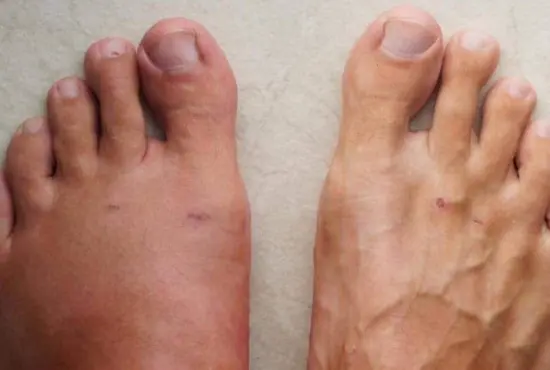
Heart attacks are often described as sudden medical emergencies, yet in many cases, the body sends warning signs long before the event occurs.
preservation of stem cells may sound like science fiction, but I assure you, it is not.

Waking Up Between 3 And 5 AM Could Indicate a Spiritual Awakening
Osteoporosis is frequently referred to as a “silent killer,” and for good reason.

When ginger may not be safe for certain health issues.

Chin Hair in Women: Causes and What It May Signal About Your Health
Finding Bruises but Don’t Remember Getting Hurt? Here’s Why
Lumps on the Neck: Causes, Warning Signs, and When to See a Doctor

Is Eating Hearts of Palm Good for You? Here’s What Happens Over Time
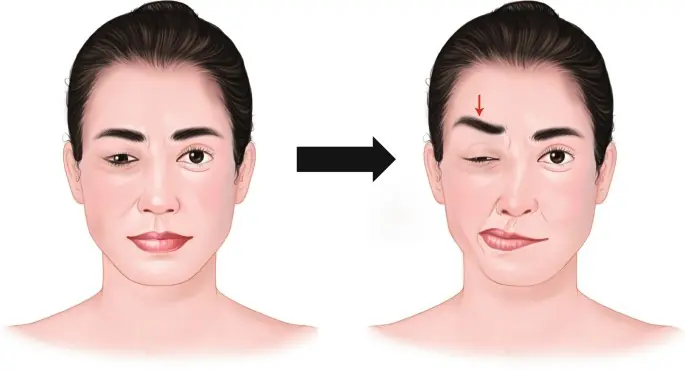
Experiencing Eye or Lip Twitching? 6 Potential Reasons to Know
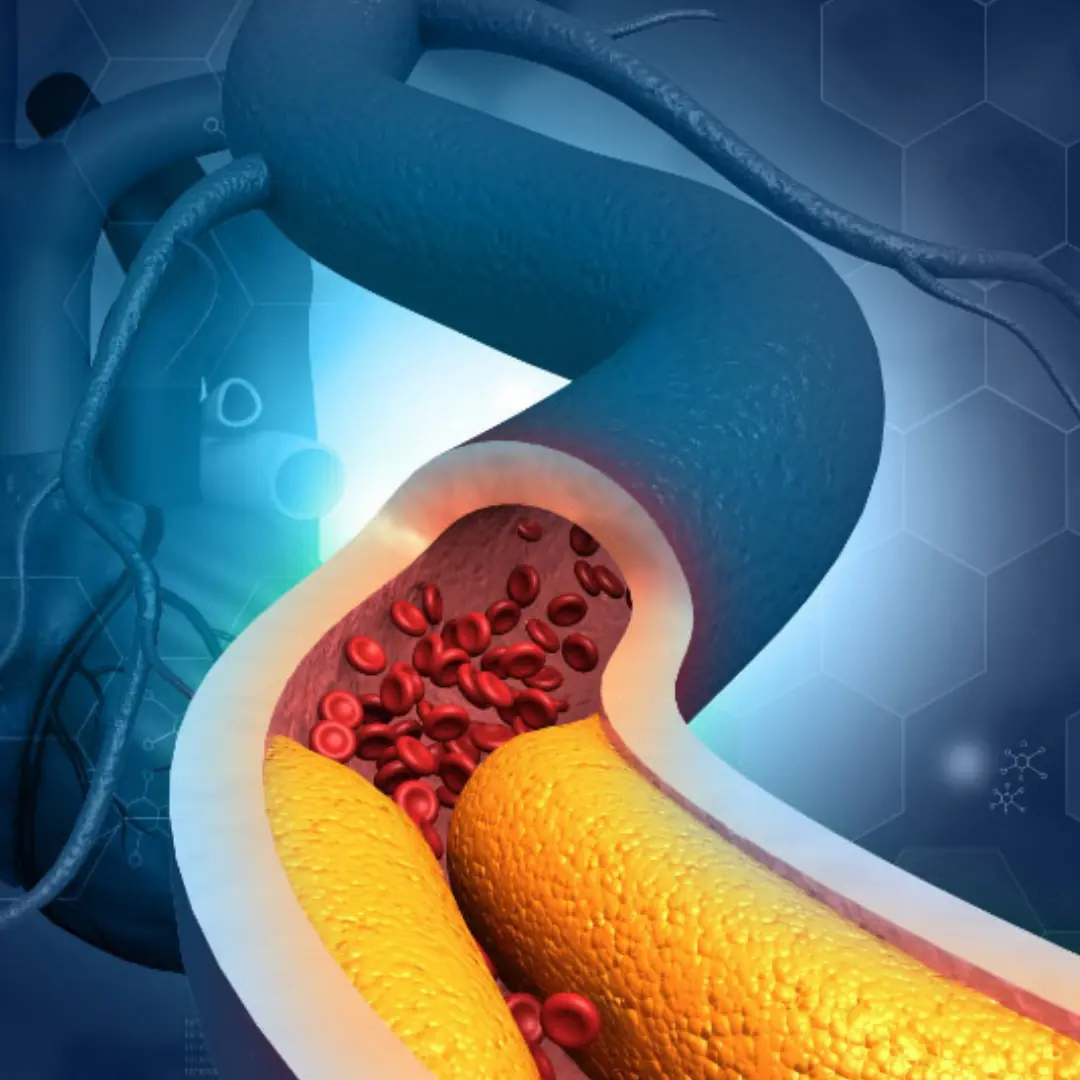
High Blood Pressure & High Cholesterol: 3 Things You Should Never Do in the Morning

The Best 4 Morning Foods for a Happier, Healthier Digestive System
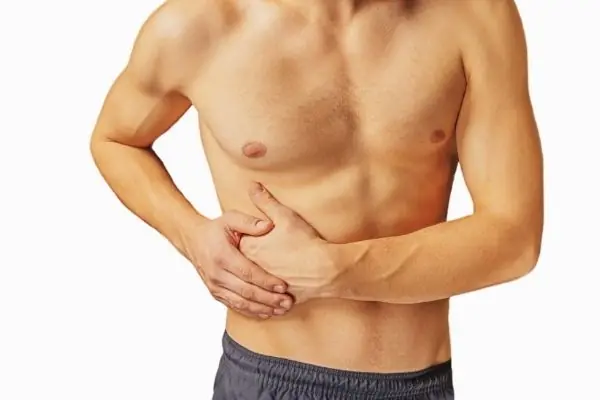
Left-Side Pain Explained: Common Causes and When to Seek Help

Is Guava Good for You? Doctors Break Down the Health Benefits

Boiled Sweet Potatoes for Breakfast: A Simple Habit with Powerful Health Benefits

My Husband Visited His Sick Uncle Every Saturday – but When I Called the Uncle, He Said, 'I Haven't Seen Him in Six Months!'

Filing for divorce, her ex-husband thought he’d leave his wife without money or a home – but he was in for a surprise

What do you mean your apartment isn’t divided? I was counting on a share after the wedding,” my husband said irritably about the apartment I had owned before our marriage

“How dared you take the keys away from my mom?” Ella’s husband snapped, lunging at her

“The perks are over,” her husband said as he announced separate finances

The Heartbreaking Moment a 23-Year-Old Girl Diagnosed with Leukemia Cries Alone in a Hospital Hallway: Don’t Ignore the Signs

I was talking to my friend the other day, who complained of yet another sinus infection.

At just 28 years old, a young woman was diagnosed with stage 4 cancer—a diagnosis that shocked not only her but also those around her.

Doctors Warn: This Common Way of Eating Boiled Eggs Can Clog Your Arteries — Yet Many Still Do It Daily Without Realizing the Risk

Heart attacks are often described as sudden medical emergencies, yet in many cases, the body sends warning signs long before the event occurs.

preservation of stem cells may sound like science fiction, but I assure you, it is not.

Waking Up Between 3 And 5 AM Could Indicate a Spiritual Awakening

Osteoporosis is frequently referred to as a “silent killer,” and for good reason.

Vera, we’ve outgrown this relationship. I’m filing for divorce. We’ll split the house and the car fifty-fifty,” her husband announced

When ginger may not be safe for certain health issues.

Chin Hair in Women: Causes and What It May Signal About Your Health

Finding Bruises but Don’t Remember Getting Hurt? Here’s Why

Lumps on the Neck: Causes, Warning Signs, and When to See a Doctor

Is Eating Hearts of Palm Good for You? Here’s What Happens Over Time