New Research Suggests That All Cancers Are Linked to a Single Protein – A Revolutionary Discovery
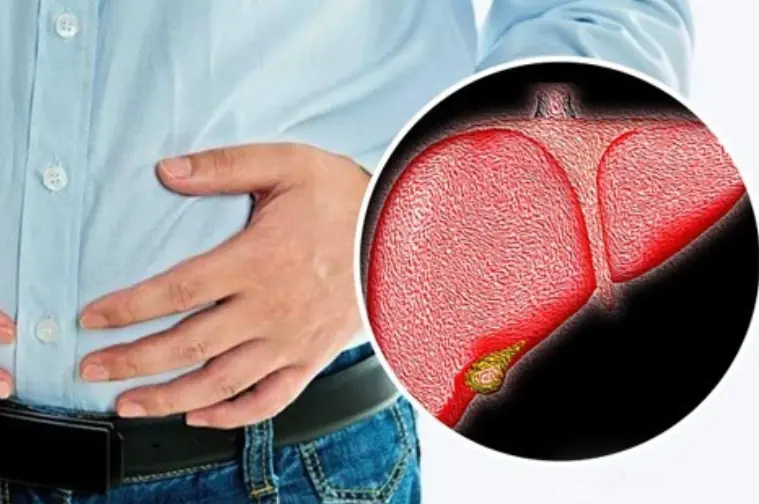
Cancer has long been one of the most complex and deadly diseases, affecting millions of people worldwide. However, a groundbreaking discovery by researchers suggests that all types of cancer may be linked to a single protein. This could revolutionize cancer treatment, early detection, and prevention strategies.
In this article, we’ll explore this new research, what this protein does, how it affects cancer growth, and what this means for future cancer treatments.
1. The Protein That Links All Cancers
For decades, scientists have struggled to understand why different types of cancer behave similarly despite originating in different tissues. Recent studies have revealed that a single protein may play a key role in all forms of cancer.
✔ What is this protein?
- Researchers have identified a protein known as p53, MYC, or KRAS (depending on the study), which is linked to uncontrolled cell growth and tumor formation.
- This protein appears to be overactive or mutated in nearly all cancer types.
🚨 Why is this important?
- If all cancers are influenced by the same protein, treatments could target this protein to stop cancer growth at its core.
- Scientists are now developing drugs that directly inhibit this protein, potentially creating a universal cancer treatment.
2. How This Protein Causes Cancer Growth
Normal cells have built-in mechanisms to regulate growth, repair DNA damage, and prevent tumors from forming. However, when this protein is mutated or overactive, it disrupts these natural defenses, allowing cancer to grow uncontrollably.
✔ How the protein contributes to cancer:
1️⃣ Prevents normal cell death (apoptosis) – Cancer cells continue growing when they should die.
2️⃣ Speeds up cell division – Cells multiply too quickly, forming tumors.
3️⃣ Encourages blood vessel formation – Tumors grow larger by hijacking the body’s resources.
4️⃣ Makes cancer cells resistant to treatment – Many cancers become harder to treat when this protein is overactive.
🚨 The result?
- Cancer becomes aggressive, spreads to other organs, and resists conventional treatments like chemotherapy.
3. What This Means for Future Cancer Treatment
If all cancers share a common protein target, this discovery could lead to groundbreaking advancements in cancer research.
1. A Universal Cancer Treatment
- Scientists are working on drugs that block or correct the function of this protein.
- This could lead to a single treatment effective for multiple cancer types.
💡 Current research:
- Clinical trials are already testing inhibitors that disable the protein in cancer cells.
- Early results show reduced tumor growth in breast, lung, and colon cancer patients.
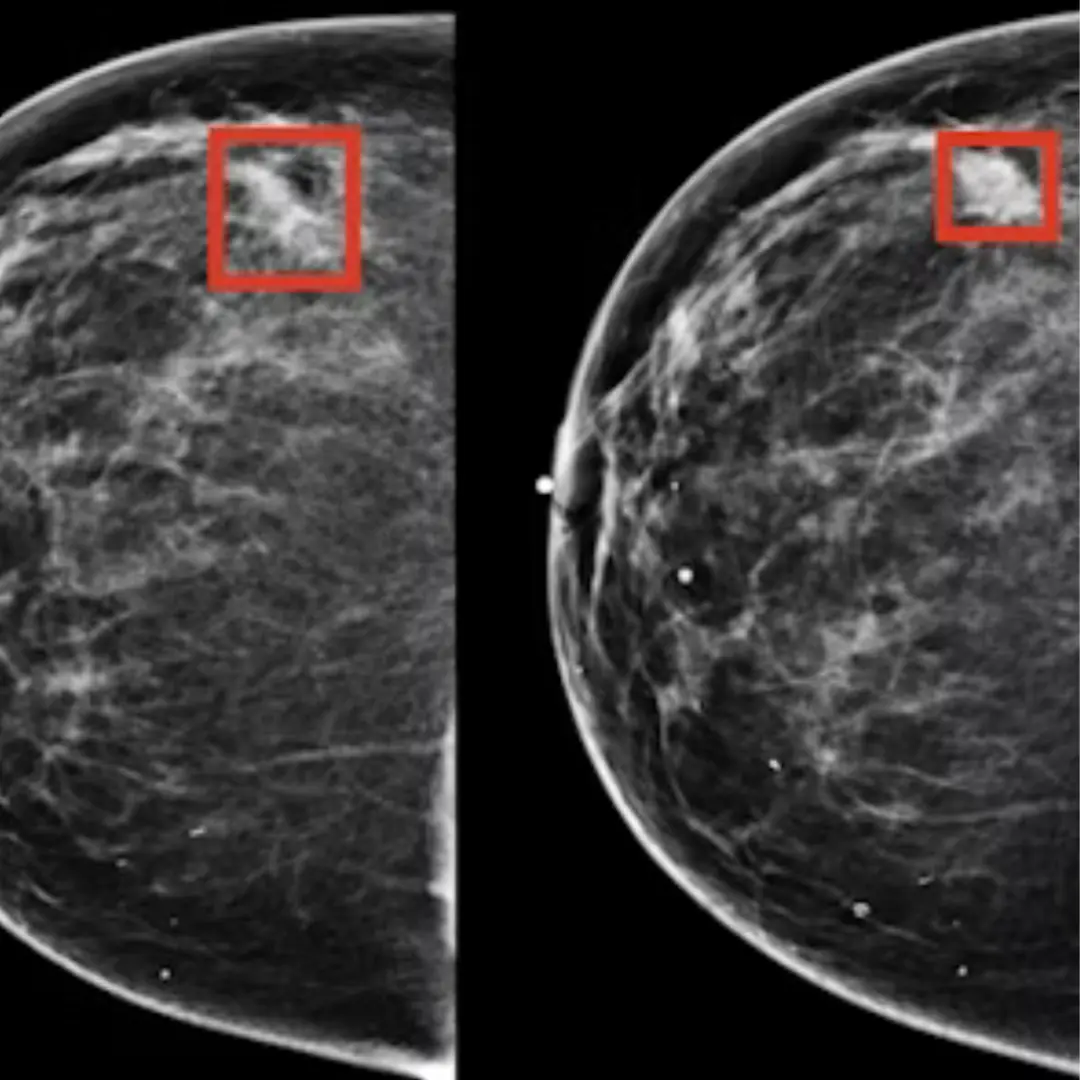
2. Early Detection & Cancer Prevention
- If doctors can detect high levels of this protein early, they can predict cancer before symptoms appear.
- Simple blood tests could identify at-risk individuals years before cancer develops.
🚨 Potential breakthrough:
- Researchers are developing a "cancer fingerprint test" that could screen for this protein in a single drop of blood.
3. More Effective and Less Toxic Treatments
- Current treatments like chemotherapy and radiation damage both cancerous and healthy cells.
- A targeted therapy focusing on this protein alone could:
✅ Kill cancer cells without harming healthy tissue.
✅ Reduce side effects like nausea, hair loss, and fatigue.
✅ Improve survival rates and recovery time.
💡 Example of success:
- Some patients in early-stage trials have shown complete tumor shrinkage after treatment with these protein-targeting drugs.
4. What Can You Do to Reduce Cancer Risk?
While scientists continue researching targeted therapies, you can take steps to lower your cancer risk naturally.
✅ Eat Anti-Cancer Foods:
- Leafy greens, turmeric, garlic, and berries help suppress cancer-promoting proteins.
✅ Exercise Regularly:
- Physical activity reduces inflammation and improves immune function.
✅ Avoid Carcinogens:
- Minimize processed foods, smoking, and excessive alcohol intake.
✅ Get Regular Screenings:
- Early detection is key—schedule routine check-ups and blood tests.
🚨 Key Takeaway:
- A healthy lifestyle combined with early detection can drastically reduce your cancer risk.
5. The Future of Cancer Treatment – Hope for a Cure?
This discovery brings new hope in the fight against cancer. If researchers can fully understand how this protein controls cancer, it could lead to:
🚀 A universal cancer cure that works across all types of cancer.
🚀 Blood tests that detect cancer before symptoms appear.
🚀 Less toxic, more effective treatments with fewer side effects.
💡 Exciting Updates:
- Scientists expect major breakthroughs in the next 5-10 years.
- Pharmaceutical companies are rushing to develop new drugs targeting this protein.
Final Thoughts – A New Era in Cancer Research
The idea that all cancers may be linked to a single protein is a game-changer in medical science. This discovery could lead to a future where cancer is no longer a deadly disease but a manageable condition.
🚨 Key Takeaways:
✅ Scientists have identified a single protein linked to most cancers.
✅ Blocking this protein could lead to a universal treatment for multiple cancer types.
✅ Early detection through blood tests could save millions of lives.
✅ Lifestyle choices and regular screenings remain essential for cancer prevention.
With continued research and breakthroughs, we may soon see the day when cancer is no longer a life-threatening disease.
Would you like to learn more about the latest medical discoveries? Let me know! 😊