New Study: Can.cer Risk Increases 5-Fold If You Drink That Popular Beverage Every Day
New Study: Can.cer Risk Increases 5-Fold If You Drink That Popular Beverage Every Day
An unhealthy diet is closely linked to can.cer risk at all ages.

According to a report by United Press International, a new study from the University of Washington found that women who drink at least one sugary beverage daily have about a 5-fold higher risk of developing oral cavity cancer (OCC) compared to those who avoid or do not habitually consume such drinks.
Study on the Link Between Oral Cavity Cancer Risk and Sugary Beverages
In a recent article published in JAMA Otolaryngology – Head & Neck Surgery, researchers from the University of Washington analyzed long-term healthcare data from over 162,000 healthcare workers and identified 124 cases of OCC among them.
Based on analyzing monthly sugar consumption reports—collected every four years—and comparing the reported sugar intake with whether the participants were diagnosed with oral cancer, the researchers found that those who drank at least one carbonated/sugary beverage per day had a 4.87-fold higher risk of developing OCC compared to those who consumed less than one such beverage per month.
For individuals who do not smoke or drink alcohol—or do so only minimally—the figures are even more concerning: those consuming one or more cans of sugary drinks per day have a 5.46-fold higher risk of developing OCC compared to those who drink less than one can per month.
Rather than implying that the sugar content in these beverages directly causes OCC, the researchers hypothesize that a higher-sugar diet may contribute to chronic inflammation. Previous studies have also highlighted the association between excessive consumption of sugary drinks and gum disease—which, in turn, is linked to oral cancer.
Conclusion
Clearly, more research is needed to further elucidate this association. In the meantime, reducing daily consumption of sugary drinks and replacing them with healthier options like water or fresh fruit juice can offer significant overall health benefits.
According to WebMD, excessive consumption of added sugars can have several negative effects on the body, including:
-
Brain: Consuming added sugars triggers a sudden surge of a feel-good chemical called dopamine in the brain. This explains why you might crave a candy bar in the early afternoon. Over time, this leads to a “must-have” response—essentially a sugar addiction. Research from scientists at UCLA School of Medicine (USA) indicates that high fructose intake adversely affects brain function and impairs memory.
-
Mood: Occasionally eating sweets or cookies can quickly boost your energy by raising blood sugar levels. However, as the sugar is absorbed and blood sugar levels drop, you might feel jittery and anxious. Relying on sweets regularly to avoid sleepiness or lack of concentration is a warning sign. Studies have also linked high sugar consumption with an increased risk of depression in adults.
-
Teeth: A high intake of added sugars increases the risk of oral health issues, such as cavities.
-
Joints: Consuming large amounts of sweets has been shown to exacerbate joint pain due to the inflammatory response triggered in the body. Additionally, studies suggest that people who consume a lot of sugar are more likely to develop rheumatoid arthritis.
-
Skin: Excess sugar binds to proteins in your blood, forming harmful molecules known as advanced glycation end products (AGEs). These molecules accelerate skin aging by damaging collagen and elastin, leading to wrinkles and sagging skin over time.
-
Liver: Fructose is processed in the liver, and in large quantities, it can be harmful. When broken down, fructose is converted into fat, which may lead to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease or non-alcoholic steatohepatitis.
-
Heart: Overconsumption of added sugars can cause an excess of insulin in the bloodstream, affecting arteries throughout the body. This results in inflammation, thickening, and hardening of arterial walls, putting stress on the heart and damaging it over time. Such changes can lead to heart conditions like heart failure, angina, and stroke.
-
Pancreas: When you eat, your pancreas releases insulin. However, excessive intake of added sugars can make your body less responsive to insulin, prompting the pancreas to produce even more. Over time, an overworked pancreas may become damaged, leading to elevated blood sugar levels and increasing the risk of type 2 diabetes and heart disease.
-
Weight: This might not be new news, but consuming more added sugars often leads to quicker weight gain. Studies have shown that individuals who regularly drink sugary beverages tend to be heavier and have a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes compared to those who don’t.
By taking steps to reduce added sugar intake, you may lower the risks associated with these health issues and improve overall well-being.
News in the same category


5 Habits Doctors Never Do During Flu Season: How They Stay Healthy Despite Daily Contact with Thousands of Patients
Signs of High Blo.od Sugar and Diabetes Risk: If You Have Any of These 6 Symptoms, Be Cautious!
7 warning signs of incurable diseases on the feet: Those who do not have them are very congratulatory
Using your phone a lot is fine, but you have to avoid 2 times
9 Warning Signs of Can.cer: Recognize Them Early to Save Your Life
At 25, She Had to Undergo a Hysterectomy to Survive: A Girl Breaks Down in Tears, Urging Everyone Not to Ignore Four Small Changes

Want Firm, Wrinkle-Free Skin? Discover 9 Collagen-Boosting Superfoods That Keep You Surprisingly Youthful!

4 things many people do in the morning that put themselves closer to a stroke
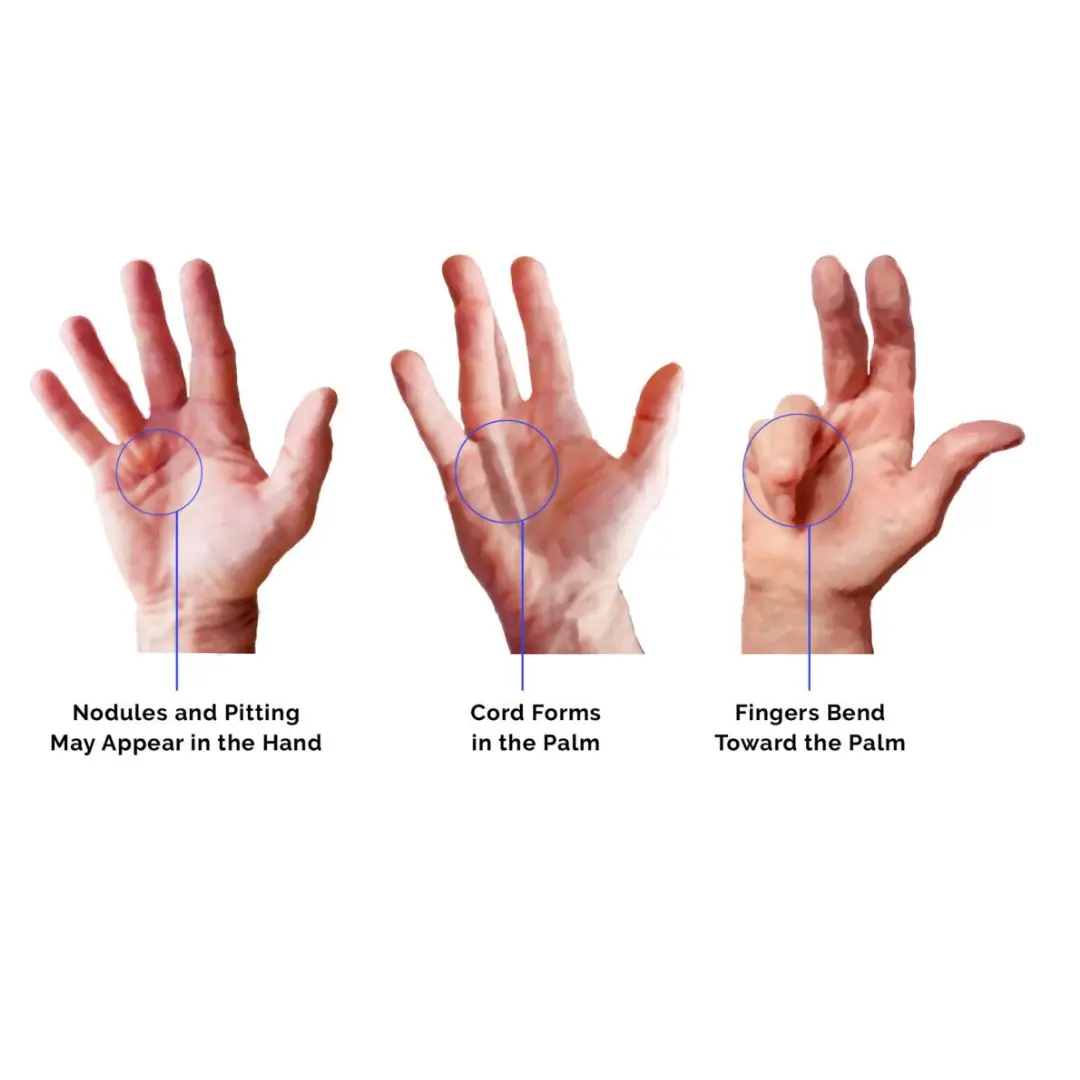
The Most Common Crippling Hand Disease That You’ve Never Heard Of: Dupuytren’s Contracture
Discover 5 Incredible Foods That Naturally Eradicate Intestinal Worms and Revitalize Your Gut Health
HERE'S WHY YOU SHOULD PUT GARLIC IN YOUR EAR:

3 Abnormal Reactions When Drinking Water That May Signal Li.ver Can.cer Warning Signs
7 Common Signs of Peripheral Facial Nerve Palsy That Many Often Overlook
Man paralyzed overnight, doctor warns of 'silent kill:er'

6 People Who Should Never Eat Red Meat, According to Dietitians

How many eggs should you eat a week?
6 Signs on Your Feet That May Warn of He.art Disease – Don’t Ignore Them
Women Who Exhibit These Signs Have a Truly Weakened Immune System and Are Far More Prone to Severe Complications When Ill
News Post

5 foods are considered "vacuum cleaners" for the l.u.n.gs: eat them regularly and your l.u.ngs will be cleaned

5 Habits Doctors Never Do During Flu Season: How They Stay Healthy Despite Daily Contact with Thousands of Patients

How can you make “5+5+5 = 550” correct with just one line?

Signs of High Blo.od Sugar and Diabetes Risk: If You Have Any of These 6 Symptoms, Be Cautious!
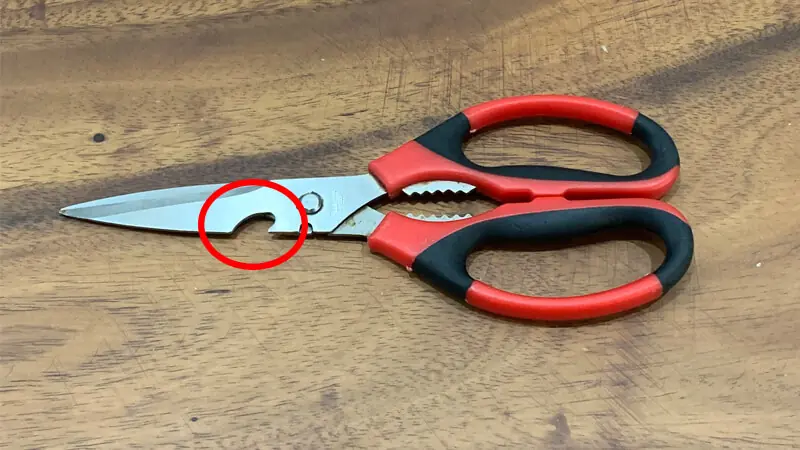

The Purpose of the Notch on Scissors: Many Homemakers Don’t Know How to Use It—What a Shame!
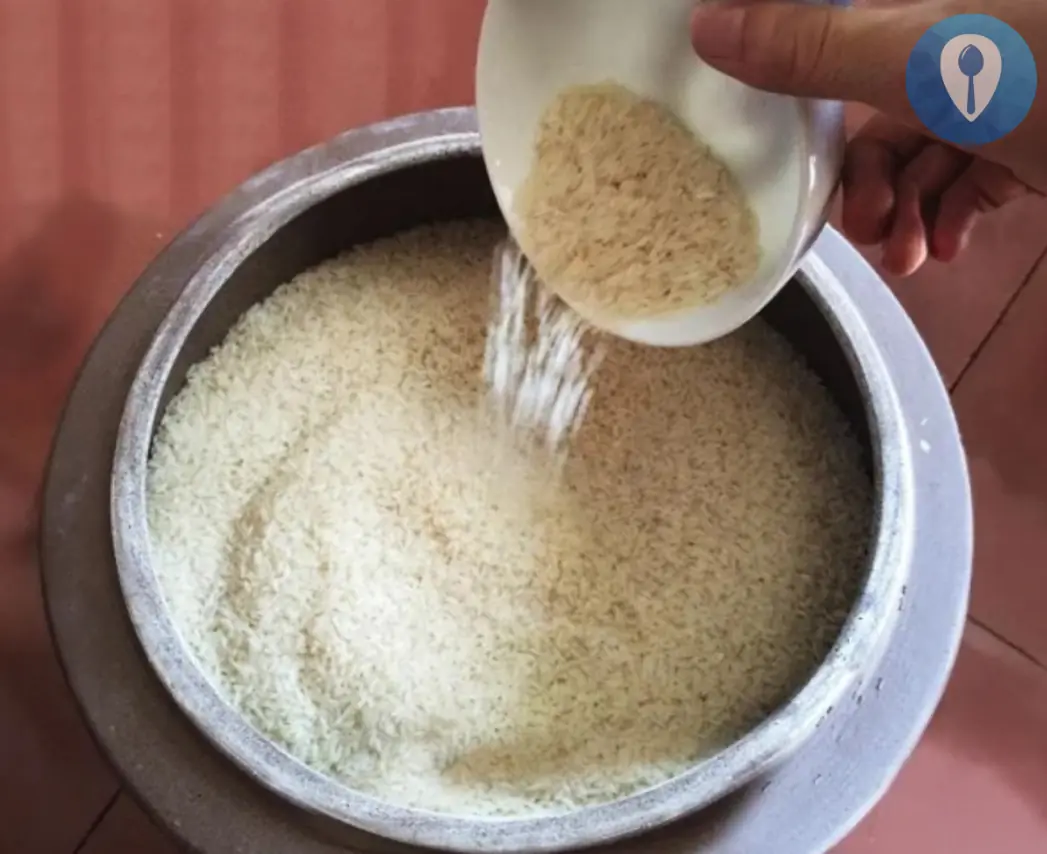

The rice barrel placed in this place will cause constant illness and difficulty
Is that girl okay?

The photo that made millions of people cry about the profession considered the di.rtiest in the world

7 warning signs of incurable diseases on the feet: Those who do not have them are very congratulatory
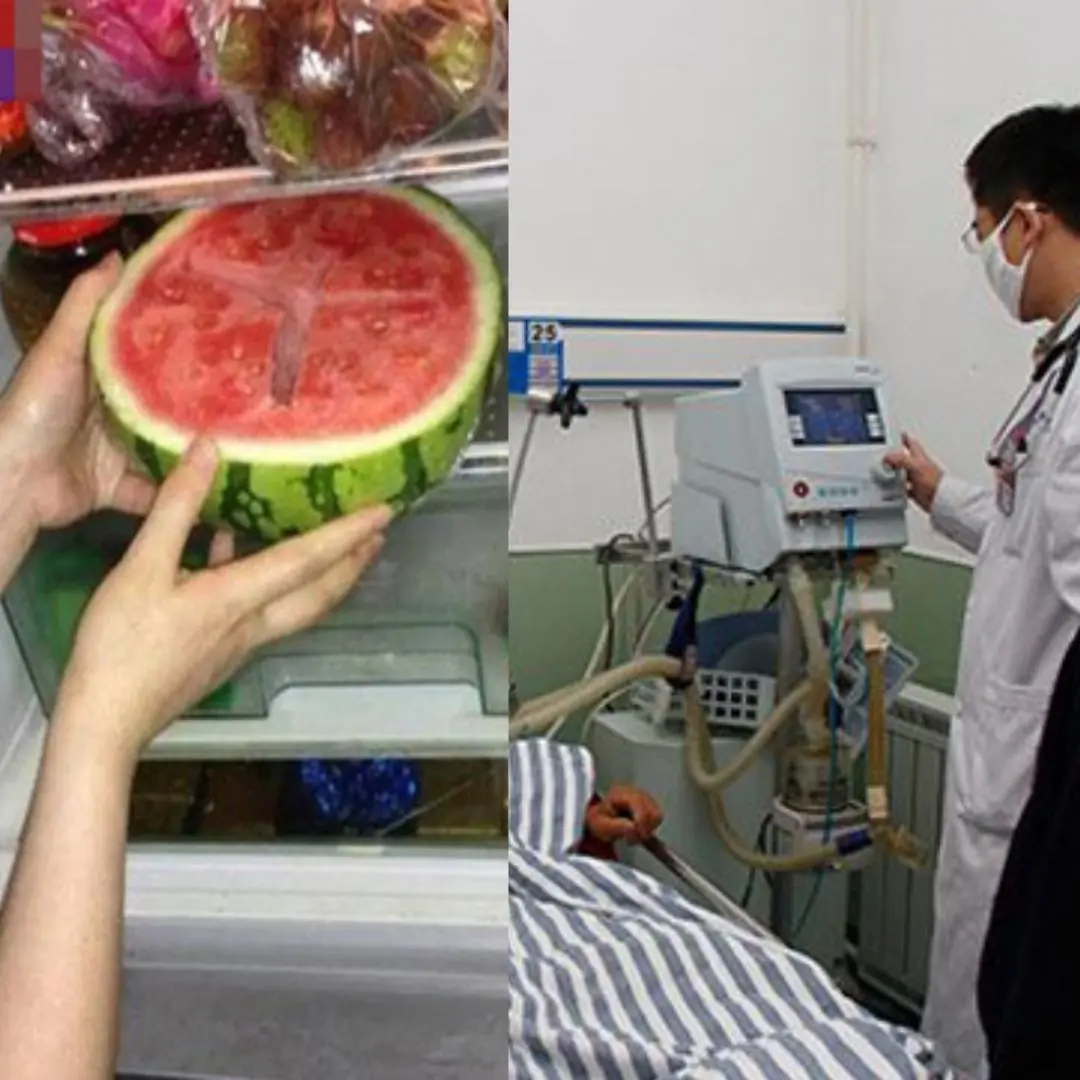

Whole family hospitalized after eating watermelon left overnight in the refrigerator: Mistakes in preserving watermelon that many people make
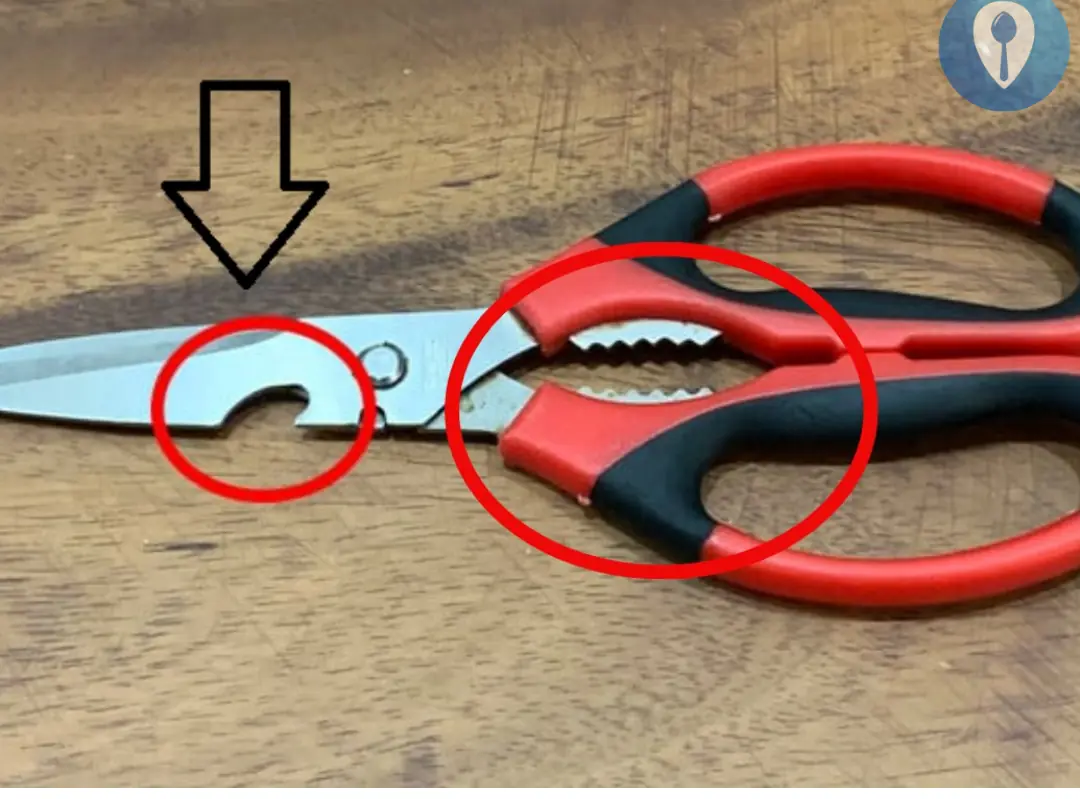

What are the buttonholes and serrated holes on scissors used for?

Using your phone a lot is fine, but you have to avoid 2 times

The old man selling lottery tickets carried a sack of change into the bank, was loo.ked d.own upon by the staff and had a surprising ending

I'm only 22 years old, but I just agreed to marry a rich 60 year old man

Who D.ie.s If ‘E’ Pushes The Stone?

Many people worry that throwing toilet paper into the toilet might cause blockages
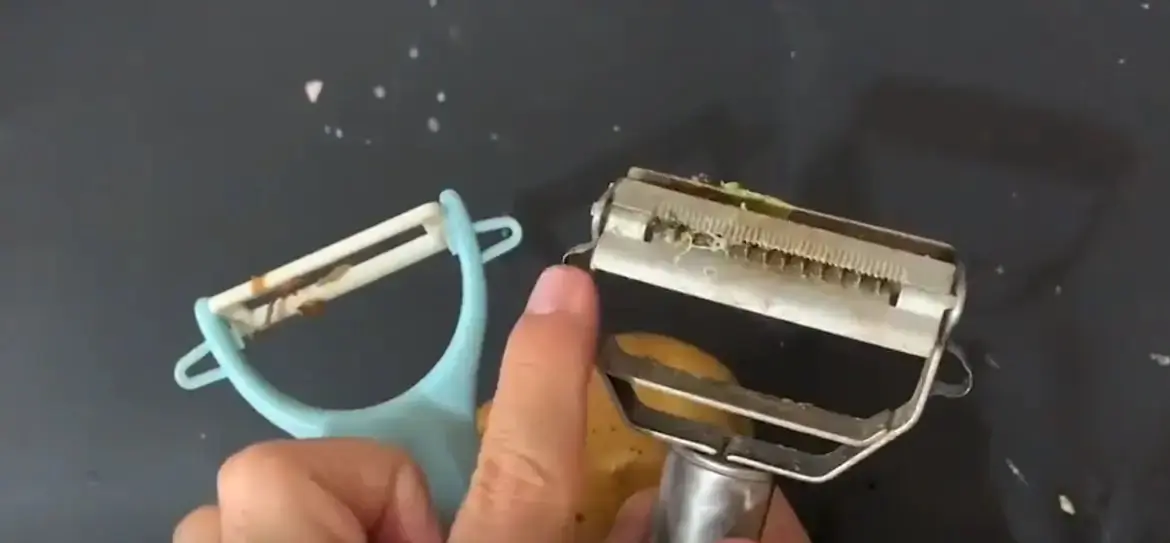

The "Secret" of the Small Hole on a Vegetable Peeler That Made Me Realize My EQ Has Been at Rock Bottom for 10 Years!

Can you spot the turtle in 15 seconds?

9 Warning Signs of Can.cer: Recognize Them Early to Save Your Life
