
Doctors reveal that eating cashews causes...
Doctors highlight the potential consequences of eating cashews

Blood Cancer: Key Facts and Early Warning Signs You Should Know
Blood cancer is one of the most common types of cancer, significantly affecting blood cells and bone marrow. So, what are the early warning signs of blood cancer? Let’s explore some important information in the article below.
Blood cancer is a disease that affects blood cells and bone marrow—the spongy tissue inside bones where blood cells are produced and develop into red blood cells, white blood cells, or platelets.
These blood cells play crucial roles: transporting oxygen throughout the body, fighting infections, and aiding in blood clotting. In blood cancer, the blood cells fail to develop and mature properly, resulting in abnormal functioning.
Blood cancer can occur in both adults and children, with three main types:
Leukemia: White blood cells are vital to the immune system. In leukemia, immature white blood cells multiply excessively and function poorly, disrupting immune balance. They also crowd out red blood cells, leading to anemia.
Lymphoma: This type affects lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell that helps fight infection) and their circulation throughout the body to support immunity. Abnormal lymphocyte growth can form tumors, weaken the immune system, and impair organ function.
Myeloma: This disease affects plasma cells (a type of white blood cell that produces antibodies). Abnormal plasma cell growth can weaken healthy cells and reduce bone marrow’s ability to produce blood cells.
Blood cancer results from mutations in the DNA of blood cells, though the exact cause remains unknown. However, certain factors can increase the risk:
Age: It can occur at any age, but middle-aged individuals face higher risk.
Gender: More common in men than women.
Race: Genetic factors and mutation tendencies can play a role—Black individuals tend to have higher risk compared to White individuals.
Family history: DNA mutations may be inherited.
Radiation and chemical exposure: Both can damage DNA and trigger mutations.
Cigarette smoke: Contains harmful substances linked to cancer.
Underlying health conditions: Chronic diseases like diabetes, cirrhosis, and hepatitis may increase risk.
Fatigue: Persistent weakness and exhaustion affecting daily life.
Prolonged high fever: May indicate immune system abnormalities, especially in white blood cells.
Night sweats: Excessive sweating at night causing discomfort or waking the patient.
Unexpected bleeding or bruising: Unexplained bruises or blood spots that don’t fade after two weeks.
Rapid weight loss: Cancer cells consume nutrients and energy, making the body more prone to infection.
In addition to the above, specific symptoms include:
Swollen lymph nodes, enlarged liver, and spleen: Common in leukemia or lymphoma due to excess cancer cells blocking lymphatic flow.
Bone pain: Typical in leukemia or myeloma, ranging from mild to severe (back, thighs, arms, or tender bone spots).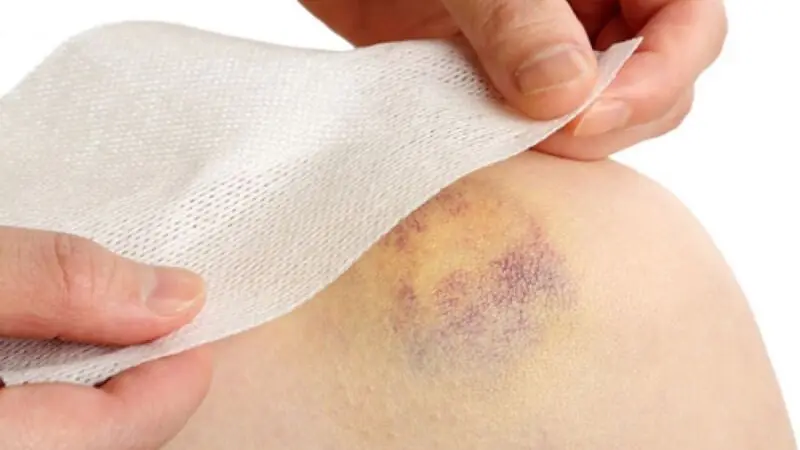
Survival rates for blood cancer have improved in recent years, especially for leukemia.
Lymphoma: 5-year survival rate ranges from 73–87%.
Multiple myeloma: Dangerous but treatable, with a 5-year survival rate of about 52%.
Prognosis can improve if the patient responds well to treatment. Maintaining a positive mindset is important for enhancing survival.
Potential complications include:
Bone fractures if cancer invades bone marrow.
Hypercalcemia from bone breakdown.
Kidney failure due to anemia and poor blood flow.
Kidney damage from excessive white blood cells.
Infections from a weakened immune system.
Anemia due to excess white blood cells.
Bleeding, nosebleeds, or even brain hemorrhage when platelet count is low.
Diagnosis can be made through medical examination or early clinical signs, but to determine the exact cause, you may need:
Clinical examination of symptoms.
Blood tests.
Imaging tests.
Bone marrow biopsy.
Blood smear test.
Seek medical attention if you experience: significant weight loss, persistent bruising, prolonged fever, or chronic infections that don’t resolve.
Treatment options include:
Chemotherapy.
Radiation therapy.
Stem cell transplantation.
CAR-T cell therapy.
Palliative care for advanced cases.
This information covers key facts about blood cancer and its typical warning signs so you can take timely action, receive appropriate treatment, and improve both your health and prognosis.

Doctors highlight the potential consequences of eating cashews
5 Critical Warning Signs That Your Kidneys Might Be Failing
If You Notice These 6 Symptoms, Your Wisdom Tooth May Be Impacted
These 5 Beverages Harm Your Liver Even More Than Alcohol
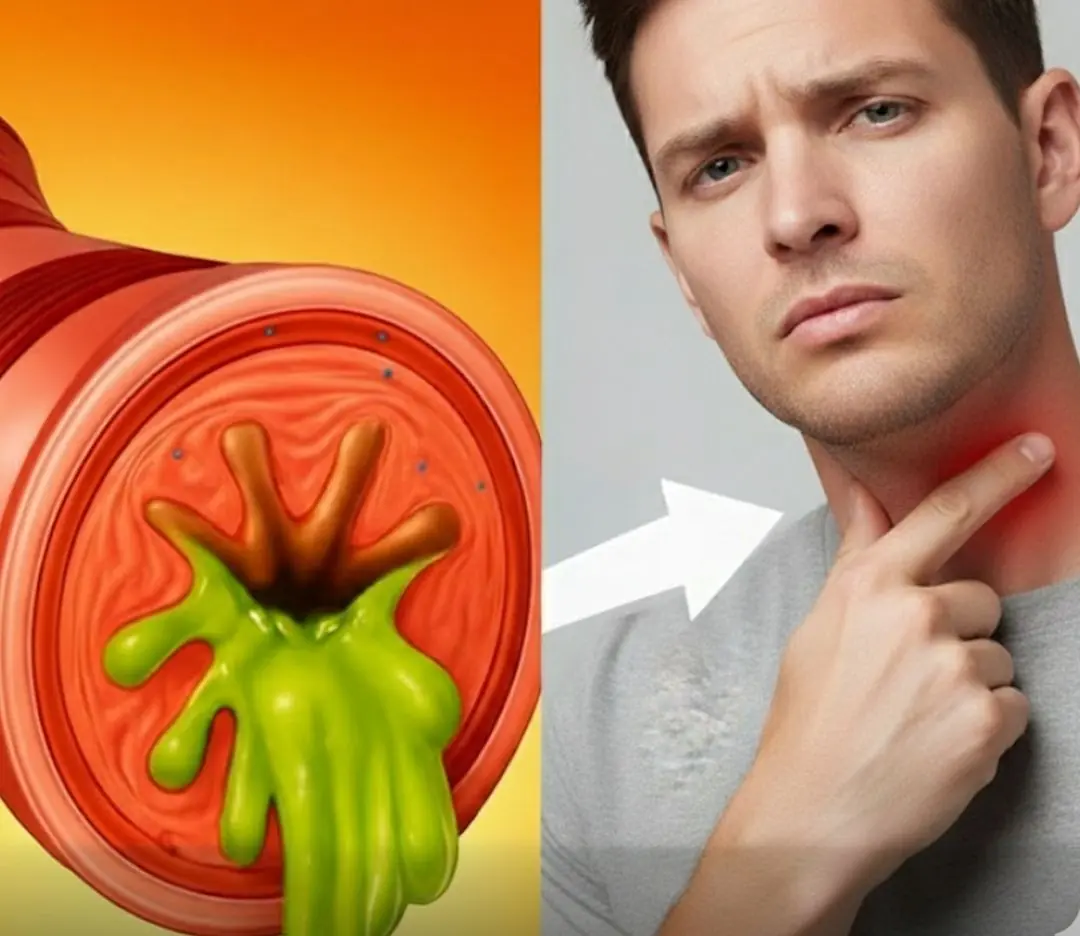
Doctors rarely explain it, but constant phlegm often comes down to 4 overlooked causes...
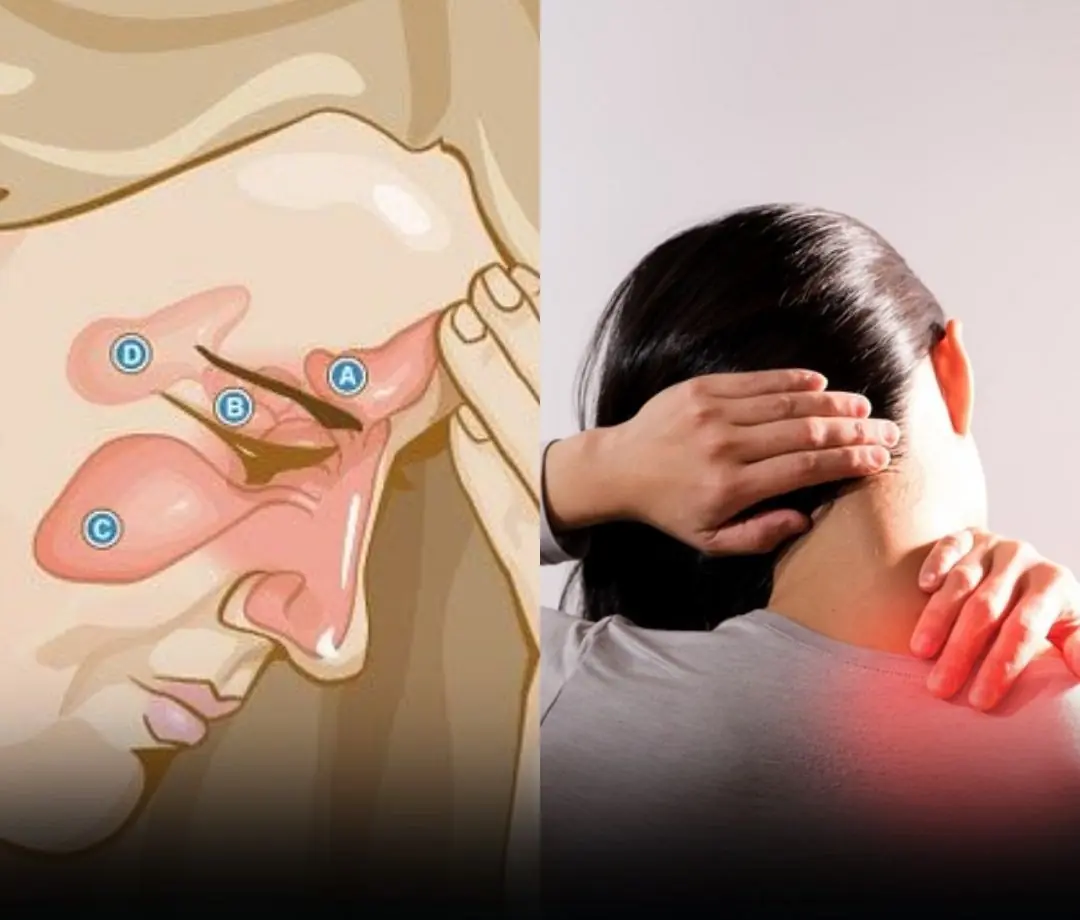
9 Early Signs of Diabetes You May Not Be Noticing
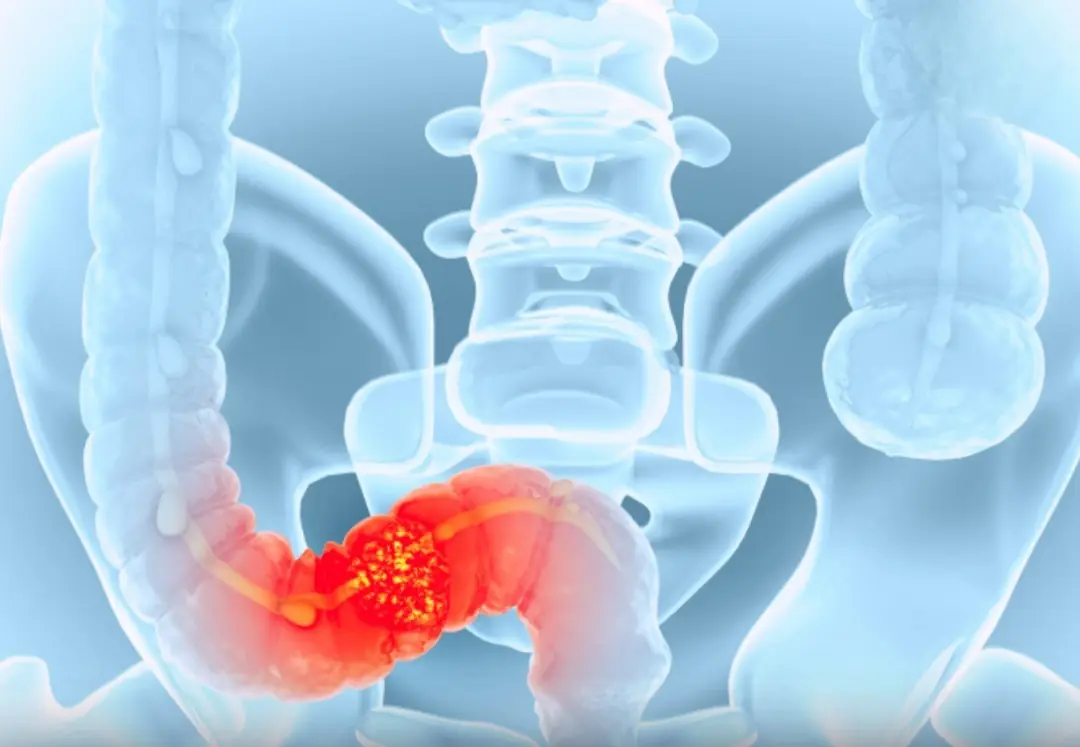
Be careful because you may have this disease
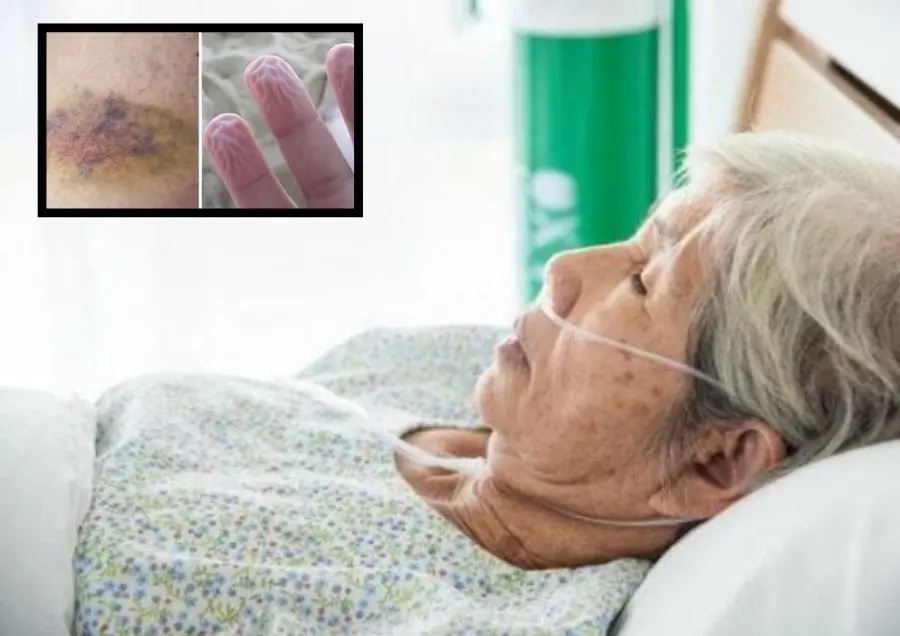
6 Warning Signs the Body May Show About a Year Before Death
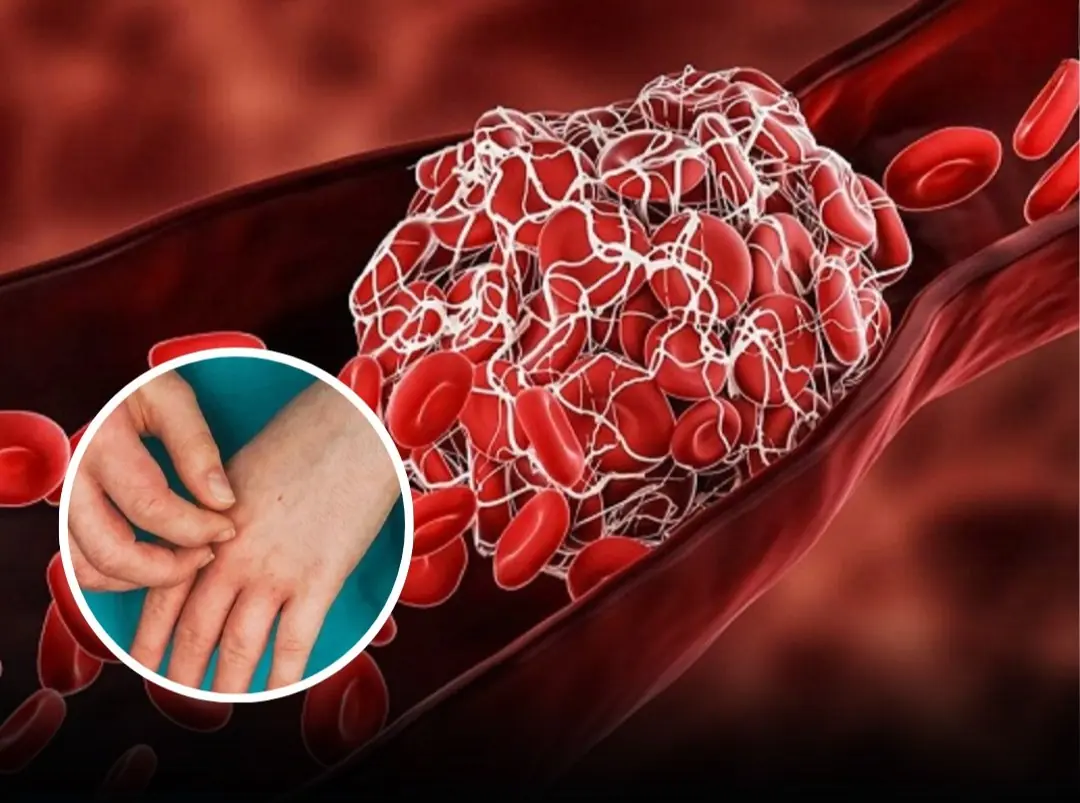
Could These 10 Symptoms Be Early Signs of Blo:od Can:cer?

Okra is nutritious — but not everyone should eat it.
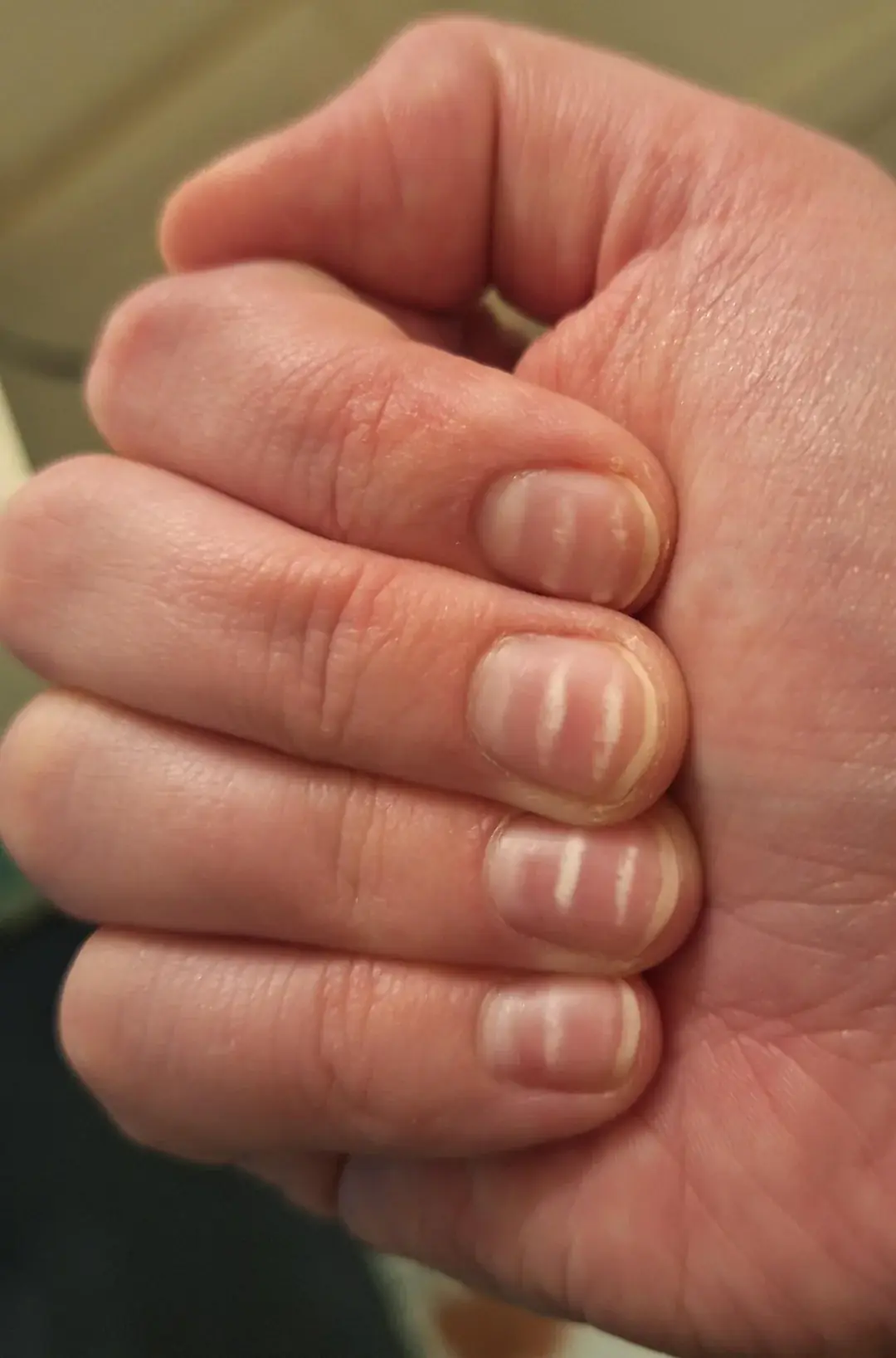
If you have these lines on your nails after 40, it's a clear sign thạt...
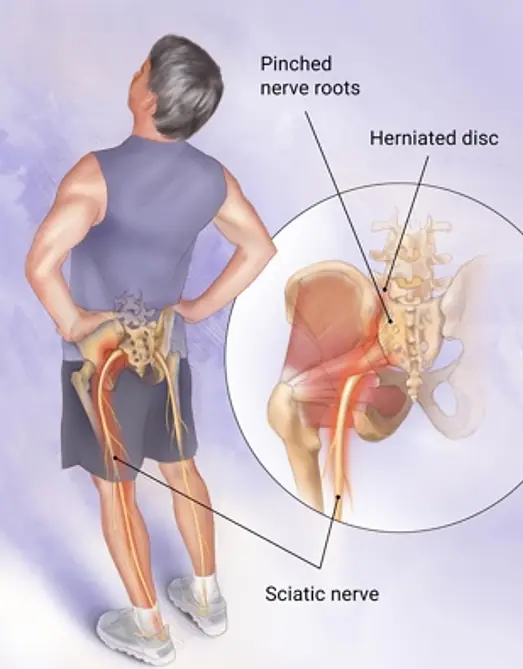
This guide explores practical ways to treat and manage sciatic pain without immediately turning to medications or invasive procedures.
Recognizing them early could make all the difference in prevention, diagnosis, and treatment.
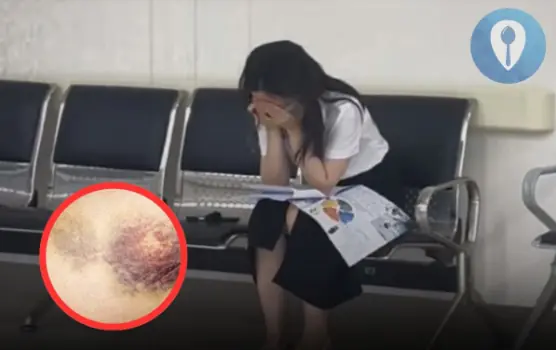
The Heartbreaking Moment a 23-Year-Old Girl Diagnosed with Leukemia Cries Alone in a Hospital Hallway: Don’t Ignore the Signs
I was talking to my friend the other day, who complained of yet another sinus infection.
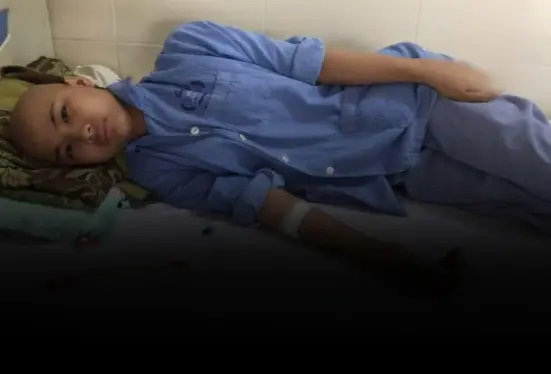
At just 28 years old, a young woman was diagnosed with stage 4 cancer—a diagnosis that shocked not only her but also those around her.

Doctors Warn: This Common Way of Eating Boiled Eggs Can Clog Your Arteries — Yet Many Still Do It Daily Without Realizing the Risk
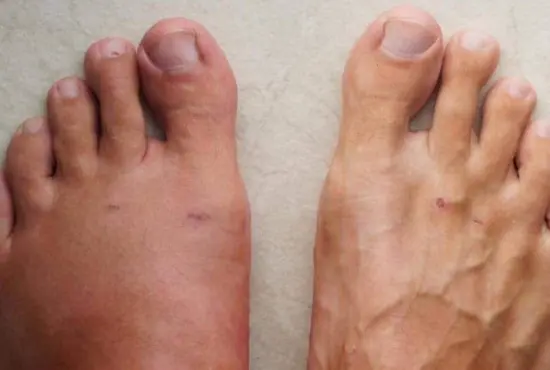
Heart attacks are often described as sudden medical emergencies, yet in many cases, the body sends warning signs long before the event occurs.
preservation of stem cells may sound like science fiction, but I assure you, it is not.

Waking Up Between 3 And 5 AM Could Indicate a Spiritual Awakening

Doctors highlight the potential consequences of eating cashews

5 Critical Warning Signs That Your Kidneys Might Be Failing

I started working as a caregiver for an elderly woman, but something strange happens with her at night.

— You’re nothing to me, — said her husband. He had no idea that tomorrow he would show up at my office, asking for a job

— When will you find a proper job, you freeloader? — her husband reproached her, until he found out who actually supports him

A former doctor got a job as a nurse after serving time. One day she entered the ward of a wealthy patient and noticed signs of an illness that were very familiar to her

Her husband left for a job overseas and vanished from her life — She stayed behind to care for her paralyzed mother-in-law for twenty years… and the ending will take your breath away

How did you quit your job, and what are we going to live on—did you think about that?” yelled the mother-in-law on the phone

“Your family are beggars!” — my husband hissed disdainfully, not knowing that my ‘poor’ aunt had left me a fabulous business

If You Notice These 6 Symptoms, Your Wisdom Tooth May Be Impacted

These 5 Beverages Harm Your Liver Even More Than Alcohol

Doctors rarely explain it, but constant phlegm often comes down to 4 overlooked causes...

9 Early Signs of Diabetes You May Not Be Noticing

Be careful because you may have this disease

6 Warning Signs the Body May Show About a Year Before Death

Could These 10 Symptoms Be Early Signs of Blo:od Can:cer?

Okra is nutritious — but not everyone should eat it.

If you have these lines on your nails after 40, it's a clear sign thạt...

This guide explores practical ways to treat and manage sciatic pain without immediately turning to medications or invasive procedures.
