What is myasthenia gravis and what are its symptoms?

Myasthenia Gravis (MG) is a chronic autoimmune neuromuscular disorder that causes weakness in the skeletal muscles. The hallmark of MG is muscle weakness that worsens with activity and improves with rest. It primarily affects voluntary muscles - the ones you control consciously - such as those involved in movement, breathing, and swallowing. Though MG is a rare condition, its impact can be profound, making it essential for patients to understand its symptoms, causes, and treatment options.
In this article, we’ll explore what myasthenia gravis is, its symptoms, and how it affects the body. We will also look at treatment options and ways to manage the condition.
What is Myasthenia Gravis?
Myasthenia Gravis is caused by a problem with the communication between the nerves and muscles. It is classified as an autoimmune disorder, meaning the body’s immune system attacks its own healthy tissues. In the case of MG, the immune system creates antibodies that block or destroy the acetylcholine receptors on the muscle cells. Acetylcholine is a neurotransmitter responsible for transmitting signals from nerves to muscles, enabling muscle contraction.
Because of this breakdown in communication, the muscles do not receive the full signal from the nerve to contract, leading to muscle weakness.
While the exact cause of MG is unknown, it is thought to be related to genetic factors and may also be linked to other autoimmune conditions. Thymus gland abnormalities (such as thymoma, a tumor of the thymus) are also commonly found in people with MG.
Symptoms of Myasthenia Gravis
The symptoms of MG can range from mild to severe and often fluctuate, meaning they can worsen after periods of activity and improve with rest. Common symptoms of myasthenia gravis include:
1. Muscle Weakness
Muscle weakness is the most common and defining symptom of myasthenia gravis. The weakness usually affects the voluntary muscles, particularly those that control eye movement, facial expression, swallowing, and breathing. It is often the eye muscles that are the first to be affected.
-
Drooping eyelids: One of the earliest signs of MG, where one or both eyelids may droop, making it difficult to keep the eyes open.
-
Double vision (diplopia): Weakness in the eye muscles can cause double vision due to improper alignment of the eyes.
2. Difficulty Swallowing and Speaking
Muscles that control swallowing and speaking may become weakened, leading to dysphagia (difficulty swallowing) and dysarthria (difficulty speaking). This can cause:
-
Choking or coughing while eating
-
A hoarse or weak voice
-
Difficulty swallowing liquids and solids
3. Limb Weakness
MG can also affect muscles in the arms and legs, causing difficulty in walking, climbing stairs, or holding objects. This weakness worsens with activity but improves with rest.
-
Weakness in the arms: Difficulty lifting objects, raising arms, or performing tasks like brushing your hair or combing your hair.
-
Leg weakness: Difficulty standing up from a sitting position, walking, or climbing stairs.
4. Breathing Difficulty
In severe cases, MG can affect the muscles that control breathing, leading to respiratory issues. This is known as a myasthenic crisis, a potentially life-threatening condition that requires immediate medical attention.
-
Shortness of breath: Difficulty breathing, especially after exertion.
-
Weakness in the diaphragm: The muscle that helps with breathing may weaken, making it difficult to breathe deeply or cough effectively.
5. Fatigue
Patients with MG often experience extreme fatigue, which worsens with activity and improves with rest. This fatigue can affect the ability to perform daily activities and can be debilitating for many people with the condition.
-
Feeling tired after small tasks: Simple tasks like walking or climbing stairs can cause exhaustion.
-
Rest improves the fatigue: Unlike other conditions, resting can temporarily relieve the fatigue caused by MG.
6. Facial Weakness
Weakness in the facial muscles can result in a lack of facial expression. This can lead to:
-
Difficulty smiling or frowning
-
Flat or mask-like expression
How is Myasthenia Gravis Diagnosed?
If you experience any of the symptoms of myasthenia gravis, it’s important to see a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis. The diagnosis typically involves several steps:
1. Medical History and Physical Exam: A doctor will review your symptoms and perform a physical examination to check for signs of muscle weakness.
2. Blo.od Tests: Blood tests can detect antibodies to the acetylcholine receptors or other proteins that cause MG.
3. Electromyography (EMG): This test measures the electrical activity of muscles and can help detect abnormal communication between nerves and muscles.
4. Nerve Conduction Study: This test evaluates how well the electrical signals travel along nerves to muscles. It can help determine if there is a problem with nerve-to-muscle transmission.
5. Imaging Tests: A CT scan or MRI can be used to check for thymus gland abnormalities (such as a thymoma, a tumor of the thymus), which is often associated with MG.
Treatment Options for Myasthenia Gravis
While there is no cure for myasthenia gravis, there are treatments available to manage the symptoms and improve quality of life. Treatment depends on the severity of the disease and may involve a combination of approaches:
1. Medications
-
Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors: These drugs, such as pyridostigmine (Mestinon), help improve nerve-to-muscle communication by inhibiting the breakdown of acetylcholine.
-
Immunosuppressive drugs: Drugs like prednisone or azathioprine may help reduce the immune system's attack on the acetylcholine receptors.
-
Plasmapheresis or intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG): In severe cases, these treatments can help remove harmful antibodies from the bloodstream.
2. Thymectomy
-
For some patients, removal of the thymus gland (thymectomy) may be recommended. This procedure can improve symptoms in some people, especially those with thymoma.
3. Supportive Care
-
Physical therapy can help improve muscle strength and prevent atrophy due to disuse.
-
Breathing support may be needed during a myasthenic crisis, including mechanical ventilation or non-invasive positive pressure ventilation.
Living with Myasthenia Gravis
While myasthenia gravis is a chronic condition, with proper treatment and management, many individuals can lead normal or near-normal lives. Here are some tips for managing MG:
-
Pacing activities: Rest frequently, and avoid overexertion, as this can worsen symptoms.
-
Good nutrition: Maintaining a balanced diet can help manage fatigue and muscle strength.
-
Regular monitoring: Stay in close communication with your healthcare team to monitor disease progression and adjust treatment.
Conclusion
Myasthenia gravis is a challenging condition, but with early diagnosis and appropriate treatment, many people can manage the symptoms effectively. If you experience symptoms such as muscle weakness, difficulty swallowing, or unexplained fatigue, it's essential to seek medical advice. Early detection and treatment can help improve quality of life and prevent complications.
If you or a loved one is diagnosed with MG, working closely with healthcare providers to tailor the treatment plan is crucial for managing the condition and maintaining overall health. With the right care and support, individuals with myasthenia gravis can live fulfilling and active lives.
News in the same category


All The Things You Need to Know About Nighttime Urination And When To Start Worrying
Umbilical Hernia: Causes, Symptoms and Treatment
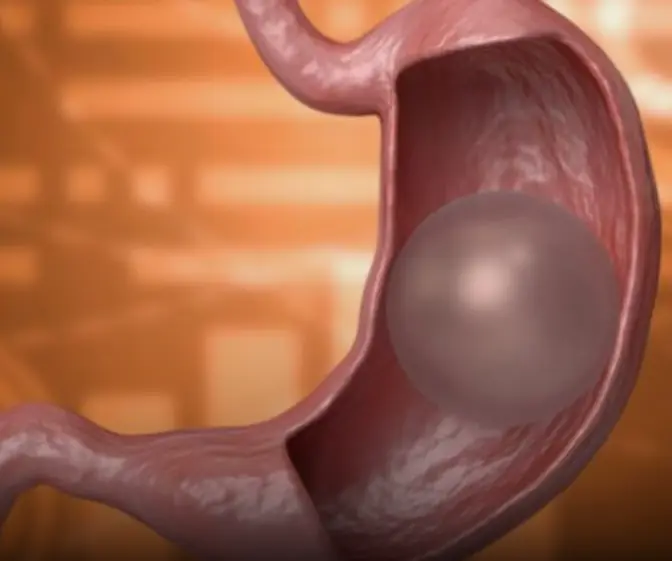
What happens if the gastric balloon bur.sts?

Gassier at Night? Here’s Why (and What To Do About It)

Eating chicken eggs is harmful to these 5 groups of people
WARNING: These 3 signs on the shoulder are signs of malig:nant tum:ors, even can:cer, do not ignore them

4 Vegetables Easily “Treated” with Chemicals

The Part of the Pig Often Dismissed as “Dirty” and Thrown Away: Turns Out It’s a “Miracle Food” with 10 Times More Iron Than Meat

An 8-Year-Old Girl Complained of “Sto.mach Pain” Every Friday Afternoon

Eating Eggs Can Be Harmful for These 5 Groups of People: Better Stay Away!
Early detection colon polyps: The key to effective can.cer prevention

Think it’s harmless? The risks of wearing bras to sleep might surprise you
What dise:ase is gr.oin pa.in a symptom of?
These 10 symptoms indicate latent diabetes

What sleeping on the left side does for our brain, stomach and lymphatic health

Eating yogurt with these 5 mistakes can bring more dis.eases into your body
8 foot massage points that help relieve issues
7 subtle symptoms that could signal serious health problems
News Post

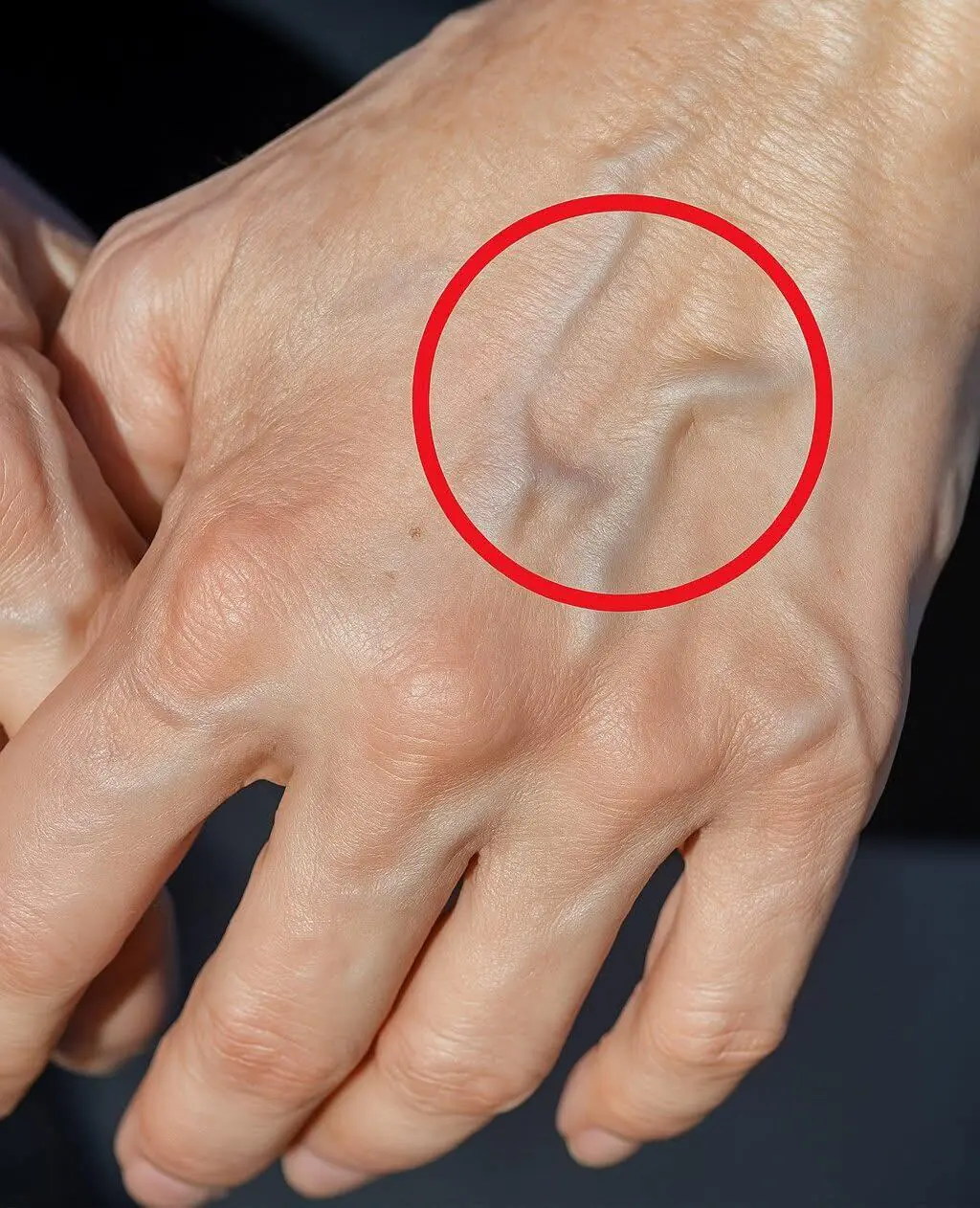
If Veins Suddenly Pop Out on Your Hands

All The Things You Need to Know About Nighttime Urination And When To Start Worrying

Don’t Throw Out Old Dish Sponges

When buying watermelon, don't choose a big one.
If You See Pork with These 4 Signs at the Market, Don’t Buy It No Matter How Cheap

Why Does Fish Often Smell Fishy? The Real Reason Many People Don’t Know

Ever noticed a greenish ring around an egg yolk? The explanation might surprise you...

Umbilical Hernia: Causes, Symptoms and Treatment

What happens if the gastric balloon bur.sts?

99% of people will throw away these 6 fruit peels when eating, but will regret it when they know their benefits

Top 2 types of seafood at the top of the list of microplastic contamination, but people still eat them every day

Gassier at Night? Here’s Why (and What To Do About It)

Eating chicken eggs is harmful to these 5 groups of people

WARNING: These 3 signs on the shoulder are signs of malig:nant tum:ors, even can:cer, do not ignore them

4 Vegetables Easily “Treated” with Chemicals

The Part of the Pig Often Dismissed as “Dirty” and Thrown Away: Turns Out It’s a “Miracle Food” with 10 Times More Iron Than Meat

An 8-Year-Old Girl Complained of “Sto.mach Pain” Every Friday Afternoon

Eating Eggs Can Be Harmful for These 5 Groups of People: Better Stay Away!
