
4 Subtle Clues on Your Body That Point to High Blo.o.d Fa.t
4 Body Signs That May Help Detect High Blood Fat — What You Need to Look Out For
High blood fat — which includes elevated cholesterol and triglyceride levels — often develops silently.
Many people don’t realize they have it until it leads to serious complications like heart disease, stroke, or fatty liver.
Because the condition rarely causes early symptoms, it’s often called a “hidden danger” inside the bloodstream.
However, doctors note that certain physical signs on the body can offer early clues.
These signs do not diagnose high blood fat on their own, but they can indicate that your lipid levels may be higher than normal and deserve a proper blood test.
Here are four important signs that may help you detect potential issues early.
1. Ear Crease Lines — A Possible Warning Sign of Artery Aging
One of the most discussed indicators is the presence of a deep crease running diagonally across the earlobe.
This is known as Frank’s sign, named after the doctor who first described the association.
Why it matters:
Researchers have found a correlation between earlobe creases and:
• high cholesterol
• arterial hardening (atherosclerosis)
• reduced blood flow to the heart
The theory is that the crease may reflect changes in microcirculation — and in some people, it appears before other symptoms of cardiovascular risk.
Not everyone with an ear crease has high blood fat, but if the line is deep or appears early in life, it may be worth checking cholesterol levels.
2. Yellowish Fat Deposits on the Skin (Xanthomas)
Another classic sign of high blood fat is the development of xanthomas — small, yellowish bumps or patches of fat under the skin.
They may appear on:
• eyelids (xanthelasma)
• elbows
• knees
• hands
• Achilles tendon
What they indicate:
Xanthomas form when excess fat circulates in the blood and accumulates in the skin.
They are strongly linked to:
• high LDL cholesterol
• high triglycerides
• hereditary lipid disorders
These deposits are not dangerous themselves, but they are a clear sign that the body is struggling to regulate fat levels.
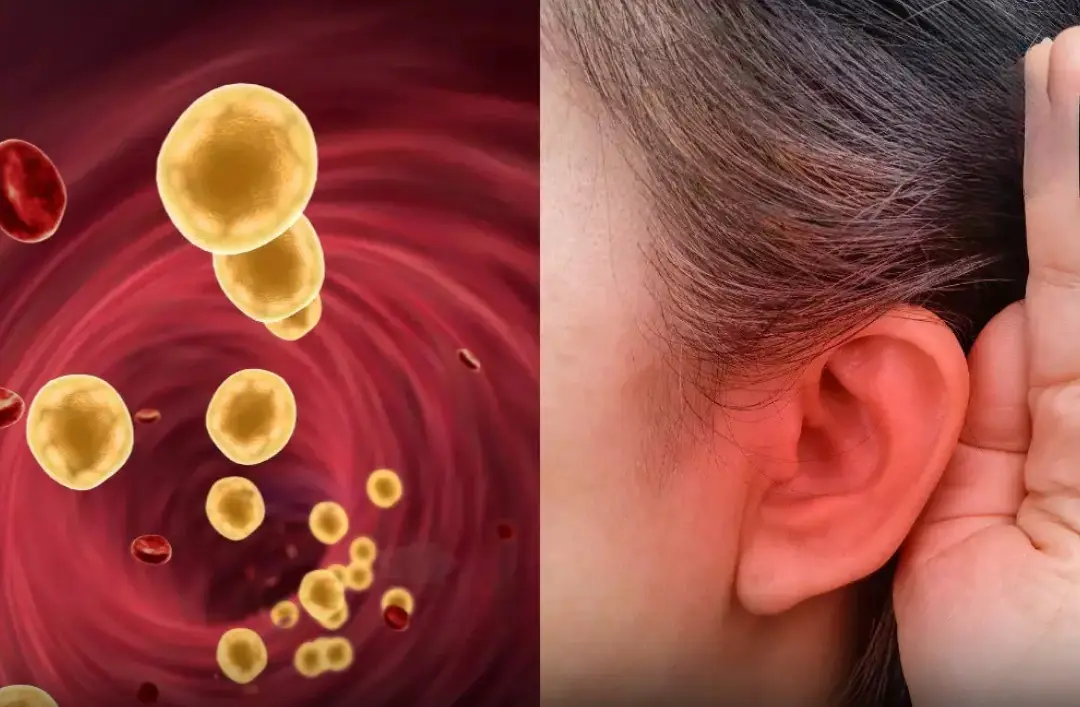
3. Frequent Dizziness or Ringing in the Ears (Tinnitus)
High blood fat can thicken the blood and impair circulation, especially to small blood vessels in the inner ear.
This may lead to:
• occasional dizziness
• imbalance
• ringing or buzzing in the ears
• a feeling of fullness or pressure
Why this happens:
The inner ear is extremely sensitive to changes in blood flow.
When circulation is reduced due to narrowed arteries or thicker blood, the ear’s delicate structures may react with persistent noise (tinnitus) or vertigo-like sensations.
While tinnitus has many causes, its association with poor blood flow makes it a potential sign of elevated lipid levels.
4. Slow Healing and Numbness in the Extremities
When blood vessels narrow due to high cholesterol buildup, circulation to the hands and feet can become weaker.
You may notice:
• numbness or tingling
• cold hands or feet
• slow healing of small cuts
• leg cramps during walking (claudication)
What this suggests:
Reduced circulation indicates that cholesterol plaques may be forming along artery walls.
This is an early sign of peripheral artery disease (PAD), which is closely related to high blood fat.
Poor circulation also increases the risk of stroke and heart disease, so these symptoms should never be ignored.
Why These Signs Matter
High blood fat quietly damages the body for years.
By the time symptoms appear in the heart or brain, the condition is already advanced.
Recognizing early physical signs can help you take action before complications occur.
However, it’s important to remember:
These signs do not confirm high blood fat. Only a lipid blood test can diagnose it.
Still, if you notice one or more of these symptoms, it’s wise to discuss them with a healthcare provider.
How to Protect Yourself
1. Get regular blood tests
Adults should check cholesterol at least every 1–2 years, or more often if at risk.
2. Improve your diet
Reduce sugary foods, fried items, processed meats, and high-saturated-fat meals.
3. Exercise regularly
Just 30 minutes a day of walking can significantly lower triglycerides and raise healthy HDL levels.
4. Maintain a healthy weight
Even modest weight loss improves cholesterol levels.
5. Avoid smoking and limit alcohol
Both contribute to abnormal lipid metabolism.
Bottom Line
High blood fat often develops without obvious symptoms, but the body sometimes sends subtle clues — including:
• earlobe creases
• xanthomas (yellow skin patches)
• dizziness or tinnitus
• numbness and slow healing in extremities
If you notice these signs, it’s a good idea to have your lipid levels checked.
Early action can protect your heart, blood vessels, and long-term health.
News in the same category


Did You Know That Waking Up At 3 Or 4 In The Morning Is A Clear Sign Of

Surprising causes of hives revealed - What may be triggering your skin
Those who have this sign should not ignore it
3 Warning about the habit of "welcoming" can:cer into the body

Sweet Potatoes Are Great for Your Health — But There Are 2 Times You Shouldn’t Eat Them

5 purple foods that are exceptionally good for your health
Warning signs of advanced sto.mach can.cer you should never ignore

The Incredible Benefits of Plantago lanceolata

The hidden power of Mimosa Pudica: 30 benefits and homemade uses
Why do ve.ins become more noticeable?

69-year-old man d.i.es after drinking coconut water: URGENT warning about a mistake when drinking coconut water that can easily cause people to “pa.ss a.way”
Turns Out Sunbathing Isn’t the Best Way to Prevent Osteoporosis! These 3 Everyday Foods Work Far Better Than Sun Exposure
His whole body was itchy, he thought it was an allergy but then he was diagnosed
6 Warning Signs of Kid.ney Failure Many People Overlook

Clean eating made delicious
At Just 20, Forced to Undergo Dialysis for Life: Doctor Shocked

More People Are Dying From Diabetes: Doctors Warn “It’s Better to Stay Thirsty Than Drink These 5 Beverages”

Dea.dly Within 24 Hours: Doctors Warn About a Fast-Progressing Disease Targeting Teenagers
News Post

Are your nails constantly splitting or breaking? Your body might be sending you a warning — and the reason may surprise you!

Crispy Fried Chicken with Creamy Potato Salad

Did You Know That Waking Up At 3 Or 4 In The Morning Is A Clear Sign Of

Surprising causes of hives revealed - What may be triggering your skin

Those who have this sign should not ignore it

3 Warning about the habit of "welcoming" can:cer into the body

How to defrost fish and still keep it fresh 😲

Sweet Potatoes Are Great for Your Health — But There Are 2 Times You Shouldn’t Eat Them

5 common mistakes when using an electric kettle

5 purple foods that are exceptionally good for your health

Warning signs of advanced sto.mach can.cer you should never ignore

The top 5 plants snakes don’t like

Why do egg yolks vary in color - and does it affect nutrition?

A simple trick to tell real honey from fake: Just flip the bottle upside down

The Incredible Benefits of Plantago lanceolata

The hidden power of Mimosa Pudica: 30 benefits and homemade uses

It’s not the air conditioner - This is the real “Power drainer” driving up your electricity bill

Why do ve.ins become more noticeable?
