
5 Types of Vegetables You Shouldn't Eat at Night: They Can Harm Your Stomach, Drain Vital Energy, and Are Especially Risky for the Elderly
When it comes to healthy eating, vegetables are often praised as essential to every meal. However, not all vegetables are suitable for consumption at night. In fact, certain types can do more harm than good—especially for older adults or those with sensitive digestion. Here are five vegetables experts recommend avoiding in the evening.
1. Garlic Chives (Chinese Leek)
Garlic chives are known for their strong flavor and "warming" properties in traditional medicine. Eating them at night may overstimulate the digestive system, leading to bloating, gas, or discomfort. For the elderly, it can even disrupt sleep due to increased metabolic activity.
2. Raw Onions
While onions are rich in antioxidants, eating them raw at night may irritate the stomach lining, trigger acid reflux, and cause indigestion. These effects are more pronounced when consumed close to bedtime.
3. Spinach
Spinach is high in oxalates, which can contribute to kidney stone formation if overconsumed. Eating large portions at night may also interfere with calcium absorption. Seniors and those with kidney issues should be especially cautious.
4. Sweet Corn
Corn is starchy and harder to digest in large quantities. Eating it late at night can lead to stomach heaviness and discomfort. The fiber content, while beneficial during the day, may cause bloating or even disrupt sleep if consumed too late.
5. Cabbage
Cabbage, especially raw or in large amounts, can produce gas and cause bloating. Fermented versions like kimchi or sauerkraut may be even more disruptive to digestion when eaten late, particularly for people with weak digestive systems.
Why Timing Matters
Your metabolism slows down at night, and your digestive system becomes less efficient. Eating heavy, fibrous, or spicy vegetables late in the evening can lead to:
-
Acid reflux or heartburn
-
Sleep disturbances
-
Impaired nutrient absorption
-
Strain on internal organs, especially in older adults
News in the same category


6 Smart Tips for Choosing Quality Honey Sellers Don’t Want You to Know

Doctors Warn: This Common Way of Eating Boiled Eggs Can Clog Your Arteries

2 Common Vegetables That Can Harbor Parasites

The 'Vitamin C King' of the Vegetable World
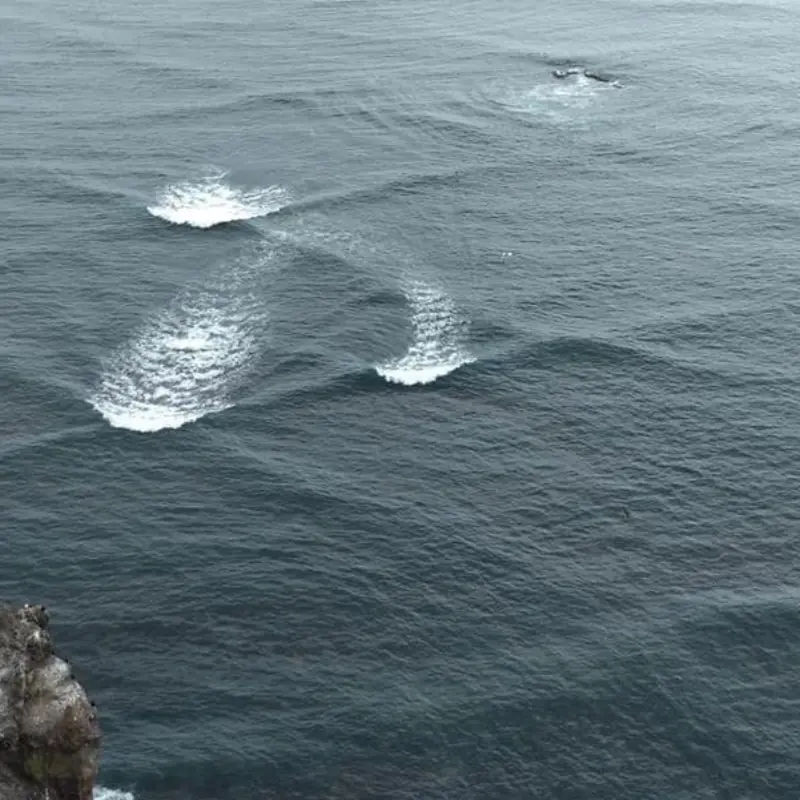

Avoid Swimming If You Spot 'Square Waves'

3 Green Vegetables Called the “King” of Sto.mach Protection
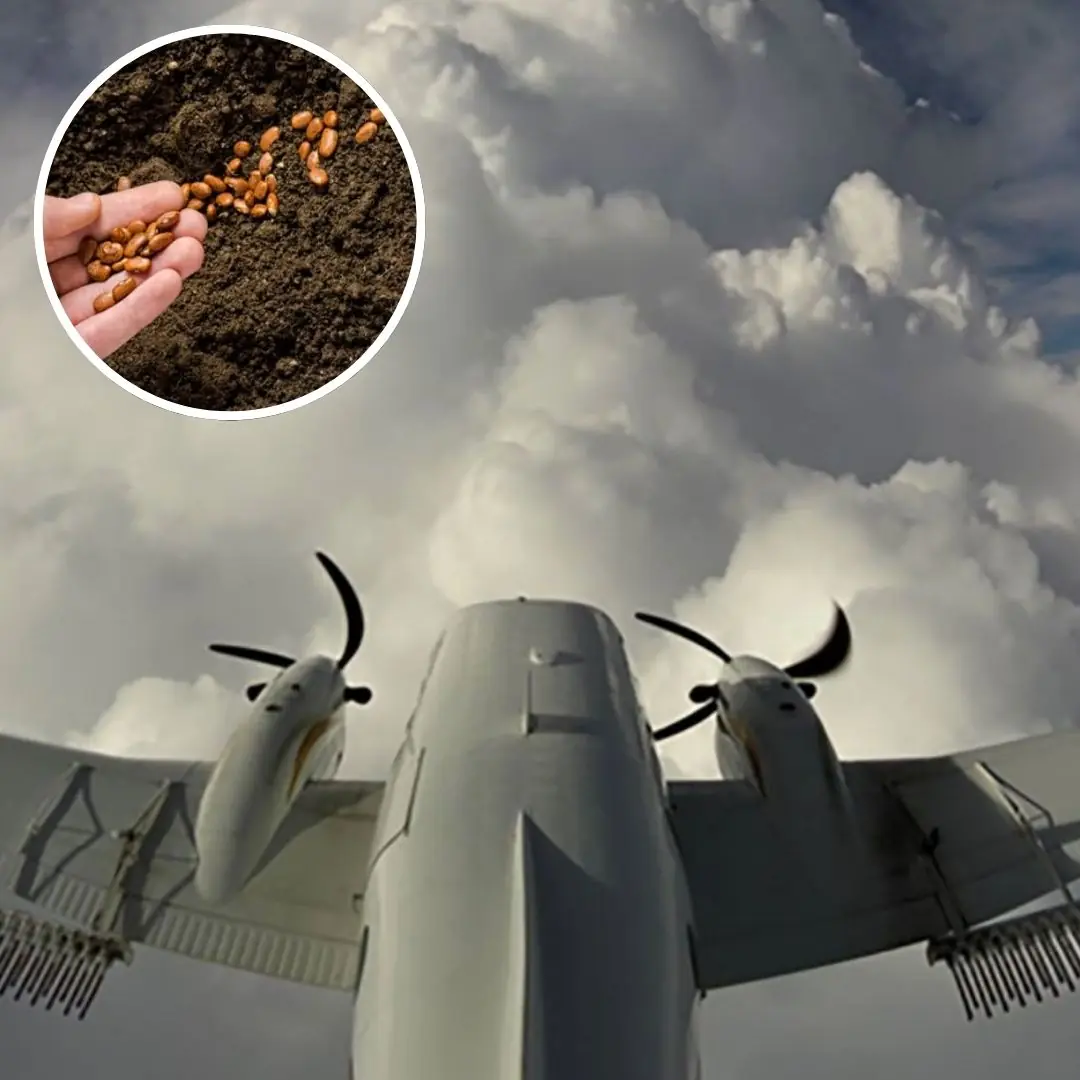

Why You Should Not Bring Seeds on a Plane: A Detailed Explanation

10 Powerful Reasons a Simple Smile Can Change Your Life

3 Common Mistakes in Storing Watermelon During Summer

When Buying Oysters, Avoid These 3 Types
Woman Suddenly Suffers Kid.ney Failure After a Meal

Why Dogs and Cats Often Hate Each Other—Most People Don’t Know This
4 Morning Habits That Increase Str.oke Risk—Avoid Them at Any Age

Smart Shoppers Avoid These 3 Types of Fish at the Market

Not a snake, this is the "kil.ler" that can crawl out of your air conditioner
Doctors Discovered 6 Morning Habits Shared by Most Can.cer Patients

Why do women grow a lot of hair on their fingers?
20 Signs of Can.cer That Women Often Ignore

4 things you do in the morning that bring you closer to a str.oke
News Post

The Most Nutritious Part of the Chicken—“Pricier than Gold” Yet Often Thrown Away by Home Cooks
Doctor Urges 4 Actions to Protect Your Body’s "Blo.od Filter"

6 Smart Tips for Choosing Quality Honey Sellers Don’t Want You to Know

Can overly hot baths harm your heart and circulation?
7 signs of brain c.a.ncer that are easily confused with other diseases

4 Things to Avoid After 5 PM to Lower Your Risk of Stro.ke

Doctors Warn: This Common Way of Eating Boiled Eggs Can Clog Your Arteries

Blanch Bones First or Simmer Directly?

2 Common Vegetables That Can Harbor Parasites

The 'Vitamin C King' of the Vegetable World

Avoid Swimming If You Spot 'Square Waves'

3 Green Vegetables Called the “King” of Sto.mach Protection

Why You Should Not Bring Seeds on a Plane: A Detailed Explanation
Bladder Ca.ncer: Symptoms You Shouldn’t Ignore
4 Healing Drinks to Prevent and Dissolve Kidney Stones

10 Powerful Reasons a Simple Smile Can Change Your Life

The Surprising Benefits of Donating Bl.o.od

5 types of vegetables and fruits help cool the liver and effectively lower liver enzymes

Top vegetable to help reduce visceral fat extremely effectively, nutritionist reveals 4 more easy ways to lose weight
