
7 Early Signs of Bile Duct Cancer You Shouldn’t Ignore
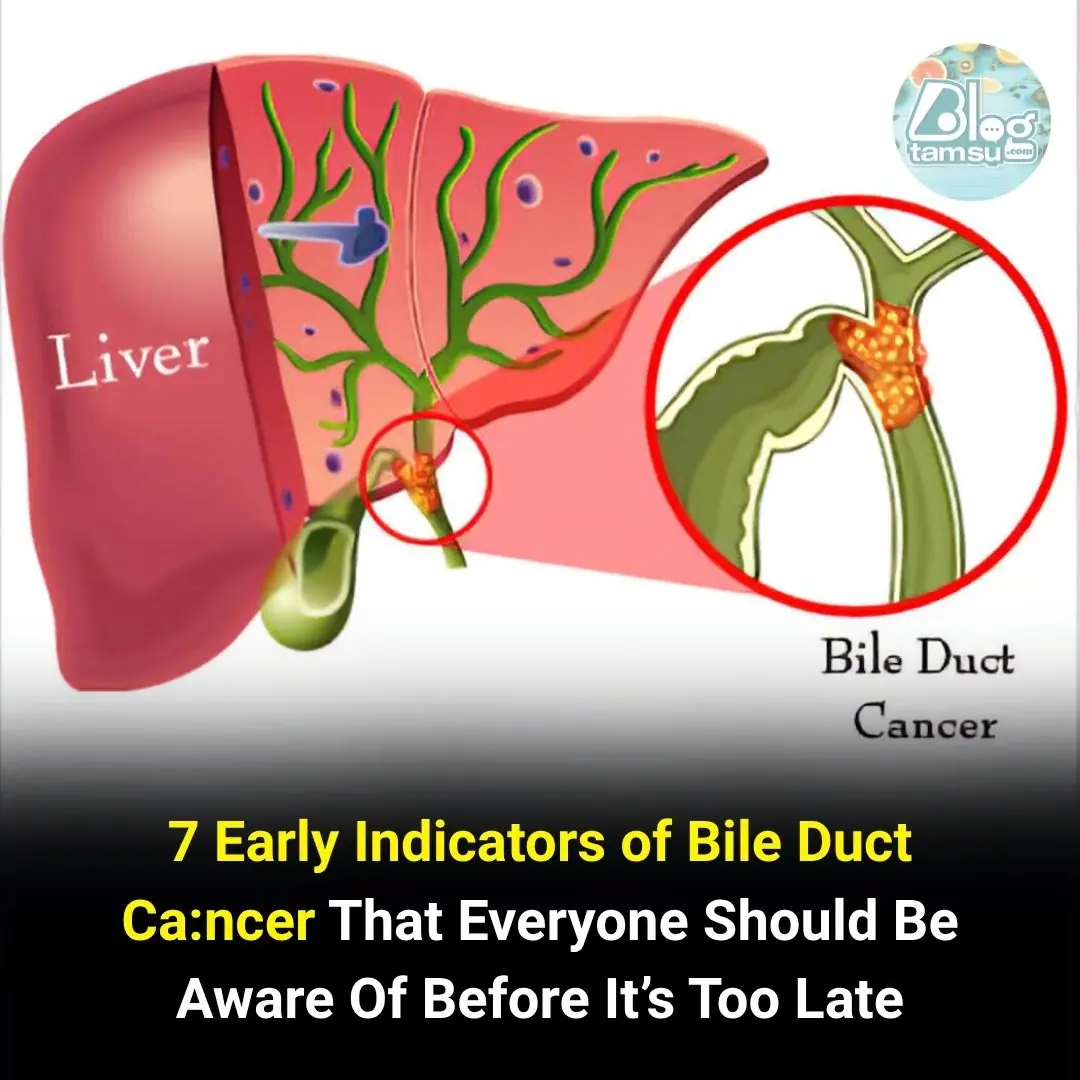
Gallbladder Cancer (also called Biliary Cancer): A Dangerous Malignant Disease with Poor Prognosis if Detected Late
Gallbladder cancer, also known as biliary cancer, is a dangerous malignancy with a poor prognosis if detected late. Its symptoms are often mistaken for liver diseases. Below, experts highlight the “key indicators” of gallbladder cancer.
1. What is Gallbladder Cancer?
Gallbladder cancer, also known as biliary cancer, is a highly dangerous disease that is difficult to detect in its early stages.
The gallbladder is a small, pear-shaped organ located on the right side of the abdomen, just beneath the liver. It stores bile, a digestive fluid produced by the liver. Thanks to bile and other digestive enzymes, the body can process fats.
Gallbladder cancer is caused by the uncontrolled growth of cells lining the gallbladder wall. It is quite rare and usually has no obvious early symptoms. However, if diagnosed in its early stages, the chances of successful treatment are high.
2. Seven “Indicator” Signs of Gallbladder Cancer
2.1. Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes) – A very typical sign of gallbladder cancer
Jaundice is the most common symptom, occurring in up to 90% of diagnosed patients. At first, jaundice can be overlooked under artificial light, as the change in skin tone is not obvious. Checking under natural light provides a clearer view. If the skin appears yellowish and pale, it may indicate liver or gallbladder conditions, including the risk of gallbladder cancer.
This occurs because bile is produced in the liver and stored in the gallbladder to help digest food. When bile flow is blocked, bilirubin (a bile pigment) builds up in the blood, leading to yellowing of the skin and eyes.
2.2. Persistent, dull abdominal pain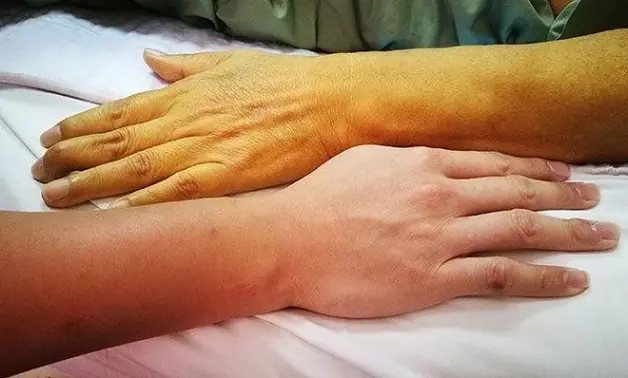
Ongoing, dull abdominal pain often makes people think they simply have digestive issues. However, persistent discomfort in the area near the liver can be a warning sign of gallbladder cancer.
2.3. Nausea and vomiting without clear cause, not related to stomach disease
While nausea and vomiting are often linked to stomach disorders, they can also signal liver or gallbladder disease. If these symptoms appear alongside liver-area pain, eye discoloration, and fatigue, you should seek medical attention promptly.
2.4. Abdominal bloating
Though bloating has many causes, persistent bloating accompanied by abdominal discomfort may also indicate gallbladder cancer.
2.5. Gallstones – An early risk factor for gallbladder cancer
Statistics show that 4 out of 5 people with gallstones are at risk of developing gallbladder cancer. Gallstones, formed from excess cholesterol and calcium, obstruct gallbladder function. If you have a history of gallstones, you should closely monitor your health and undergo regular check-ups for early detection.
2.6. Loss of appetite, fatigue, and weight loss
When bile cannot flow properly and builds up in the bloodstream, it not only causes jaundice but also leads to appetite loss. Patients often lose interest in foods they previously enjoyed, eat very little, and consequently lose weight.
2.7. Family history of gallbladder cancer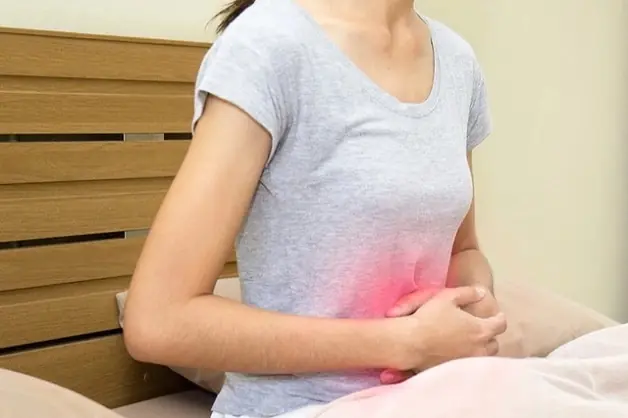
As with other cancers, such as breast cancer, family history is an important risk factor. While no direct genetic link has been confirmed, statistics show that people with relatives who had gallbladder cancer should be especially vigilant.
3. Treatment of Gallbladder Cancer
Currently, the following treatment methods are used:
3.1. Surgery to completely remove the gallbladder
This is applied in the early stages to eliminate the tumor entirely. Surgery removes the gallbladder and the tumor. In advanced stages where the cancer spreads to nearby tissues or other organs, surgery may help relieve symptoms and extend survival. At this stage, surgery may be combined with bile duct stenting or bypass procedures.
3.2. Radiation therapy
Radiation may be used before or after surgery, or both. If the tumor is too large, radiation can shrink it to make surgical removal possible. After surgery, radiation is used to destroy any remaining cancer cells. Side effects may include hair loss, fatigue, and loss of appetite.
3.3. Chemotherapy
This involves oral or intravenous medication, often combined with radiation to destroy residual cancer cells and reduce recurrence risk. Chemotherapy also helps ease symptoms and extend survival but comes with side effects similar to radiation.
Additionally, palliative care is provided to reduce pain and improve comfort for patients.
Conclusion:
Gallbladder cancer (biliary cancer) is a dangerous disease. Only early detection offers a good chance of treatment. If diagnosed late, the mortality rate is very high. Therefore, recognizing warning signs and undergoing regular check-ups are essential to protecting yourself and your loved ones.
News in the same category

The Feet of People “Hiding” Can.cer Often Show 5 Differences
12 signs that may signal a brain aneurysm — Don’t ignore them
hese 4 Changes on the Soles of Your Feet May Signal Poor Liver Health — Not Having Them Is a Blessing
Strange theory for those who’ve never br.oken a bone

Purple leaf plant: A natural remedy for headaches and more
This poi.son des.troys your bones, but you drink it everyday
5 Red Flags of Kidney Stones That Everyone Should Watch Out For
Garlic eliminates infections: Sinusitis, UTIs, Sore Throat & More – 12 benefits and how to use it
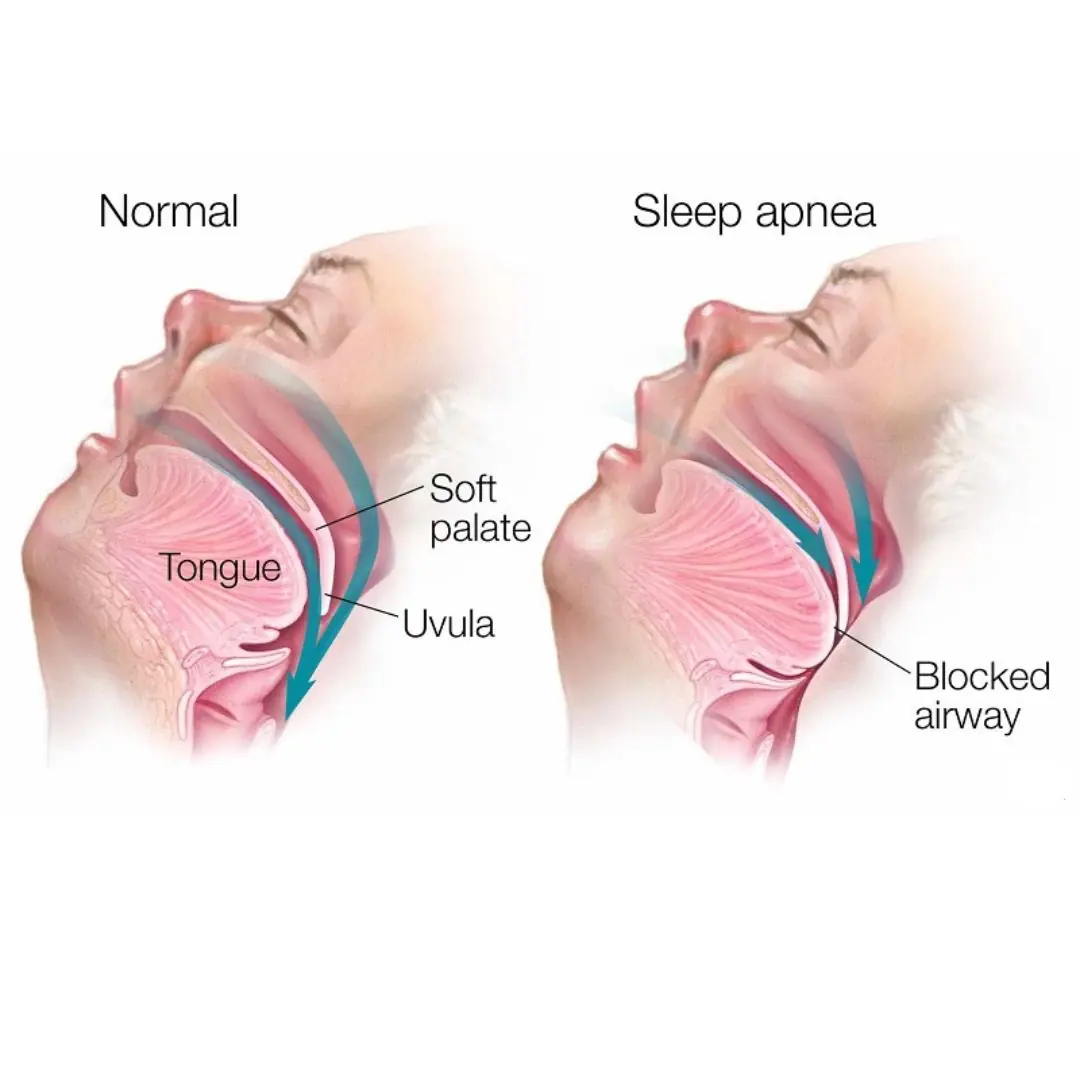
4 Signs You Might Have Sleep Apnea

Frequently waking up at 3-4 AM: Be careful of these 4 sc.ary dis.eases

12 noticeable benefits of eating banana and avocado every morning for just one month
If Veins Suddenly Pop Out on Your Hands

All The Things You Need to Know About Nighttime Urination And When To Start Worrying
Umbilical Hernia: Causes, Symptoms and Treatment
What happens if the gastric balloon bur.sts?

Gassier at Night? Here’s Why (and What To Do About It)
What is myasthenia gravis and what are its symptoms?

Eating chicken eggs is harmful to these 5 groups of people
News Post

Smart Women Take Advantage of Their Peri.od to Do These 4 Things: Relieve Fatigue, Cleanse the Ute.rus, and Detox the Body

The Feet of People “Hiding” Can.cer Often Show 5 Differences

Hotel Staff Confess: 5 “Clean-Looking” Items in Motels & Hotels That Are Actually Filthy – Number 4 Will Sho.ck You Most!

Sign Someone Might Be Planning to Leave

If the paint inside a rice cooker or non-stick pan is scratched or peeling

12 signs that may signal a brain aneurysm — Don’t ignore them

hese 4 Changes on the Soles of Your Feet May Signal Poor Liver Health — Not Having Them Is a Blessing

Strange theory for those who’ve never br.oken a bone

Purple leaf plant: A natural remedy for headaches and more

This poi.son des.troys your bones, but you drink it everyday

5 Red Flags of Kidney Stones That Everyone Should Watch Out For

Garlic eliminates infections: Sinusitis, UTIs, Sore Throat & More – 12 benefits and how to use it

Few People Realize the Real Reason Behind That Little Hole Above the Sink

4 Signs You Might Have Sleep Apnea
There is a button on the washing machine that if turned on, the clothes will be cleaner and last longer, but many people still don't know about it.

Pests Are Secretly Taking Over Your House — Watch Out for These 7 Warning Signs

Frequently waking up at 3-4 AM: Be careful of these 4 sc.ary dis.eases

12 noticeable benefits of eating banana and avocado every morning for just one month
