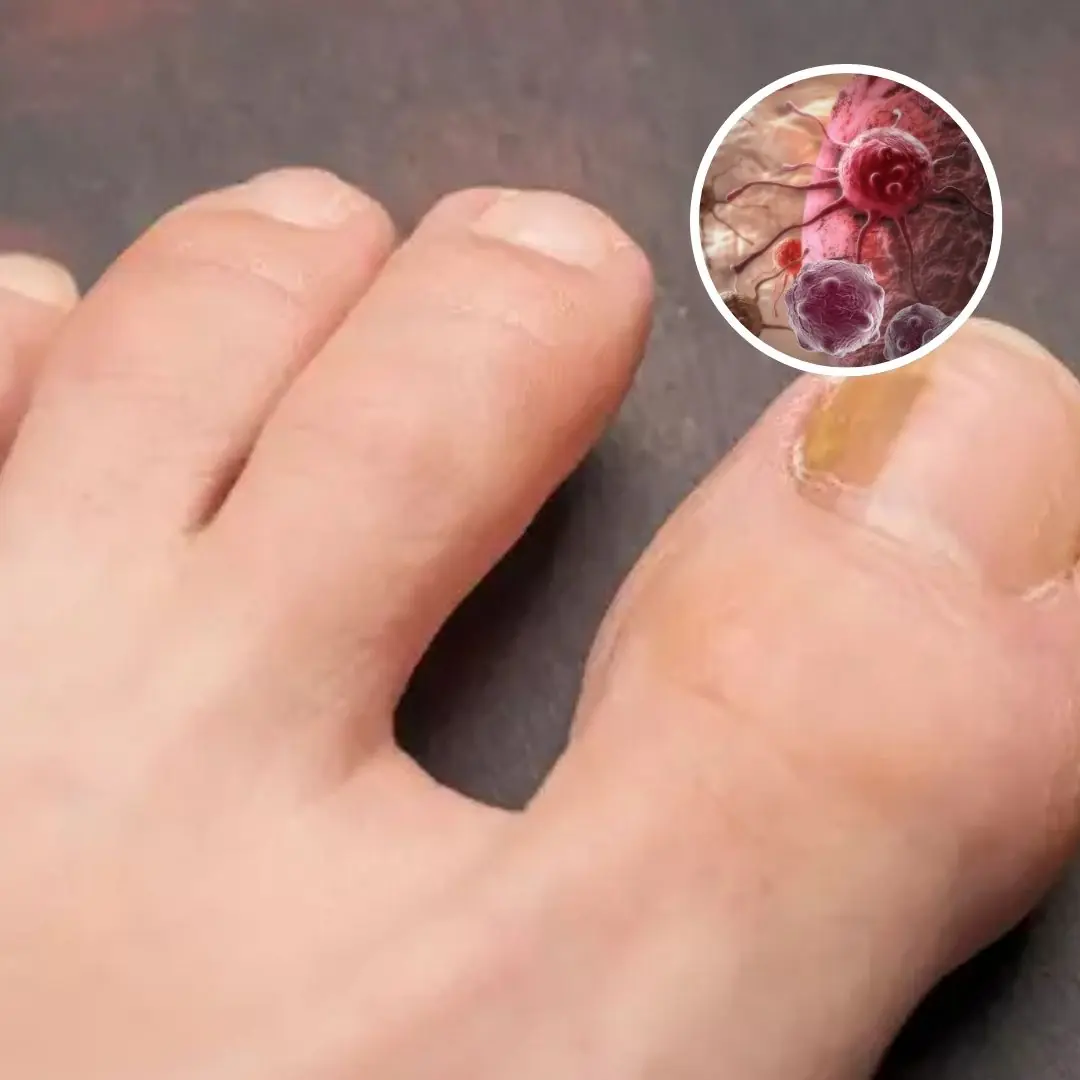
Doctors warn of little-known cancer symptom you can see on your toenails
Doctors warn of little-known cancer symptom you can see on your toenails
Cervical cancer is widely recognized as one of the most preventable and treatable cancers when it is detected early. Yet despite this, many
women do not recognize its early warning signs. The disease often develops slowly and quietly, allowing symptoms to go unnoticed until it
reaches a more advanced stage. Learning to identify these early signals and understanding how to reduce risk can truly be life-saving.
Below is a clear, in-depth guide to the early warning signs of cervical cancer, why they matter, and the most effective steps women can take
to protect their long-term health.
One of the earliest and most common warning signs of cervical cancer is bleeding that occurs outside of normal menstrual cycles. This
may present as:
Bleeding between periods
Bleeding after sexual intercourse
Bleeding after menopause
Menstrual periods that are heavier or last longer than usual
This type of bleeding happens because cancerous or precancerous cells can make cervical tissue fragile and easily irritated. While hormonal
changes or infections can also cause irregular bleeding, persistent or unexplained bleeding always requires medical evaluation.
Changes in vaginal discharge are another potential early indicator. Warning signs include:
A watery or unusually thin texture
A strong or foul odor
Pink, brown, or blood-stained discharge
A noticeable increase in discharge volume
These changes may occur when abnormal cells begin breaking down cervical tissue, leading to inflammation and fluid buildup. Although
infections are more common causes, discharge that persists, worsens, or appears abnormal should never be ignored.
Pelvic pain is not always present in early cervical cancer, but when it occurs, it may feel like:
A dull ache in the lower abdomen or pelvic area
Sharp or stabbing pain during movement
Discomfort while exercising or sitting for long periods
Cramping unrelated to menstruation
As abnormal cells grow, they can put pressure on nearby tissues, nerves, or organs. Pelvic pain that is ongoing and unexplained deserves
prompt medical attention.
Painful intercourse can be an early warning sign of cervical cancer. Inflammation or tissue damage caused by abnormal cells may make the
cervix sensitive or painful during sex.
This symptom may also occur with:
Light bleeding after intercourse
Pelvic or lower back discomfort
A sensation of pressure or fullness
While many non-cancerous conditions can cause painful s.e.x, ongoing discomfort should always be evaluated by a healthcare provider.:format(webp)/ung_thu_co_tu_cung_giai_doan_1_6011e8414b.png)
Persistent fatigue can be an early symptom of many cancers, including cervical cancer. This fatigue often:
Does not improve with rest
Interferes with daily activities
Occurs alongside appetite changes or weight loss
Chronic inflammation and slow blood loss can lead to anemia, contributing to weakness and exhaustion. If fatigue cannot be explained by
stress, sleep issues, or lifestyle factors, medical evaluation is important.
Cervical cancer has a very high survival rate when detected early, particularly in the precancerous stage or Stage I. Early diagnosis often
means simpler treatment, fewer complications, and better long-term outcomes.
Routine screening plays a vital role:
Pap tests detect abnormal cervical cells before cancer develops
HPV tests identify high-risk virus strains
Pelvic exams help identify physical abnormalities
Because most cervical cancers are caused by HPV, vaccination and screening together provide powerful protection.
Seek medical care if you experience:
Persistent abnormal bleeding
Unusual or foul-smelling discharge
Pelvic or lower back pain
Pain during intercourse
Unexplained fatigue or weakness
Even mild symptoms can signal early disease. Early evaluation can prevent progression and save lives.
Although cervical cancer can be serious if detected late, it is also one of the most preventable cancers. Prevention is most effective when
multiple strategies are combined.
HPV is the leading cause of cervical cancer. Vaccination provides strong protection against high-risk strains.
Recommended for girls and boys ages 9–14
Catch-up vaccination available up to age 26
Adults ages 27–45 may still benefit (consult a doctor)
Vaccination can reduce cervical cancer risk by up to 90%.
Routine screening can detect abnormalities before symptoms appear.
General guidelines:
Ages 21–29: Pap test every 3 years
Ages 30–65: Pap test every 3 years or Pap + HPV test every 5 years
Women with higher risk may need more frequent screening.
HPV spreads through skin-to-skin sexual contact.
Risk-reducing steps include:
Consistent condom use
Limiting number of sexual partners
Avoiding partners with multiple partners
Safer sex lowers risk, though it does not eliminate HPV exposure entirely.
Smoking weakens immune defenses and increases cervical cancer risk by damaging cervical cells. Women who smoke are significantly more
vulnerable to HPV-related cell changes. Quitting smoking greatly improves cervical health.
A strong immune system can often clear HPV naturally. Support immune health by:
Eating a nutrient-rich diet
Exercising regularly
Getting adequate sleep
Managing stress
Staying hydrated
Those with weakened immunity should be especially diligent with screening.
When abnormal cells are found, early treatment can stop cancer from developing. Common procedures include freezing, laser therapy, or
removal of affected tissue. Early intervention has extremely high success rates.
You may need closer monitoring if you have:
A family history of cervical cancer
Previous abnormal Pap results
A weakened immune system
Early sexual activity or multiple pregnancies
Understanding your risk helps guide personalized prevention plans.
Cervical cancer often progresses quietly, but the body sends early warning signs if you know how to recognize them. Abnormal bleeding,
unusual discharge, pelvic pain, painful intercourse, and unexplained fatigue are signals that should never be ignored.
With vaccination, routine screening, and healthy lifestyle choices, most cases of cervical cancer can be prevented or caught early.
Knowledge, vigilance, and early action empower women to protect their health and save lives.

Doctors warn of little-known cancer symptom you can see on your toenails
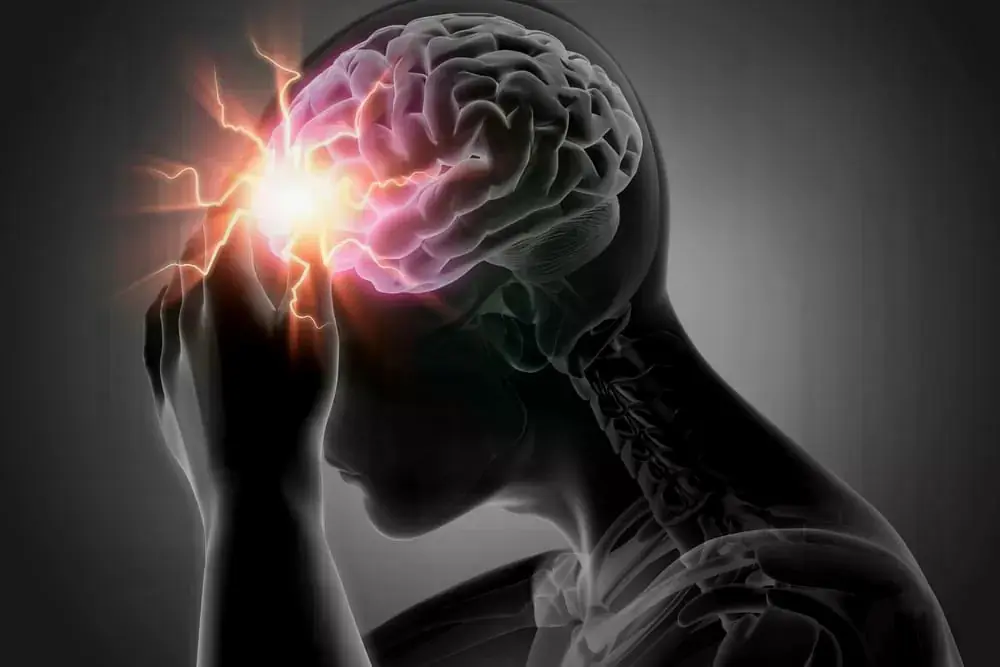
Doctors warn: The body may signal a str.oke 15 minutes before it happens - act fast

4 finger changes that may indicate lung can.cer
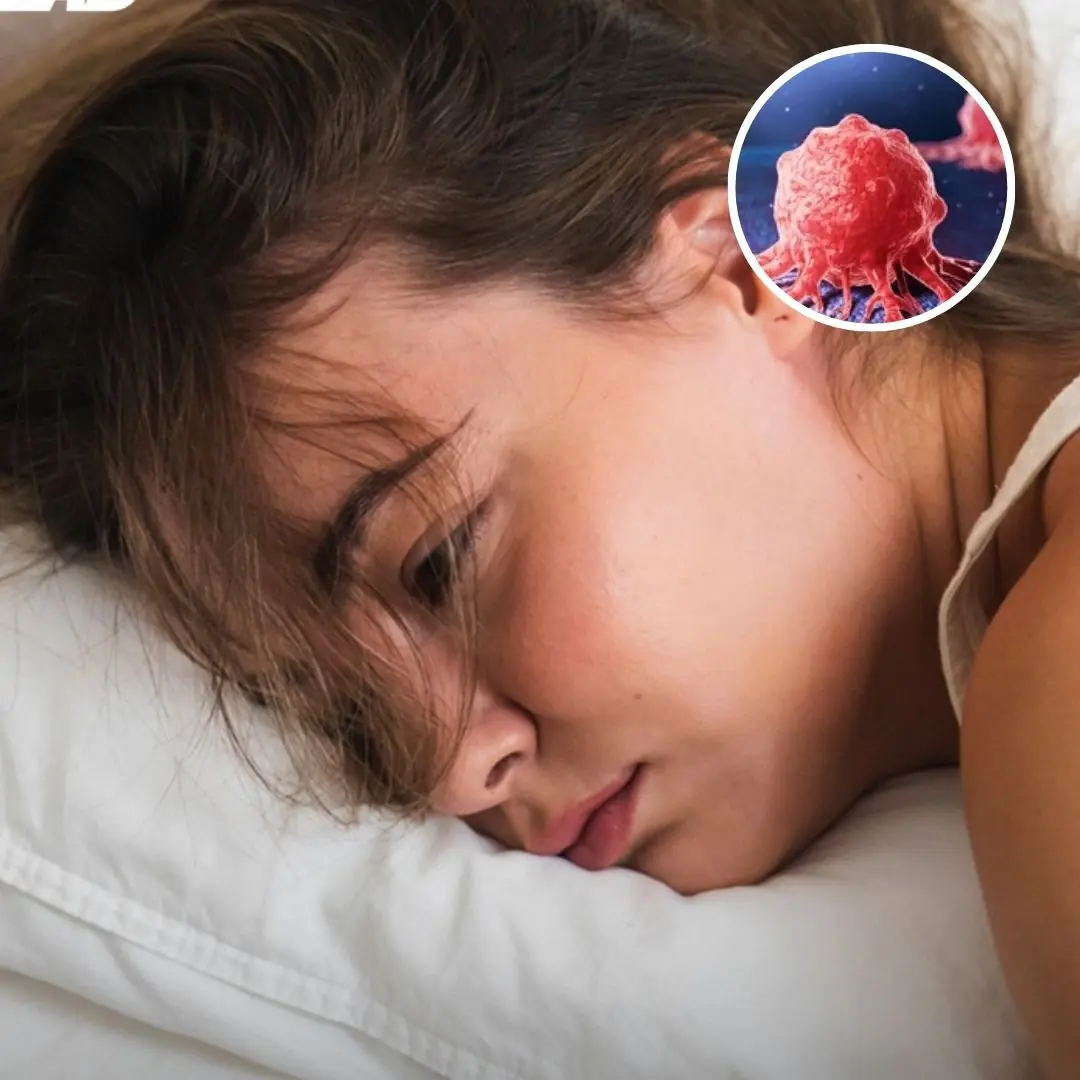
Experts issue warning for cancer symptom that can appear on pillows in the morning

Hand-related warning signs associated with advanced liver dis.ease
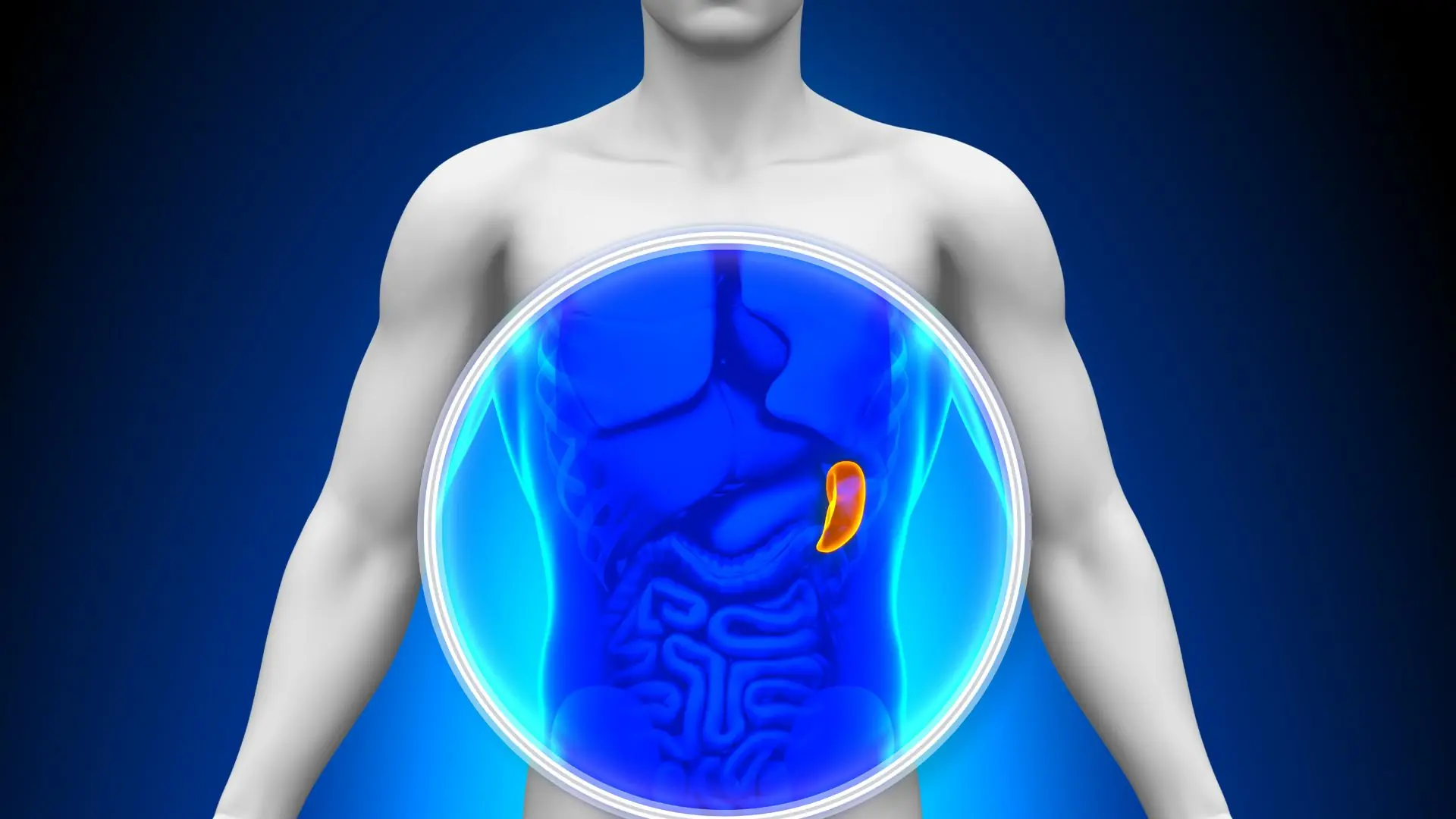
Spleen Cancer: A Rare But Dangerous Disease - You Need To Know!








Doctors warn: 3 types of cough that may signal lung cancer

This precious vegetable can ease joint and bone pa:in — yet most people pull it out without knowing its value

Doctors warn of little-known cancer symptom you can see on your toenails

Doctors warn: The body may signal a str.oke 15 minutes before it happens - act fast

Woman who died and came back to life after stroke reveals exactly what she saw

4 finger changes that may indicate lung can.cer

Experts issue warning for cancer symptom that can appear on pillows in the morning

Hand-related warning signs associated with advanced liver dis.ease

The hidden reason you should stop charging your phone to 100%

Spleen Cancer: A Rare But Dangerous Disease - You Need To Know!











