Effective Ways to Reduce the Risk of Cerebral Ischemia and Protect Brain Health
Effective Ways to Reduce the Risk of Cerebral Ischemia and Protect Brain Health
Cerebral ischemia occurs when the brain does not receive enough blo.od supply, depriving brain cells of oxygen and essential nutrients. If left unaddressed, this condition can increase the risk of a stroke in the future.
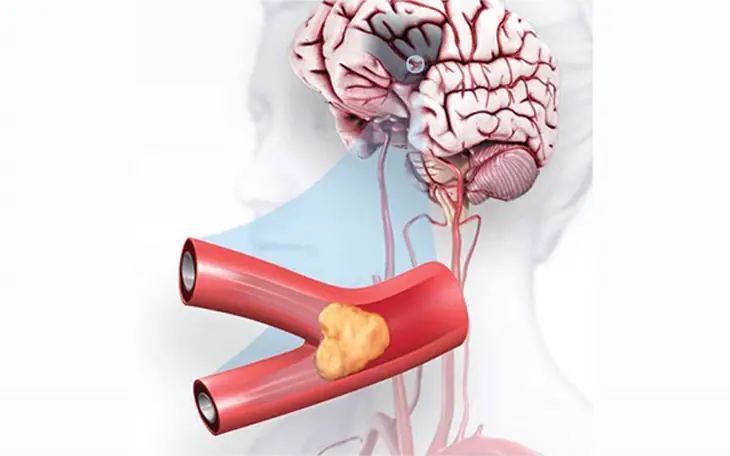
What Is Cerebral Ischemia?
Cerebral ischemia refers to reduced blood flow to the brain, which can impair its function. Each region of the brain is supplied by specific blood vessels. If these vessels become narrowed or blocked, the affected brain area may struggle to function properly. Since different parts of the brain control various body functions—such as movement, speech, and sensory perception—a lack of blood flow can cause symptoms like:
- Weakness or paralysis in the limbs
- Slurred speech or loss of speech
- Numbness on one side of the body
- Dizziness, blurred vision, or sudden loss of balance
Causes and Symptoms of Cerebral Ischemia
Cerebral ischemia often develops gradually with mild, hard-to-detect symptoms, which worsen over time. Common signs include:
- Headaches, dizziness, and nausea
- Sleep disturbances and chronic fatigue
- Memory decline and trouble concentrating
- Temporary weakness or numbness in the limbs
- Sudden loss of vision in one or both eyes
- Difficulty walking or maintaining balance
The condition is more common in the elderly and those with cardiovascular diseases or high blood pressure. However, the number of young people experiencing cerebral ischemia is rising.
The symptoms usually last between 1 to 10 minutes and rarely exceed an hour. If symptoms persist beyond an hour, it could indicate a stroke, which may cause permanent brain damage.
Common Causes of Cerebral Ischemia:
- Atherosclerosis: Accounts for over 80% of cerebral ischemia cases due to narrowed or blocked arteries.
- High Blood Pressure: Weakens blood vessel walls, increasing the risk of aneurysms, brain hemorrhages, and blood clots.
- Heart Disease: Reduces the heart’s ability to pump blood efficiently to the brain.
- Spinal and Cervical Issues: Can compress arteries supplying blood to the brain.
- Lifestyle Factors: Stress, sedentary habits, poor diet, excessive alcohol, and smoking can all contribute to reduced brain circulation.
How to Reduce the Risk of Cerebral Ischemia
While there is no absolute cure, proactive treatment and lifestyle adjustments can help manage and prevent the condition effectively.
1. Maintain a Healthy and Balanced Diet
Nutrition plays a vital role in brain and cardiovascular health. Key nutrients to include in your diet:
- Iron: Enhances blood production and oxygen transport.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Supports heart and brain function (found in salmon, herring, and cod).
- Nitrates: Improve blood circulation (found in spinach and lettuce).
- Polyphenols: Reduce inflammation and boost circulation (found in tea, cocoa, and nuts).
Avoid processed foods, trans fats, excessive alcohol, and artificial additives, which can negatively impact circulation.
2. Exercise Regularly
Regular physical activity improves circulation and strengthens the cardiovascular system, reducing the risk of cerebral ischemia. Aim for at least 30 minutes of exercise per day, such as:
- Walking
- Yoga
- Cycling
- Stretching exercises
- Dancing
3. Reduce Stress and Get Enough Rest
Chronic stress and lack of sleep can worsen blood flow issues. To promote brain health:
- Ensure 7-8 hours of sleep per night, ideally before 11 PM.
- Practice relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, or listening to calming music.
- Avoid overworking and take regular breaks to rest your mind and body.
4. Follow Medical Treatment as Prescribed
If prescribed medication or supplements for cerebral circulation, follow your doctor’s instructions carefully. Managing the condition requires a combination of medication, lifestyle changes, and a healthy diet.
5. Schedule Regular Health Check-Ups
Cerebral ischemia can lead to serious complications, including stroke, cognitive decline, and memory loss. Regular medical check-ups can help detect and manage risk factors early.
By making proactive lifestyle changes and monitoring your health, you can reduce the risk of cerebral ischemia and protect your brain from long-term damage.
News in the same category


After many years, doctors realized that cancer patients always have 6 things in common in the morning

3 Types of Food Are the 'Kings of Liver Damage' That Not Everyone Knows About

Is Washing Your Hair in the Morning or Evening Worse for Your Health? Many People Are Still 'Unwittingly Shortening Their Lifespan' Without Realizing It

Can Eating Steamed Sweet Potatoes Every Day Affect Your Liver?
Can.cer Cells Eliminated with a Juice in 42 Days

These 5 Common Habits Are Actually Very Harmful to Your Brain
5 things not to do to protect the health of the nervous system

What should you avoid eating with durian? 8 dishes you should not eat with durian

List of 5 "golden foods" that effectively prevent Alzheimer's disease

The habit of picking your nose may seem harmless, but research shows it can increase your risk of Alzheimer's disease

5 Common Alzheimer's Symptoms You Can't Ignore

Drooling in Your Sleep?
Age 46-55 is 'high risk period in life': 10 signs in people prone to stroke, 'early de.a.th'

Goosegrass: Health Benefits and Uses

6 types of fish, no matter how cheap
8 new compounds that pose a risk of causing can:cer

7 miraculous effects of Bryophyllum pinnatum that you never expected
Early examination still has a chance of treatment
A new can.cer vaccine trains the immune system to recognize and attack tumor cells.
News Post

Take this stuff, stick it in a lemon

What is the actual function of these thorns?

The photo is beautiful but there's something strange

Just turn it on, and the dirty water will drain immediately

Seven indicators that your kidneys are functioning well—check

Don't rush to throw away lemon peels after using them up

After many years, doctors realized that cancer patients always have 6 things in common in the morning

Sharpen Blender Blades with Aluminum Foil

Why did the woman look back

Don't keep these things as it will bring b.a.d luck to your family

3 Types of Food Are the 'Kings of Liver Damage' That Not Everyone Knows About

Don’t Place the Washing Machine on the Balcony

Humans Glow In The Dark, It’s Just Too Weak For Our Eyes To See

Why Aren’t Electric Kettles as Popular Abroad?

Is Washing Your Hair in the Morning or Evening Worse for Your Health? Many People Are Still 'Unwittingly Shortening Their Lifespan' Without Realizing It

Young man 'goes viral' for marrying his landlord, 20 years his senior

Don’t wash a moldy wooden cutting board with soap

Does anyone remember?

Can Eating Steamed Sweet Potatoes Every Day Affect Your Liver?
