Esophagus "cut off" because of bad habits! Many people like to do this
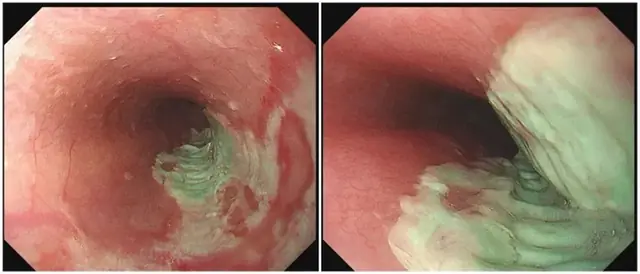
In daily life, many people simply take medicine with a sip of water. However, don’t underestimate the issue of taking medication. If the method of taking medicine is incorrect, a good medicine for treating a disease can turn into a "deadly poison."
Not long ago, Mr. Trương, 35 years old, from Ningbo (China), had a sore throat and self-medicated by taking doxycycline capsules that are designed to dissolve in the intestines. When taking the medicine, he only drank a small sip of water and hastily lay down to sleep.
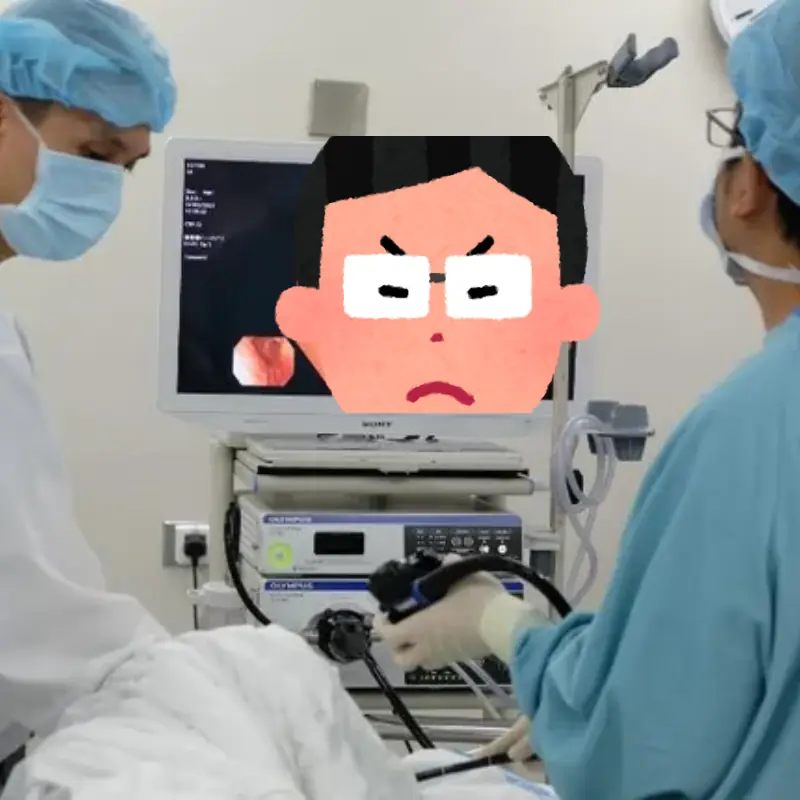
The next morning, Mr. Trương experienced chest pain, difficulty swallowing, and other symptoms. After being treated in the emergency room, the doctor performed an endoscopy and discovered that the mucous membrane of his esophagus was ulcerated. Upon analysis, it was determined that this was "medication-induced esophagitis" caused by the medication remaining in the esophagus for too long.
It turns out that when taking medication, if we do not drink enough water, the medication can stick to the esophageal wall. Taking doxycycline as an example, this antibiotic itself causes irritation, and if left in the esophagus too long, it starts to erode the mucous membrane. Lying flat slows the passage of the medication through the esophagus, causing repeated damage to the mucous membrane and ultimately leading to ulcers.
In addition to the doxycycline that Mr. Trương used, antibiotics (such as tetracycline) and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (aspirin, ibuprofen) can also cause damage to the esophagus and ulcers. Therefore, you must strictly follow the doctor's instructions when using these medications.
Bad habits when taking medication
Taking medicine when you're sick is a "normal activity," but are you really "taking" your medicine correctly? Are you making these common mistakes?
-
Not drinking enough water: Taking medicine with only a sip of water can leave the medication still stuck in the esophagus.
-
Swallowing dry pills: Not using water to swallow the medicine causes the pills to stick directly to the mucous membrane of the esophagus.
-
Incorrect posture: Lying down or bending over immediately after taking medicine slows the time it takes for the medicine to travel through the esophagus.
-
Swallowing multiple types of medication at once: This causes the medication to accumulate in the esophagus, prolonging exposure time.
-
Taking medicine with beverages: Fruit juices, milk, tea, coffee... can alter the properties of the medicine or worsen irritation.
-
Grapefruit juice, orange juice, and pomegranate juice contain components that can inhibit the metabolism of some medications by certain enzymes in the intestines and liver, leading to excessive absorption of these medications and increased concentrations, causing toxicity or amplifying side effects.
-
Calcium in milk reacts with levofloxacin to form compounds that the body cannot absorb, affecting the absorption rate and efficacy of the medication.
-
Tea and coffee contain significant amounts of theophylline and caffeine. If consumed with certain antidepressants, antibiotics, or slow-release theophylline tablets, they can severely stimulate the central nervous system.
-
Exercising immediately after taking medication: Shaking the body may cause the medication to get stuck in the folds of the esophagus.
-
Not paying attention to the timing of taking the medication: Taking medication on an empty stomach or after meals in ways not prescribed by the doctor will affect the medication's dissolution rate.
News in the same category


Teeth Grinding in Your Sleep? Here's How to Fix It from Home

No matter how much you like these 3 spices, eat less of them: 1 type is harmful to the kidneys and bones, 1 type is harmful to the liver and causes can:cer, 1 type causes fatty liver.

25-year-old girl's face is paralyzed after 3 days of maintaining a nighttime habit of many people
If you wake up in the morning and feel these 4 things, then SORRY! Kidney disease is growing in your body every day
Drinking orange juice every day to 'increase resistance', woman unexpectedly suffers serious consequences
Doctor reveals the "seed" that causes can:cer, advises doing 1 thing to eliminate 90% of the risk

4 skin changes that warn of liver disease
3 Intimate Habits of Husbands That May Increase Wives’ Risk of Cervical Can.cer

6 things that will happen if you don't quit biting your nails immediately

Here are five kidney-friendly breakfasts.
7 Early Warning Signs of Lu.ng Can.cer: Get Checked Before It Spreads
Shocking Mirror Moment: 3 Tongue Signs Reveal You're Aging Hour by Hour Without Realizing It!

Why do many flight attendants always carry a banana with them? Today I learn the secret behind it

Doctor warns: This critical sign could mean your h3adache is an aneurysm
How to lower uric acid: Top diet choices and foods to prevent gout

Major medical breakthrough: Korean researchers discover “Undo” mechanism to transform tumor cells back to normal
If you often notice ringing in your ears, this might be a sign that you will suffer from ...

Drink water on an empty stomach right after waking up for 1 month
News Post

8 Early Signs of Kid.ney Failure You Shouldn’t Ignore

The Seeds of Cancer Start from a Common Kitchen Item: The More You Misuse It, the Shorter Your Lifespan Becomes
How to relieve bee sting pain at home
Early Warning Signs of a Rising Cancer — Especially Common Among Young People

Here's What Happens to Your Body if You Eat Sweet Potatoes Every Day, According to Registered Dietitians

Teeth Grinding in Your Sleep? Here's How to Fix It from Home

Turning on the air conditioner all day or turning it on and off again? Don't make these 4 costly, unhealthy mistakes anymore!
Mild kidney failure symptoms you need to know

No matter how much you like these 3 spices, eat less of them: 1 type is harmful to the kidneys and bones, 1 type is harmful to the liver and causes can:cer, 1 type causes fatty liver.

25-year-old girl's face is paralyzed after 3 days of maintaining a nighttime habit of many people

4 things in the kitchen are "the king of liver rot", every house has them but no one knows

The best part of the pig: No one paid attention before, now you have to go to the market early to buy it!

If you wake up in the morning and feel these 4 things, then SORRY! Kidney disease is growing in your body every day

Drinking orange juice every day to 'increase resistance', woman unexpectedly suffers serious consequences

Doctor reveals the "seed" that causes can:cer, advises doing 1 thing to eliminate 90% of the risk

4 skin changes that warn of liver disease
Young Woman Diagnosed with Stomach Cancer: Doctor Warns Against 3 Common Fridge Items

3 Intimate Habits of Husbands That May Increase Wives’ Risk of Cervical Can.cer