What You'll Need
Equipment / Tools
- Watering can
- Garden trowel
Materials
- Strawberry crowns or seedlings
- Planting container
- Potting mix
- Liquid fertilizer
Instructions
Prepare the Plants
You can start strawberries from either bare-root crowns (the spot where the stem meets the roots) or transplants. Transplants will look lush and pretty in containers, but you'll need to wait for dormant bare-root crowns to establish and produce leaves.
- Plant only three strawberry plants per square foot of soil (12-inch by 12-inch pot). Strawberry plants dislike crowded conditions.
- Measure the surface area of the container to determine the space it will have (as long as the container doesn't taper sharply.) Strawberry plant roots are relatively shallow.

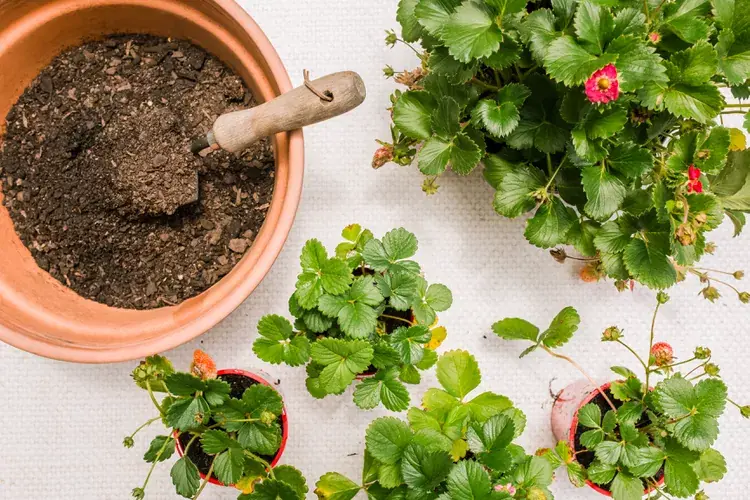
Add Soil
Fill the container with soil. The best soil for strawberries in pots is a loose, loamy potting mix that will hold moisture but quickly drain any excess water. Use a container with a drainage hole in the bottom.
Plant the Strawberries
- Plant the strawberry plants so their crowns are just above the soil surface.
- Make a small mound in the potting mix, and spread out the roots over the mound.
- Cover the roots up to the crown with the potting mix.
- Water the soil well. After the soil settles from the watering, add more potting mix as needed, but do not cover the crown with soil.
Place the Container
- Set the pot in a location that receives at least eight to 12 hours of sun daily to ensure plenty of flowers and fruits.
- If the sunlight comes from only one direction, rotate the container every three to four days for the plants to grow evenly.
- Protect the plants with netting or fencing. Insects, birds, and rodents will still be attracted to the plants.

Water the Plants
- Water your strawberries whenever the soil feels dry, about 1 inch below the surface, usually about twice per week.
- Soil in containers dries out faster than ground soil. During long periods of hot, dry weather, you might need to give water twice daily.
- Keep the soil slightly damp—not dry or soggy—to provide the best environment for fruits to form. Plants should not be sitting in water or soggy soil.
Feed Your Strawberries
Most container plants benefit from supplemental feeding.
- Feed your strawberries with a balanced liquid fertilizer every three to four weeks.
- Apply a balanced fertilizer in the fall, as the plants will begin forming buds in the crown that will become next year's flowers and fruit.
Provide Winter Protection
Strawberries produce best if they are allowed to go dormant in winter.
- Roots might freeze in colder areas, and some containers will crack if left out in freezing temperatures. To protect your plant, move your containers into an unheated garage or under a deck for winter protection.
- In zones 5 through 8, you also might be able to layer with mulch, surround the container, and leave it outdoors in winter.
- Water only when the soil becomes excessively dry.
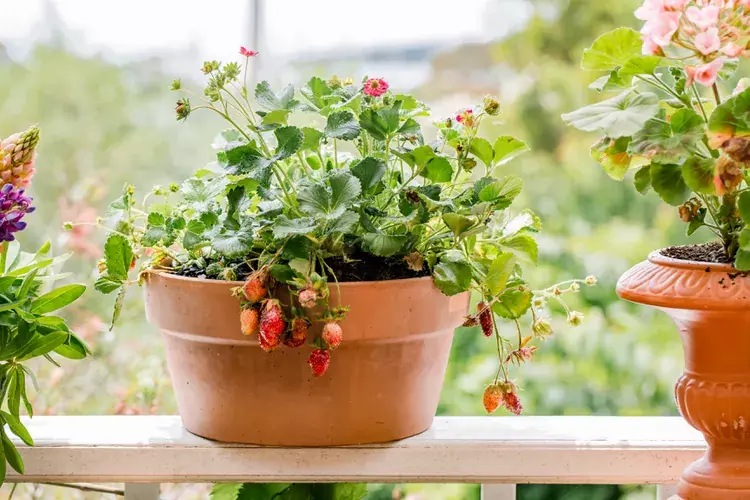

Reasons to Grow Strawberries in Containers
Strawberries are a great choice as container plants for a few primary reasons:
- Space: Strawberries are a compact plant; even gardeners with limited space typically can manage a few pots.
- Beauty: Some varieties of strawberries produce flowers that look like miniature wild roses, making them both aesthetically pleasing and delicious.
- Convenience: Place pots of strawberries close to your kitchen or outdoor seating area for easy picking.
- Pest, disease, and chemical control: Growing strawberry plants off the ground can help reduce pest problems and bacterial and fungal diseases. It's also easier to prevent unwanted lawn and garden chemicals, such as pesticides and herbicides, from reaching your plants.
Types of Containers for Growing Strawberries
Considerations when choosing a container for growing strawberries:
- Drainage: Whether it is a specialized strawberry pot, a hanging basket, or a planter, the best container for growing strawberries is one with good drainage. Use a container with several drainage holes at the bottom or multiple holes throughout the container.
- Size: Strawberries have a relatively small root ball, so they don't need a deep planter. They can be grown in containers as small as 10 to 12 inches in diameter and 8 inches deep. However, the smaller the container, the more frequently you must water it. If you want to grow June-bearing strawberries, it's best to plant them in a wood-framed raised bed rather than a pot.
- Material and color: Synthetic and light-colored pots will keep the roots cooler than dark colors and natural materials that conduct heat, such as clay and metal. Strawberry plants dislike extremely hot temperatures, so opt for light-colored containers if you live in a hot climate.1
When to Replace Strawberries in Pots
Even with the best care, strawberries are short-lived perennials. Your plants likely need to be replaced roughly every three years when their output diminishes and they begin to die. However, you can snip the runners and space them out in the pot to create new strawberry plants for free.
-
Can I grow strawberries in pots indoors?
Yes, you can grow strawberries in pots indoors in well-draining containers and potting mix. Plant them indoors any time during the year, give them plenty of sun, and supplement them with growing lighting (12 to 16 hours of artificial lighting). The only significant difference is that you may have to pollinate the plants by hand.
-
Do strawberries come back every year in a planter?
Since strawberries are perennial plants, they can come back every year in a planter. Double-check your zone to see which variety is ideal for withstanding the winter conditions if you live in a colder area.
-
Do strawberries grow better in pots or in the ground?
There are pros and cons when it comes to growing strawberries in pots or in the ground. Strawberry plants may last longer if planted in the ground. However, you can better control weeds and the quality of soil and drainage when you plant them in pots.
-
Do strawberries like full sun or shade?
Strawberries need plenty of sun to thrive so choose an area where your strawberry plant will receive six to eight hours of sunlight.
-
Do strawberries in pots require water daily?
Strawberries growing in pots may require water once or twice daily, depending on the soil and climate. Check the soil moisture level every day—at the start and end of the day.