
How your feet can reveal early signs of dia.betes
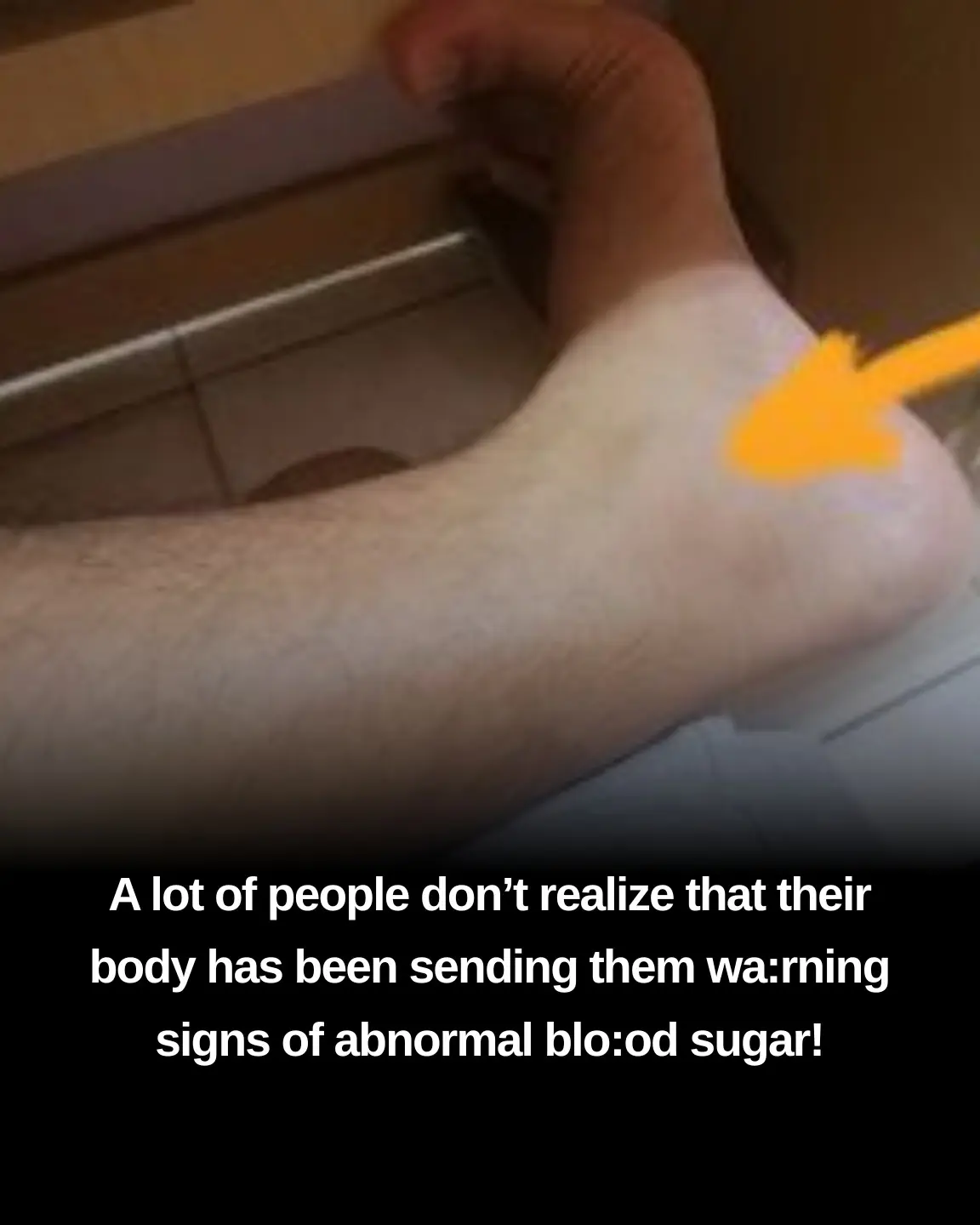
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. If left unmanaged, diabetes can lead to severe complications such as heart disease, kidney failure, and nerve damage. One area of the body that may reveal early signs of diabetes is the feet. The connection between foot health and diabetes is more significant than most people realize. In fact, issues with the feet can often be an early warning sign that someone is at risk of developing diabetes or that their diabetes is not well-controlled.
In this article, we will explore how diabetes affects the feet, the early warning signs to look out for, and how proper foot care can help prevent complications associated with diabetes.
How Diabetes Affects the Feet
1. Poor Blood Circulation
One of the primary ways that diabetes affects the feet is by reducing blood circulation. High blood sugar levels can damage blo.od vessels over time, especially the small blood vessels in the extremities (like the feet and hands). This reduced blood flow means that oxygen and nutrients have a harder time reaching the cells in the feet, which can lead to slow healing, increased infection risk, and nerve damage.
2. Nerve Damage (Neuropathy)
Another common complication of diabetes is nerve damage, also known as diabetic neuropathy. Elevated blood sugar levels can damage the nerves, particularly in the feet and legs. This condition leads to a loss of sensation, making it harder to feel pain, cuts, or blisters on your feet. As a result, small injuries can go unnoticed and develop into serious infections or ulcers.
3. Increased Risk of Infections
Because diabetes can weaken the immune system and reduce blood flow to the feet, infections are more likely to occur and may be more difficult to treat. Even a small injury, like a blister or an ingrown toenail, can quickly become infected and lead to more severe complications if not addressed promptly.
Early Signs of Diabetes in Your Feet
1. Frequent Foot Infections
If you notice that cuts, blisters, or sores on your feet are taking longer than usual to heal, this could be a sign of diabetes. High blood sugar levels can impair the immune system and delay the body's natural healing process. You may also notice recurrent foot infections that do not improve with typical treatments.
2. Numbness or Tingling Sensation
A tingling or burning sensation in the feet, known as paresthesia, is one of the most common symptoms of diabetic neuropathy. If you experience numbness or tingling in your feet or toes, it could indicate that the nerves in your feet are being damaged due to prolonged high blood sugar levels. In severe cases, this can lead to complete loss of sensation, making it harder to detect injuries or infections.
3. Foot Ulcers or Sores
Foot ulcers or sores that won’t heal are another significant warning sign of diabetic complications. These wounds are often caused by poor circulation and nerve damage. Even minor cuts can turn into ulcers because the reduced blood flow and nerve damage prevent proper healing and make it difficult to detect injuries until they become serious.
4. Dry or Cracked Skin
People with diabetes often experience dry, cracked skin on their feet. This is because high blood sugar levels can reduce moisture in the skin and impair the skin’s ability to repair itself. Dry skin is more prone to cracking, which can lead to painful fissures and open wounds, increasing the risk of infection.
5. Calluses or Corns
If you notice thickened areas of skin (calluses) or painful corns on your feet, it may be due to abnormal pressure caused by nerve damage. Neuropathy can affect the way you walk or stand, which may put additional pressure on certain areas of your feet, leading to the development of calluses or corns. If not treated properly, these can develop into ulcers.
6. Color Changes or Swelling
Diabetes can affect blood flow to the feet, leading to visible changes in color or swelling. If you notice that your feet appear red, purple, or pale, it could be a sign that blood is not circulating properly. Swelling in the feet and ankles can also occur due to poor circulation or kidney problems, which are often related to diabetes.
Foot Care Tips for People with Diabetes
Taking care of your feet is crucial for preventing complications related to diabetes. Here are some essential foot care tips:
1. Inspect Your Feet Daily
Check your feet every day for any signs of injury, cuts, blisters, redness, swelling, or infection. Since nerve damage may prevent you from feeling pain, daily inspections will help you catch any problems early before they worsen.
2. Keep Your Feet Clean and Dry
Wash your feet daily with lukewarm water and mild soap, but avoid soaking them as this can lead to dryness. Dry your feet thoroughly, especially between the toes, to prevent fungal infections.
3. Moisturize Your Feet
Use a good quality, fragrance-free moisturizer to keep your feet soft and prevent dry, cracked skin. Avoid putting lotion between your toes, as moisture in this area can promote fungal growth.
4. Wear Proper Footwear
Always wear comfortable, well-fitting shoes that provide adequate support. Avoid shoes that are too tight, too loose, or have high heels, as they can cause blisters, calluses, and sores. You may also want to consider diabetic socks that help with circulation and reduce friction.
5. Avoid Walking Barefoot
Walking barefoot increases the risk of stepping on sharp objects that could injure your feet. Always wear shoes, even when indoors, to protect your feet from injury.
6. Trim Your Nails Properly
Cut your toenails straight across to avoid ingrown nails. Be careful not to cut them too short, and use a nail clipper rather than scissors. If you have trouble trimming your nails, consider visiting a podiatrist for assistance.
7. Seek Medical Attention for Any Issues
If you notice any unusual symptoms such as swelling, redness, or pain, consult your healthcare provider immediately. Early intervention is crucial for preventing infections or complications from worsening.
How to Prevent Foot Complications from Diabetes: Essential Precautions
For individuals with diabetes or those at risk, foot complications are a significant concern. Diabetes can lead to poor circulation, nerve damage, and a weakened immune system, all of which increase the risk of foot problems like infections, ulcers, and in severe cases, amputations. However, with the right precautions, foot health can be maintained, and complications can often be prevented or managed effectively.
Here are some important precautionary measures to protect your feet from the damaging effects of diabetes:
1. Inspect Your Feet Regularly
Why It’s Important:
Daily foot inspections allow you to detect early signs of damage or infection, such as cuts, blisters, redness, or swelling, before they worsen.
Prevention Tips:
-
Check your feet every day: Use a mirror or ask a family member to help if you cannot see the bottoms of your feet.
-
Look for signs of irritation: Examine for any new cuts, sores, blisters, redness, or swelling. Pay special attention to areas between your toes and the heels.
-
Don’t ignore small issues: Even minor injuries can lead to serious complications if left untreated.
2. Keep Your Feet Clean and Dry
Why It’s Important:
Proper hygiene helps prevent fungal infections, bacterial growth, and other complications that can arise from diabetes. Diabetes can cause dry skin, which can crack and lead to infections.
Prevention Tips:
-
Wash your feet daily: Use lukewarm water and mild soap to clean your feet. Avoid hot water, as it can dry out the skin.
-
Dry thoroughly: After washing, dry your feet completely, especially between the toes. Moisture trapped in these areas can promote fungal infections like athlete’s foot.
-
Avoid soaking your feet: Soaking your feet can lead to skin dryness and damage, particularly in the diabetic foot.
3. Moisturize Your Feet
Why It’s Important:
Moisturizing prevents the skin on your feet from becoming too dry, which can lead to cracks and fissures that make your feet more vulnerable to infection.
Prevention Tips:
-
Use a fragrance-free moisturizer: Apply a generous amount of lotion or cream to the tops and bottoms of your feet, avoiding the areas between your toes.
-
Use a thicker cream or ointment for especially dry areas. If the skin on your feet is excessively dry, you may need a heavier ointment like petroleum jelly.
-
Avoid using lotion between toes: Excess moisture between the toes can cause fungal infections, so keep these areas dry.
4. Wear Proper Footwear
Why It’s Important:
Wearing the wrong shoes can cause blisters, calluses, and sores, increasing the risk of foot injury and infection. Proper footwear protects your feet from friction, cuts, and other damage.
Prevention Tips:
-
Wear well-fitting shoes: Shoes that are too tight or too loose can cause blisters and sores. Always make sure your shoes provide a snug fit but are not tight or restrictive.
-
Choose breathable shoes: Opt for shoes made from materials that allow your feet to breathe, like leather or mesh.
-
Use diabetic socks: These are designed to provide extra comfort, reduce pressure points, and promote circulation. They also minimize the risk of skin irritation.
-
Avoid high heels: High heels or shoes with pointed toes can cause unnecessary pressure on your feet and lead to calluses, blisters, or misalignment of the foot.
5. Trim Your Toenails Properly
Why It’s Important:
Improper nail trimming can lead to ingrown toenails or painful cuts. It is important to cut your toenails straight across to prevent them from growing into the skin.
Prevention Tips:
-
Trim nails carefully: Cut your toenails straight across using a nail clipper and avoid cutting them too short. Avoid rounded edges as they can cause ingrown nails.
-
File rough edges: If you have any sharp or jagged edges after trimming, use a nail file to smooth them.
-
Seek help if needed: If you have difficulty trimming your nails or notice problems like thickened nails, consult a podiatrist.
6. Monitor Foot Temperature and Sensation
Why It’s Important:
Diabetic neuropathy can cause a loss of feeling in the feet, which makes it harder to detect injuries, burns, or other problems. Additionally, poor circulation can affect the temperature of the feet, making them feel cold or warm unexpectedly.
Prevention Tips:
-
Check for unusual temperatures: If your feet feel unusually hot or cold, this could be a sign of poor circulation or nerve damage. Be mindful of any changes.
-
Perform sensory checks: Gently test your feet for areas where you might have lost sensation, particularly if you experience numbness or tingling. Consult a healthcare provider if you notice any loss of feeling.
7. Manage Blo.od Sugar Levels
Why It’s Important:
Keeping blood sugar levels within the target range can prevent the nerve damage and circulation problems that lead to foot complications. High blood sugar levels can weaken the immune system, making infections more difficult to treat.
Prevention Tips:
-
Monitor your blood sugar: Check your blood glucose levels regularly and work with your healthcare provider to keep them within the target range.
-
Follow a balanced diet: Eat a diet rich in fiber, lean proteins, healthy fats, and whole grains. Limit sugary and processed foods.
-
Exercise regularly: Physical activity helps regulate blood sugar levels, improve circulation, and promote overall foot health.
8. Seek Professional Foot Care
Why It’s Important:
If you have diabetes, it’s essential to have regular check-ups with a podiatrist, especially if you experience foot problems. A professional can catch issues early, provide advice on proper foot care, and treat conditions like calluses, infections, or nail problems.
Prevention Tips:
-
Visit a podiatrist regularly: Aim for a check-up at least once a year, or more often if you have foot issues.
-
Ask for professional assistance with foot care: A podiatrist can help trim toenails, remove calluses, and offer specialized advice on foot health.
-
Follow medical advice: If you have an existing foot condition or notice any issues, seek professional help immediately to prevent complications.
9. Take Immediate Action for Injuries or Infections
Why It’s Important:
Even small cuts or injuries can become infected and lead to severe complications in people with diabetes. Early treatment is essential to prevent these injuries from escalating.
Prevention Tips:
-
Clean and treat wounds immediately: If you have a cut, scrape, or blister, wash the area gently with soap and water and apply an antibiotic ointment.
-
Seek medical attention for persistent issues: If you notice signs of infection (redness, swelling, warmth, or pus), contact a healthcare provider promptly.
Conclusion: Proactive Foot Care for Diabetes Prevention
Proper foot care is essential for everyone, but it becomes even more critical for those with diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition. Diabetes can lead to a range of foot problems, from reduced circulation and nerve damage to increased vulnerability to infections. By following the above prevention tips - such as inspecting your feet regularly, keeping them clean and moisturized, wearing proper footwear, managing your blo.od sugar levels, and seeking professional care - you can significantly reduce the risk of serious foot complications.
Taking proactive steps to care for your feet can prevent costly and painful problems down the line, ensuring that you maintain good foot health for years to come.
Your feet are a vital indicator of your overall health, and they can offer early signs of serious conditions like diabetes. High blood sugar can lead to poor circulation, nerve damage, and an increased risk of infection, making it essential to monitor your foot health. By recognizing the early warning signs of diabetes, such as numbness, slow-healing wounds, and dry skin, you can take proactive steps to prevent complications and protect your health.
If you have diabetes or are at risk, it's crucial to regularly monitor your feet, practice good foot care, and seek medical advice if you notice any changes or concerns. Early detection and proper foot care can help you avoid serious complications, allowing you to live a healthy, active life.
News in the same category


If You Love Napping During the Day, This Is for You!

4 air conditioner installation locations do more harm than good
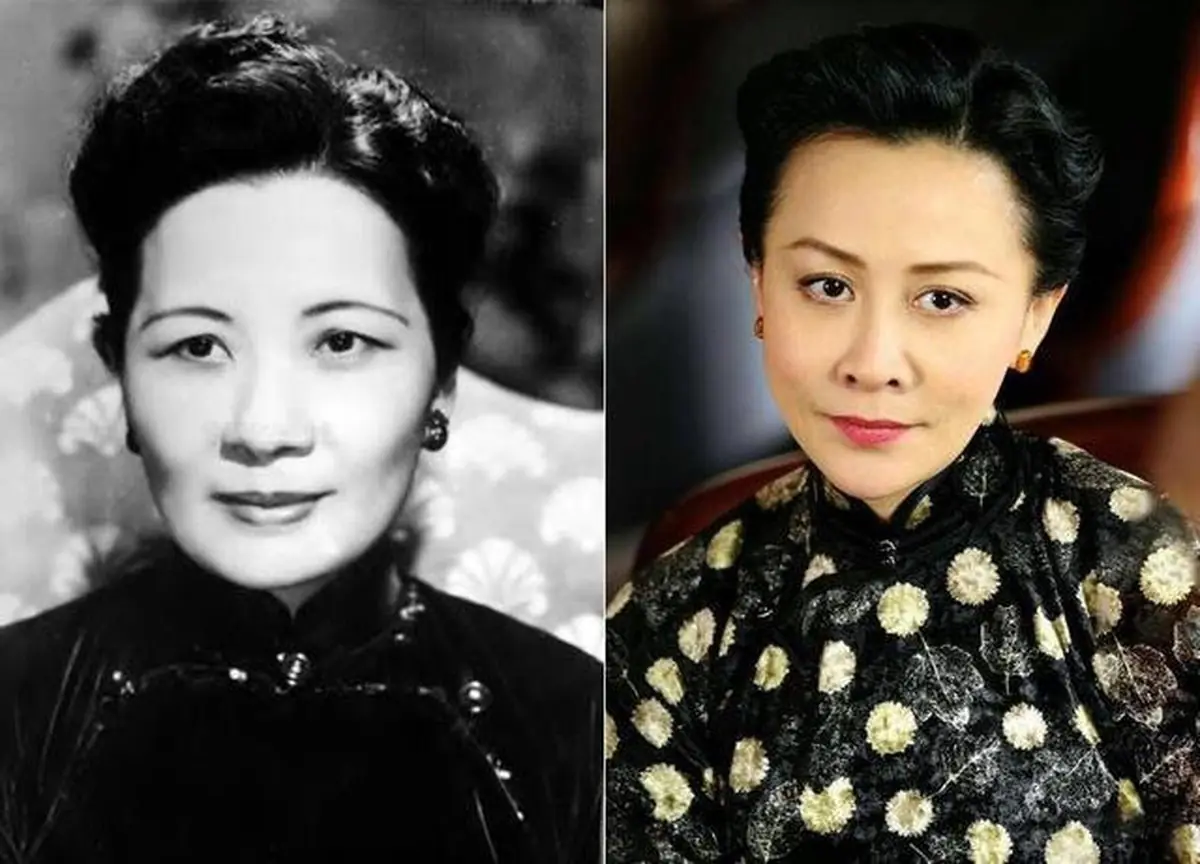
Soong Mei-ling Lived Past 100 Despite Can.cer: Her Two Favorite Drinks Are Still Popular Today
5 foods you should never keep overnight
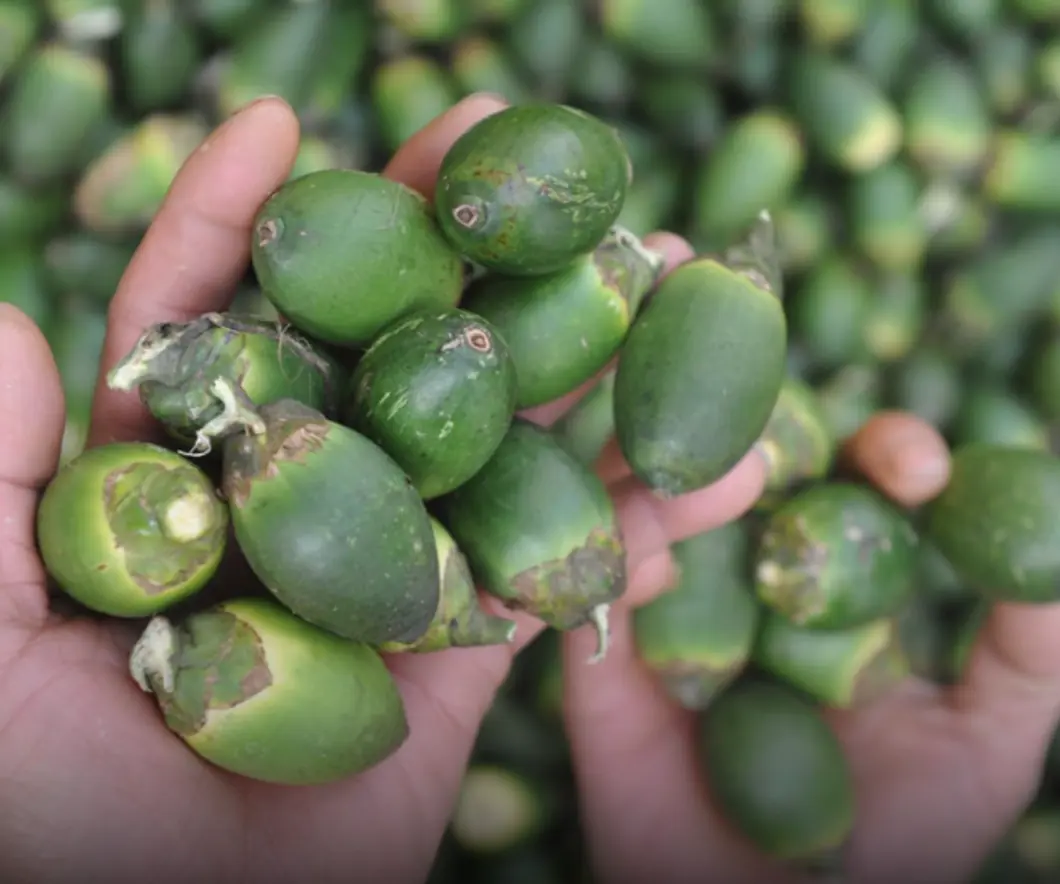

4 everyday fruits doctors warn could fuel can.cer growth
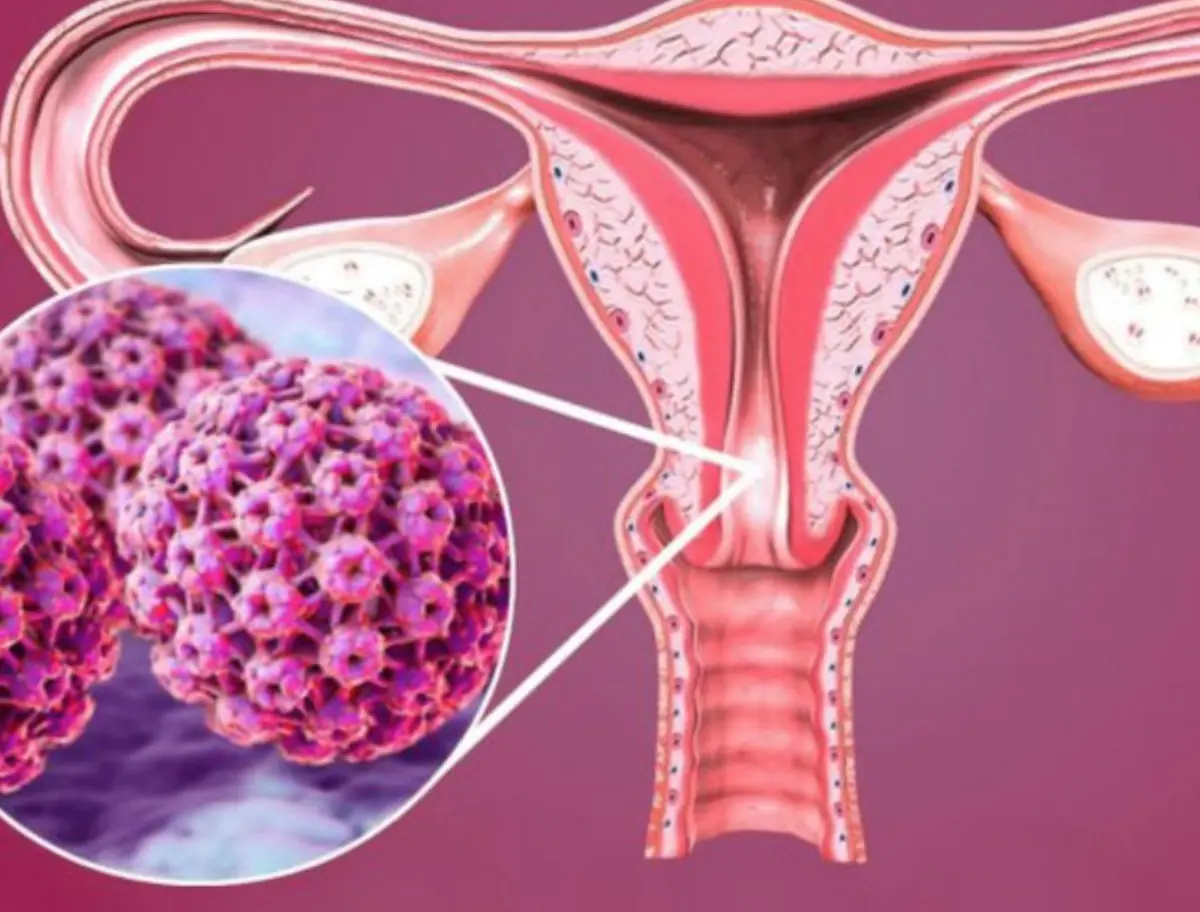
5 early warning signs of cervical can.cer
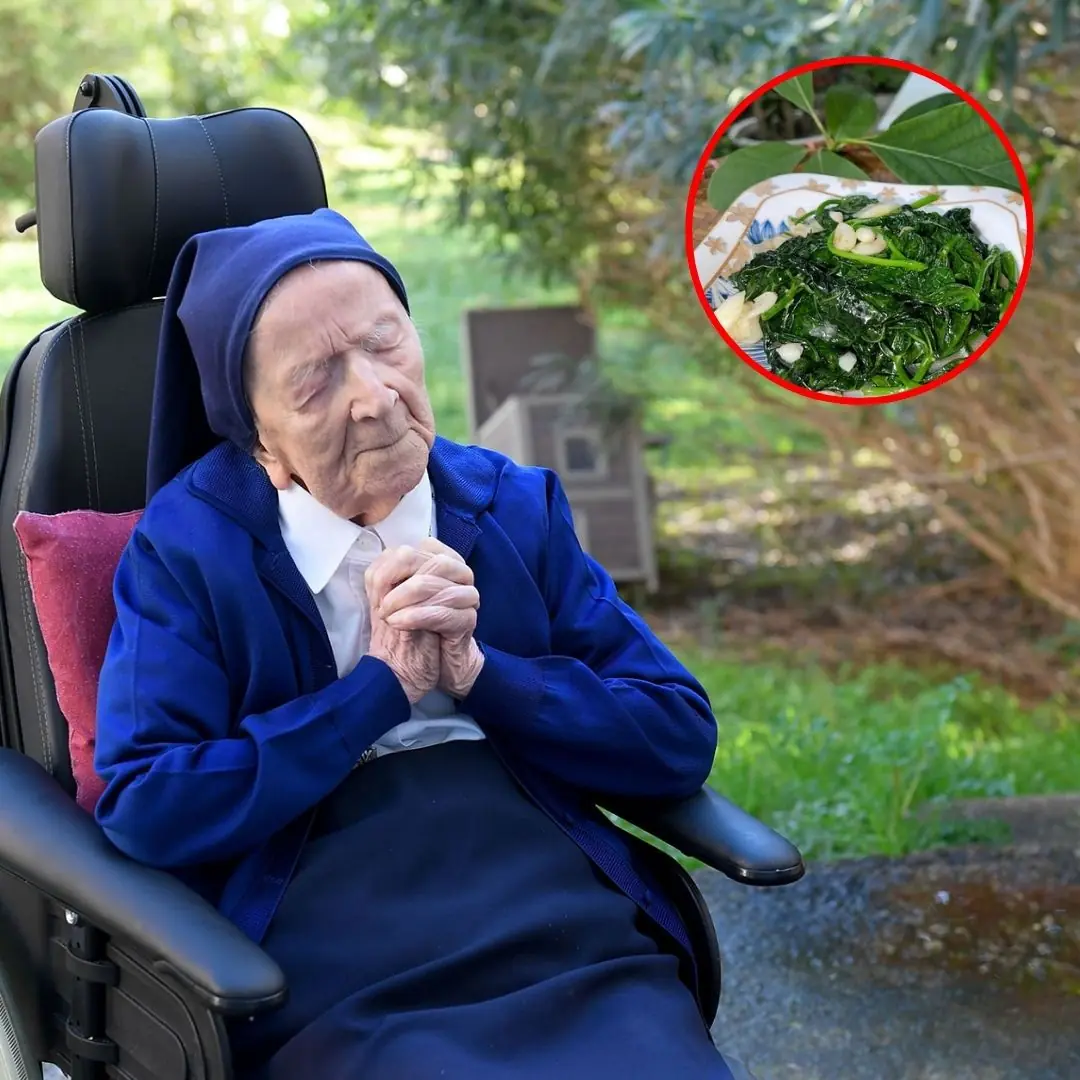

Secret to longevity: 3 eating habits that helped an old woman live to 118 years old
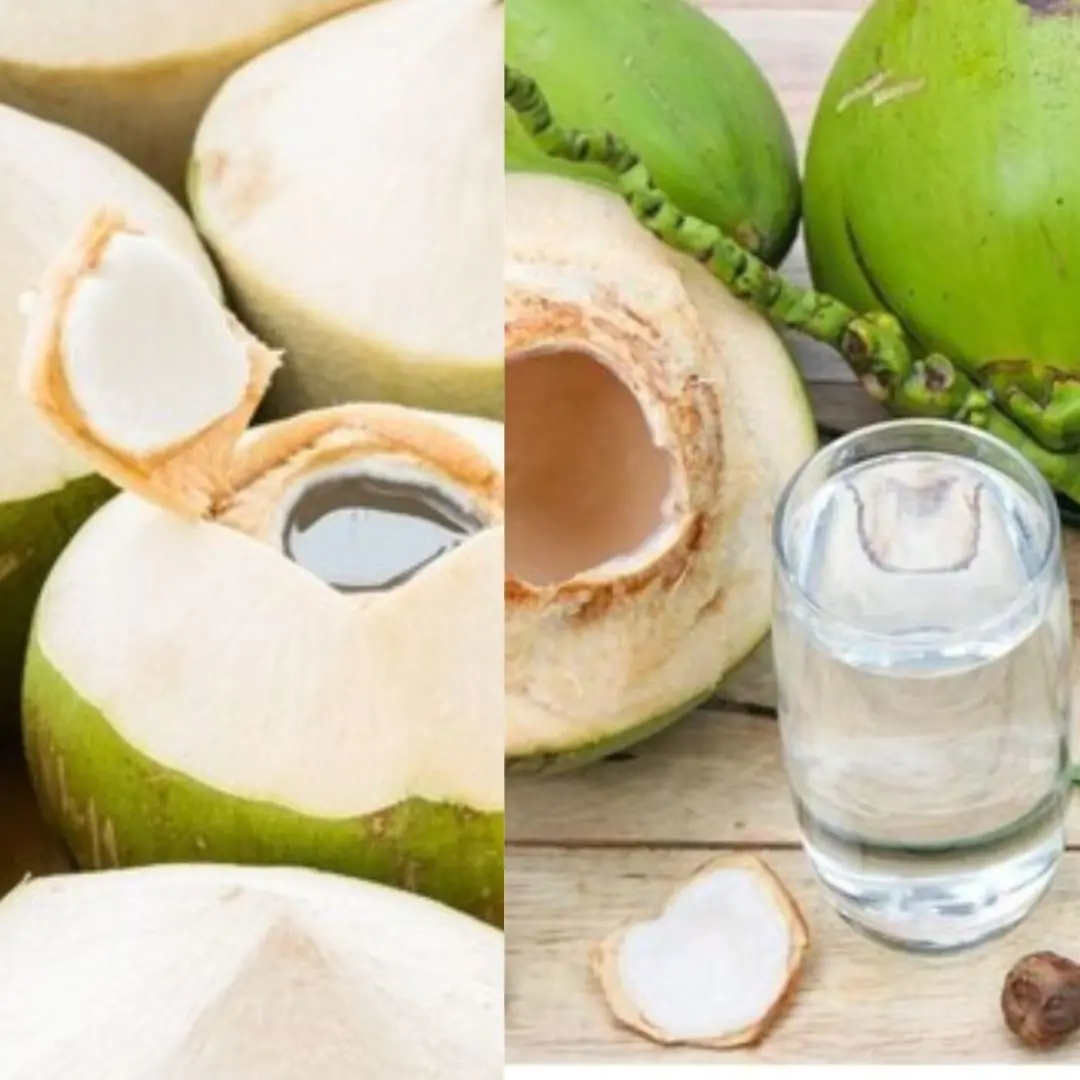

Great effects of drinking coconut water on an empty stomach for 7 days, the results will surprise you

Orange juice is nutritious but there are 5 groups of people who should not drink it

A Man Di.ed of Colon Can.cer Despite Going to Bed Early, Waking Up Early, and Walking Daily
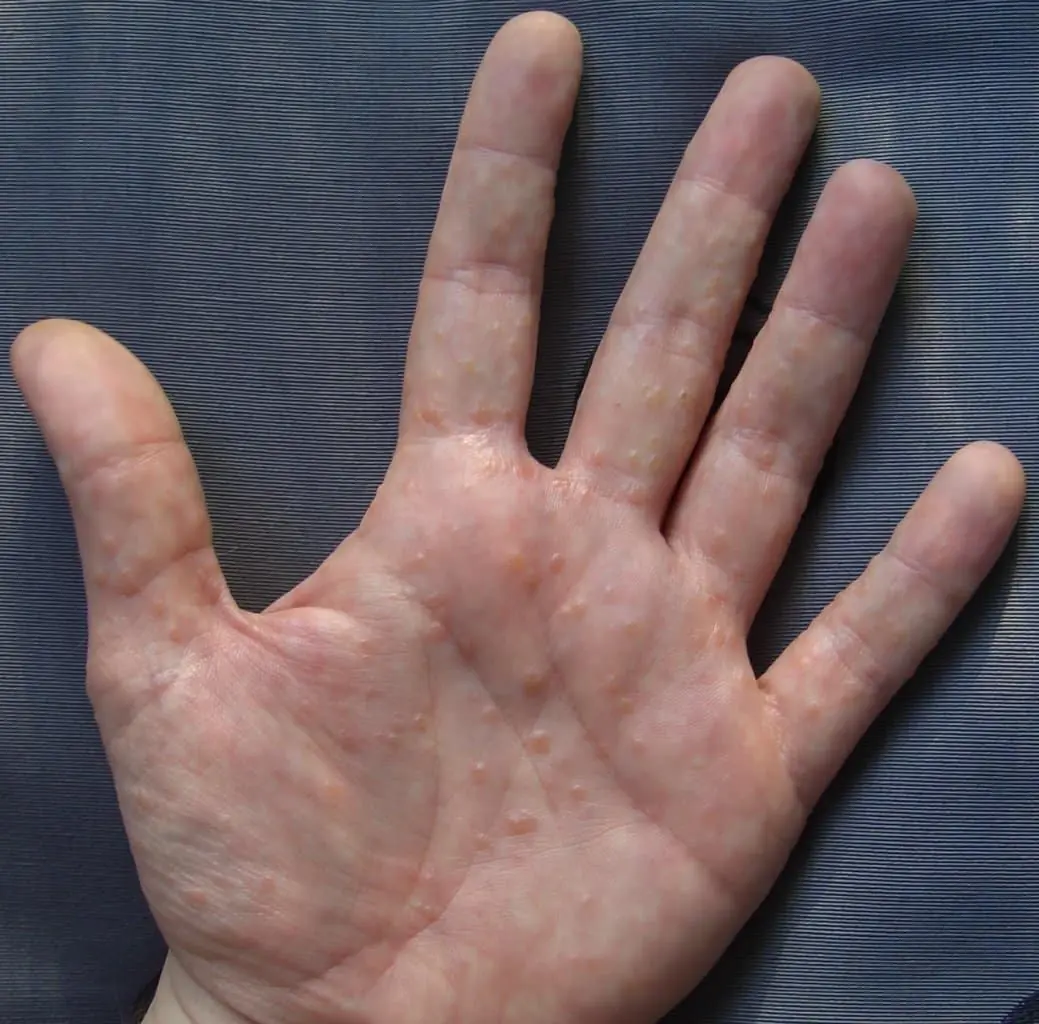
Painful Red Bumps on Skin? It Might Be Dyshidrotic Eczema

Young Woman Dies at 27 from Late-Stage Thyroid Cancer

Are You at Risk? Doctor Reveals Who’s Twice as Likely to Have a Heart Attack While Sleeping
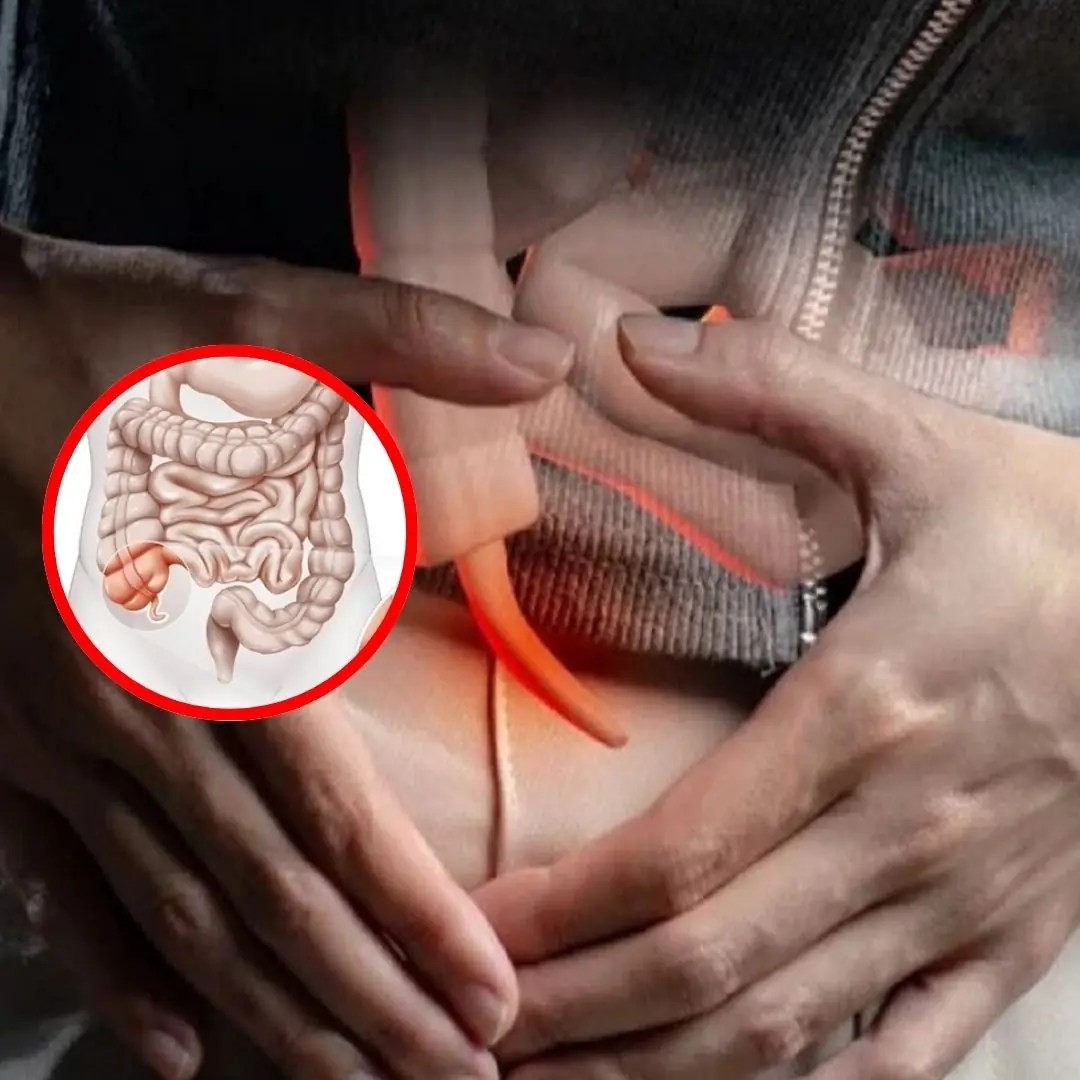
4 warning signs from the appendix, do not ignore!

You Should Never Ignore These 9 Things Your Fingernails Reveal About Your Health
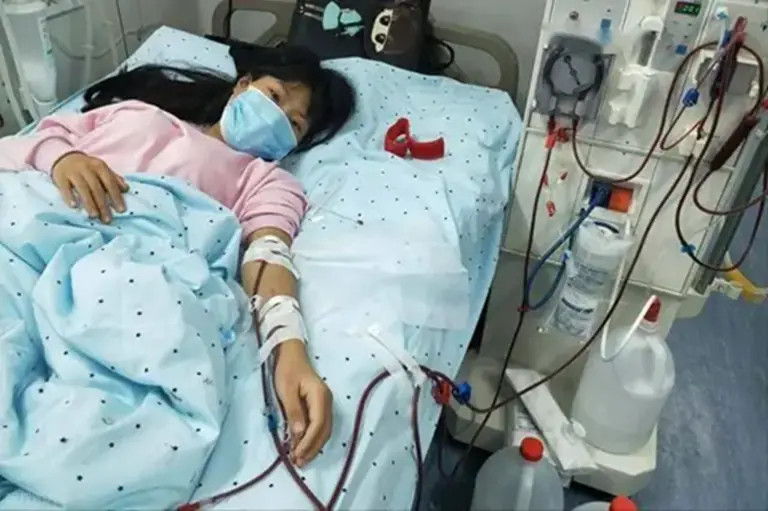
People with Kid.ney Problems Often Experience 3 Strange Symptoms During Sleep

Surprisingly, These 6 Fruits Act Like “Med.icine”
News Post

People with Blo.od Clots Often Experience 4 Unusual Symptoms While Walking

If You Love Napping During the Day, This Is for You!

Tips to Keep Rice Fresh and Free from Weevils

4 air conditioner installation locations do more harm than good

Soong Mei-ling Lived Past 100 Despite Can.cer: Her Two Favorite Drinks Are Still Popular Today

5 foods you should never keep overnight

5 types of vegetables that help detoxify and lower liver enzymes

Most of you can't find the frog hiding in the picture, what about you?

My Husband Demanded I Dance for Him Like His Brother's Wife – the Lesson He Got Left Him Pale

4 everyday fruits doctors warn could fuel can.cer growth

I Got a Free First-Class Seat – My Entitled Brother Thought He Deserved It Just for Existing & My Family Took His Side

5 early warning signs of cervical can.cer

Secret to longevity: 3 eating habits that helped an old woman live to 118 years old

Why are rocks spread along railway tracks?

Great effects of drinking coconut water on an empty stomach for 7 days, the results will surprise you

Put a plastic bottle in the toilet tank: A simple thing with great benefits, it's a waste if you don't know

Orange juice is nutritious but there are 5 groups of people who should not drink it

The Best Part of Pork
