
She Was Just Peeling a Boiled Egg… Until She Saw What Was Hidden Inside
She Was Just Peeling a Boiled Egg… Until She Saw What Was Hidden Inside
The idea of regrowing teeth may seem like science fiction, but in Japan, it’s edging closer to reality. Leading this groundbreaking effort is Dr. Katsu Takahashi, an oral surgeon based at Kitano Hospital in Osaka. His team has discovered that humans possess dormant tooth buds—a third set of teeth that typically remain undeveloped.
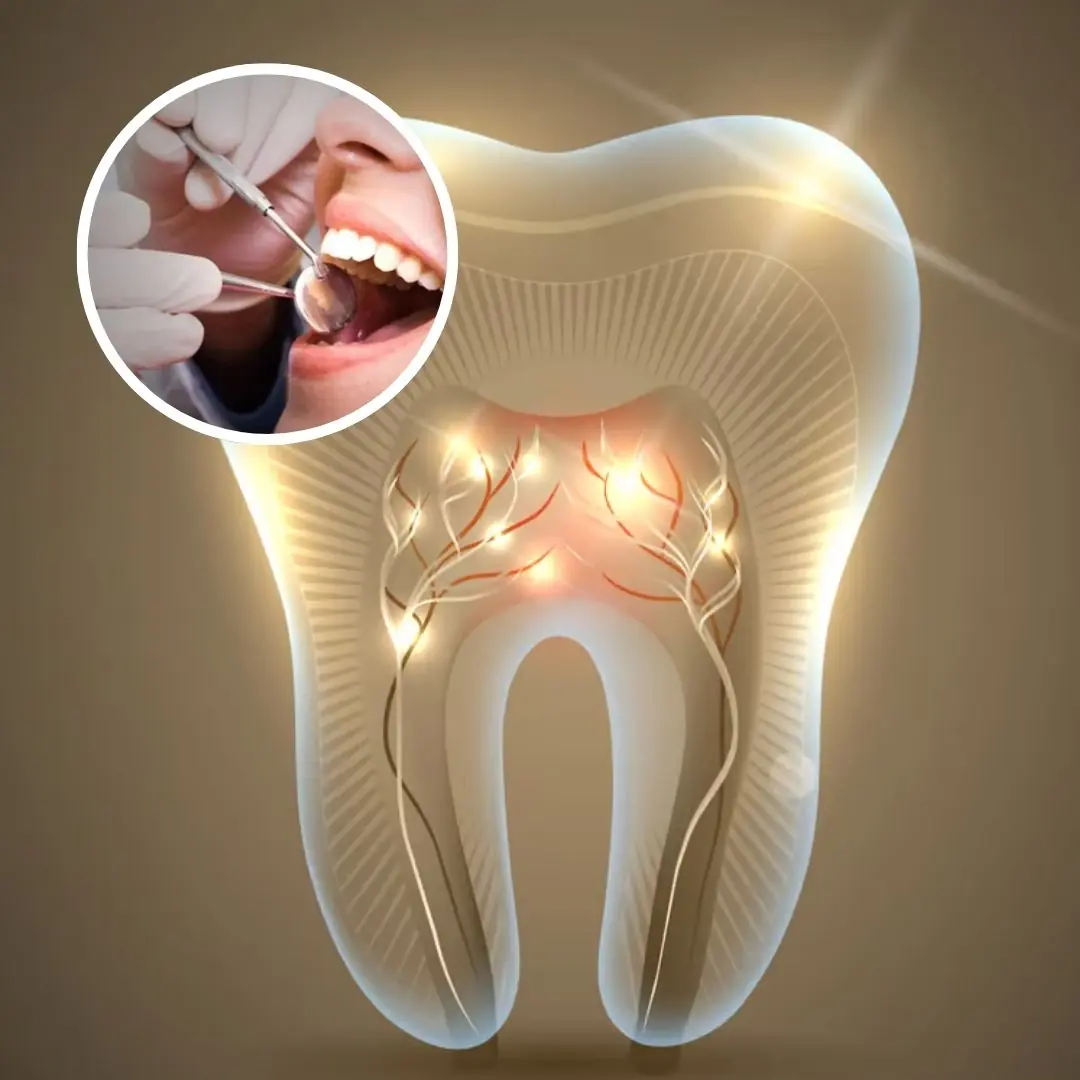
Their research pinpointed a protein, USAG-1, which inhibits these buds from forming. By creating an antibody drug to neutralize this protein, the scientists have triggered tooth regrowth, achieving success first in mice and ferrets, and now advancing to human trials.
The journey began in the 1990s at Kyoto University, with a pivotal moment in 2005 when mice deficient in USAG-1 sprouted additional teeth.
Fast forward to 2024, and clinical trials in Kyoto are underway, targeting adults who have lost molars. Looking ahead, the team plans to test the drug in 2025 on children born with missing teeth. If successful, this cutting-edge treatment could render dentures obsolete, with a projected availability by 2030 and an estimated price tag of $9,800 per procedure.
Significant hurdles remain, including ensuring the teeth grow correctly and confirming the therapy’s durability in humans. Yet, with Japan’s aging demographic in focus, this advancement holds the potential to redefine dental care entirely.
Imagine a world in which losing a tooth does not require the use of dentures or implants. Scientists in Japan have unearthed an important first in regenerative medicine: a medication that could enable humans develop a third set of teeth. This study, which focusses on a single gene responsible for tooth growth, has begun clinical testing and could be accessible for general use by 2030. If successful, this finding has the potential to improve dental treatment and provide hope to millions of people who are missing teeth.
A team of Japanese researchers, lead by Dr. Katsu Takahashi of the Medical Research Institute Kitano Hospital in Osaka, has been studying the genetic principles of tooth development. Their findings build on a 2021 study published in Scientific Reports, which found that reducing the USAG-1 gene in mice resulted in the creation of new teeth.
The USAG-1 gene produces a protein that suppresses tooth development. Researchers discovered that employing an antibody that disables this protein allowed mice to regenerate teeth. Encouraged by these findings, the team has shifted its focus to humans, assuming that comparable genetic systems exist within us.
One of the most intriguing aspects of this discovery is that humans already have the potential to grow a third set of teeth. “The idea of growing new teeth is every dentist’s dream,” Dr Takahashi told Mainichi. “We’re hoping to see a time when tooth regrowth medicine is a third choice alongside dentures and implants.”
While most people develop only two sets of teeth—baby teeth and permanent teeth—some individuals with a condition called hyperdontia naturally grow extra teeth. This suggests that the body already has the biological framework for an additional set. Scientists believe that activating these latent tooth buds using gene-targeting therapy could stimulate controlled regrowth in the general population.

The potential benefits of this breakthrough extend far beyond cosmetic dentistry. Around 1% of the global population suffers from anodontia, a genetic condition in which some or all permanent teeth fail to develop. Current treatment options, such as dental implants and dentures, are expensive and often come with complications.
A medication that allows the body to regrow its own teeth could be life-changing for those affected by tooth loss due to genetic disorders, accidents, or aging. “The number of teeth varied through the mutation of just one gene,” Dr. Takahashi explained. “If we make that the target of our research, there should be a way to change the number of teeth people have.”
The Japanese research team has already begun human clinical trials and hopes to make the drug available for general use by 2030. If successful, this treatment could mark one of the most significant advances in dental medicine.
A 2023 paper published in Regenerative Therapy highlighted the lack of existing treatments for tooth regrowth and emphasized the potential of anti-USAG-1 antibody therapy as a breakthrough. The researchers believe that continued progress could lead to a practical and widely available solution in the coming years.

She Was Just Peeling a Boiled Egg… Until She Saw What Was Hidden Inside

When Your Parent Shows These 4 Signs, Emotional Preparation Matters

Here’s What That Little Pocket in Women’s Underwear Is Actually For

Not Just Fluid Retention: 10 Reasons Your Lower Legs May Be Swollen

Regardless of How Much You Earn, Get Rid of These 4 Things Without Delay
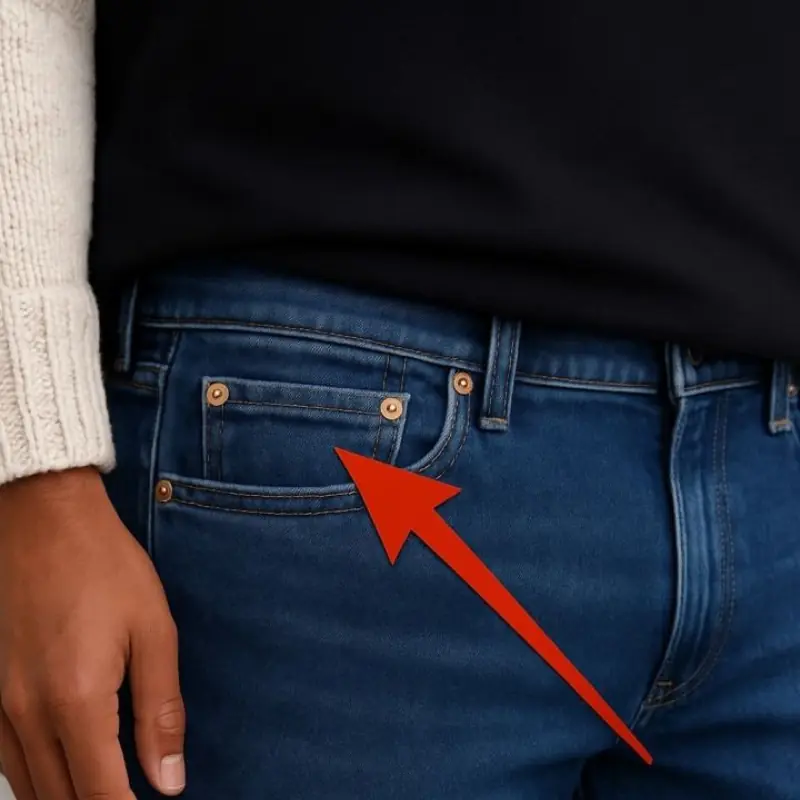

That tiny pocket on your jeans has a surprising history you probably never knew.

Keep these 3 mindsets, and success will follow

Not all garlic is safe to buy—learn which cloves you should avoid at the market today.

She Di:ed From a Stroke and Came Back: What She Saw Will Sho:ck You

The meaning of a ring worn on the right hand is not widely known

Most people THROW IT AWAY — but this tiny metal ring on sausages is actually saving your health!
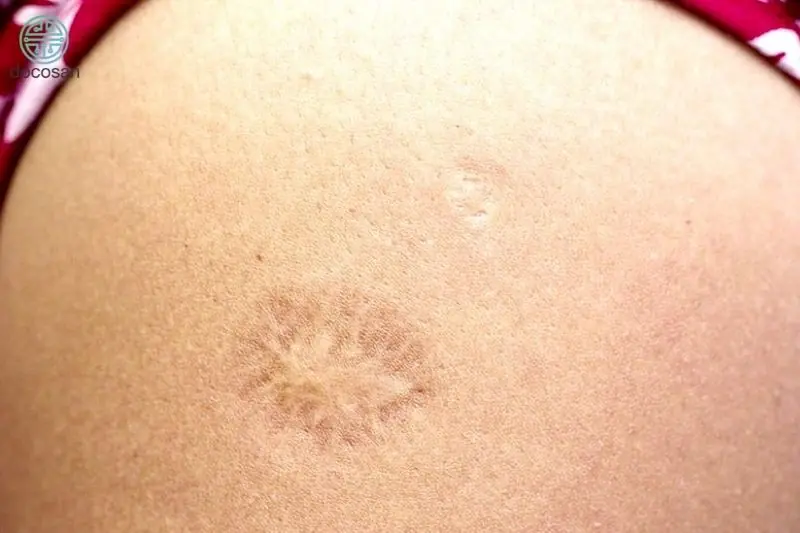
Do you know why there’s a small scar on the upper left arm and what it means?

Using an electric kettle daily? Here are 4 errors you should watch out for

If a millipede crawls indoors, don’t eliminate it immediately

If You Don’t Unplug These 5 Electrical Devices at Home, Your Electricity Bill Could Skyrocket!

Don’t rush to call a technician — just do this simple fix to keep your fridge running smoothly

Why do nail clippers include a small hole? The hidden reason revealed

Nothing drains your energy more than the battles you fight inside your own mind. Release what is beyond your control

The Truth about Sleepwalking

The surprising reasons why your cat loves sleeping in your bed

Grilled Corn Lovers: 8 Things to Keep in Mind

What Lym.phoma Survivors Say They Felt Before Being Diagnosed: 6 Key Signs
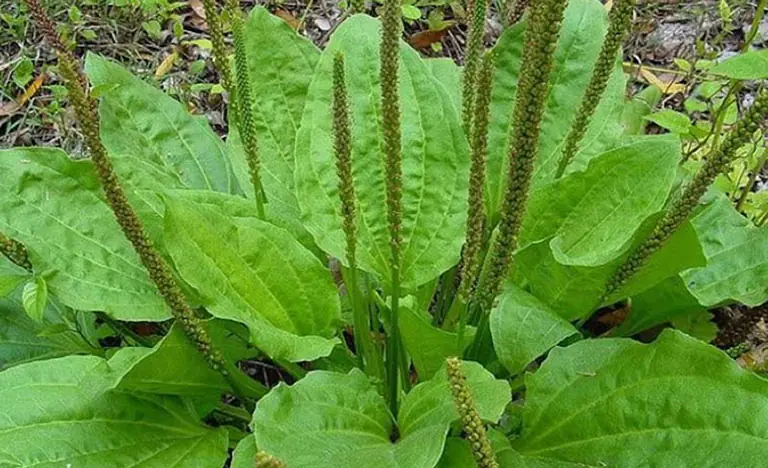

Plantago lanceolata: The Humble Plant with Extraordinary Healing Power
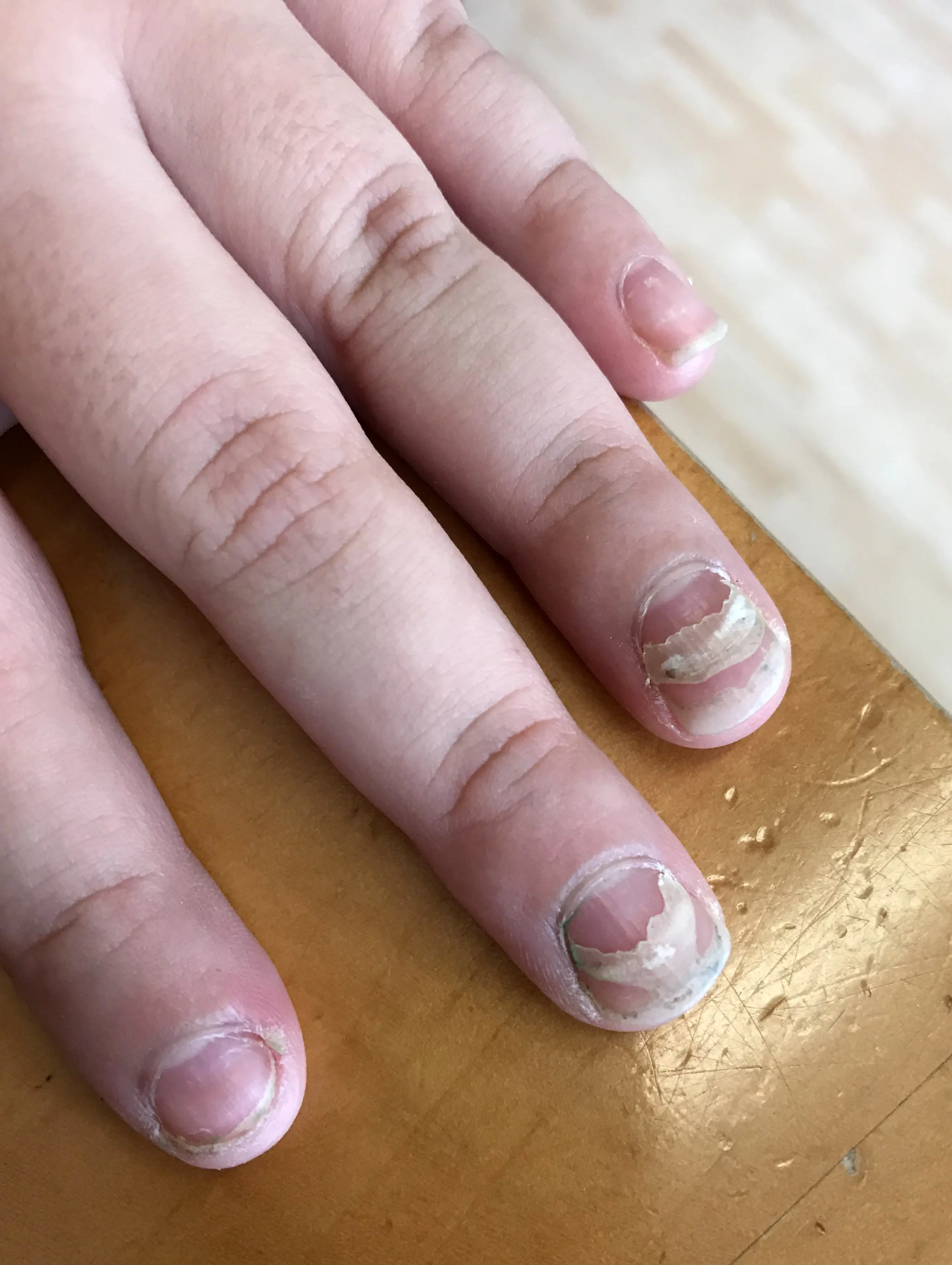
Cracked and Fragile Nails? The Hidden Health Clues Behind Them
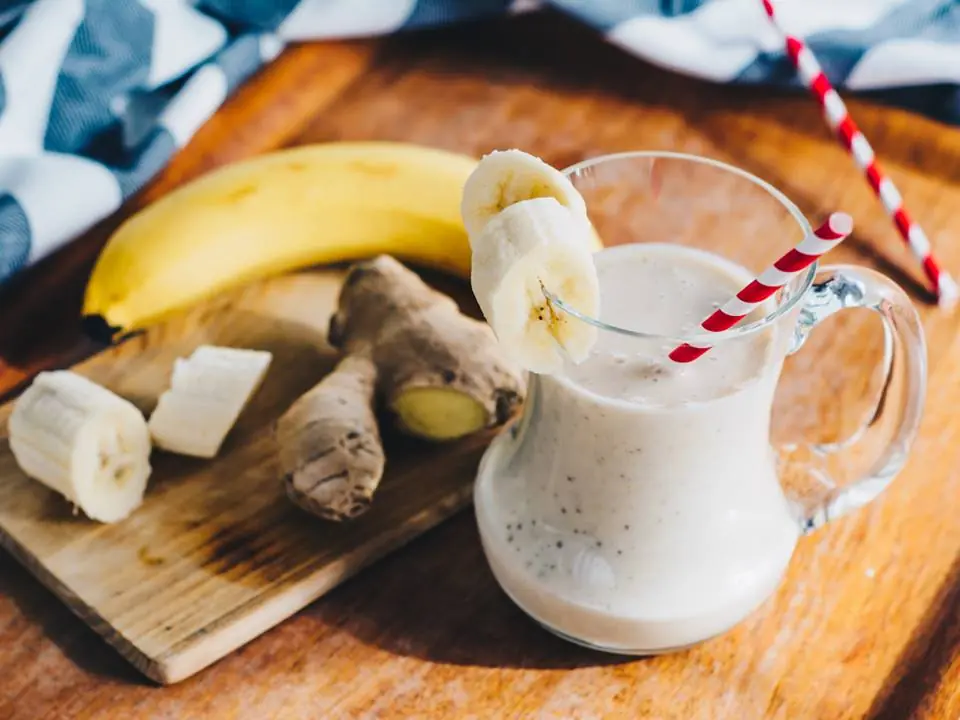

A Zesty Banana Lemon Ginger Smoothie to Power Your Morning
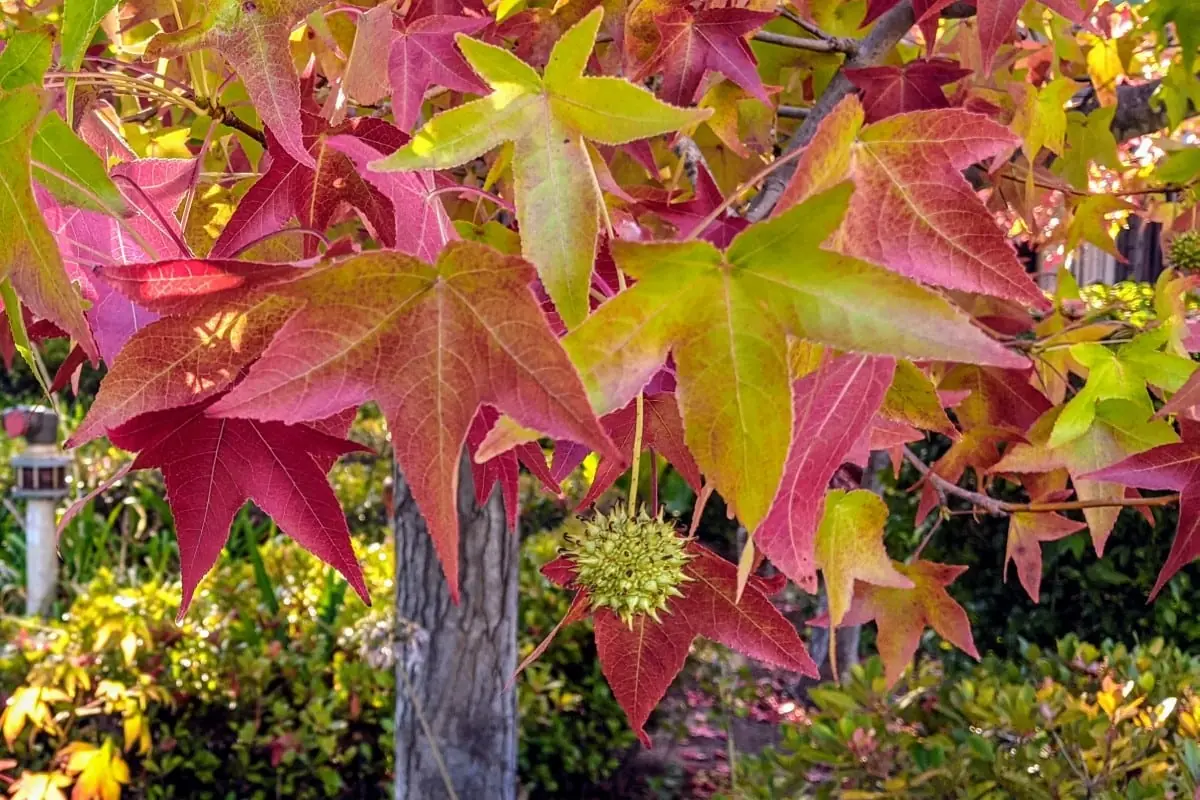

The Healing Legacy of the American Sweetgum (Liquidambar styraciflua)
Is 46–55 a Turning Point for Your Health? 10 Signs to Take Seriously

Eat Banana and Avocado in the Morning: 15 Benefits You Should Know

She Was Just Peeling a Boiled Egg… Until She Saw What Was Hidden Inside
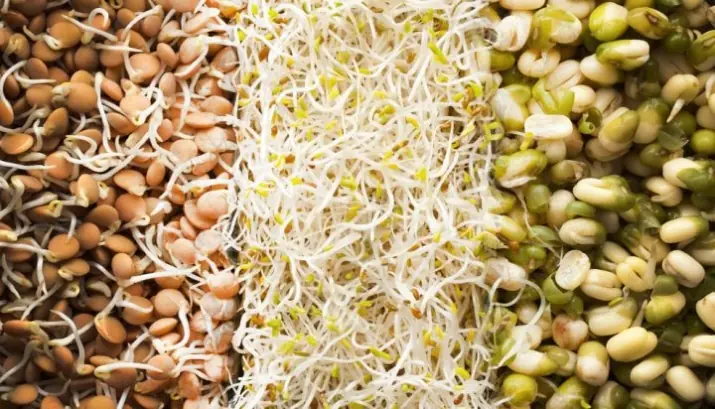

3 Germinated Foods Known for Their Impressive Nutritional Value

5 Groups of People Who Should Be Careful with Chicken Eggs

When Your Parent Shows These 4 Signs, Emotional Preparation Matters
What’s Behind Those White Spots on Your Skin?

Here’s What That Little Pocket in Women’s Underwear Is Actually For

Not Just Fluid Retention: 10 Reasons Your Lower Legs May Be Swollen
9 Red Flags of Diabetes That Deserve Your Attention
Don’t Overlook These 3 Morning Symptoms

A Dentist Reveals Why Teeth Still Turn YellowYou Brush All the Time
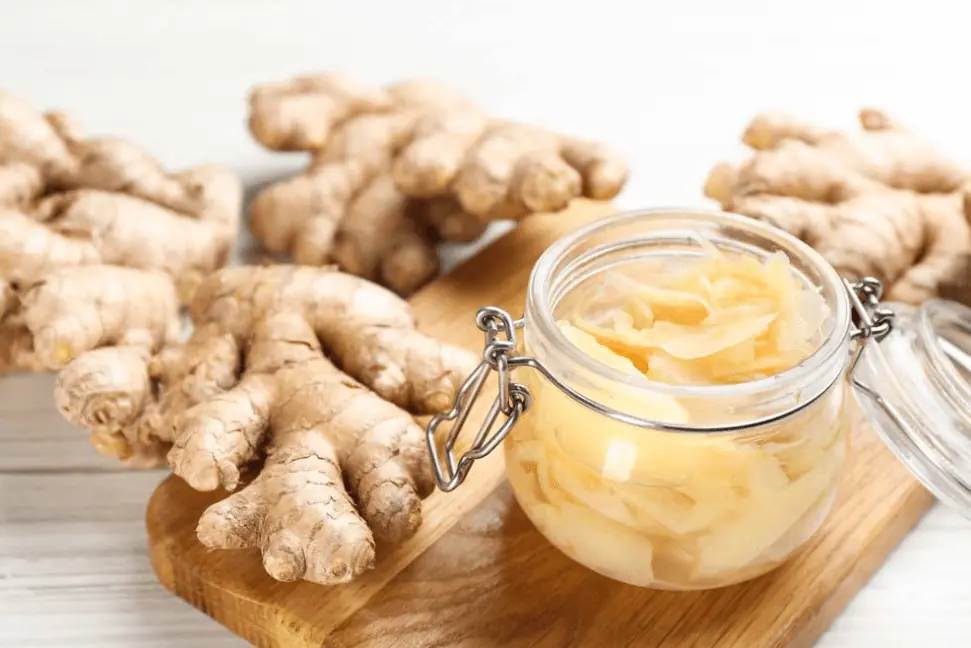

Keep Ginger Fresh for Up to 6 Months with This Easy Storage Trick

Regardless of How Much You Earn, Get Rid of These 4 Things Without Delay