
If this sign appears in the genital area after s*x, women need to see a doctor immediately
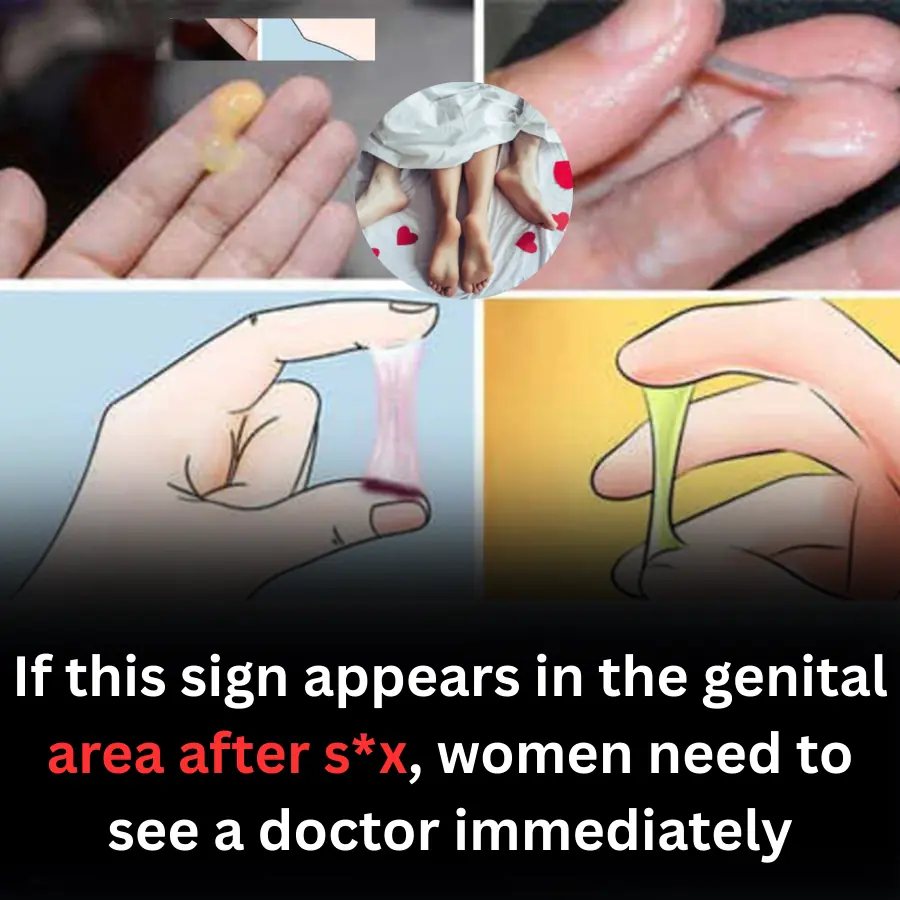
Normal Vaginal Discharge
Vaginal discharge is a normal physiological secretion. It helps keep the vagina moist, regulates the vaginal environment, and protects it from external pathogens. Vaginal discharge is important for reproductive health and sexual activity, acting as lubrication during intercourse to facilitate fertilization.
Normal discharge is white or slightly cloudy, similar to egg whites, odorless, slightly sticky, and mucous-like.
Signs of Abnormal Vaginal Discharge
-
Thick white discharge, like cottage cheese
-
Condition: Vaginal yeast infection
-
Accompanying symptoms: Itching, burning, pain in the vagina or vulva; some may experience pain during intercourse or urination, along with redness and swelling of the genital area.
-
-
White, yellow, or gray discharge
-
Condition: Bacterial vaginosis
-
Accompanying symptoms: Foul odor, itching, swelling.
-
-
Thick yellow or green discharge
-
Condition: Trichomonas infection
-
Accompanying symptoms: Foul odor.
-
-
Brown or blood-stained discharge
-
Condition: Irregular menstruation or uterine/ovarian conditions
-
Accompanying symptoms: Pelvic pain, vaginal bleeding.
-
-
Bright yellow or green discharge
-
Condition: Gonorrhea
-
Accompanying symptoms: Pelvic pain, blood or pus in the urine.
-
Causes of Blood in Vaginal Discharge After Intercourse
-
Physical trauma: Small injuries to the vagina or vulva during sexual activity, often due to incorrect technique or excessive force.
-
Gynecological conditions:
-
Uterine polyps: Discharge may contain blood, be abundant, foul-smelling, and yellow; bleeding during intercourse is common. Severe cases may cause heavy bleeding similar to menstruation.
-
Vaginitis: Yellowish discharge, sometimes with pus and a small amount of blood; inflammation can make the vaginal lining swollen and fragile, causing minor bleeding during intercourse. Minor injuries may heal naturally, but improper care can lead to infection and repeated bleeding.
-
Cervical ectropion (cervical erosion): Discharge may be white, foamy, sticky, and foul-smelling; severe cases can include blood in the discharge or bleeding during intercourse.
-
Serious conditions: Cervical or endometrial cancer, and sexually transmitted infections such as gonorrhea or syphilis, may also cause bleeding during intercourse.
-
Recommendations
-
Monitor blood-stained discharge after intercourse and during subsequent menstrual cycles.
-
If the condition persists more than 7 days with abnormal discharge, consult a gynecologist for timely diagnosis and treatment.
-
Maintain daily genital hygiene, during menstruation, and after sexual activity.
News in the same category


3 intimate habits of husbands that may increase wives' ri.sk of cer.vical can.cer: Stop before it's too late
HOW TO DETECT LUNG CAN.CER EARLY ?

Garlic is highly beneficial, but for these four groups of people, consuming it may cause unwanted reactions
5 nose-related warning signs that may point to underlying di.sea.ses

Eating eggs every day can help you live longer
6 things you should absolutely never do when you have neck and shoulder pain
Many people are surprised to find out they have a disease that can cause blindness

Severe headache, deep coma due to ruptured cerebral aneurysm

What Happens to People Who Eat Sweet Potatoes for Breakfast Over a Long Period of Time?
Doctors Warn That Odors in 3 Areas of the Body May Signal Li.ver Failure
Can Onions Really Help Lower Uric Acid? Warning: These 3 Foods May Trigger a Sudden Str.oke

Seven Food Groups Considered “Natural Eye Drops” Found Right on Your Dining Table
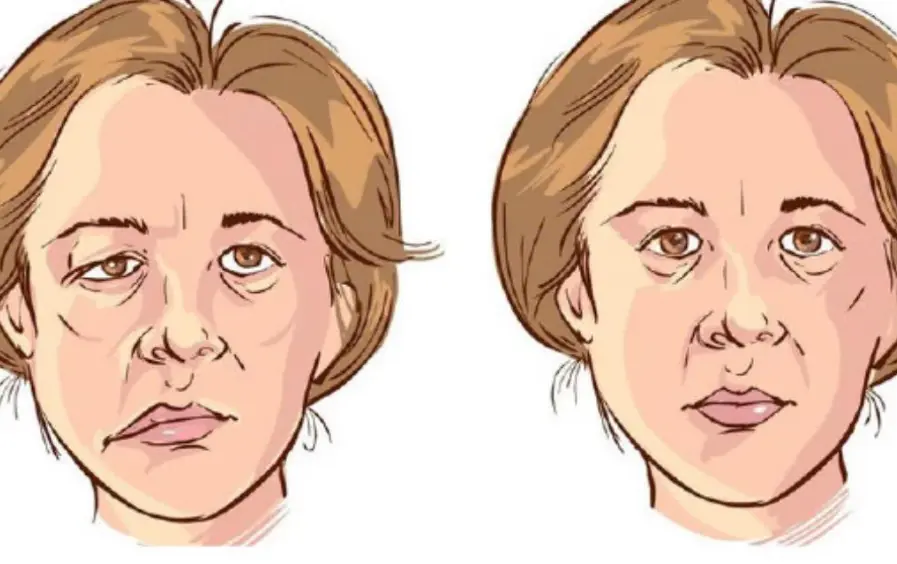
Early Warning Signs of a Str.oke That May Appear 90 Days in Advance
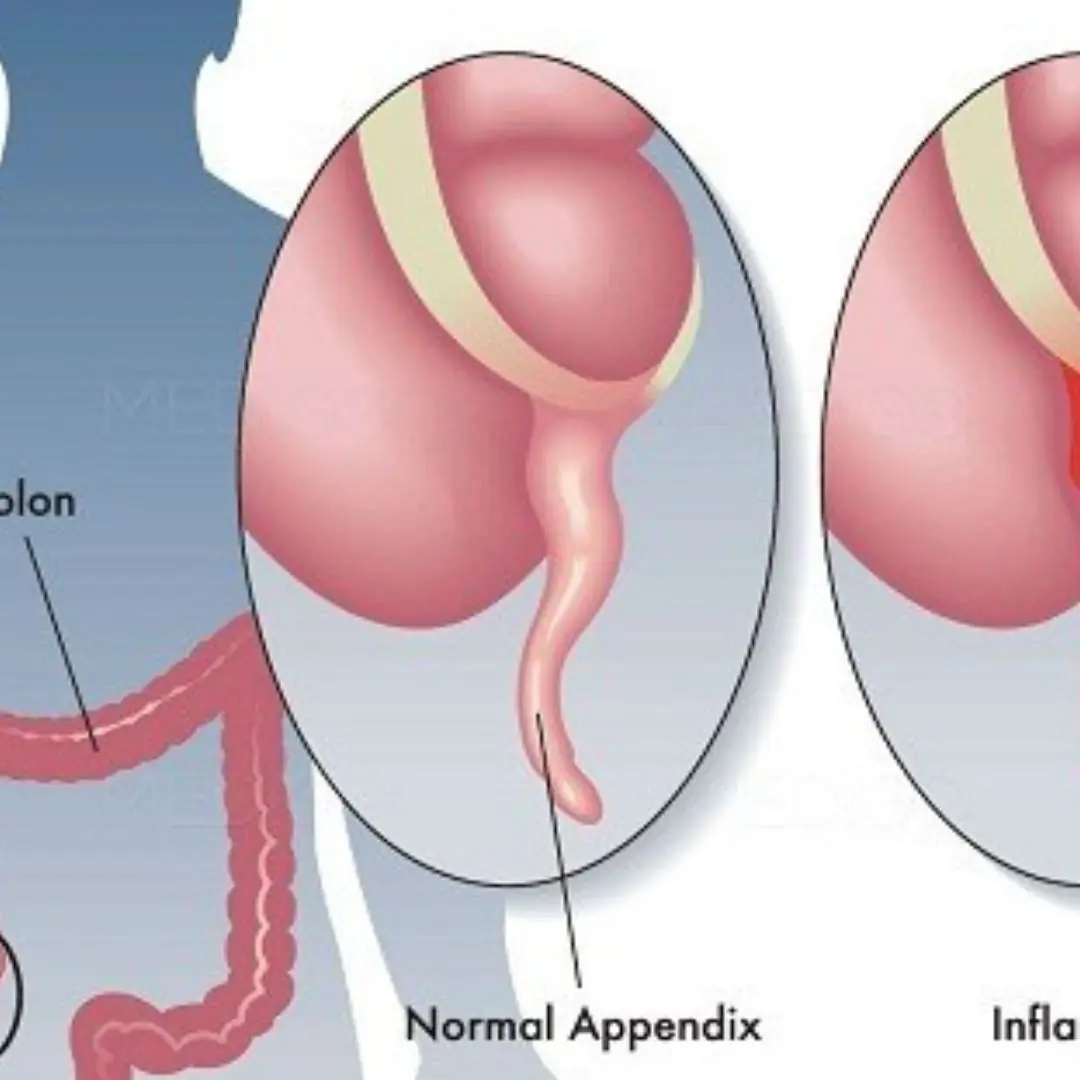
5 warning signs of appen:dicitis you should never ignore!
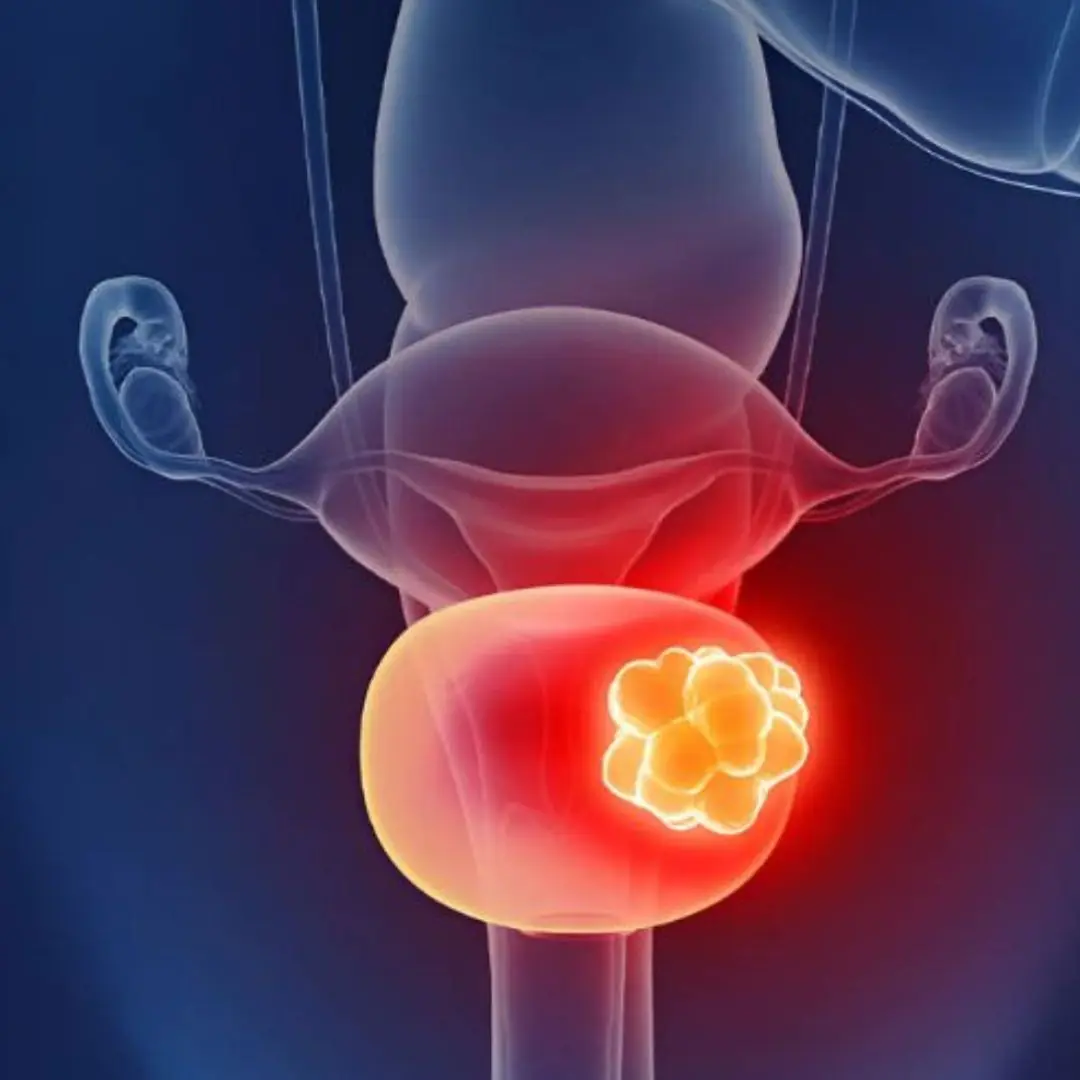
Early Warning Signs of Bladder Ca.n.cer

12 Powerful Benefits of Garlic and How It Helps Fight Infections Naturally

Avocados Are Nutritious, but These 5 Groups of People Should Avoid Them

Common Motherwort: Nature’s Comfort Herb for the Heart and Mind
News Post
Husbands With These 2 Bad Habits May Put Their Wives at Higher Risk of Br:east Can:cer

Most stomach ca.nce.rs are detected late. Doctors say there are five post-meal symptoms that may warrant early endoscopy

3 intimate habits of husbands that may increase wives' ri.sk of cer.vical can.cer: Stop before it's too late

HOW TO DETECT LUNG CAN.CER EARLY ?

Garlic is highly beneficial, but for these four groups of people, consuming it may cause unwanted reactions

5 nose-related warning signs that may point to underlying di.sea.ses

6 unexpected effects of perilla leaves

Eating eggs every day can help you live longer

6 things you should absolutely never do when you have neck and shoulder pain

Many people are surprised to find out they have a disease that can cause blindness

Severe headache, deep coma due to ruptured cerebral aneurysm

What Happens to People Who Eat Sweet Potatoes for Breakfast Over a Long Period of Time?

Doctors Warn That Odors in 3 Areas of the Body May Signal Li.ver Failure

Can Onions Really Help Lower Uric Acid? Warning: These 3 Foods May Trigger a Sudden Str.oke

The “Black List” of 5 Household Items: Cheap, Eye-Catching, but Quietly Harmful to Your Family’s Health

Seven Food Groups Considered “Natural Eye Drops” Found Right on Your Dining Table

My mother-in-law humiliated me in front of the guests, and I cut her allowance in front of everyone

At her anniversary party, my mother-in-law suddenly demanded that I give back the gold earrings she had given me for my wedding
