Muscle pain behind the knee, a dangerous symptom that should not be ignored
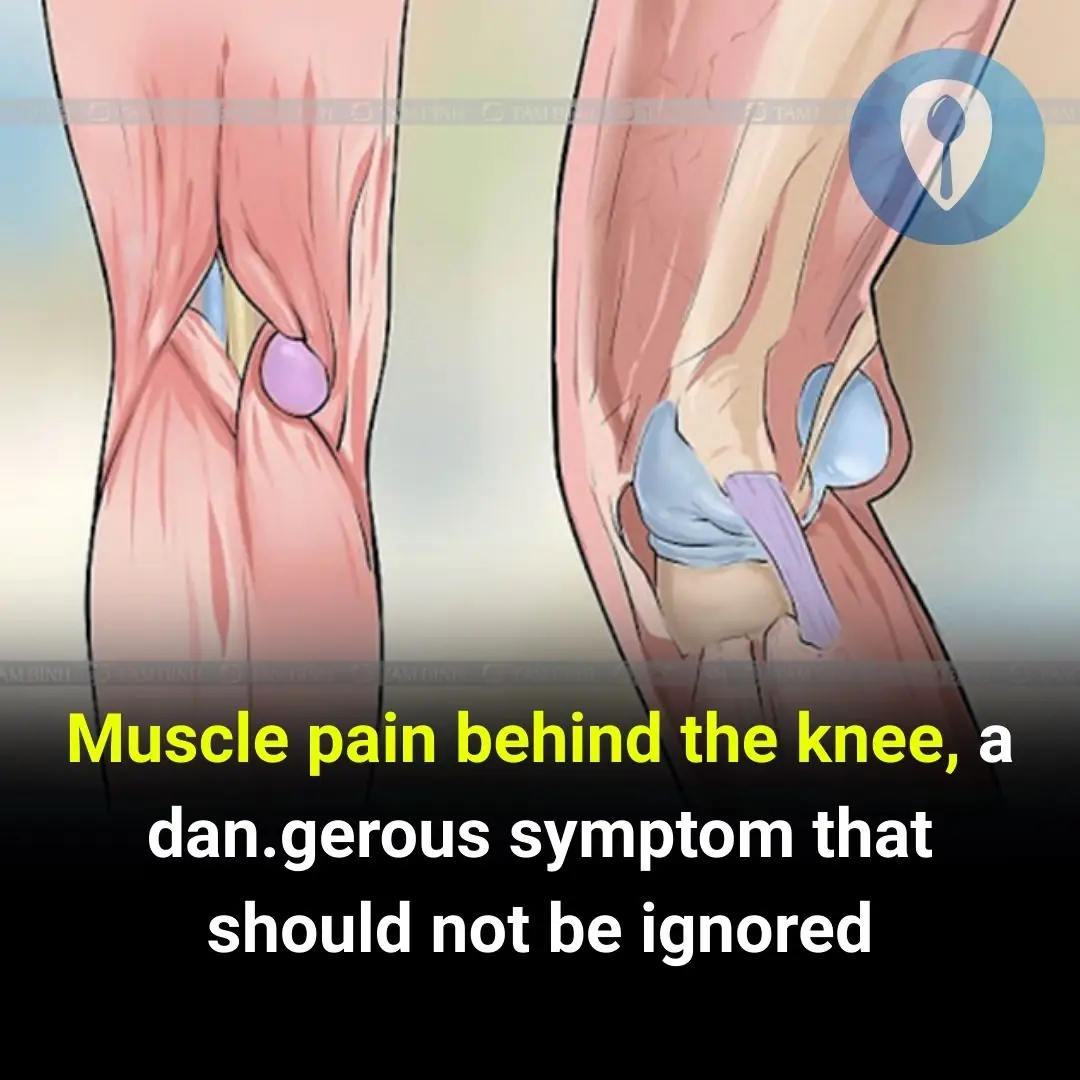
1. Symptoms of Muscle Pain Behind the Knee
Statistics show that more than 10% of middle-aged people experience pain behind the knee. Recognizing the basic symptoms of this condition can help patients detect it early.
1.1. Pain Behind the Knee
The most typical symptom is pain located at the back of the knee. The pain may be dull or sharp and often worsens with movement, making daily activities difficult.
1.2. Knee Swelling
Swelling around the knee is visible to the naked eye. This occurs due to fluid buildup inside or around the joint, often accompanied by warmth in the knee.
1.3. Knee Stiffness
Knee stiffness, especially in the morning, is another common sign. Patients may find it difficult to lift the leg or perform normal movements.
1.4. Grinding or Cracking Sounds
Loose cartilage caused by muscle pain behind the knee may lead to abnormal joint sounds. Patients may hear grinding or cracking noises, particularly when climbing stairs.
1.5. Weak Knees
As the condition progresses, the knee becomes weaker. Numbness in the legs may also occur.
1.6. Knee Buckling
Injury-related muscle pain can damage cartilage in the front, back, or middle of the knee. Prolonged damage may lead to knee buckling and deformity.
Other accompanying symptoms may include fever and fatigue.
2. Causes of Muscle Pain Behind the Knee
2.1. Injuries
Sports injuries, traffic accidents, or workplace accidents can damage cartilage, joints, and ligaments, leading to pain behind the knee.
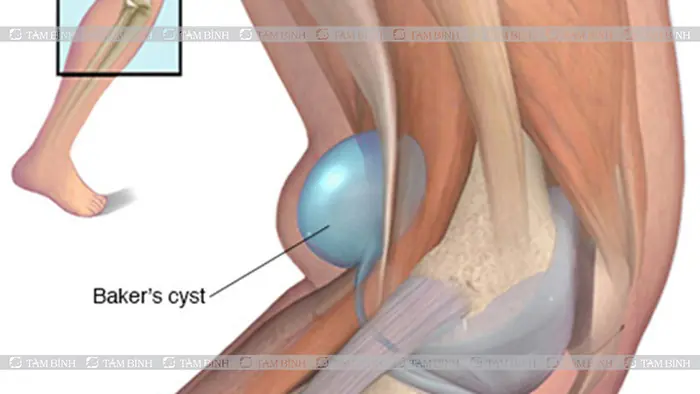
2.2. Baker’s Cyst
This occurs when a sac of fluid builds up at the back of the knee, causing pain and swelling. Small cysts may be painless, but as they grow, they put pressure on tendons and nerves. A Baker’s cyst can grow as large as a ping-pong ball.
2.3. Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
DVT occurs when a blood clot forms in a deep vein in the leg. Overweight individuals, the elderly, smokers, and those with a sedentary lifestyle are at higher risk.
2.4. Bone and Joint Disorders
Although less common than general knee pain, muscle pain behind the knee can result from underlying joint conditions.
-
Knee Arthritis: Symptoms include localized or cyclical pain, worsening discomfort, joint stiffness, and grinding sounds. Untreated arthritis may lead to complications such as osteoarthritis, ligament tears, and joint effusion.
-
Tendonitis: Tears or ruptures in tendons or ligaments may cause pain, often behind the left knee.
-
Knee Effusion (Fluid on the Knee): Excess fluid leaks into surrounding areas, causing swelling and pain behind the knee.
-
Bursitis: Repeated strain on the bursa (fluid-filled sacs around the joint) leads to inflammation, redness, and swelling.
3. Treatment for Muscle Pain Behind the Knee
While not life-threatening, untreated muscle pain behind the knee can interfere with daily life and cause complications. Medical consultation is recommended to determine the appropriate treatment plan.
3.1. Western Medicine
Commonly prescribed medications include:
-
NSAIDs: Ibuprofen, Aleve, corticosteroids to reduce pain and inflammation.
-
COX-2 inhibitors: Etoricoxib, parecoxib, rofecoxib, valdecoxib, lumiracoxib.
⚠️ Long-term use may cause side effects affecting the liver, kidneys, and stomach. Medication should only be taken under a doctor’s guidance.
3.2. Traditional Remedies
Safer, natural alternatives are often chosen to avoid side effects:
-
Gac Seed Remedy: Roast gac seeds, soak them in 2 liters of white wine for one month, and use the liquid to massage the painful area 2–3 times daily.
-
Mugwort Remedy: Wash a handful of mugwort leaves, pound them with salt, dry-roast the mixture, and apply it to the painful knee area.
3.3. Hot and Cold Compresses
Applying heat or cold helps improve blood circulation, relax muscles, and reduce pain.
3.4. Acupuncture and Acupressure
These techniques help relieve pain immediately by improving energy flow and stimulating the body’s natural painkillers.
3.5. Surgery
Surgical intervention is recommended in severe cases where conservative treatments fail. The procedure removes or repairs internal knee damage.
✅ Muscle pain behind the knee may seem minor but can indicate underlying injuries or diseases. Early recognition and timely treatment are essential to prevent long-term complications.
News in the same category

Li.ver Can.cer “Fears” These 7 Foods

5 Types of Vegetables That “Naturally Contain Toxi.ns”
Waking up with foamy urine: Warning of 3 serious illnesses, number 1: Go to the hospital quickly

These common garden leaves could be a natural remedy for bone and joint problems—yet many overlook their power
Waking up with 6 strange tastes in your mouth, watch out for internal organs being sic.k

Headaches at these times warn of extremely dang.erous diseases

2 Hygiene Habits That “Damage” the Inti.mate Area
3 Types of Autumn Vegetables Known as the “Kings of Calcium” Everyone Should Eat Regularly

Groups of people absolutely abstain from eating chayote squash to avoid bringing disaster upon themselves
People with weak kidneys often have pain in 5 places: If you have 1, you need to see a doctor immediately!

5 abnormalities that appear at night warn of "blood flooding the street", even young people should not be subjective
If Your Kidneys Are in Danger, the Body Will Show these 10 Signs
Young Woman Dies at 27 from Late-Stage Thyroid Cancer

The Meaning Of The Intriguing Gesture Of Scratching The Palm Of Another Person’s Hand
One Month Before A Heart Attack, Your Body Will Warn You Of These 7 Signs
5-Year-Old Loses Battle With Cancer — Doctors Reveal 5 Foods Parents Must Never Give Their Children

If you drool while sleeping often, check for these 6 diseases

Which canc.ers are hereditary?
News Post

If your saliva smells bad, you may have...

Li.ver Can.cer “Fears” These 7 Foods

Cabbage Is Nutritious but Harmful for These 5 Groups of People

5 Types of Vegetables That “Naturally Contain Toxi.ns”

Sweet Potato vs. Potato: The Truth About Their Health Benefits

Waking up with foamy urine: Warning of 3 serious illnesses, number 1: Go to the hospital quickly

These common garden leaves could be a natural remedy for bone and joint problems—yet many overlook their power

Waking up with 6 strange tastes in your mouth, watch out for internal organs being sic.k

Headaches at these times warn of extremely dang.erous diseases

These 4 parts of a pig may be delicious and inexpensive, but you shouldn’t eat them too often—don’t let greed harm your health

Reasons why you should stop eating tilapia as soon as possible

Rich in nutrients, these 3 vegetables are considered by the Japanese as a longevity eli.xir
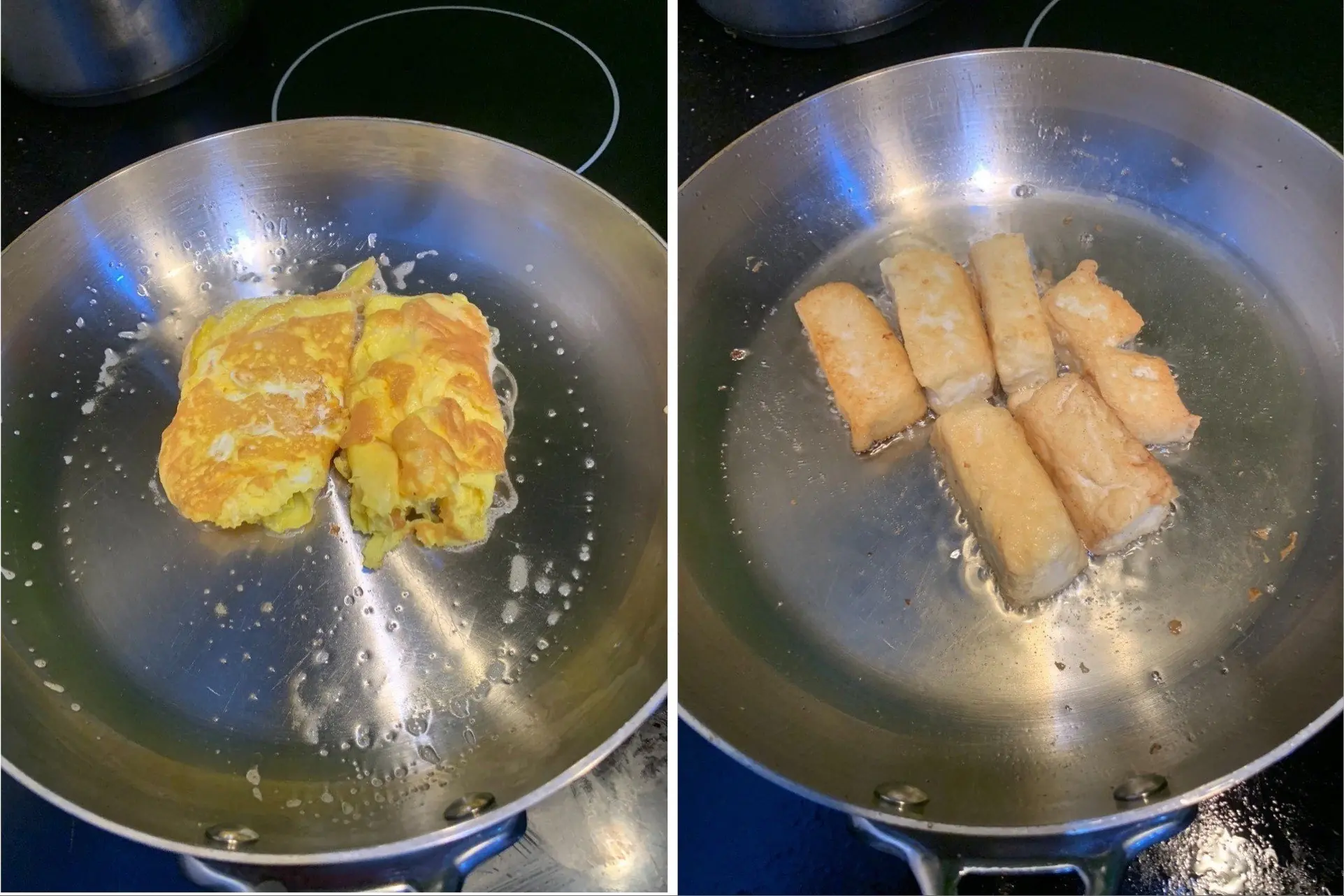

Frying Anything Without Sticking: Just Add This Liquid to the Pan

2 Hygiene Habits That “Damage” the Inti.mate Area

Eliminate Refrigerator Odors with Just Two Common, Cheap Items

3 Types of Autumn Vegetables Known as the “Kings of Calcium” Everyone Should Eat Regularly

Does eating boiled eggs every day benefit or harm the li.ver?

Groups of people absolutely abstain from eating chayote squash to avoid bringing disaster upon themselves
