Should you reheat cold rice?

Rice is a staple food enjoyed by billions worldwide, often prepared in large batches to serve multiple meals. Naturally, leftover rice is common in many households, but a frequent question arises: Is it safe to eat leftover rice? The answer is yes - but only if handled and stored properly. Nutrition experts emphasize that while leftover rice can be a convenient and nutritious option, improper storage and reheating can lead to serious health risks, including food poisoning.
In this article, we explore what experts recommend to ensure leftover rice remains safe to consume and retains its nutritional value.
Why Is Leftover Rice a Concern?
The primary safety issue with leftover rice lies in its potential to harbor harmful bacteria, particularly Bacillus cereus. This bacterium is commonly found in uncooked rice and can survive the cooking process. If cooked rice is left at room temperature too long, the bacteria can multiply and produce toxins that cause foodborne illness.
Symptoms of Bacillus cereus poisoning include nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea, often occurring within hours of consumption. This is why understanding proper rice handling is critical for food safety.
Expert Recommendations for Safe Storage of Leftover Rice
1. Store Rice Promptly in the Refrigerator
To minimize bacterial growth, leftover rice should be cooled and refrigerated as soon as possible—ideally within one hour after cooking. Leaving rice out at room temperature allows bacteria to multiply rapidly.
Use shallow containers to cool rice quickly before placing it in the fridge. Nutrition experts recommend keeping leftover rice in the refrigerator at or below 40°F (4°C). Under these conditions, rice should be consumed within 24 hours for safety.
2. Reheat Thoroughly Before Eating
Heating leftover rice until it is steaming hot (at least 165°F or 74°C) is essential to kill bacteria that may have grown during storage. Avoid reheating rice only partially or to lukewarm temperatures.
Use a microwave or stovetop to reheat rice evenly. Stir the rice during reheating to eliminate cold spots where bacteria might survive.
3. Avoid Reheating Rice Multiple Times
Repeated reheating and cooling cycles increase the risk of bacterial growth and toxin production. Each reheating cycle also degrades the texture and nutritional quality of the rice.
Experts advise reheating leftover rice only once and consuming it immediately after.
4. Watch for Signs of Spoilage
Before reheating, inspect the rice carefully. If it smells sour, has a slimy texture, or shows discoloration, discard it immediately. These are clear signs that the rice has spoiled and is unsafe to eat.
Tips to Minimize Leftover Rice Waste
While leftovers can save time, cooking the exact amount of rice needed per meal reduces the risks associated with storage and reheating.
Additionally, when preparing meals, consider using fresh rice or preparing smaller batches that can be consumed in one sitting. This approach ensures maximum freshness, better flavor, and reduced food safety concerns.
Nutritional Considerations
Rice is a good source of carbohydrates, and leftover rice retains most of its nutritional value if stored and reheated properly. However, overcooking or reheating multiple times can degrade some vitamins and alter the texture.
Pairing rice with vegetables and proteins in your meal enhances its overall nutritional profile, making it a wholesome part of your diet.
Conclusion
Leftover rice can be safe and nutritious if handled correctly. Prompt refrigeration, thorough reheating, and avoiding repeated reheating are key steps to prevent foodborne illness. Always be vigilant about the condition of leftover rice before consuming it.
By following expert advice and practicing proper food safety habits, you can enjoy the convenience of leftover rice without compromising your health.
News in the same category


These 3 Meats Can Harbor Parasites if Not Cleaned Thoroughly

If the engine fails, will the plane fall straight down?

Tips to Choose Fresh Beef and Avoid Fake, Frozen, or Water-Injected Meat: Pick the Right Cut for Each Cooking Method

3 Types of Fruit Full of Parasites — Be Careful or You Might Get Sick

Why do Japanese people prefer sleeping on the floor?

Don’t Eat Sunflower Seeds Until You Know These 11 Facts

3 Highly Nutritious Parts of a Pig: Don’t Hesitate to Buy Them When You See Them at the Market

This 'Humble' Vegetable Contains 36 Times More Calcium Than Bone Broth

When you go to the market and see these 4 items, you must consider carefully before spending money to buy them and bring them home
What happens if you hold in your fart?

Have you ever wondered why when you wake up, mysterious bruises appear on your body?

Are These Mutant Eggs Safe to Eat? The Truth About Double Yolks and Rainbow Shells

Eating These 5 Foods for Breakfast Is Like Shortening Your Lifespan — But Many People Still Love Them

5 Foods That Stay Edible for a Whole Month at Room Temperature — But Spoil Quickly in the Fridge!

Putting plastic bags in the refrigerator causes can.cer? After hearing the truth, many people immediately ran to do 1 thing

The Peels of These 3 Fruits Are Actually 'Pesticide-Free Vegetables': Cook 3 Delicious Dishes That Also Beautify Your Skin and Aid in Weight Loss

One Person Boils Water, the Whole Family Gets Cancer

5 Foods That Seem Edible but Are Actually Harmful — Tell Your Parents to Throw Them Out
News Post

4 parts of chicken you should not eat

Tips to smooth clothes without an iron

How to Grow a Lemon Tree From Seed Indoors or Outside, According to Horticulturists

7 Brilliant Uses For Eggshells In Your Garden

Drinking coffee at the wrong time can ha.rm your heart

Tips to save money with toilet paper rolls

Two Types of Vegetables That Are Unlikely to "Absorb" Pesticides — The Top One Is Surprisingly Unknown to Many

Grow Plump, Flavorful Eggplants with These Smart Growing Tips

These 3 Meats Can Harbor Parasites if Not Cleaned Thoroughly

A Little Cloud

Boil potatoes without water: This way the potatoes will be soft, fragrant, and not bland.

If the engine fails, will the plane fall straight down?
6 wa.rning signs your bo.dy might be “nurturing” can.cer
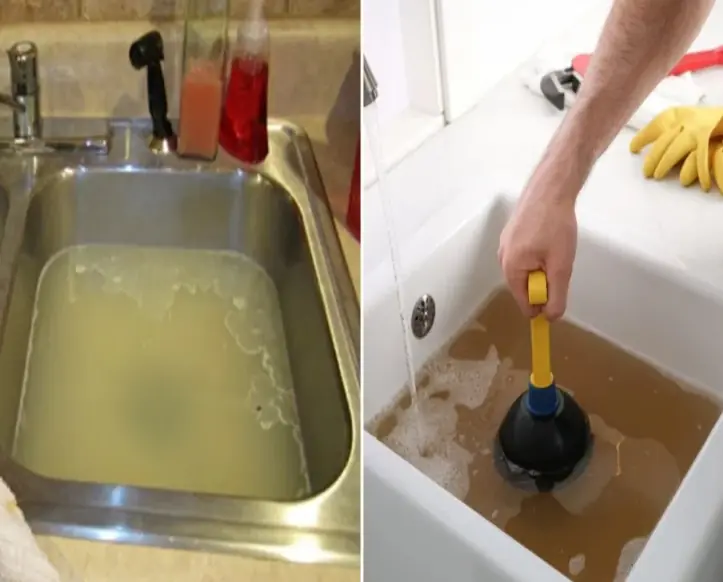

How to clean sink drain easily
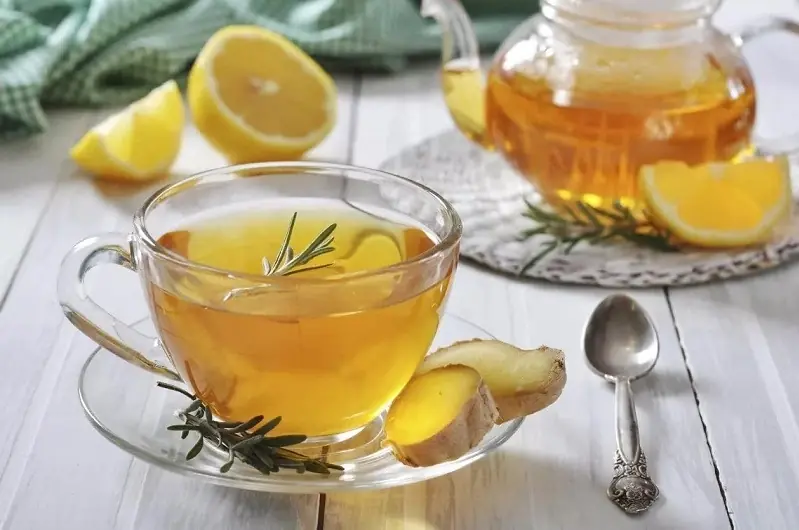

5 effective liver de.tox drinks to have before bed
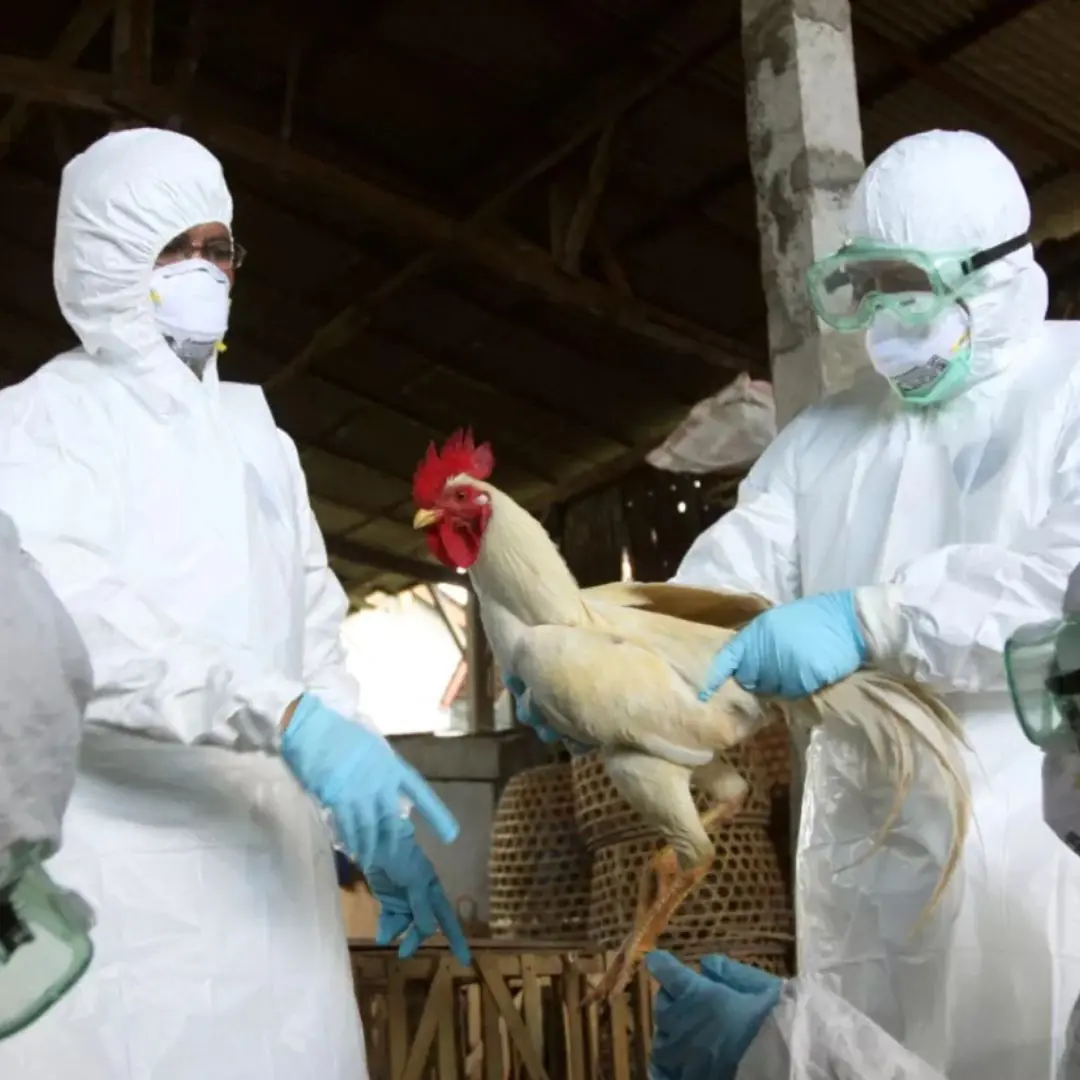

Experts Warn of Rising Bird Flu Th.r.eat: Could Avian Influenza Become the Next Pa.nd.emic?
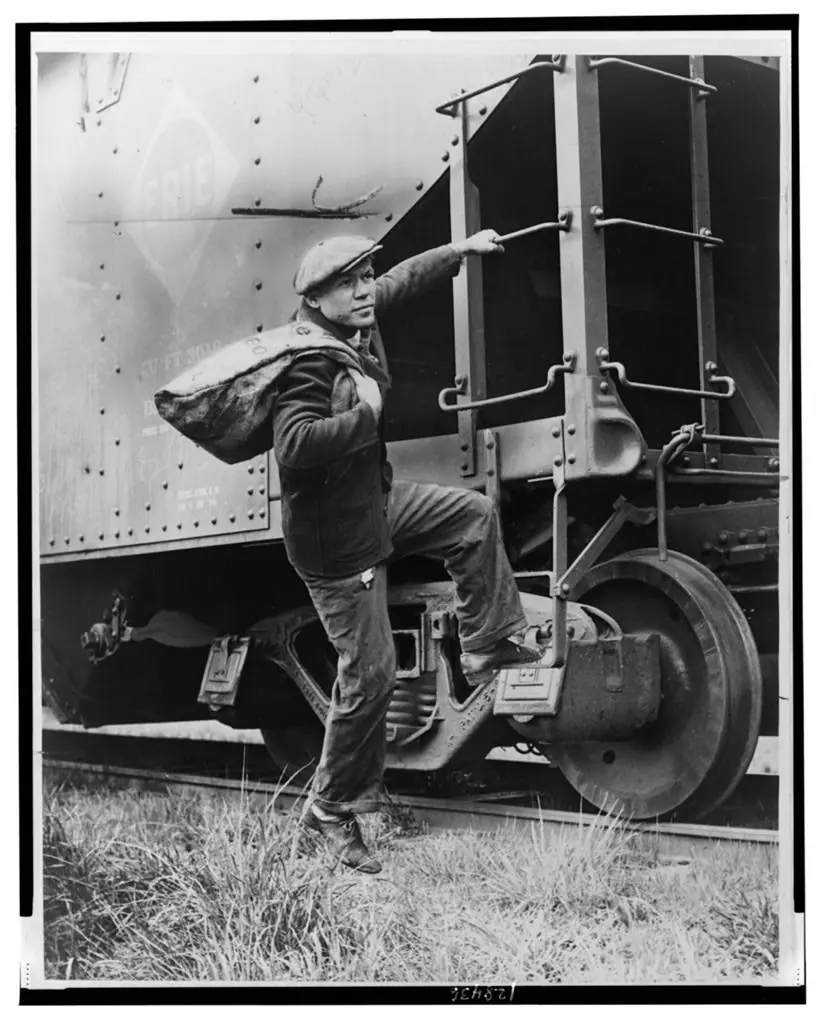

Whistling Dick's Christmas Stocking

3 Fruits That May Harbor Parasites – Eat with Caution to Avoid Illness

5 amazing health benefits of black bean water
