Ginkgo Tree (Maidenhair Tree, Ginkgo Biloba)
The ginkgo tree (Ginkgo biloba), also known as maidenhair tree, belongs to the Ginkgoaceae family. It is a tall tree, reaching heights of 20–30 meters, with numerous long branches. The branches have many short twigs that bear leaves with long petioles.
Characteristics of Ginkgo Leaves and Fruit
- Leaves: Fan-shaped, tapering towards the base, and divided into two lobes by a central vein. The petiole (leaf stalk) is notably longer than the leaf blade.
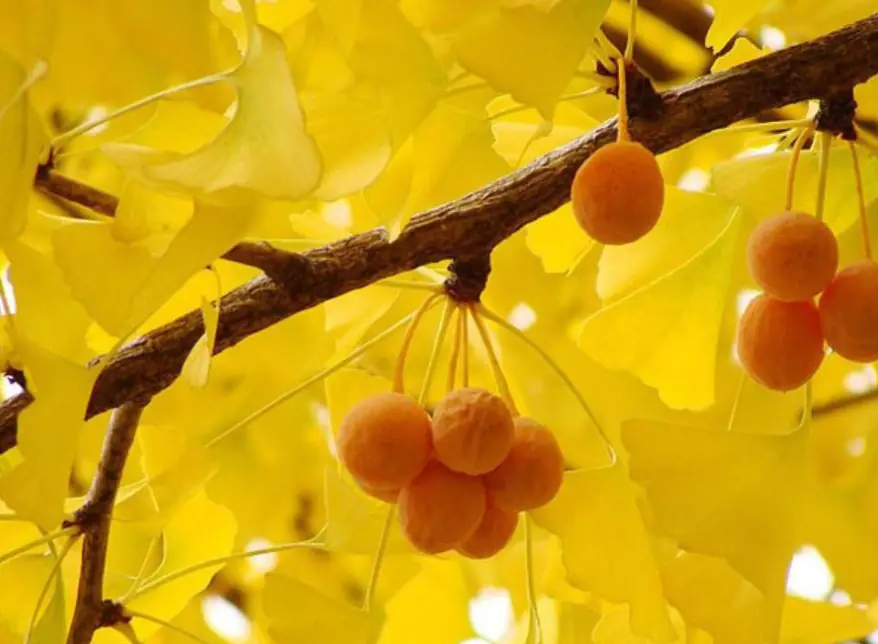
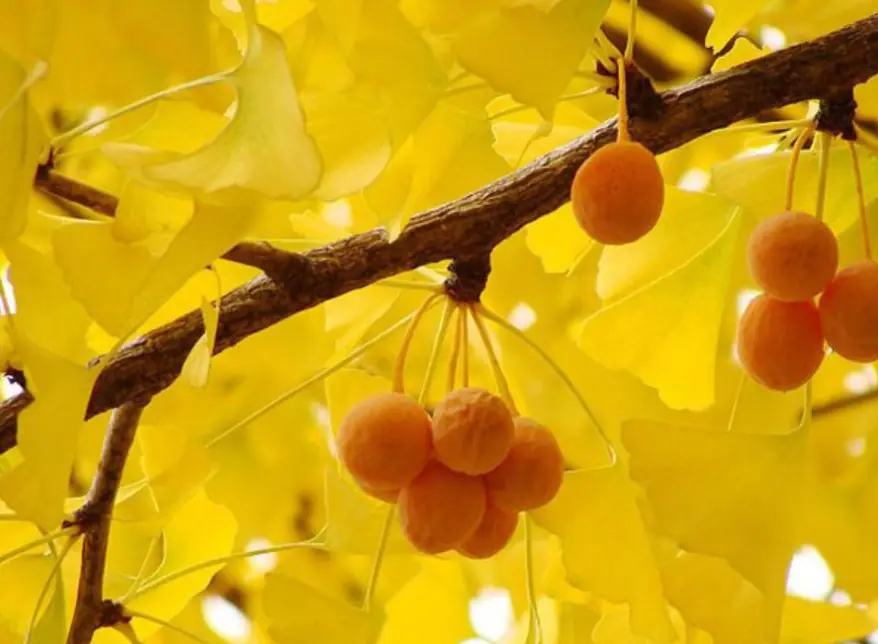
- Fruit: Resembling small plums, the ginkgo fruit has a thick, yellowish flesh that emits a strong, unpleasant odor similar to rancid butter.
Reproduction and Pollination
Ginkgo trees are dioecious, meaning there are separate male and female trees. Some trees bear only male flowers, while others bear only female flowers. Pollination between male and female trees is necessary for fruit production.
Global Distribution
The ginkgo tree is widely found in North and East Asia, particularly in Korea, Japan, China, and North Korea.
Ginkgo fruit is about the size of a plum, has yellow flesh, and has a very unpleasant burnt butter smell