Warning: 20 early signs your body may be indicating can.cer
Can.cer is one of the most feared diseases globally, affecting millions of people every year. While it’s common for people to associate cancer with painful or visible symptoms, many early signs of cancer can be subtle and easily ignored. Early detection is crucial because it dramatically increases the chances of effective treatment and survival.
Experts emphasize the importance of early detection and listening to your body when it comes to identifying cancer in its early stages. If you notice any of these 20 early warning signs, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional to discuss your symptoms.
In this article, we’ll explore 20 early signs of can.cer that shouldn’t be ignored and what they might mean for your health.
1. Unexplained Weight Loss
Unintentional weight loss of more than 5% of your body weight over a short period of time, without changes in diet or exercise habits, could be an early warning sign of cancer. This is particularly common in pancreatic, stomach, and esophageal cancers.
-
What to Watch For: Rapid weight loss that isn’t associated with diet or physical activity changes.
2. Persistent Fatigue
Chronic fatigue that doesn’t improve with rest can be a signal of various cancers, such as leukemia, colon cancer, or stomach cancer. This type of fatigue is different from typical tiredness; it persists even after adequate sleep.
-
What to Watch For: Exhaustion that prevents you from doing your regular activities and doesn’t get better after rest.
3. Changes in Skin Appearance
Changes to your skin, such as new moles or changes to existing moles, could be a sign of skin cancer, especially melanoma. Look for moles that are asymmetrical, have uneven borders, or have changed in color.
-
What to Watch For: New or changing moles, sores that won’t heal, or unusual skin growths.
4. Persistent Cough or Hoarseness
A persistent cough that lasts more than a few weeks or hoarseness that doesn’t go away could signal lung cancer or throat cancer.
-
What to Watch For: Coughing up blood, difficulty breathing, or a sore throat that doesn’t resolve.
5. Pain in the Abdomen or Digestive Problems
Unexplained pain in the abdomen, swelling, bloating, or persistent digestive issues could indicate colon cancer, pancreatic cancer, or ovarian cancer.
-
What to Watch For: Pain that doesn't go away or is accompanied by changes in bowel habits, such as constipation or diarrhea.
6. Difficulty Swallowing
Difficulty swallowing (known as dysphagia) that becomes worse over time may be a symptom of esophageal cancer, stomach cancer, or throat cancer.
-
What to Watch For: A feeling of food getting stuck in your throat, regurgitation, or pain while swallowing.
7. Unexplained Fever
A persistent or unexplained fever that lasts for weeks could be a sign of cancer, particularly blood cancers such as leukemia or lymphoma.
-
What to Watch For: Continuous fever without other apparent illness, especially when accompanied by night sweats or weight loss.
8. Unexplained Bleeding
Unexplained bleeding, such as coughing up blood, blood in urine, rectal bleeding, or unusual vaginal bleeding, can be signs of cancers in areas like the lungs, bladder, colon, or reproductive organs.
-
What to Watch For: Blood in stool, urine, coughing, or abnormal menstrual bleeding.
9. Changes in Bowel Habits
Changes in your bowel movements, such as chronic diarrhea, constipation, or a change in stool appearance (like narrower stools), could be indicative of colon cancer.
-
What to Watch For: Frequent changes in your bowel habits that last for weeks or more, along with blood in the stool.
10. Swelling or Lumps in the Body
A lump or swelling, particularly in the neck, armpits, abdomen, or groin, can be an early indicator of cancer. Breast can.cer, lymphoma, and testicular cancer often cause lumps.
-
What to Watch For: A lump that feels hard, painless, or grows in size.
11. Painful Urination or Blo.od in Urine
Painful urination or blood in the urine could be a sign of bladder cancer or kidney cancer.
-
What to Watch For: Persistent pain when urinating, blood in the urine, or changes in urine color or odor.
12. Trouble Breathing or Shortness of Breath
Shortness of breath, especially when it occurs unexpectedly or without physical exertion, could be a sign of lung cancer or other cancers affecting the respiratory system.
-
What to Watch For: Difficulty catching your breath, wheezing, or feeling out of breath when at rest.
13. Pain in the Back
Unexplained back pain that worsens over time could be a sign of pancreatic cancer, colon cancer, or spinal cancer.
-
What to Watch For: Back pain that does not improve with rest or treatment, particularly if it is severe or radiates to other areas.
14. Loss of Appetite
An unexplained loss of appetite, combined with weight loss, can signal stomach cancer, pancreatic cancer, or other abdominal cancers.
-
What to Watch For: Feeling full after eating only small amounts of food, or not feeling hungry at all.
15. Nausea or Vomiting
Persistent nausea or vomiting that isn’t related to food or illness could be related to gastrointestinal cancer, particularly cancers of the stomach or pancreas.
-
What to Watch For: Frequent nausea or vomiting that doesn’t resolve with typical remedies.
16. Unexplained Muscle or Joint Pain
If you experience unexplained pain in your muscles or joints, and the pain persists for no apparent reason, it could be a sign of cancer, particularly bone cancer or cancers that have metastasized to the bones.
-
What to Watch For: Persistent pain or soreness that doesn’t respond to typical treatments.
17. Night Sweats
Night sweats that soak your sheets, without any fever or infection, could be indicative of lymphoma or other cancers that affect the lymphatic system.
-
What to Watch For: Excessive sweating during the night, often without a clear cause, that disrupts sleep.
18. Changes in Breast Tissue or Nipple Discharge
Changes in the breast, such as lumps, skin changes, or unusual discharge from the nipple, are common signs of breast cancer.
-
What to Watch For: Lumps, skin dimpling, or any unusual discharge or bleeding from the nipple.
19. White Patches or Sores in the Mouth
White patches or sores that don’t heal in the mouth could be a sign of oral cancer or throat cancer. These patches are often caused by tobacco use or HPV (human papillomavirus).
-
What to Watch For: Persistent white patches, sores, or bleeding in the mouth or throat.
20. Persistent Indigestion or Heartburn
Frequent heartburn, indigestion, or acid reflux that does not improve over time could be an early symptom of esophageal cancer or stomach cancer.
-
What to Watch For: Ongoing acid reflux or indigestion that worsens with time, especially if accompanied by difficulty swallowing.
How to Prevent Cancer: Tips for Lowering Your Risk
While many cancers are caused by genetic factors that you can’t control, lifestyle choices play a significant role in lowering the risk of developing cancer. By adopting healthy habits, you can reduce your risk of cancer and improve your overall health. Here are practical ways to help prevent cancer and stay healthier for longer.
1. Maintain a Healthy Diet
A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins is one of the most effective ways to reduce your risk of cancer. Many cancers are linked to poor nutrition, particularly diets high in processed foods and saturated fats.
Prevention Tips:
-
Eat more fruits and vegetables: These foods are packed with antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals that help fight free radicals, which can damage cells and lead to cancer.
-
Limit red meat: High consumption of red meat and processed meats like sausages, bacon, and hot dogs has been linked to colon and stomach cancer. Try to limit these foods in your diet.
-
Choose whole grains: Whole grains such as brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat contain fiber, which can help protect against colorectal cancer.
-
Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to support digestion and keep your body functioning optimally.
2. Exercise Regularly
Regular physical activity is not only good for maintaining a healthy weight but also plays a critical role in preventing various cancers, including breast cancer, colon cancer, and endometrial cancer.
Prevention Tips:
-
Aim for 30 minutes of moderate activity most days: Regular physical activity helps maintain a healthy weight, improves circulation, and boosts your immune system, all of which reduce cancer risk.
-
Stay active throughout the day: In addition to structured exercise, try to avoid sitting for long periods. Take breaks to walk around and stretch to improve blood flow.
3. Avoid Smoking and Limit Alcohol Consumption
Tobacco use is the leading cause of lung cancer and is also linked to other cancers such as oral, throat, bladder, and pancreatic can.cer. Alcohol consumption also increases your risk of several cancers, particularly breast, liver, and colon cancer.
Prevention Tips:
-
Quit smoking: If you smoke, quitting is the most important step you can take to reduce your risk of cancer. Seek help from a healthcare professional if needed. There are many programs and resources available to assist in quitting.
-
Limit alcohol: The risk of cancer increases with the amount of alcohol consumed. For men, limit alcohol to no more than two drinks per day, and for women, no more than one drink per day.
4. Protect Your Skin from the Sun
Sun exposure is the leading cause of skin cancer, including melanoma, basal cell carcinoma, and squamous cell carcinoma. Protecting your skin from harmful UV rays is essential for cancer prevention.
Prevention Tips:
-
Wear sunscreen: Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30 on all exposed skin, even on cloudy days. Reapply every two hours, and more often if you swim or sweat.
-
Avoid sun exposure during peak hours: Try to stay out of the sun from 10 a.m. to 4 p.m., when UV rays are the strongest.
-
Cover up: Wear protective clothing such as hats, sunglasses, and long sleeves to shield your skin from the sun.
5. Get Vaccinated
Certain types of cancer are caused by infections that can be prevented through vaccines. Two vaccines that help prevent cancer are:
HPV Vaccine:
-
The human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine helps prevent cervical cancer, as well as anal, oral, and throat cancers caused by HPV infection.
-
It is recommended for both boys and girls starting at age 11-12, but it can be administered up to age 26 for those who missed it earlier.
Hepatitis B Vaccine:
-
Hepatitis B is a virus that can cause liver cancer. The hepatitis B vaccine is recommended for newborns, as well as adults at higher risk for the infection, such as those with chronic liver disease or those who engage in high-risk behaviors.
6. Regular Health Screenings
Routine cancer screenings can help detect certain types of cancer in their early stages when they are most treatable. Early detection through screening can significantly reduce the risks and improve survival rates.
Screening Recommendations:
-
Breast cancer: Women should begin mammograms at age 50, or earlier if they have a family history of breast cancer.
-
Cervical cancer: Women should begin Pap tests at age 21 and continue every 3 years.
-
Colorectal cancer: Start screenings at age 45, with options like colonoscopy or fecal occult blood tests.
-
Skin cancer: Regularly check your skin for new or changing moles. See a dermatologist if you notice any unusual growths or spots.
7. Manage Stress and Mental Health
Chronic stress can contribute to inflammation and hormonal imbalances, both of which can increase cancer risk. Taking care of your mental health is just as important as physical health when it comes to cancer prevention.
Prevention Tips:
-
Practice mindfulness: Activities like meditation, yoga, and deep breathing can help reduce stress and promote emotional well-being.
-
Seek support: Talk to friends, family, or a therapist if you are dealing with long-term stress, anxiety, or depression.
8. Avoid Environmental Toxins
Certain environmental toxins are known to increase cancer risk. These can include pollutants, chemicals, and radiation.
Prevention Tips:
-
Limit exposure to carcinogens: Try to avoid environmental factors such as secondhand smoke, pesticides, and industrial chemicals.
-
Use natural cleaning products: Whenever possible, opt for chemical-free cleaning supplies to reduce exposure to toxic substances.
-
Be mindful of indoor air quality: Consider using an air purifier to help reduce airborne toxins.
Conclusion
While we cannot control all the factors that contribute to cancer, we can take proactive steps to reduce our risk. By making smart lifestyle choices, such as eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, quitting smoking, and limiting alcohol, we can significantly lower our cancer risk. Additionally, protecting our skin from the sun, staying on top of regular screenings, and managing stress all play vital roles in cancer prevention. Vaccination against cancer-causing viruses like HPV and Hepatitis B is also a crucial measure for protection.
By adopting these healthy habits, we can live more fulfilling lives while reducing the likelihood of developing cancer in the future. If you notice any concerning symptoms or changes in your body, it’s essential to seek medical attention early for the best possible outcomes.
News in the same category

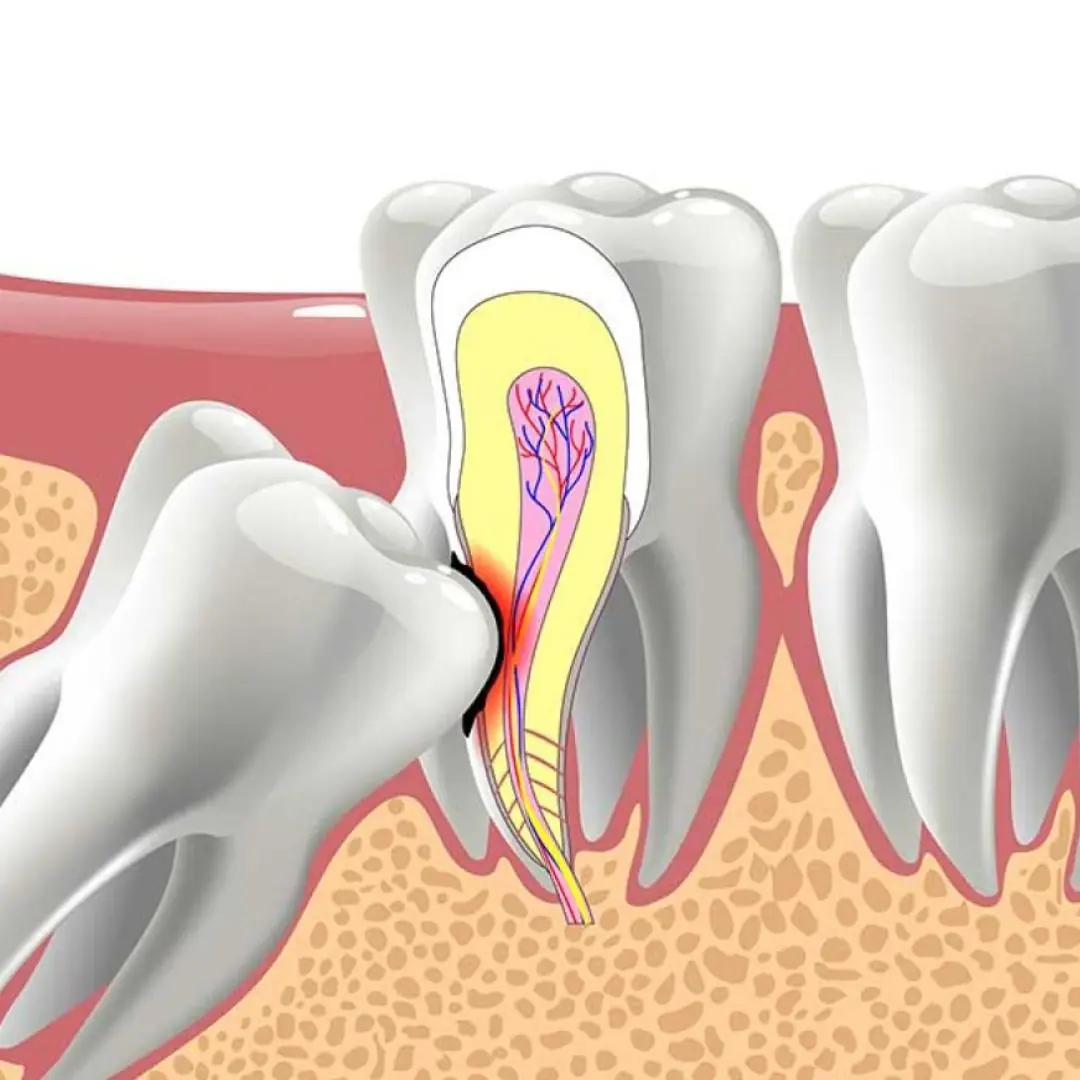
If You Notice These 6 Symptoms, Your Wisdom Tooth May Be Impacted
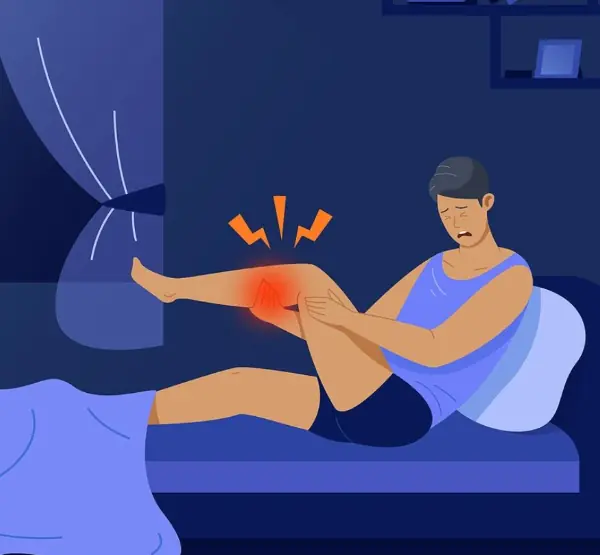
If you have night cramps, this is what your body is trying to tell you
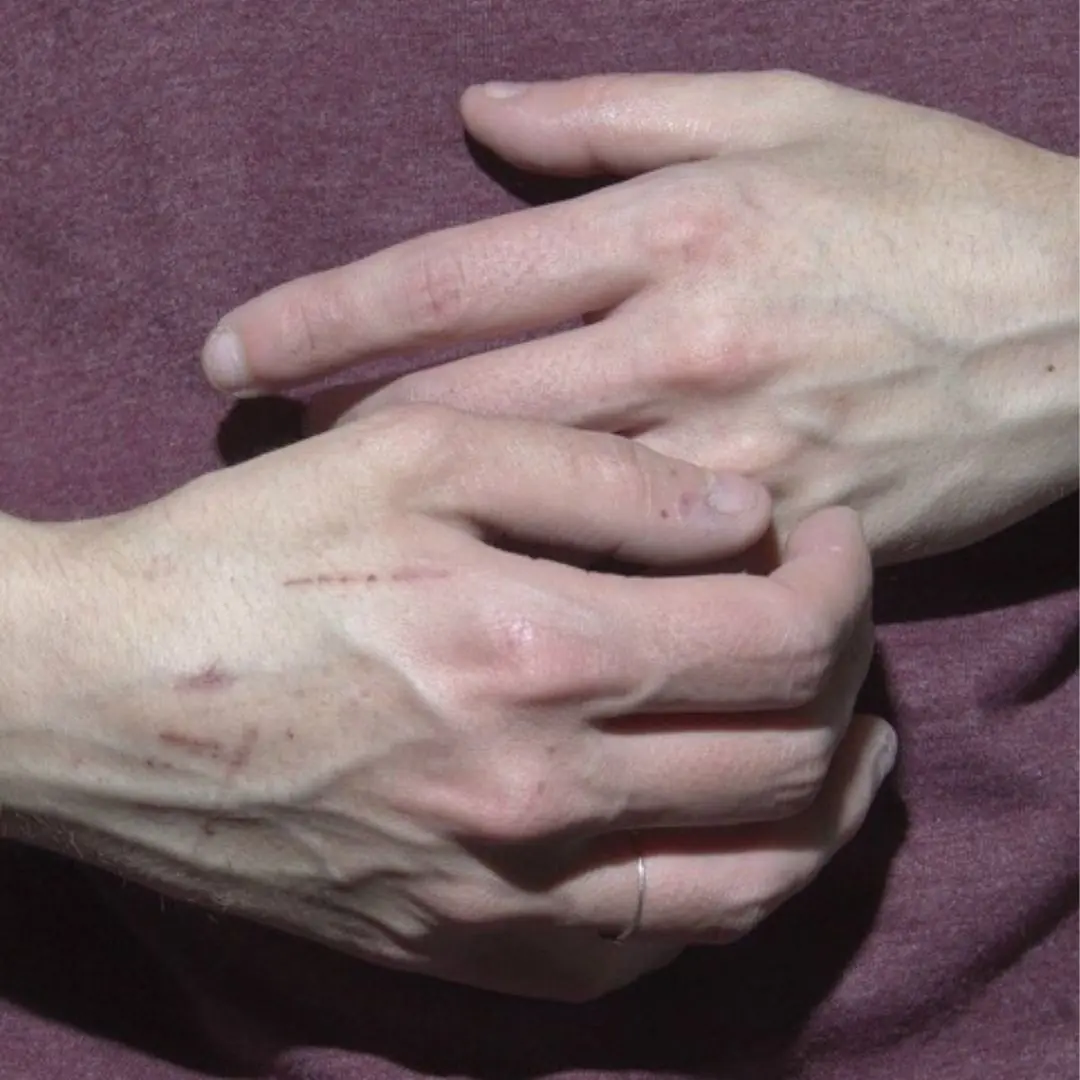
If you see someone with bulging veins, you must tell them these things...
Doctors Find Tapeworms in a US Man's Brain Who Ate Undercooked Pork
Doctors identify the blo.od type most at risk developing stomach can.cer
Surprising causes of hives revealed - What may be triggering your skin
Most stomach can.cers are detected late: Doctors say there are 5 symptoms after meals

Doctor's War:ning: Stop Eating These 4 Foods Immediately They Contain Lots of Parasites

Expert reveals “Military Sleep Method” that helps you fall asleep in just two minutes

Put this thing in a lemon and put it in the corner of the house
The 6 Earliest Symptoms of Liv.er Can.cer Most People Overlook

Too Much Saliva in Your Mouth? It Could Be a Warning of Health Issues
6 types pa.in you shouldn’t ignore

The benefits of carrot and lemon for skin health
Pay attention to these eight major causes of swelling that can occur throughout the body

Experts reveal 5 can.cer symptoms that are easy to ignore
Scientists discover the maximum age a human can live to

Coconut water offers many health benefits — but these 5 groups of people should never drink it, as it could do more harm than good
News Post

The ring you pick will reveal your truest trait
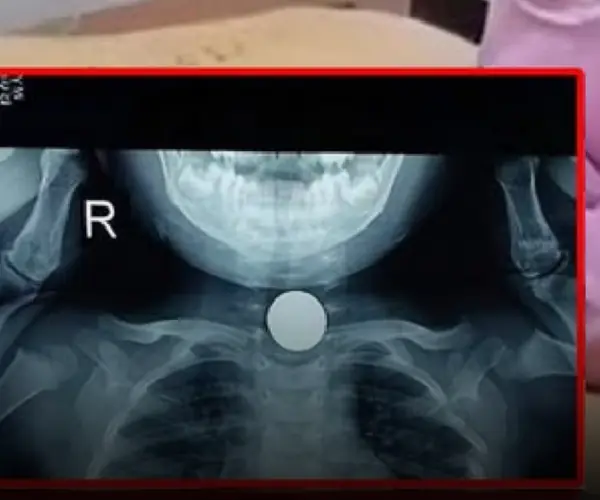
Tra.gedy strikes as 3-year-old girl di.es suddenly while playing with dad - A heartbrheaking reminder about cho.king ha.zards

8 reasons to drink ginger tea before bed

If You Notice These 6 Symptoms, Your Wisdom Tooth May Be Impacted

If you have night cramps, this is what your body is trying to tell you

If you see someone with bulging veins, you must tell them these things...

My In-Laws Demanded I Kick Out My Nephew from Our Wedding Because of His Scars — My Wife Gave Them a Wake-Up Call

Why you shouldn’t sleep with a fan at night?

4 parts of the chicken contain many pa.rasites but many people still eat them without worry

I Bought Food for a Poor Old Man – But a Few Months After He Died, A Dusty Box He'd Owned Arrived for Me

Sweet Potatoes: Who Should Skip Them and Why

Doctors Find Tapeworms in a US Man's Brain Who Ate Undercooked Pork

If you have these two small dimples on your lower back, they reveal something fascinating

Old Farmer’s Advice: “When Buying a Pumpkin, Don’t Look at Its Size — Focus on These 4 Things to Pick the Best One!”

Add These Two Ingredients When Cooking Rice

My Mom Abandoned Me for Money – Years Later, She Came Crawling Back on Her Knees

Cops Target a Homeless Veteran at a Diner, Until He Makes One Phone Call and Ends Their Career

Extraordinary Visual Skills If You Can Spot The Cat
