What happens when joints degenerate?
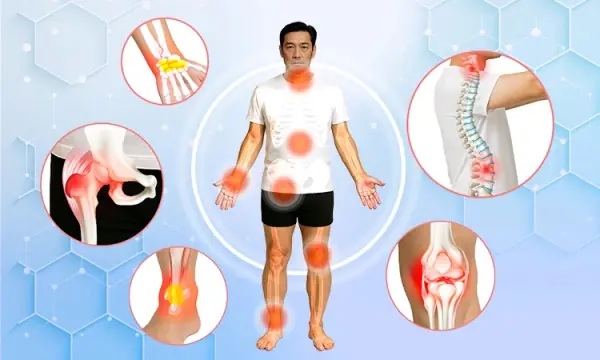
What Happens When Joints Degenerate?
Joint degeneration, also known as osteoarthritis, occurs when the parts of the joint gradually get damaged over time, especially the cartilage that covers the bone ends. This is a natural process often associated with aging, but it can also result from other factors such as injury, genetics, obesity, or other underlying conditions. When a joint degenerates, the symptoms and complications can significantly affect the quality of life. Here's what happens when joints degenerate:
1. Wearing Down and Damage to Cartilage
Cartilage is a smooth, flexible material that cushions the ends of bones in a joint, allowing smooth movement. As joints degenerate, the cartilage wears down and becomes unable to repair itself, causing bones to rub directly against each other. This friction leads to pain and limited mobility of the joint.
2. Joint Pain
Pain is the primary symptom when a joint degenerates. Initially, the pain may only occur during movement, but over time, it can occur even at rest or with changes in weather. The pain tends to worsen after physical activity or long periods of rest.
3. Stiffness
As cartilage wears away, the tissues and fluids in the joint change, making the joint feel stiff and difficult to move, especially after sitting for long periods or upon waking in the morning.
4. Swelling and Inflammation
When cartilage is damaged, the body tries to protect the joint by increasing the production of joint fluid, which can lead to swelling. Inflammation can also occur during the degeneration process, especially when the bones rub against each other, causing irritation and swelling in the area.
5. Reduced Mobility
When a joint degenerates, its ability to move becomes restricted. This makes everyday activities such as walking, climbing stairs, or even sitting down difficult and painful. The loss of flexibility can significantly reduce the quality of life.
6. Joint Deformity
In advanced stages, joint degeneration can lead to deformities, causing the joint to become misaligned and lose its normal shape. This can make it even harder to use the joint and increase pain levels.
7. Grinding or "Cracking" Sounds
When cartilage wears away and bones come into contact with one another, you may hear a grinding or "cracking" sound during movement. This is a clear sign that the parts of the joint are no longer moving smoothly as they should.
Causes of Joint Degeneration:
-
Age: Joint degeneration is a natural process that occurs with age, especially after 40.
-
Joint Injuries: Previous injuries, such as fractures or sprains, can increase the risk of joint degeneration later on.
-
Genetics: Some people are more prone to joint degeneration due to genetic factors.
-
Obesity: Excess body weight puts extra pressure on joints, especially the knees, and speeds up the degeneration process.
-
Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of physical activity reduces joint flexibility and weakens surrounding muscles, leading to faster degeneration.
Treatment for Joint Degeneration:
-
Pain Relief and Anti-inflammatory Medications: Medications like paracetamol or NSAIDs can help reduce pain and inflammation.
-
Physical Therapy: Exercises help strengthen muscles, improve flexibility, and reduce joint stiffness.
-
Surgical Interventions: In severe cases, joint replacement surgery (such as knee or hip replacement) or arthroscopy may be needed to clean the joint.
Conclusion:
Joint degeneration is a natural process, but if left untreated, it can lead to serious health problems and significantly impact quality of life. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, regular exercise, and controlling body weight can help prevent and slow down the degeneration process.
News in the same category

5 habits to prevent colorectal can:cer
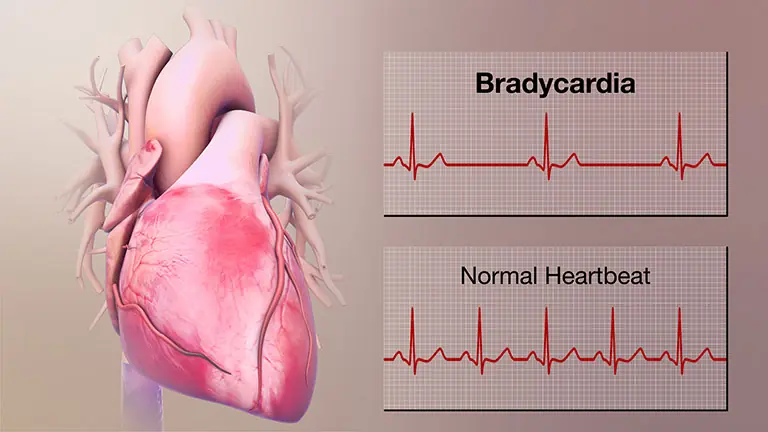
What is the disease of irregular fast and slow heartbeat?
Potential way to cure HIV permanently found

What happens when you eat too much saturated fat?

Japanese Doctor Reveals 3 Everyday Foods That Naturally Boost Immunity and Reduce Frequent Illness

Can.cer May Reveal Itself Through These 2 Nighttime Warning Signs — Everyone Should Be Aware

5 warning signs of oral can:cer

15 Years Can.cer-Free: Japanese Doctor Shares 5 Simple Habits to Keep Can.cer Cells from Returning

Diabetics are ‘very afraid’ of a spice that is abundant in the market: American experts say it is ‘as good as prescription drugs’

Rub Ginger on the Soles of Your Feet Before Bed, and You’ll Experience Its “Miraculous” Health Benefits

Pare de comer estes 4 alimentos imediatamente Eles contêm muitos parasitas

What happens to your body if you drink orange juice every day?

A cup of hot water can offer many health benefits
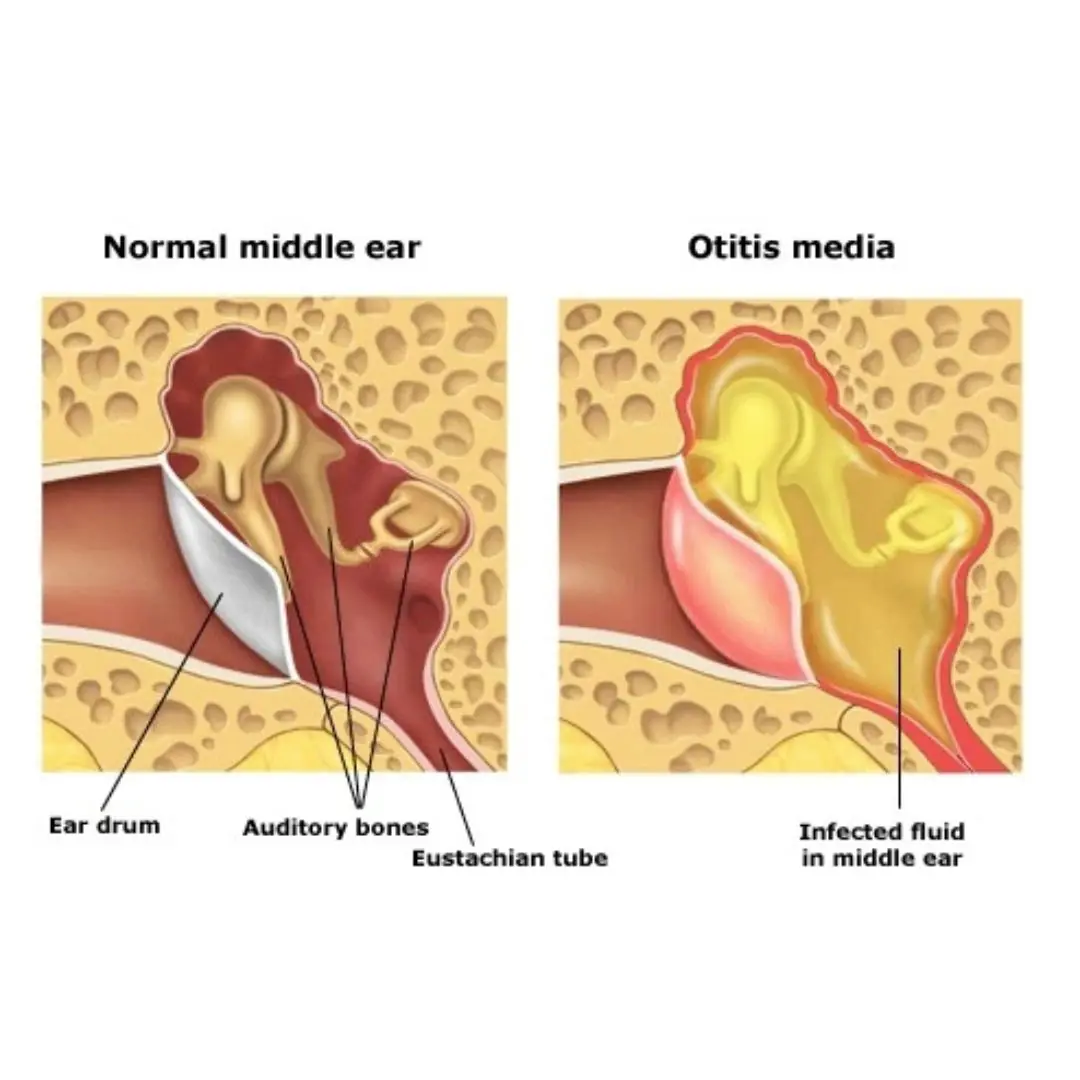
Otitis media – the “hidden culprit” causing vestibular disorders that many people ignore

Don't drink water before bed but still urinate at night, beware of these 3 diseases

4 changes in fingers that could be signs of lung can.cer
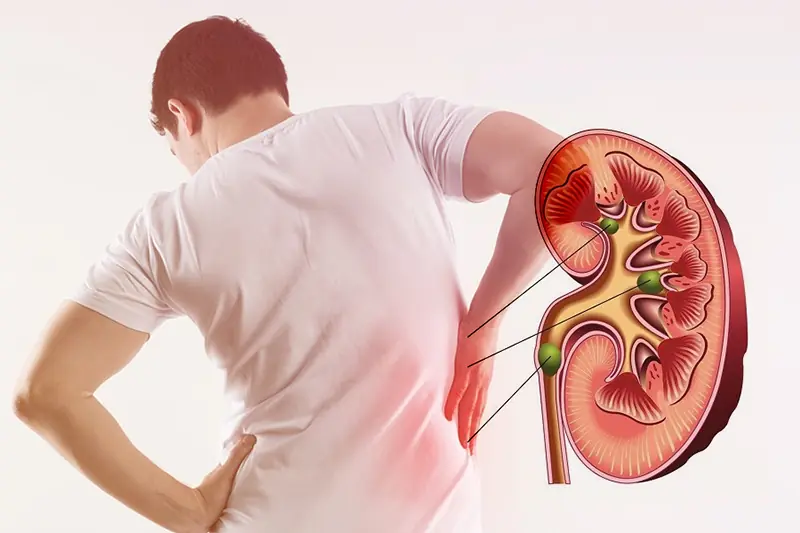
8 symptoms of kidney fai.lure you should never ignore

3 things that don’t go well with eggs
News Post

Growing Beautiful Bell Peppers in Sunny SoCal

Should you turn the lights on or off when sleeping in a hotel?

10 Brilliant Uses For Eggshells In Your Garden

What To Eat During Your Period: Foods That Help Reduce Cramps and Foods To Avoid

5 Tips to Grow Basil Like a Boss

RM, V, Jung Kook, and Jimin will soon be discharged from the military

5 habits to prevent colorectal can:cer

What is the disease of irregular fast and slow heartbeat?

How many eggs should you eat a week?

Potential way to cure HIV permanently found

What happens when you eat too much saturated fat?

Transform your garden with the magic of turmeric!

Japanese Doctor Reveals 3 Everyday Foods That Naturally Boost Immunity and Reduce Frequent Illness

Is Tightly Wrapped or Loosely Wrapped Cabbage Better?

3 Common Mistakes When Eating Shrimp That Strip Away All Its Nutrients — Especially the Second One

Can.cer May Reveal Itself Through These 2 Nighttime Warning Signs — Everyone Should Be Aware

When Buying Shrimp, Be Extra Cautious to Avoid These 5 Types of Harmful “Hormone Shrimp”
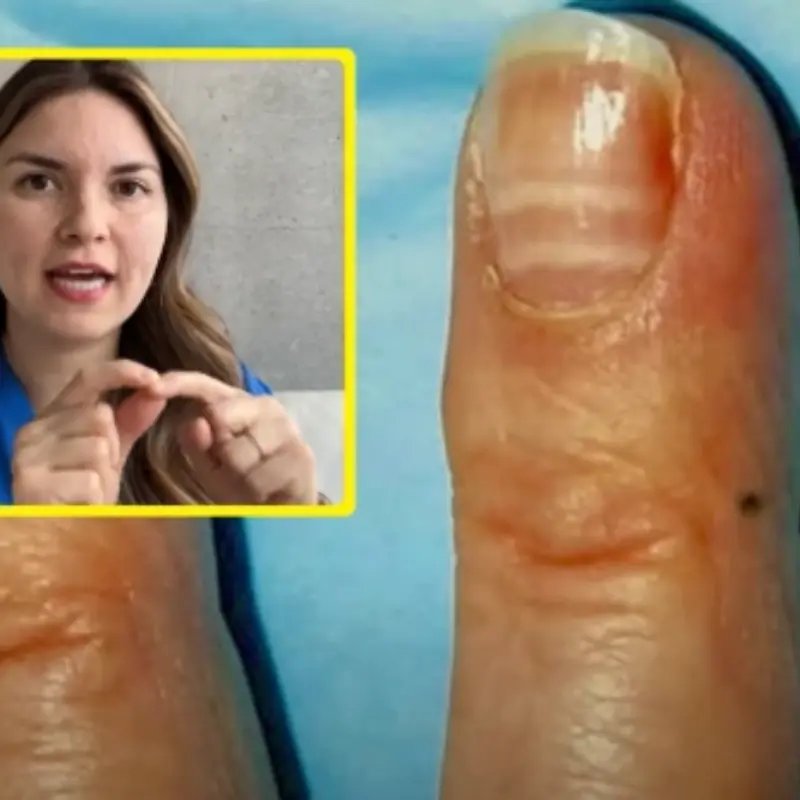
10 Visible Signs of Liver Damage You Can Spot with the Naked Eye
