When you have a painless lump, don't 'guess' whether it's good or bad, a late examination can lead to a disability
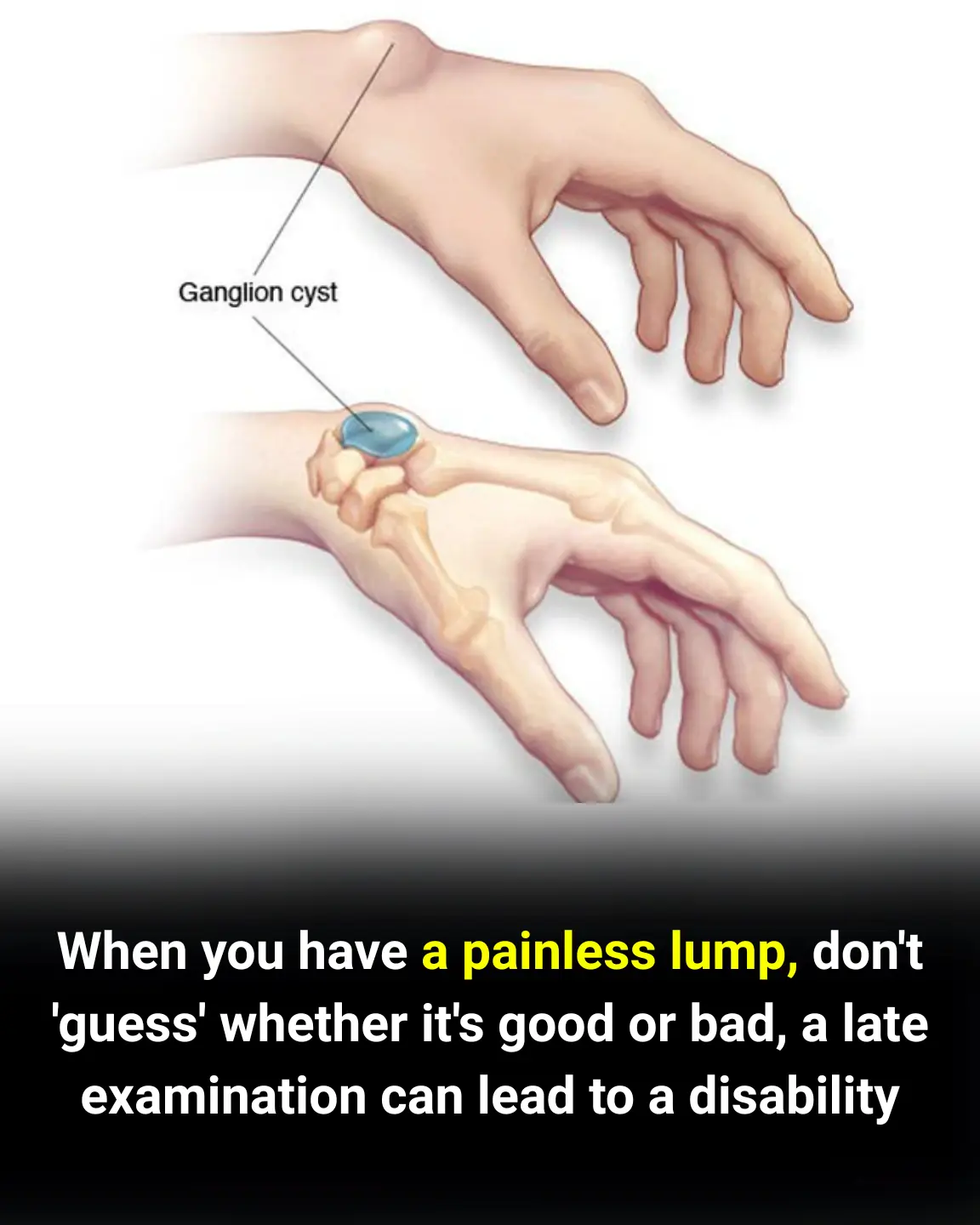
Is It Cancer? Understanding Painless Lumps That Appear on the Wrist, Ankle, or Other Areas
In daily life, we often notice small lumps forming on our own or our family members’ bodies — commonly around the wrist, ankle, or other joints. These lumps may feel smooth, soft, movable under the skin, and painless, yet they often cause concern. Many wonder: could it be cancer?
This article is based on insights from Associate Professor Dr. Ma Tan Binh, Department of Surgery, First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, China.
So, are these lumps dangerous? Are they benign or malignant? Could they cause harm or turn cancerous over time?
🧠 What Is a Ganglion Cyst?
These lumps are most commonly ganglion cysts, also referred to as synovial cysts or "Bible cysts." They frequently occur in women and are common among people who work with their hands, such as craftsmen, laborers, athletes, or homemakers.
Medically, a ganglion cyst is a noncancerous lump that develops along joints or tendons, usually on the wrist or hand, but also commonly seen on the ankle or foot. It resembles a fluid-filled sac — although the fluid is typically a thick, clear, jelly-like substance. The lump may feel soft or firm depending on the consistency and depth.
Ganglion cysts vary in size and may sometimes appear larger due to the presence of multiple interconnected small cysts. Although usually harmless, they account for approximately 50% of soft tissue tumors in the hand.
Besides the wrist, these cysts can also form near the fingers, fingertips, the side of the knee, ankle, or top of the foot — often becoming a cosmetic concern, especially for women.
🧬 What Causes Ganglion Cysts?
The exact cause remains unclear. One theory suggests that joint or tendon irritation or trauma leads to the degeneration of surrounding tissue, resulting in fluid accumulation that forms a cyst.
Additionally, repetitive stress, fixed working postures, or the habit of frequently pressing or rubbing certain areas can contribute to cyst formation.
🔍 How to Identify a Ganglion Cyst?
Ganglion cysts typically present with the following features:
-
A single or multiple lumps appear suddenly or gradually
-
Usually soft and round, measuring 1–3 cm in diameter
-
Generally immobile or slightly movable
-
May fluctuate in size — enlarging, shrinking, disappearing, or reappearing
-
About 35% of people experience no symptoms
-
If painful, it’s often due to joint movement or nerve compression
-
When attached to a tendon, it may cause weakness or reduced function in nearby fingers
Is Every Lump a Ganglion Cyst?
Not necessarily. Some lumps could be due to tenosynovitis (inflammation of the tendon sheath). Early symptoms include localized pain or stiffness. As the condition progresses, patients may find it difficult to bend the affected fingers or wrist.
In wrist tenosynovitis, morning stiffness is common, and clicking sounds may be heard during movement. Symptoms typically improve with warmth or massage, but if left untreated, it can lead to limited motion or even deformity.
⚠️ When to See a Doctor?
In most cases, ganglion cysts are not dangerous and primarily affect appearance. However, a medical evaluation is recommended if:
-
You feel concerned or anxious
-
The lump is rapidly growing or painful
-
There is a loss of function or sensation in the affected area
-
You want to rule out malignancy or other rare conditions
Rarely, vascular tumors like glomus tumors may present as small (≈2 mm), extremely painful lumps near the nails or under the skin, with burning or tingling sensations. These should be evaluated promptly.
🧑⚕️ Final Note
Most ganglion cysts grow slowly and may remain stable or even resolve spontaneously. However, some may compress nearby nerves or tendons and require treatment. While not an emergency, it's advisable to consult a healthcare professional — especially if the lump changes, causes discomfort, or affects movement — to ensure accurate diagnosis and peace of mind.
News in the same category


Woman hospitalized in coma, doctor warns: "Eating dinner like this will only k.i.ll you"
Doing These 4 Things at Night Could Trigger an Early Stro.ke—Be Wa.rned!
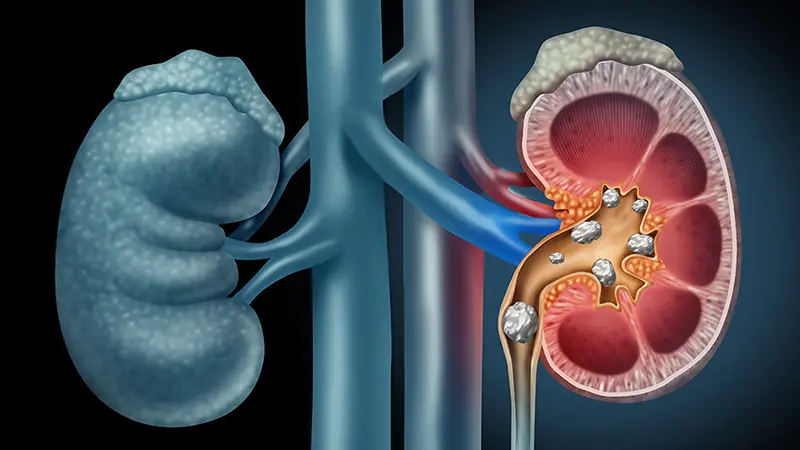
5 Drinks That Help Dissolve Kid.ney Stones and Promote Easy Elimination

Is static electricity in winter dan.g.erous to health?

Don’t Miss These 9 Key Signs of Depression — Early Awareness Can Save Lives

Doctor reveals the "golden key" to healthy blood: Very easy to do but few people pay attention
Silent Signs of Kid.ney Can.cer That Are Easy to Overlook
Silent signs of kidney can.cer are easily overlooked

Diabetes Alert: 6 Fruits That Could Sabotage Your Bl.o.od Sugar Levels

These 3 vegetables have a high risk of causing ca.n.cer. Know early to avoid them and tell your loved ones!

If you suddenly wake up between 3:07 and 3:15 a.m., you must be very careful.
14-Year-Old Patient Suffers Facial Paralysis Due to Common Habit During Hot Weather

4 Vegetables You Should Never Eat Raw — They Could Do More Harm Than Good!

6 familiar dishes that are extremely dan.ger.ous if left overnight
Doctor Urges 4 Actions to Protect Your Body’s "Blo.od Filter"

Can overly hot baths harm your heart and circulation?
7 signs of brain c.a.ncer that are easily confused with other diseases

4 Things to Avoid After 5 PM to Lower Your Risk of Stro.ke
News Post

6 dishwashing habits that "invite trouble" that many families are making!

Eating habits d.e.stroy 18 year old girl's kidneys
Alzheimer’s May Not Originate in the Brain, Scientists Suggest

Don’t rinse r.a.w chicken: nine food safety tips from microbiologists

Woman hospitalized in coma, doctor warns: "Eating dinner like this will only k.i.ll you"

Doing These 4 Things at Night Could Trigger an Early Stro.ke—Be Wa.rned!

Even If You're Loaded, Don't Buy These 5 Types of Shrimp at the Market

Connect to Free Wi-Fi Without a Password in Just One Step

Beleaguered Weather Service defends its forecasts as Texas officials point fingers over flood warnings

Say Goodbye to Yellow Stains: Best Ways to Clean Your Phone Case

A Glass of Milk a Day Could Help Lower Women's Risk of Color.ec.tal Can.cer

A Common Ingredient in Energy Drinks May Be Linked to Blo.od Can.cer

What Your Finger Length Could Reveal About Your Cardio Fitness

Is 'Razor Blade Throat' Really a Sign of the Newest COVID Variant?
USA: Successfully tested a special dru.g that can elimi.nate up to 70 types of can.cer

See These 5 Fish at the Market? Grab Them Before They're Gone

5 Drinks That Help Dissolve Kid.ney Stones and Promote Easy Elimination

Place This Bunch of Leaves in Your Room
