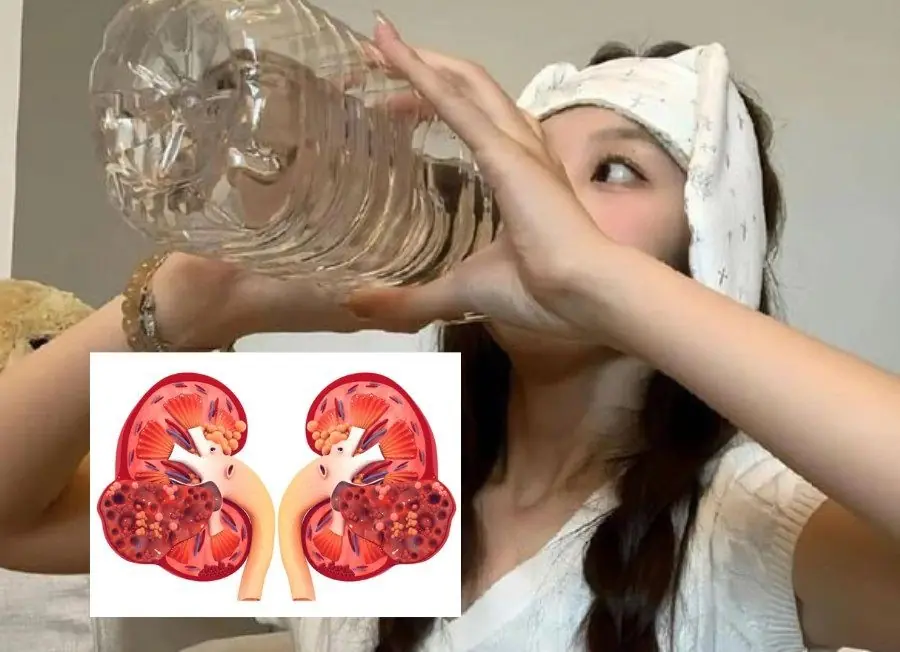
You may be damaging your kidneys and liver every day
You may be damaging your kidneys and liver every day




You may be damaging your kidneys and liver every day
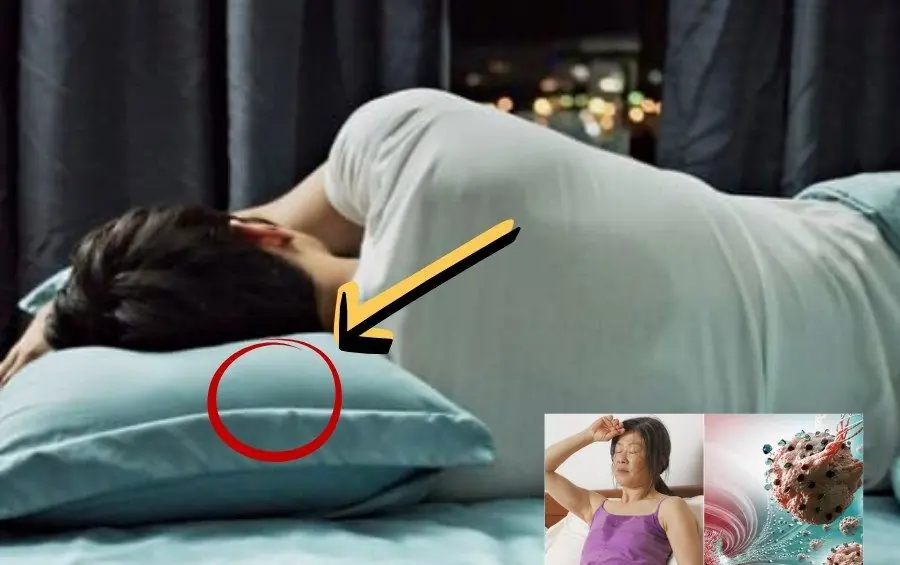

Strange marks on your pillow don’t automatically mean can:cer
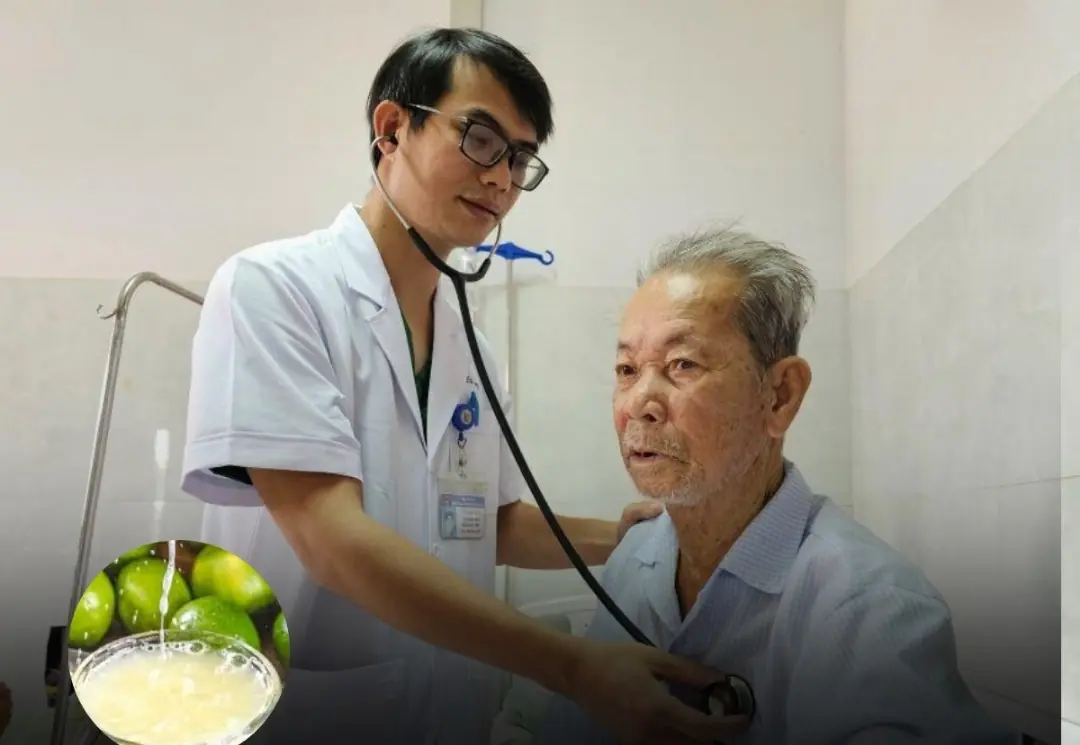
70-year-old man drinks lemon water to treat high blo.od pressure for 2 years
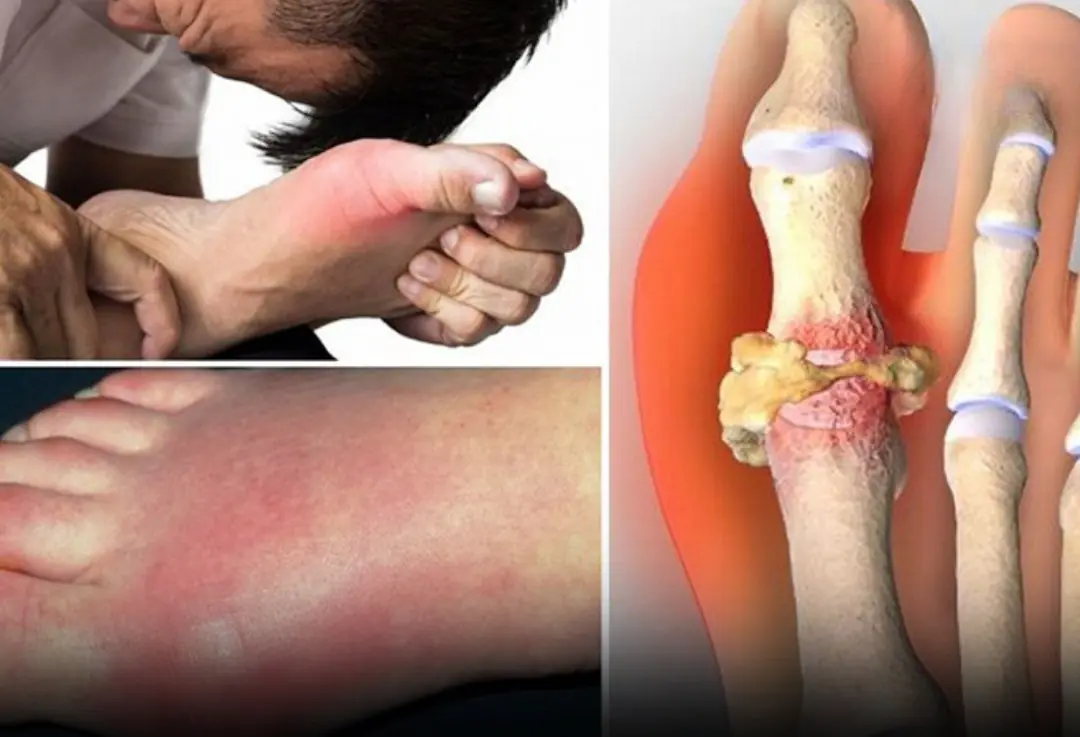
Gout is becoming increasingly common, and if you have it, certain foods should be strictly avoided to prevent painful flare-ups
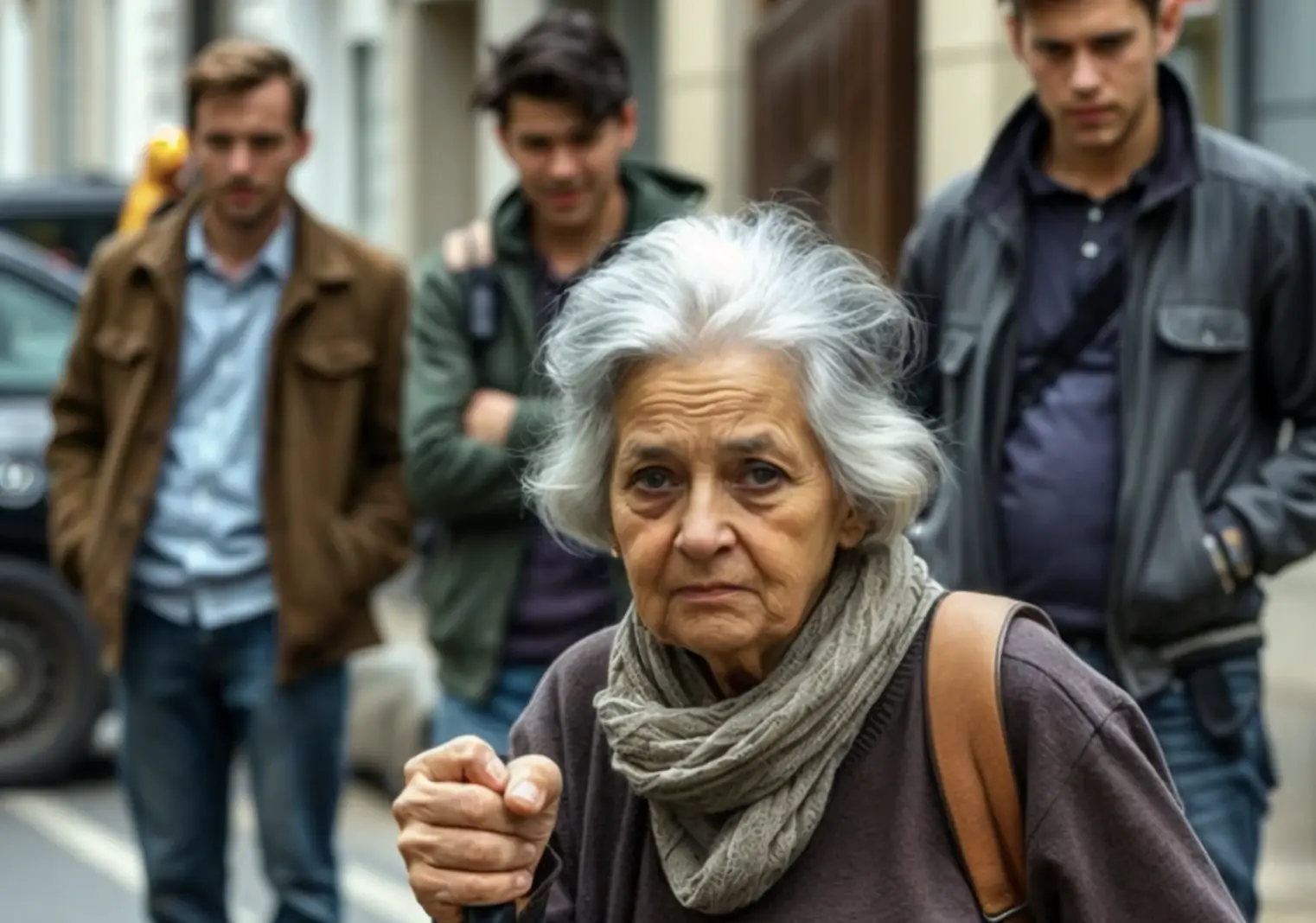

The lonely old woman admonished the swearing teenagers on the playground. But then something happened…
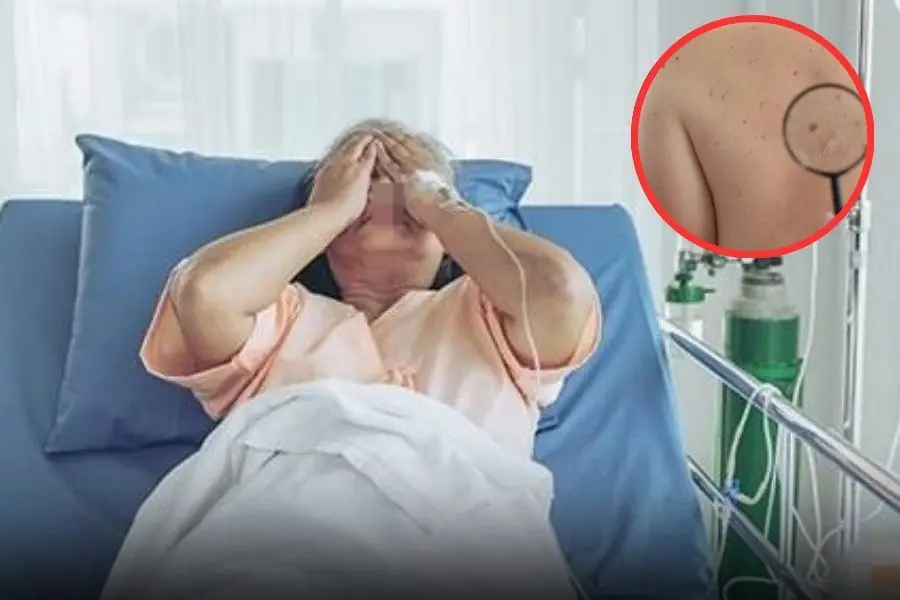
These 6 warning signs often appear late — ignoring them could cost precious time.














You may be damaging your kidneys and liver every day

Strange marks on your pillow don’t automatically mean can:cer

“My ex said, ‘We’ve got nowhere to live with my new wife, let us stay at your summer house.’ I let them in… then I called the police and filed a report for breaking and entering.”

70-year-old man drinks lemon water to treat high blo.od pressure for 2 years

Gout is becoming increasingly common, and if you have it, certain foods should be strictly avoided to prevent painful flare-ups

The lonely old woman admonished the swearing teenagers on the playground. But then something happened…

These 6 warning signs often appear late — ignoring them could cost precious time.











