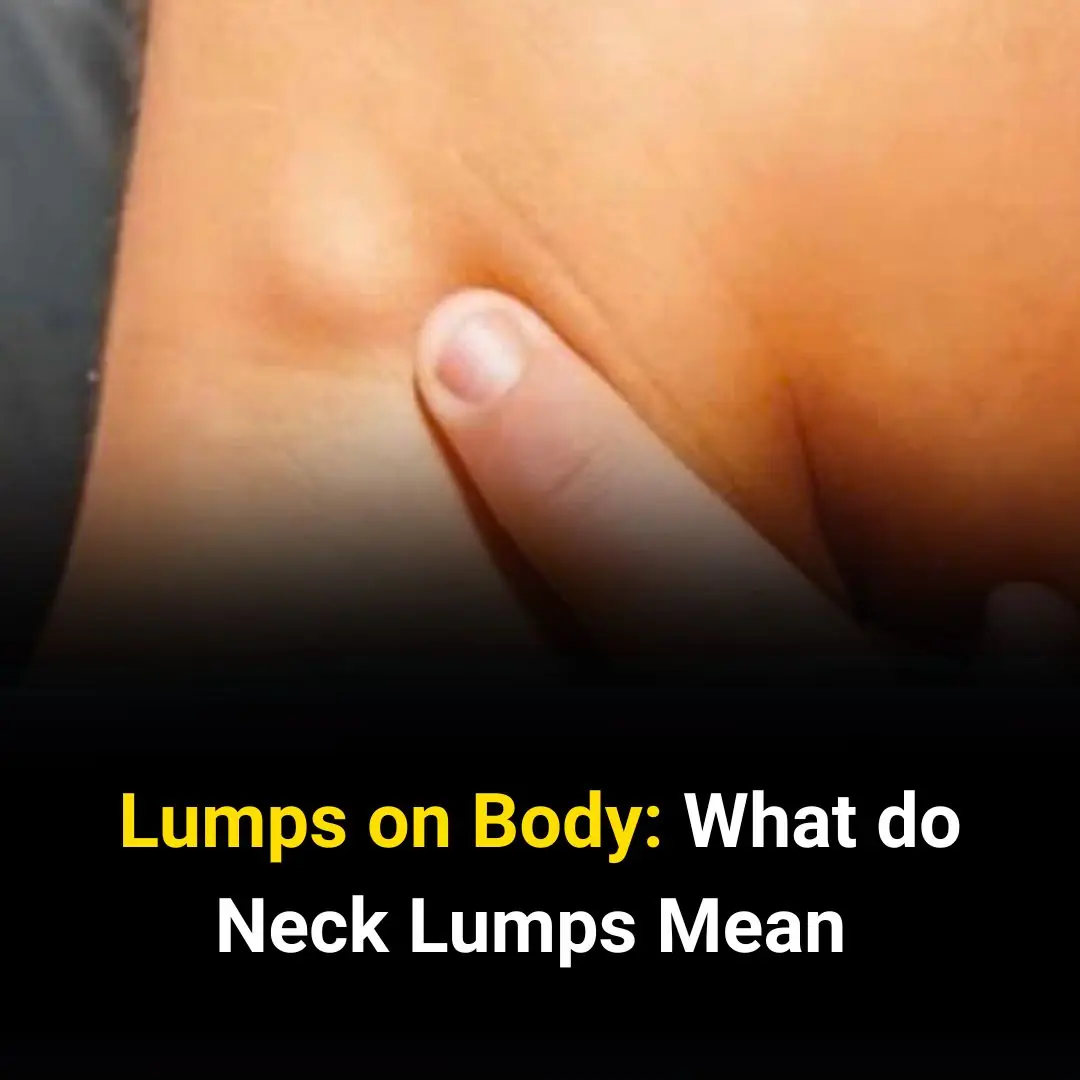
Neck lumps, or swollen lymph nodes, can indicate a variety of conditions. While some are harmless, others may require medical attention. Here are the most common causes of neck lumps:
1. Infections:
- Viral Infections: Common colds, the flu, or mononucleosis (mono) can cause the lymph nodes in your neck to swell as your body fights the infection.
- Bacterial Infections: Throat infections like strep throat, abscesses, or skin infections can also lead to swollen lymph nodes.
- Tuberculosis: This bacterial infection can sometimes cause lumps in the neck, particularly in the lymph nodes.
2. Enlarged Lymph Nodes (Lymphadenopathy):
- Causes: Lymph nodes can enlarge due to infection, inflammation, or more serious conditions like cancer. Lymph nodes are part of the immune system and become swollen when fighting infections or diseases.
- Tenderness: Lumps that are tender or painful are often due to infections, whereas painless lumps may suggest other underlying conditions.
3. Cysts:
- Types of Cysts: A branchial cleft cyst is a congenital abnormality that can cause lumps on the side of the neck. Thyroglossal duct cysts can also form in the midline of the neck.
- Symptoms: Cysts are usually round, smooth, and can move when touched. They might not be painful unless infected.
4. Thyroid Disorders:
- Goiter: An enlargement of the thyroid gland can lead to a visible lump in the neck. This is commonly caused by iodine deficiency, autoimmune diseases like Hashimoto's thyroiditis, or thyroid nodules.
- Thyroid Cancer: A hard, painless lump in the neck, especially one that changes in size or texture, could be a sign of thyroid cancer.
5. Cancer:
- Metastatic Cancer: Lumps in the neck could be a sign of cancer that has spread from other parts of the body, such as head and neck cancers, lymphoma, or cancers of the lungs, breast, or digestive tract.
- Lymphoma: Swollen, painless lymph nodes that do not shrink or go away could be indicative of lymphoma, a type of blood cancer.
6. Salivary Gland Issues:
- Infections or Blockages: Swelling near the jaw or under the ear can be due to infections or blockages in the salivary glands. Sialadenitis (salivary gland infection) or sialolithiasis (salivary gland stones) can cause lumps.
7. Injury or Trauma:
- Lumps from Injury: If you've recently sustained an injury to the neck, it could cause swelling or a lump due to the accumulation of fluids or blood under the skin.
8. Lipomas:
- Benign Growths: Lipomas are non-cancerous fatty growths that can appear as soft lumps under the skin. They are usually harmless and painless but may need to be removed if they grow too large or cause discomfort.
When to See a Doctor:
While neck lumps are often benign and related to common conditions like infections, you should see a doctor if:
- The lump is hard, fixed in place, or doesn’t move.
- It is painless but continues to grow.
- You experience other symptoms like unexplained weight loss, fever, night sweats, or fatigue.
- The lump persists for more than two weeks without improvement.
A healthcare provider can perform a physical exam, order tests, and possibly a biopsy to determine the cause of the lump. Early detection and treatment can be crucial, especially in cases of cancer or other serious conditions.