
3 signs at night while you’re sleeping that could mean can.cer

Can.cer is often diagnosed when its symptoms become apparent during the day or when individuals seek medical attention for unusual physical changes. However, certain signs of cancer can appear during the night, while you're sleeping, or as you wake up. These subtle changes may not immediately raise alarms, but they could be early indicators of underlying health issues, including can.cer. Recognizing these signs could potentially lead to early diagnosis and improve treatment outcomes. In this article, we will discuss three signs you might notice during the night while you're sleeping that could be related to can.cer.
1. Persistent Night Sweats
Night sweats, or excessive sweating during the night, are more than just an inconvenience. While night sweats can happen due to a variety of reasons, including menopause, infections, or certain medications, they can also be a sign of more serious conditions like cancer. For instance, night sweats are a common symptom of lymphoma, a type of cancer that affects the lymphatic system.
When cancer cells multiply in the lymph nodes or other parts of the body, they can trigger the body’s immune response, leading to fever and night sweats. These sweats often occur in episodes, soaking through pajamas or sheets, and may be accompanied by a low-grade fever.
Why it’s important:
Night sweats are a symptom that should not be ignored, especially if they occur regularly without an obvious cause. While they’re often attributed to hormonal changes or infections, persistent night sweats that occur over a period of weeks or months warrant a visit to the doctor for further investigation.
What to do:
If you experience frequent and unexplained night sweats, consult a healthcare provider to rule out infections or more serious underlying conditions, including cancer. A thorough medical evaluation and possible blood tests or imaging may be needed to identify the root cause.
2. Unexplained Weight Loss While Sleeping
Unintentional weight loss is one of the more alarming symptoms that can be associated with can.cer. This weight loss often occurs gradually and without any change in diet or exercise habits. If you find yourself losing weight during the night without any clear explanation, this could be a sign that something more serious is going on, such as cancer.
Certain can.cers, particularly those that affect the digestive system, lungs, or pancreas, can cause weight loss as they interfere with the body's ability to absorb nutrients or lead to increased metabolic demands. Additionally, night sweats and fatigue that often accompany can.cer can further contribute to this weight loss.
Why it’s important:
Unexplained weight loss can signal that the body is fighting off something significant, such as can.cer. While weight loss can also be a symptom of many other conditions, can.cer-related weight loss is often accompanied by other symptoms, like fatigue, pain, or changes in appetite.
What to do:
If you are noticing unexplained weight loss over time, along with other concerning symptoms like fatigue or night sweats, it’s important to seek medical attention. Your doctor can perform a physical examination and recommend appropriate tests, such as blo.od work, imaging, or a biopsy, to rule out can.cer or other underlying health problems.
3. Trouble Breathing or Shortness of Breath While Sleeping
Shortness of breath, or difficulty breathing while lying down, can be a concerning symptom that might not immediately be linked to can.cer. However, in certain can.cers, particularly lung cancer or cancers that have metastasized to the lungs, shortness of breath can be a key indicator.
When can.cer grows in the lungs or surrounding areas, it can block airways or compress lung tissue, making it difficult to breathe, even when you’re resting at night. If you notice that you’re waking up suddenly in the middle of the night feeling out of breath, or if you need to prop yourself up to breathe comfortably, this could be a sign of lung or pleural cancer. Additionally, if you wake up with a dry cough or find that you’re feeling short of breath after minimal exertion, it could also point to something more serious, including cancer.
Why it’s important:
Difficulty breathing or shortness of breath should always be taken seriously, as it can indicate that the lungs or heart are not functioning properly. If you notice this symptom during the night, it’s crucial to seek medical help to get a proper diagnosis.
What to do:
If you experience sudden or unexplained shortness of breath at night, or if you find yourself waking up gasping for air, see your doctor immediately. A thorough examination, which may include imaging like a chest X-ray or CT scan, can help determine whether cancer is affecting your lungs or other respiratory structures.
Additional Night-Time Symptoms to Watch For
While the three signs above are the most commonly associated with cancer, there are other subtle symptoms that could also appear during the night, including:
-
Persistent coughing or wheezing: A cough that worsens at night, particularly if it’s producing blood or mucus, can be a sign of lung cancer or respiratory infections associated with cancer.
-
Severe headaches: If you experience frequent headaches that seem to worsen when you lie down, or if they are accompanied by nausea or vision problems, it could indicate a brain tumor or metastasis.
-
Changes in sleep patterns: Difficulty falling or staying asleep, especially if it’s linked to pain or discomfort, should be addressed by a healthcare provider.
Conclusion: Why Early Detection Matters
When it comes to can.cer, early detection is crucial for improving treatment outcomes and survival rates. Many can.cers, particularly lung, lymphoma, and gastrointestinal cancers, have subtle symptoms that develop gradually and may be overlooked as normal bodily changes. By recognizing these warning signs, particularly those that occur while you’re sleeping, you can take proactive steps to seek medical attention early.
If you experience any of the symptoms discussed in this article - whether it’s persistent night sweats, unexplained weight loss, or difficulty breathing during the night - don’t wait to seek medical advice. Early intervention can significantly improve the prognosis and make treatment more effective, potentially saving lives.
Remember, your health is your responsibility, and recognizing the subtle signs your body gives you, even at night, is one of the most important steps you can take toward staying healthy and preventing cancer. Always listen to your body, and never hesitate to consult a healthcare professional if something feels wrong.
Additional Ways to Prevent Cancer: Lifestyle Changes and Healthy Habits
While recognizing the early signs of cancer is crucial for early detection and treatment, prevention is always the best approach. Adopting healthy habits and making informed lifestyle choices can significantly reduce the risk of developing cancer. Here are some additional ways to prevent cancer and support your overall health.
1. Quit Smoking and Avoid Tobacco Products
Tobacco use is the leading cause of preventable cancer, responsible for an estimated 22% of all cancer-related deaths. Smoking is strongly linked to lung cancer, but it also increases the risk of other cancers, including those of the mouth, throat, pancreas, bladder, and kidneys.
Why it’s important:
-
Smoking damages DNA in cells and weakens the body’s ability to repair itself, promoting the development of cancer.
-
Secondhand smoke is also dangerous, raising the risk of lung cancer and other cancers in non-smokers who are exposed to it regularly.
What to do:
-
Quitting smoking, no matter your age, can drastically reduce your cancer risk. Seek support through smoking cessation programs, nicotine replacement therapies, or counseling.
-
Avoid exposure to secondhand smoke by staying away from smoky environments and advocating for smoke-free areas.
2. Limit Alcohol Consumption
Drinking alcohol is linked to a higher risk of developing several types of cancer, including breast cancer, liver cancer, colorectal cancer, and esophageal cancer. The more alcohol you drink, the higher the risk, and there is no "safe" amount of alcohol when it comes to cancer prevention.
Why it’s important:
-
Alcohol can increase the levels of certain hormones, like estrogen, which is linked to breast cancer.
-
It also damages cells in the body and promotes inflammation, both of which can lead to cancerous mutations.
What to do:
-
Limit your alcohol intake to reduce your cancer risk. The American Cancer Society recommends no more than one drink per day for women and two for men.
-
Consider cutting back or eliminating alcohol from your life to protect your overall health.
3. Maintain a Healthy Weight
Obesity is a significant risk factor for cancer, contributing to the development of cancers such as breast, colon, endometrial, and kidney cancer. Excess body fat, especially visceral fat (fat around the organs), can lead to inflammation and hormonal changes that increase cancer risk.
Why it’s important:
-
Maintaining a healthy weight reduces the risk of cancer by improving the body's ability to regulate hormones, reduce inflammation, and maintain optimal immune function.
-
Being overweight or obese also contributes to other health problems, such as diabetes and heart disease, which can further increase cancer risk.
What to do:
-
Aim for a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Limit the consumption of processed foods and sugary drinks.
-
Incorporate regular exercise into your routine to help maintain a healthy weight. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week.
4. Protect Your Skin from the Sun
Skin cancer is one of the most common types of cancer, and exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun is the primary cause. Sunburns, especially in childhood, can increase the risk of developing melanoma and other types of skin cancer later in life.
Why it’s important:
-
UV radiation can damage the skin’s DNA, leading to skin cancer.
-
Even on cloudy days or in winter, UV rays can penetrate the skin and cause damage.
What to do:
-
Protect your skin by applying sunscreen with a broad-spectrum SPF of 30 or higher whenever you’re outside. Reapply every two hours, or more often if swimming or sweating.
-
Wear protective clothing, such as hats, sunglasses, and long sleeves, especially during peak sun hours (10 a.m. to 4 p.m.).
-
Avoid tanning beds, as they also emit harmful UV radiation.
5. Get Vaccinated Against Cancer-Related Viruses
Certain viruses are known to increase the risk of developing specific types of cancer. Vaccines are available to protect against these viruses and reduce the likelihood of cancer development.
-
HPV Vaccine: The human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine helps prevent HPV-related cancers, such as cervical, anal, and throat cancers. HPV is a common sexually transmitted virus that can cause changes in the cells of the cervix and other areas, which may lead to cancer.
-
Hepatitis B Vaccine: Hepatitis B is a viral infection that can cause liver damage, leading to liver cancer. Getting vaccinated against hepatitis B can lower the risk of liver cancer, particularly for those at higher risk of contracting the virus.
Why it’s important:
-
Vaccines help protect against viruses that are responsible for a significant percentage of cancer cases worldwide.
-
Early vaccination before exposure to these viruses is most effective in preventing cancer.
What to do:
-
Ensure that children and adolescents receive the HPV vaccine as recommended by healthcare providers.
-
Consider the hepatitis B vaccine if you’re at increased risk, particularly for healthcare workers or people with chronic liver conditions.
6. Exercise Regularly
Regular physical activity not only helps maintain a healthy weight but also improves overall health and reduces cancer risk. Exercise helps regulate hormones like estrogen, which is linked to breast cancer, and reduces inflammation, which can contribute to cancer development.
Why it’s important:
-
Physical activity helps improve blood circulation, boosts immune function, and reduces the levels of growth factors in the body that contribute to cancer development.
-
It also improves cardiovascular health, reducing the risk of heart disease and other chronic conditions.
What to do:
-
Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise, such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming, five times a week.
-
Include strength training exercises to improve muscle mass and support metabolic health.
7. Limit Exposure to Environmental Toxins
Environmental factors like pollution, chemicals, and radiation can increase the risk of cancer. Certain industrial chemicals, pesticides, and asbestos have been linked to lung cancer, mesothelioma, and other cancers. Additionally, air pollution is now recognized as a carcinogen that increases the risk of lung cancer.
Why it’s important:
-
Long-term exposure to carcinogenic substances can damage cells and increase cancer risk.
-
Minimizing exposure to harmful chemicals and pollutants is essential for reducing environmental cancer risks.
What to do:
-
Reduce exposure to chemicals by using natural or organic products when possible, particularly in your home and garden.
-
Advocate for cleaner air policies and reduce personal exposure to polluted environments.
8. Practice Regular Cancer Screenings
Even if you’re living a healthy lifestyle, regular cancer screenings can help detect cancer early when it is most treatable. For example, mammograms can detect breast cancer, Pap smears and HPV tests can screen for cervical cancer, and colonoscopies can find colorectal cancer in its early stages.
Why it’s important:
-
Screening tests help detect cancer before symptoms appear, improving the chances of successful treatment.
-
Early-stage cancers are often easier to treat, less aggressive, and less likely to spread.
What to do:
-
Talk to your doctor about your risk factors and when to begin regular screenings based on your age, family history, and lifestyle.
-
Follow the recommended screening schedules for various cancers, such as breast, cervical, colorectal, and prostate cancer.
Conclusion: Prevention is Empowerment
While not all cancers can be prevented, many can be reduced by making healthier choices and adopting preventive measures. Quitting smoking, maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, protecting your skin from the sun, and getting vaccinated against cancer-related viruses are key steps in reducing cancer risk.
In addition to these preventive measures, regular check-ups and screenings can catch cancer in its earliest, most treatable stages. By taking proactive steps today, you can improve your health and reduce the likelihood of developing cancer, ultimately leading to a longer, healthier life. Remember, prevention starts with awareness and action. Stay informed, make healthy choices, and always consult with your healthcare provider about your personal cancer risk and prevention plan.
News in the same category

6 Foot Symptoms That May Warn of a Heart Attack Weeks in Advance
12 signs that may signal a brain aneurysm — Don’t ignore them

If Your Legs Cramp at Night You Need to Know This Immediately
3 Dangerous Habits of Husbands That Secretly Put Their Wives at Higher Risk of Cervical Cancer

Husbands With These 2 Bad Habits May Put Their Wives at Higher Risk of Br:east Can:cer
Only 20 years old but the liver is already old: The 'culprit' is a type of water and a type of food that many people love

Why should m.en eat a slice of ginger after waking up in the morning?

3 types of fruit cooked are many times better than eating them raw, help brighten skin, cure diseases well without wasting money on medicine

Caution! 3 Groups of People Should Stay Away from Perilla Leaf Water

8 war.ning signs of unhealthy kidneys
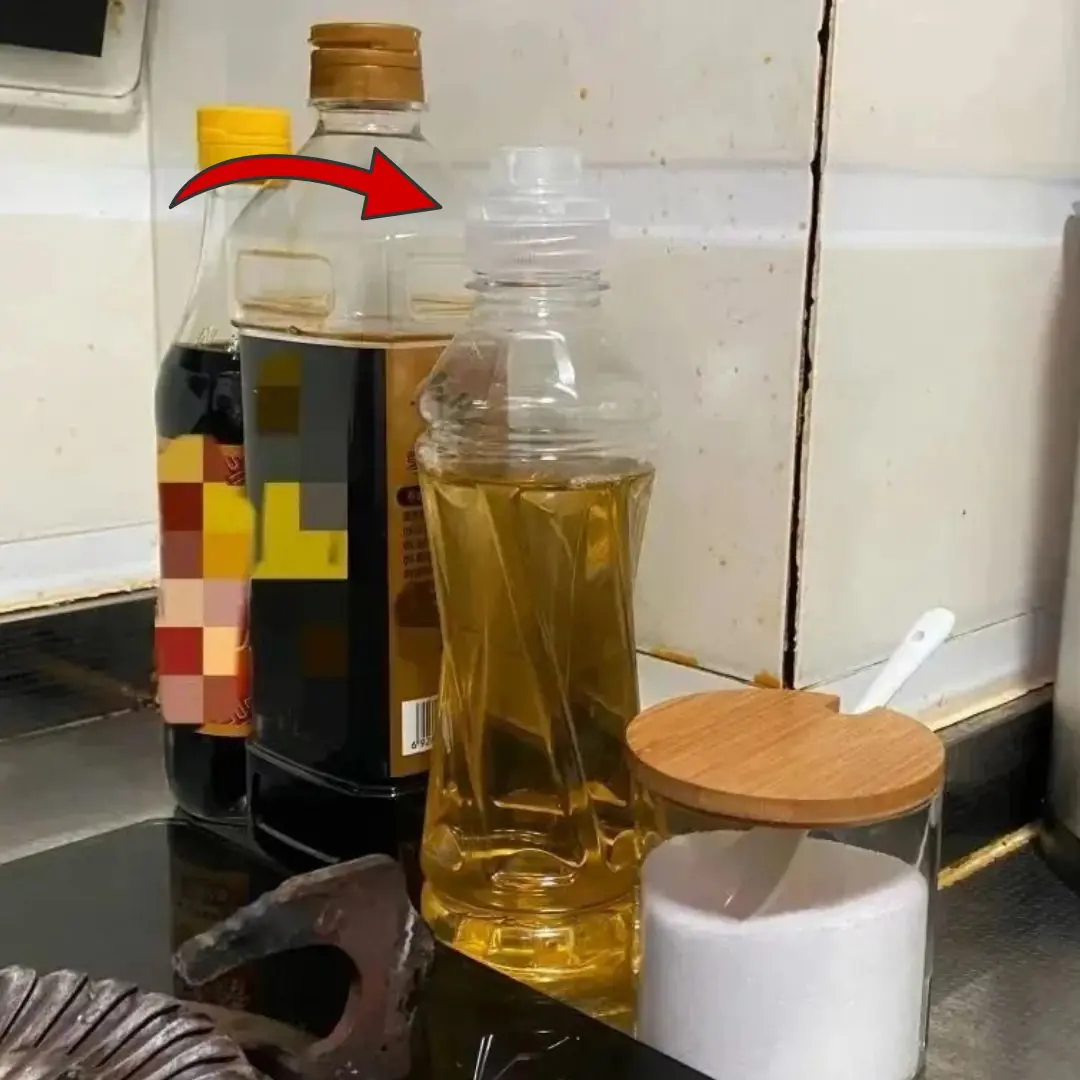

Stop Using Plastic Bottles Like This: 3 Habits That Could Increase Cancer Risk
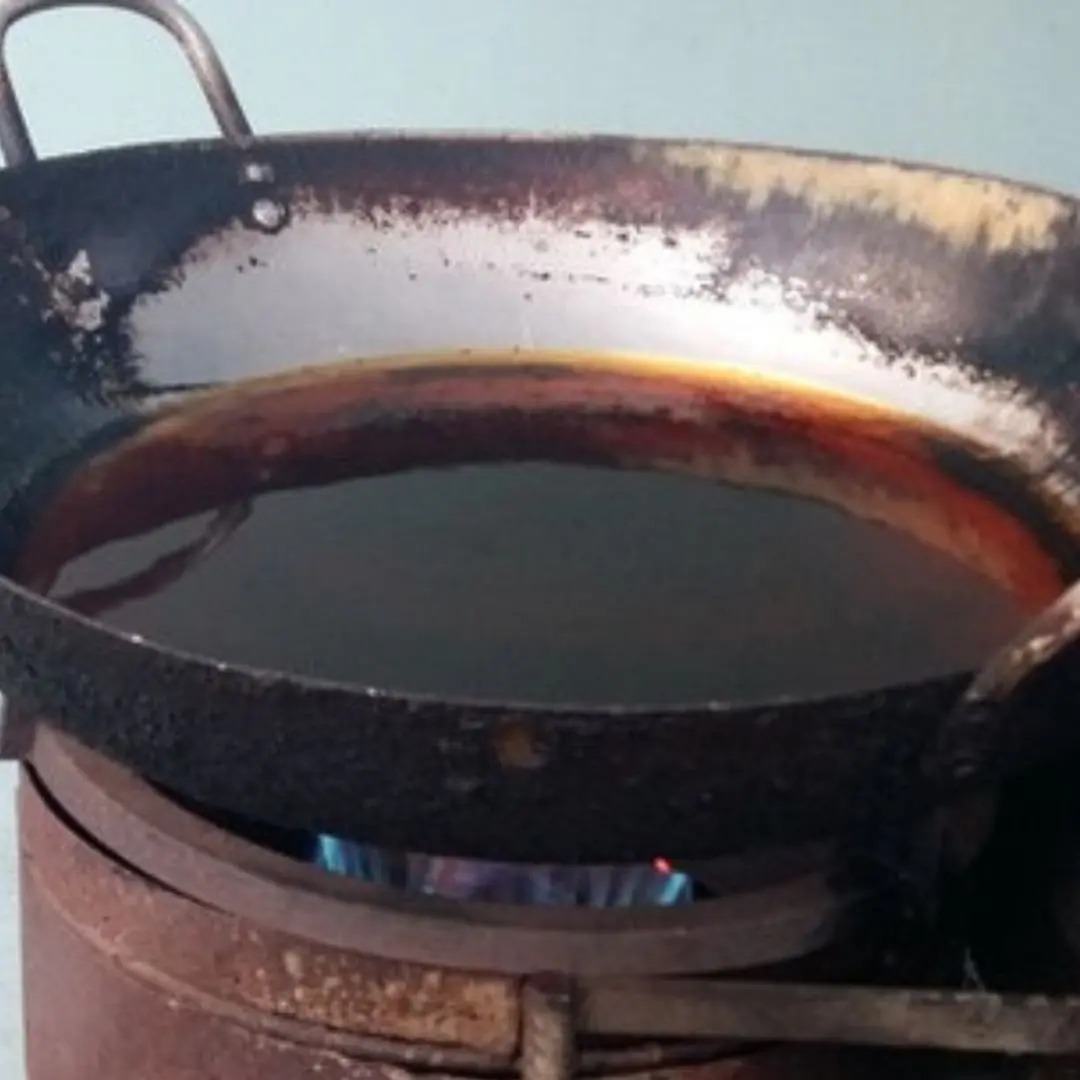

2 Cooking Oils You Should Never Use (and 4 Healthy Ones to Replace Them)
10 Warning Signs Your Kidneys May Be in Serious Danger

The Power of Gyan Mudra: Benefits and How to Practice It
8 Early Warning Signs Of Ovarian Cancer You Shouldn’t Ignore
35-Year-Old Man’s Sore Throat Turned into Cancer After 5 Chemotherapy Sessions—Doctor Urges

The Leaf Known as a Natural Remedy, But Often Overlooked
News Post

Condolences to those who are using these 4 types of electric kettles

6 Foot Symptoms That May Warn of a Heart Attack Weeks in Advance

3 Super Nutritious Freshwater Fish

12 signs that may signal a brain aneurysm — Don’t ignore them

If Your Legs Cramp at Night You Need to Know This Immediately

3 Dangerous Habits of Husbands That Secretly Put Their Wives at Higher Risk of Cervical Cancer

Husbands With These 2 Bad Habits May Put Their Wives at Higher Risk of Br:east Can:cer

Only 20 years old but the liver is already old: The 'culprit' is a type of water and a type of food that many people love

Why should m.en eat a slice of ginger after waking up in the morning?

5 types of fruit that help reduce the risk of cancer you should eat regularly

Do you know how to read (and avoid) sticky labels on fresh fruit?

5 Ways to Keep Pill Bugs from Destroying Your Garden

3 types of fruit cooked are many times better than eating them raw, help brighten skin, cure diseases well without wasting money on medicine

Caution! 3 Groups of People Should Stay Away from Perilla Leaf Water

8 war.ning signs of unhealthy kidneys

Stop Using Plastic Bottles Like This: 3 Habits That Could Increase Cancer Risk

2 Cooking Oils You Should Never Use (and 4 Healthy Ones to Replace Them)

Doctor finally answers question of whether it is better to shower in the morning or at night
