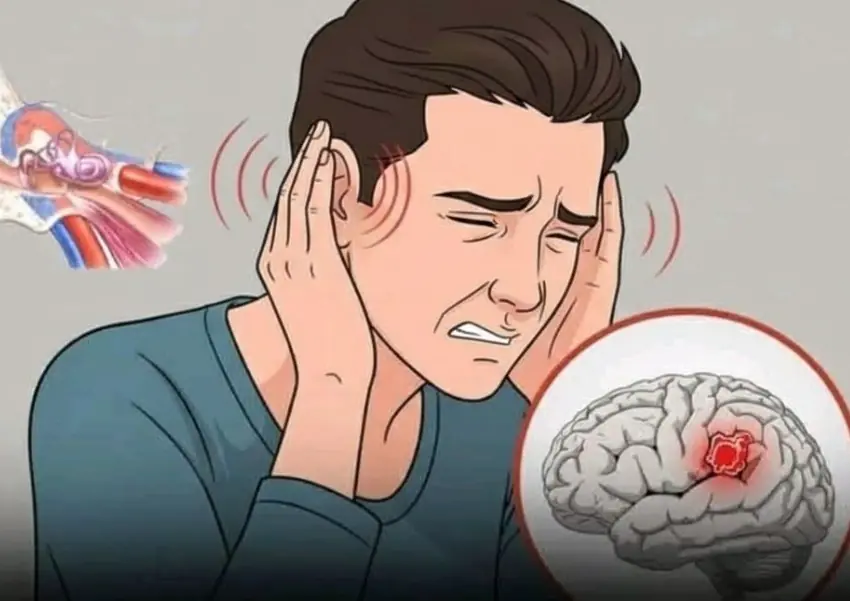
5 nighttime habits doctors warn may raise the risk of str.oke

Stroke is often thought of as a sudden daytime emergency, but medical research shows that a large number of strokes actually occur at night or in the early morning hours. This is not a coincidence. During sleep, the body undergoes complex physiological changes that can make the brain more vulnerable - especially if certain unhealthy habits are present.
Understanding these habits and correcting them early can significantly reduce the risk of nighttime stroke, particularly in middle-aged and older adults or people with chronic health conditions.
Why Nighttime Is a High-Risk Period for Stroke
While you sleep, several changes occur naturally:
-
Blood pressure fluctuates instead of staying stable
-
Heart rate slows and may become irregular
-
Blood becomes more concentrated due to mild dehydration
-
Oxygen levels can drop slightly, especially during deep sleep
For healthy individuals, the body adapts to these changes. But when harmful habits are added, they can trigger blo.od clots, vessel rupture, or reduced blood flow to the brain - leading to a stroke during sleep or shortly after waking.
1. Going to Bed with Poorly Controlled High Blood Pressure
The most dangerous nighttime habit
High blood pressure is the leading cause of stroke worldwide, and nighttime blood pressure plays a crucial role.
Why this habit is risky:
-
Blood pressure should naturally dip during sleep
-
In many people, it stays high or spikes at night (“non-dipping hypertension”)
-
This constant pressure weakens blood vessel walls in the brain
Early-morning strokes often occur when blood pressure suddenly surges as the body prepares to wake.
Warning signs:
-
Morning headaches
-
Feeling dizzy or heavy upon waking
-
History of uncontrolled hypertension
How to prevent it:
-
Monitor blood pressure in the evening, not just during the day
-
Take blood pressure medication consistently and on schedule
-
Reduce salt intake at dinner
-
Avoid heavy, late-night meals

2. Chronic Sleep Deprivation or Poor Sleep Quality
Consistently getting less than 6 hours of sleep per night significantly increases stroke risk.
How poor sleep affects the brain:
-
Raises cortisol and stress hormones
-
Increases inflammation in blood vessels
-
Disrupts blood sugar control
-
Prevents proper blood pressure regulation
Over time, sleep deprivation damages the cardiovascular system and increases the risk of nighttime stroke.
How to improve sleep:
-
Aim for 7–8 hours of uninterrupted sleep
-
Maintain a consistent sleep schedule
-
Avoid screens at least one hour before bedtime
-
Keep the bedroom dark, quiet, and cool
3. Drinking Alcohol Late at Night
Alcohol may feel relaxing, but it has serious hidden effects on the brain and heart during sleep.
Why late-night drinking is dangerous:
-
Raises blo.od pressure while sleeping
-
Triggers irregular heart rhythms (especially atrial fibrillation)
-
Causes dehydration, thickening the blood
-
Disrupts deep sleep stages
Even moderate drinking late in the evening can increase stroke risk, especially in people with existing heart or blood pressure issues.
Prevention strategies:
-
Avoid alcohol within 3–4 hours of bedtime
-
Limit alcohol intake overall
-
Choose calming alternatives such as herbal tea or warm milk
4. Sleeping with Undiagnosed or Untreated Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea is one of the most underestimated risk factors for nighttime stroke.
What happens during sleep apnea:
-
Breathing repeatedly stops during sleep
-
Oxygen levels drop suddenly
-
Blood pressure spikes repeatedly
-
The brain and heart experience constant stress
People with untreated sleep apnea have a much higher risk of stroke during sleep.
Common warning signs:
-
Loud snoring
-
Gasping or choking during sleep
-
Waking up tired or with headaches
-
Excessive daytime sleepiness
How to reduce risk:
-
Seek medical evaluation if symptoms are present
-
Use CPAP or prescribed devices consistently
-
Maintain a healthy weight

5. Going to Bed Dehydrated or After Heavy Late-Night Eating
What you eat and drink before bed can directly affect blood flow during sleep.
Why this habit matters:
-
Dehydration thickens the blood, increasing clot risk
-
Heavy meals raise blood pressure and blood sugar
-
Digestive stress competes with circulation during sleep
These factors increase the likelihood of nighttime ischemic stroke.
Prevention tips:
-
Drink enough water during the day
-
Avoid heavy, salty, or sugary meals late at night
-
Finish dinner at least 2–3 hours before bedtime
Additional Nighttime Habits That Increase Stroke Risk
-
Ignoring atrial fibrillation or heart rhythm disorders
-
Smoking before bedtime
-
Excessive late-night stress or anxiety
-
Skipping prescribed medications
Nighttime Stroke Prevention: What You Can Do Today
Control Chronic Conditions
-
Manage blood pressure, diabetes, and cholesterol carefully
-
Take medications exactly as prescribed
Protect Sleep Health
-
Treat sleep disorders early
-
Prioritize quality sleep as seriously as diet and exercise
Reduce Evening Stress
-
Practice relaxation or breathing exercises
-
Avoid emotionally intense content before bed
Know the Emergency Signs
Call emergency services immediately if you notice:
-
Facial drooping
-
Weakness on one side of the body
-
Slurred speech
-
Confusion or vision problems
Even if symptoms occur at night, do not wait until morning.
Final Thoughts
Stroke prevention doesn’t end when the lights go out. In fact, what you do before bed may be just as important as what you do during the day.
By avoiding these five dangerous nighttime habits and building healthier evening routines, you can greatly reduce your stroke risk while your body rests. Small changes - better sleep, controlled blood pressure, hydration, and stress management - can quietly protect your brain through the night.

News in the same category


Bull thistle (Cirsium vulgare): A wild plant with surprising benefits
Common routines you ignore every day that may raise your risk of colon cancer
7 Powerful Exercises to Relieve Heel Pain and Treat Plantar Fasciitis Naturally

Important News for Everyone Who Loves a Daytime Nap
Man Says Goodbye To His Wife As They Took Her Off Life Support, But Then She Utters 5 Words
The Vitamin & Mineral Deficiencies That May Be Behind Leg and Bone Pain

What it says about your relationship when your partner sleeps with their back to you
Surprising Causes Of Hives Revealed — What May Be Triggering Your Skin Reaction
4 foods to eat on an empty stomach in the morning to cleanse the gut, boost digestion, and lower cancer risk

7 Ways How To Deal With A Cheating Husband

People who nap during the day should definitely read this
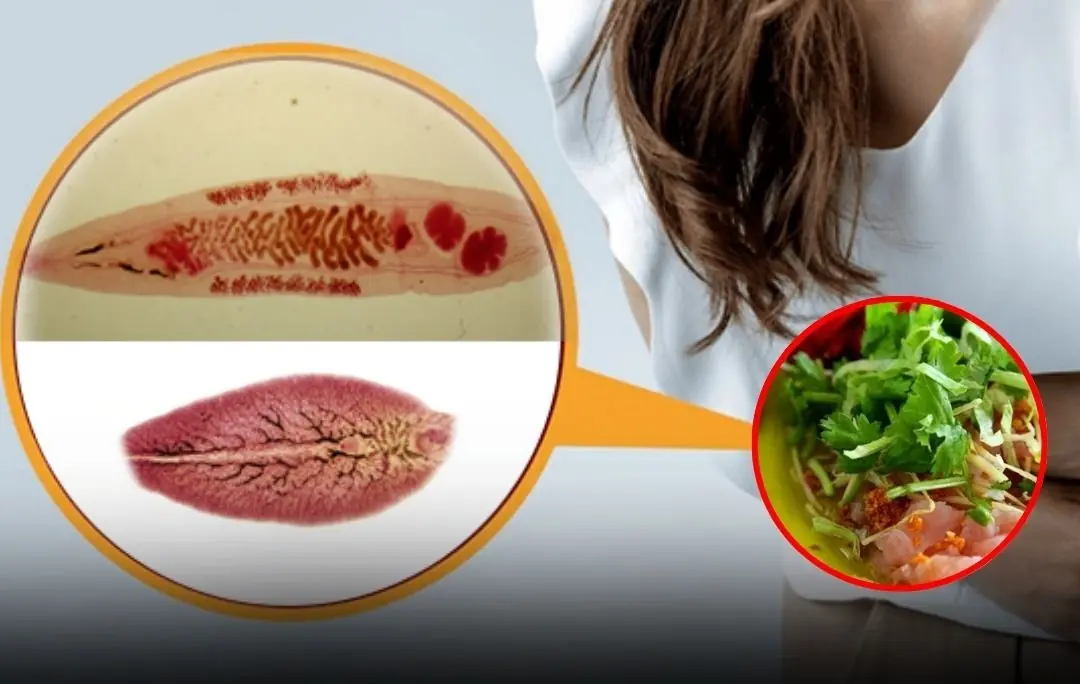

How your daily eating habits could expose you to liver fluke infection
Science backs it up: 3 fruits that fight fatty liver, regulate sugar and cholesterol
21-year-old male student with severe kidney and heart fai.lure: The “culprit” is a familiar drink, not al.cohol

7 Signs of Mini Stroke in The Elderly

It’s More Than Stress! Doctors Say This Symptom Shouldn’t Be Ignored
8 signs of kidney failure that if ignored may require lifelong dialysis
Using a phone while going to the bathroom is a har.mful habit
News Post

Why we help waiters: The psychology behind a simple act of kindness

If you often notice ringing in your ears, this might be a sign that you are dealing with an underlying health issue

Bull thistle (Cirsium vulgare): A wild plant with surprising benefits

Stuffed Lemon Cookies
3 morning symptoms of people with undiagnosed can.cer

Common routines you ignore every day that may raise your risk of colon cancer

7 Powerful Exercises to Relieve Heel Pain and Treat Plantar Fasciitis Naturally

This Button on Your Car Key Is Something 90% of Owners Have Never Used — Yet It Could Save Your Life in an Emergency

Important News for Everyone Who Loves a Daytime Nap

Man Says Goodbye To His Wife As They Took Her Off Life Support, But Then She Utters 5 Words

The Vitamin & Mineral Deficiencies That May Be Behind Leg and Bone Pain

What it says about your relationship when your partner sleeps with their back to you

Surprising Causes Of Hives Revealed — What May Be Triggering Your Skin Reaction

4 foods to eat on an empty stomach in the morning to cleanse the gut, boost digestion, and lower cancer risk

7 Ways How To Deal With A Cheating Husband

People who nap during the day should definitely read this

Say Goodbye to Joint and Foot Pain with a Relaxing Rosemary Bath

How your daily eating habits could expose you to liver fluke infection
