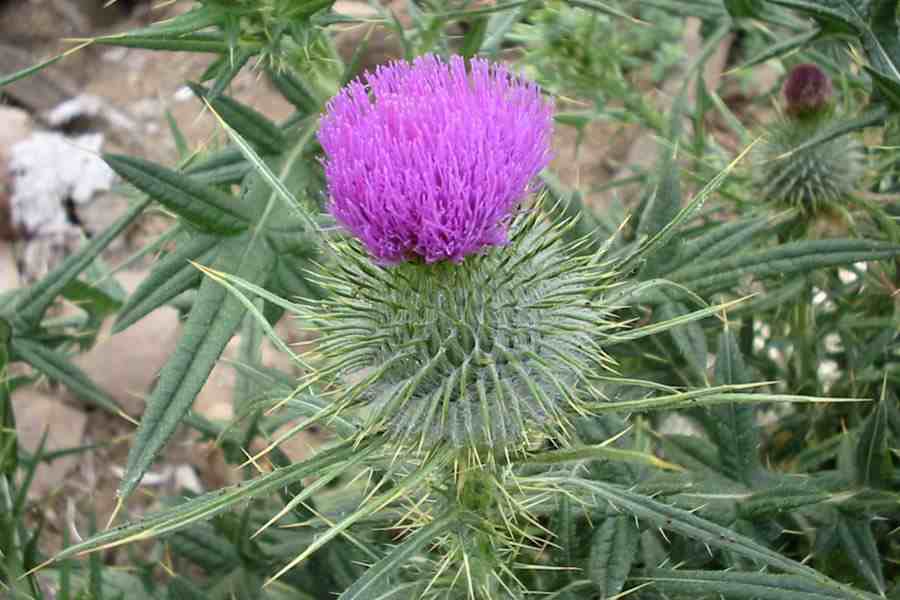
Bull thistle (Cirsium vulgare): A wild plant with surprising benefits
Bull thistle (Cirsium vulgare) is often dismissed as a stubborn weed - spiny, invasive, and unwanted in fields and roadsides. Yet beneath its sharp exterior lies a plant with a long history of traditional use and a growing reputation among herbalists and foragers. Far from being useless, bull thistle has been valued in folk medicine, survival food practices, and ecological systems for centuries.
While modern science is still catching up, early research and traditional knowledge suggest that bull thistle may offer nutritional, medicinal, and environmental benefits worth understanding.
What Is Bull Thistle?
Bull thistle is a biennial plant native to Europe, Western Asia, and North Africa, now widely naturalized in North America and other regions. It is easily recognized by:
-
Tall stems (up to 2 meters)
-
Purple-pink flower heads
-
Sharp spines covering leaves and stems
-
Deep taproot system
Despite its rough appearance, many parts of the plant—when handled and prepared correctly—have been used historically for food and healing.
Traditional Uses of Bull Thistle
Folk Medicine
In European and Indigenous traditions, bull thistle was used to:
-
Support liver and gallbladder health
-
Reduce inflammation
-
Promote wound healing
-
Aid digestion
Poultices, teas, and decoctions were made from the roots, leaves, or flower heads, depending on the purpose.
Survival and Foraged Food
During times of scarcity, bull thistle served as a wild food source:
-
Young leaves (with spines removed) were cooked like greens
-
Stems were peeled and eaten raw or boiled
-
Roots were roasted or boiled for starch

Nutritional Value (When Properly Prepared)
Bull thistle contains:
-
Dietary fiber
-
Minerals such as potassium, calcium, and magnesium
-
Antioxidant compounds (flavonoids and polyphenols)
-
Small amounts of protein in young plant parts
While not a staple food, it can supplement nutrition in foraged diets.
Surprising Health Benefits of Bull Thistle
⚠️ Important note: Most benefits are based on traditional use and preliminary research. Bull thistle is not a substitute for medical treatment.
1. Liver and Detox Support
Bull thistle has traditionally been associated with liver support, similar (though weaker) to milk thistle.
Potential effects include:
-
Supporting bile flow
-
Helping the body process toxins
-
Reducing oxidative stress in liver cells
2. Anti-Inflammatory Properties
The plant contains compounds that may help reduce inflammation when used externally or in mild internal preparations.
Historically used for:
-
Joint discomfort
-
Muscle aches
-
Swelling
3. Antioxidant Activity
Flavonoids found in bull thistle help neutralize free radicals, which play a role in aging and chronic disease development.
This antioxidant action supports:
-
Cellular protection
-
Immune balance
-
Tissue repair
4. Digestive Support
Traditional herbal use included mild digestive tonics made from thistle roots or leaves.
Possible benefits:
-
Stimulating appetite
-
Reducing bloating
-
Supporting gut motility
5. Wound Healing and Skin Care
Crushed leaves or root poultices were historically applied to:
-
Minor cuts
-
Insect bites
-
Skin irritation
The antimicrobial and astringent properties may help protect wounds and promote healing.
6. Diuretic Effects
Bull thistle was sometimes used to encourage urination, helping the body eliminate excess fluid and waste.
This use requires caution and moderation.
7. Immune System Support
Through its antioxidant and mild antimicrobial properties, bull thistle may indirectly support immune resilience.
Ecological and Environmental Benefits
Beyond human use, bull thistle plays an important ecological role:
-
Pollinator support: Its flowers provide nectar for bees, butterflies, and other insects
-
Soil stabilization: Deep roots help prevent erosion
-
Wildlife value: Birds feed on the seeds
Despite being invasive in some regions, it contributes to biodiversity when managed responsibly.
How Bull Thistle Is Used Today
Modern herbalists may use:
-
Dried leaves for tea (mild preparations only)
-
Root extracts under professional guidance
-
External applications for skin support
Foragers still value the plant, especially in survival contexts, though careful handling is essential.
Safety and Precautions
Bull thistle is generally considered low toxicity, but caution is still necessary.
Avoid or Use Carefully If You:
-
Are pregnant or breastfeeding
-
Have kidney or liver disease
-
Are on diuretic medications
-
Have allergies to plants in the Asteraceae family
Handling Tips:
-
Always remove spines thoroughly
-
Never consume raw mature leaves or stems
-
Start with very small amounts
Common Misconceptions
-
“It’s just a weed.”
→ Many medicinal plants were once considered weeds. -
“All thistles are the same.”
→ Different thistles have different chemical profiles. -
“Natural means safe.”
→ Incorrect—dosage and preparation matter.
Modern Perspective: Should You Use Bull Thistle?
Bull thistle is best viewed as:
-
A traditional support plant, not a cure
-
A foraged food in limited contexts
-
An ecological resource worth understanding
Safer, better-studied herbs are often preferred for daily health use. However, bull thistle remains a fascinating example of how nature hides value in unexpected places.
Conclusion
Bull thistle (Cirsium vulgare) may look harsh and unwelcoming, but its history tells a different story. Used for centuries as food, medicine, and a natural support plant, it offers antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, digestive, and liver-supportive properties when used carefully.
While not a mainstream remedy, bull thistle reminds us that many overlooked wild plants hold surprising benefits—if we take the time to learn, respect, and use them wisely.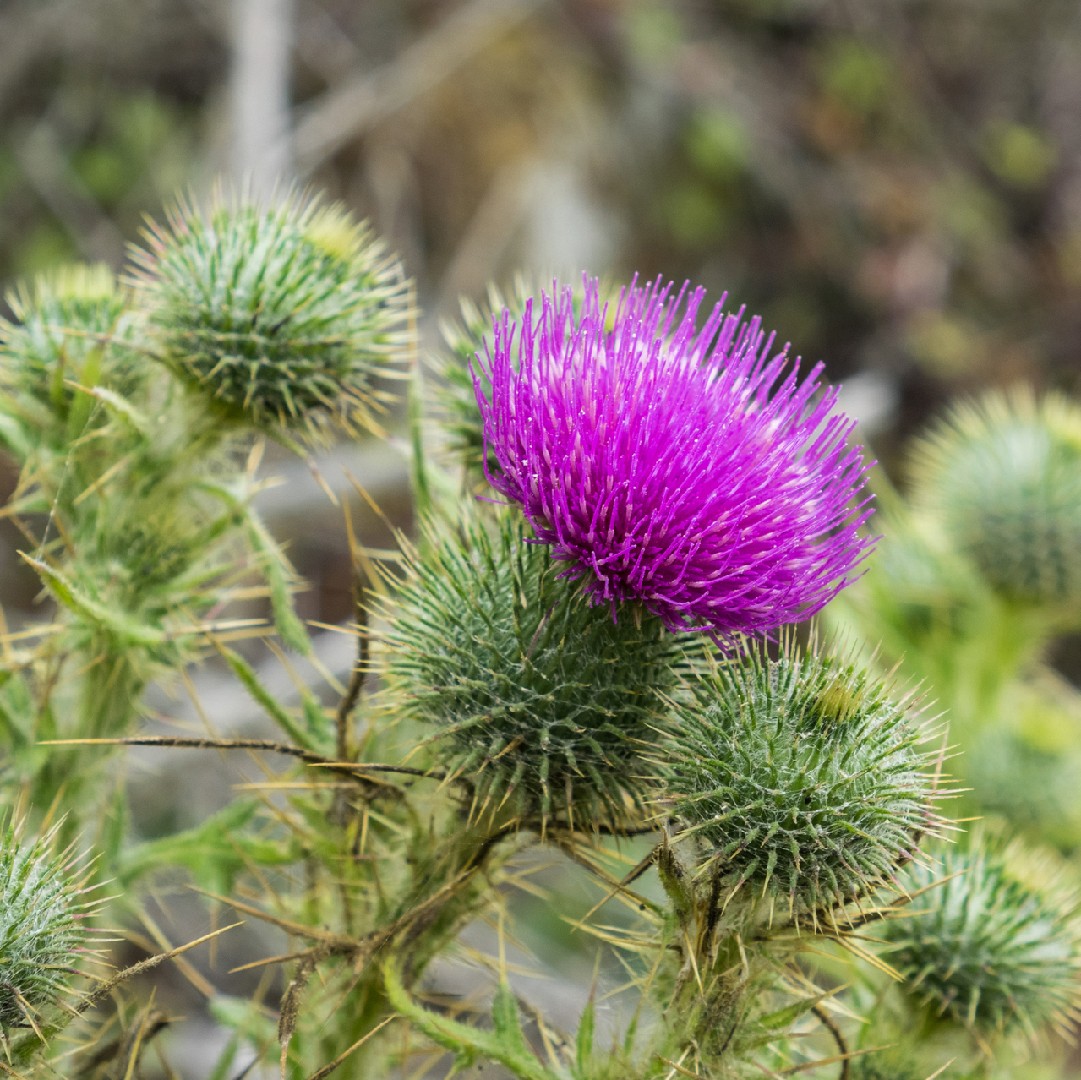
News in the same category

Common routines you ignore every day that may raise your risk of colon cancer
7 Powerful Exercises to Relieve Heel Pain and Treat Plantar Fasciitis Naturally

Important News for Everyone Who Loves a Daytime Nap
Man Says Goodbye To His Wife As They Took Her Off Life Support, But Then She Utters 5 Words
The Vitamin & Mineral Deficiencies That May Be Behind Leg and Bone Pain

What it says about your relationship when your partner sleeps with their back to you
Surprising Causes Of Hives Revealed — What May Be Triggering Your Skin Reaction
4 foods to eat on an empty stomach in the morning to cleanse the gut, boost digestion, and lower cancer risk

7 Ways How To Deal With A Cheating Husband

People who nap during the day should definitely read this
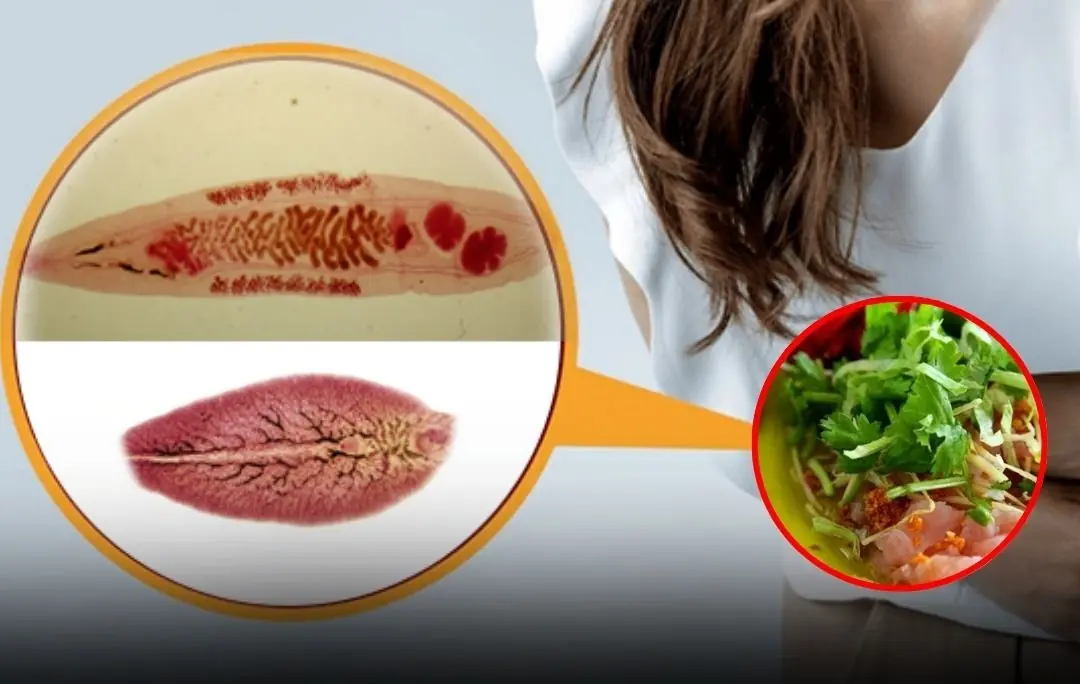

How your daily eating habits could expose you to liver fluke infection
Science backs it up: 3 fruits that fight fatty liver, regulate sugar and cholesterol
21-year-old male student with severe kidney and heart fai.lure: The “culprit” is a familiar drink, not al.cohol

7 Signs of Mini Stroke in The Elderly

It’s More Than Stress! Doctors Say This Symptom Shouldn’t Be Ignored
8 signs of kidney failure that if ignored may require lifelong dialysis
Using a phone while going to the bathroom is a har.mful habit
They may look harmless now, but if ignored, these signs could slowly lead to c.an.cer
The moments right after you wake up are when your body reveals its true state of health most clearly
News Post

Stuffed Lemon Cookies

3 morning symptoms of people with undiagnosed can.cer

Common routines you ignore every day that may raise your risk of colon cancer

7 Powerful Exercises to Relieve Heel Pain and Treat Plantar Fasciitis Naturally

This Button on Your Car Key Is Something 90% of Owners Have Never Used — Yet It Could Save Your Life in an Emergency

Important News for Everyone Who Loves a Daytime Nap

Man Says Goodbye To His Wife As They Took Her Off Life Support, But Then She Utters 5 Words

The Vitamin & Mineral Deficiencies That May Be Behind Leg and Bone Pain

What it says about your relationship when your partner sleeps with their back to you

Surprising Causes Of Hives Revealed — What May Be Triggering Your Skin Reaction

4 foods to eat on an empty stomach in the morning to cleanse the gut, boost digestion, and lower cancer risk

7 Ways How To Deal With A Cheating Husband

People who nap during the day should definitely read this

Say Goodbye to Joint and Foot Pain with a Relaxing Rosemary Bath

How your daily eating habits could expose you to liver fluke infection

Science backs it up: 3 fruits that fight fatty liver, regulate sugar and cholesterol

There's actually a rule, and now I finally understand the reason

Ever Wonder Why Japanese People Wear Socks to Bed All Year Round? Here’s the Surprising Reason

21-year-old male student with severe kidney and heart fai.lure: The “culprit” is a familiar drink, not al.cohol
