
Common routines you ignore every day that may raise your risk of colon cancer
People at Higher Risk of Colorectal Cancer:
People with long-term ulcerative colitis:
Those who have had chronic ulcerative colitis but have not treated it thoroughly, leading to an increase in the spread of ulcerations.
Family history:
If a parent or sibling has had colorectal cancer, the risk of developing the disease is 2–3 times higher than in the general population, especially if the cancer occurred before the age of 60.
Older age:
Colorectal cancer is more commonly found in individuals over 50. However, the disease is becoming more common among younger people, with some diagnosed in their 20s or 30s, although the number of cases is lower at this age.
History of colorectal polyps:
Some types of polyps increase the risk of colorectal cancer, particularly large polyps or multiple polyps.
Dietary habits:
Foods high in fat, especially animal fats, increase the risk of colorectal cancer. Additionally, preservatives in vegetables, growth enhancers, and lean meat additives in pork, as well as stimulants, can contribute to cancer. If you frequently consume fermented foods, salted foods, or processed foods with preservatives such as salted meats, pickled vegetables, smoked meats, sausages, or soy sauce, you should reduce their intake, as these are common causes of colorectal cancer.

Lack of physical activity:
People who do not exercise regularly and sit for long periods may be at increased risk of developing colorectal cancer.
Obesity:
Uncontrolled weight gain is one of the factors that increase the risk of colorectal cancer.
Smoking:
Nearly all individuals with colorectal cancer use tobacco, especially men. Smokers are at higher risk of developing the disease compared to non-smokers. Therefore, smoking can be considered a cause of colorectal cancer, and it also increases the risk of many other types of cancer.
Excessive alcohol consumption:
Drinking large amounts of alcohol increases the risk of colorectal cancer.
Early Signs of Colorectal Cancer You Should Not Ignore:
Digestive disorders:
Colorectal cancer affects various parts of the digestive system. Common symptoms include bad breath, frequent burping, acid reflux, and pain or discomfort in the stomach before or after eating. Abdominal cramping and bloating can be symptoms of digestive issues caused by infections. However, in some cases, these may indicate the presence of tumors in the stomach or intestines. Loss of appetite, indigestion, and bloating near the navel are often observed in people with colorectal cancer. If persistent, this condition can lead to fatigue and weight loss.
Unexplained weight loss:
Sudden and unexplained weight loss should never be ignored, as it may be a sign of colorectal cancer, stomach cancer, or other digestive system cancers.
Bowel movement disturbances:
Early-stage colorectal cancer may cause irregular bowel movements, such as alternating constipation and diarrhea, which can persist over time.
Thin or narrow stools:
Pencil-thin or unusually narrow stools may indicate an obstruction, such as a tumor, blocking waste from passing normally.
Blood in stool:
Passing fresh red blood in the stool is a common symptom. In advanced stages, patients may experience rectal prolapse, severe weight loss, and frequent bowel movement changes.
Fatigue and weakness:
This is one of the most common yet overlooked symptoms. It is often related to anemia caused by chronic blood loss in the stool, leading to constant exhaustion even after rest.
How to Prevent Colorectal Cancer:
Limit meat and animal fat consumption.
Increase fiber intake from whole grains, fruits, and fresh vegetables, along with vitamins E, C, A, and calcium.
Maintain an active lifestyle and exercise regularly.
Get regular health check-ups every six months to detect diseases early.
News in the same category


5 nighttime habits doctors warn may raise the risk of str.oke
If you often notice ringing in your ears, this might be a sign that you are dealing with an underlying health issue

Bull thistle (Cirsium vulgare): A wild plant with surprising benefits
3 morning symptoms of people with undiagnosed can.cer
7 Powerful Exercises to Relieve Heel Pain and Treat Plantar Fasciitis Naturally

Important News for Everyone Who Loves a Daytime Nap
Man Says Goodbye To His Wife As They Took Her Off Life Support, But Then She Utters 5 Words
The Vitamin & Mineral Deficiencies That May Be Behind Leg and Bone Pain

What it says about your relationship when your partner sleeps with their back to you
Surprising Causes Of Hives Revealed — What May Be Triggering Your Skin Reaction
4 foods to eat on an empty stomach in the morning to cleanse the gut, boost digestion, and lower cancer risk

7 Ways How To Deal With A Cheating Husband

People who nap during the day should definitely read this
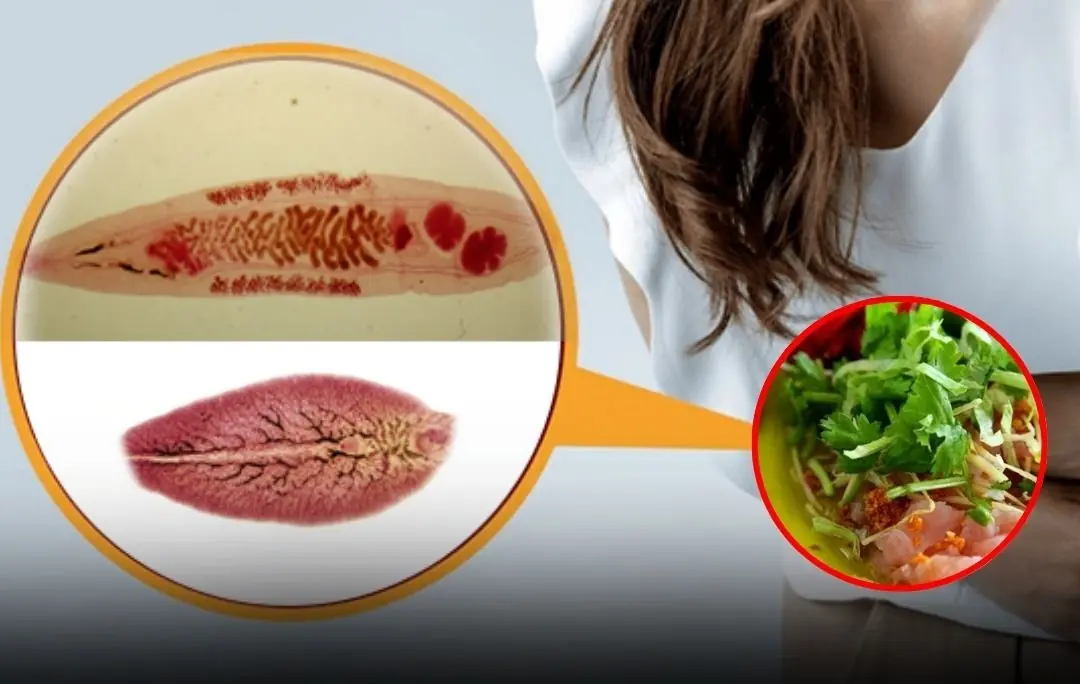

How your daily eating habits could expose you to liver fluke infection
Science backs it up: 3 fruits that fight fatty liver, regulate sugar and cholesterol
21-year-old male student with severe kidney and heart fai.lure: The “culprit” is a familiar drink, not al.cohol

7 Signs of Mini Stroke in The Elderly

It’s More Than Stress! Doctors Say This Symptom Shouldn’t Be Ignored
News Post

The surprising reason you should never sleep with a fan on at night
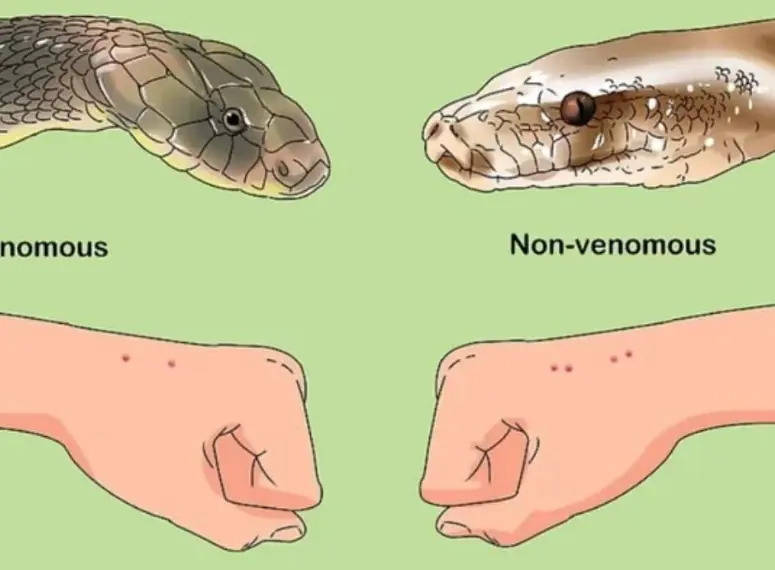
When bit.ten by a snake, you should do these things first

Tiny “Bags” on your walls? Here’s what they really are and how to get rid of them for good

5 nighttime habits doctors warn may raise the risk of str.oke

Why we help waiters: The psychology behind a simple act of kindness

If you often notice ringing in your ears, this might be a sign that you are dealing with an underlying health issue

Bull thistle (Cirsium vulgare): A wild plant with surprising benefits
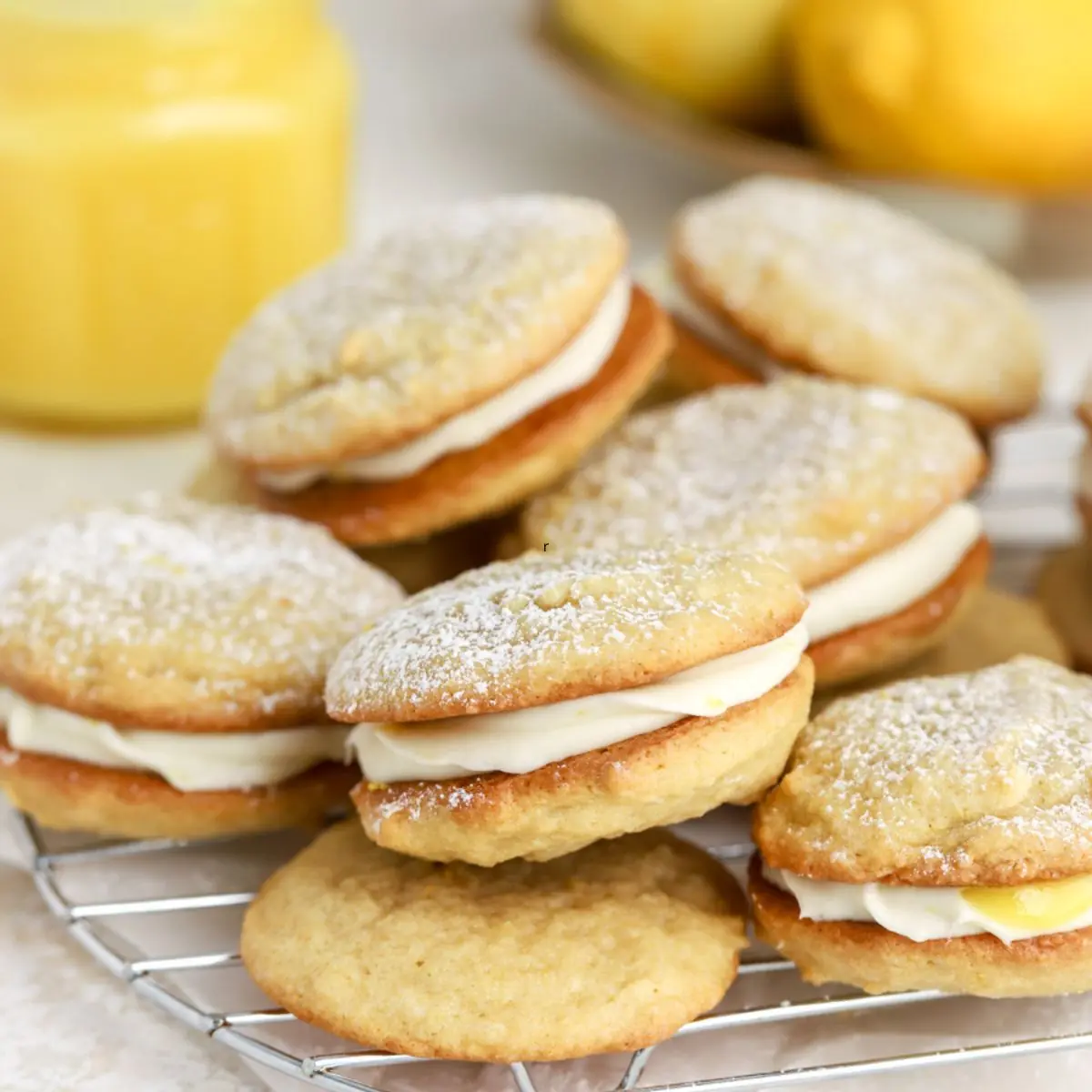

Stuffed Lemon Cookies

3 morning symptoms of people with undiagnosed can.cer

7 Powerful Exercises to Relieve Heel Pain and Treat Plantar Fasciitis Naturally

This Button on Your Car Key Is Something 90% of Owners Have Never Used — Yet It Could Save Your Life in an Emergency

Important News for Everyone Who Loves a Daytime Nap

Man Says Goodbye To His Wife As They Took Her Off Life Support, But Then She Utters 5 Words

The Vitamin & Mineral Deficiencies That May Be Behind Leg and Bone Pain

What it says about your relationship when your partner sleeps with their back to you

Surprising Causes Of Hives Revealed — What May Be Triggering Your Skin Reaction

4 foods to eat on an empty stomach in the morning to cleanse the gut, boost digestion, and lower cancer risk

7 Ways How To Deal With A Cheating Husband
