
If you often notice ringing in your ears, this might be a sign that you are dealing with an underlying health issue
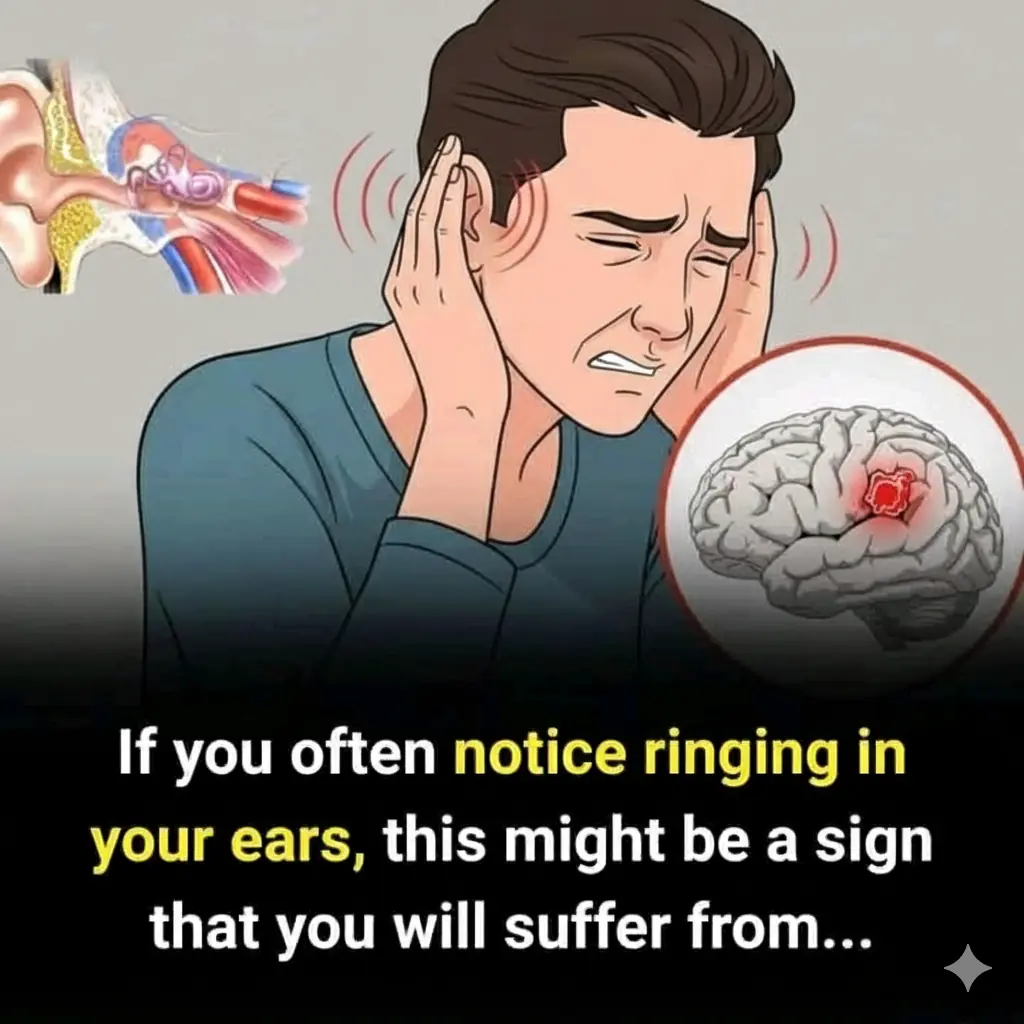
Occasional ringing in the ears is something most people experience at least once - after a loud concert, a stressful day, or temporary fatigue. However, frequent or persistent ringing in the ears should not be ignored. This condition, known medically as tinnitus, can be a signal that something deeper is happening in the body.
While tinnitus itself is not a disease, it is often a symptom of an underlying problem. Understanding what your body may be trying to tell you can help you take action early and protect your long-term health.
What Is Ringing in the Ears (Tinnitus)?
Tinnitus is the perception of sound when no external noise is present. It may sound like:
-
Ringing
-
Buzzing
-
Hissing
-
Whistling
-
Clicking
The sound can affect one ear or both, come and go, or persist continuously. For some people, it is mild and manageable. For others, it can interfere with sleep, concentration, and quality of life.
Possible Conditions Linked to Frequent Ear Ringing
1. Hearing Loss or Inner Ear Damage
One of the most common causes of tinnitus is damage to the tiny hair cells in the inner ear.
Why it happens:
-
Prolonged exposure to loud noise
-
Aging-related hearing decline
-
Sudden acoustic trauma
When these cells are damaged, they send abnormal signals to the brain, which the brain interprets as sound.
Warning sign:
Ringing that worsens in quiet environments or is accompanied by difficulty hearing conversations.
2. High Blo.od Pressure or Circulatory Problems
Ringing in the ears can sometimes be related to blood flow changes near the ears.
Conditions associated with this include:
-
High blood pressure
-
Atherosclerosis (narrowed blood vessels)
-
Irregular blo.od flow near the ear
In some cases, the sound may pulse in rhythm with the heartbeat - known as pulsatile tinnitus.
3. Chronic Stress and Anxiety
Mental and emotional stress can significantly affect the nervous system, triggering or worsening tinnitus.
How stress plays a role:
-
Increases cortisol levels
-
Heightens nervous system sensitivity
-
Disrupts sleep and recovery
Many people notice their tinnitus becomes louder during periods of emotional strain.
4. Ear Infections or Earwax Buildup
Blockages or infections in the ear canal can trap sound and alter pressure.
Possible causes include:
-
Impacted earwax
-
Middle ear infections
-
Eustachian tube dysfunction
Once the blockage or infection is treated, tinnitus often improves or disappears.
5. Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) Disorders
The jaw joint is located very close to the ear. TMJ dysfunction can irritate nearby nerves, leading to ear ringing.
Clues pointing to TMJ:
-
Jaw pain or clicking
-
Teeth grinding
-
Headaches or facial tension

6. Medication Side Effects
Some medications are known to cause or worsen tinnitus, especially at high doses or with long-term use.
These may include:
-
Certain antibiotics
-
Aspirin (in high doses)
-
Some antidepressants
-
Chemotherapy drugs
Never stop medication without consulting a healthcare provider.
7. Neurological Conditions (Rare but Serious)
In rare cases, persistent tinnitus may be linked to neurological disorders such as:
-
Vestibular migraines
-
Multiple sclerosis
-
Acoustic neuroma (a non-cancerous tumor affecting the auditory nerve)
If tinnitus is accompanied by dizziness, facial numbness, or balance issues, medical evaluation is essential.
When Ringing in the Ears May Signal Something More Serious
Seek medical attention promptly if tinnitus:
-
Appears suddenly and intensely
-
Is accompanied by hearing loss or dizziness
-
Occurs after a head injury
-
Pulses with your heartbeat
-
Persists longer than two weeks without improvement
Early diagnosis can prevent complications.
How to Reduce the Risk and Manage Tinnitus
Protect Your Hearing
-
Use ear protection in loud environments
-
Limit headphone volume and listening time
Manage Blood Pressure
-
Reduce salt intake
-
Stay physically active
-
Monitor blood pressure regularly
Reduce Stress
-
Practice relaxation techniques
-
Improve sleep quality
-
Take regular breaks from screens and noise
Avoid Ear Damage
-
Do not insert objects into the ear canal
-
Seek professional ear cleaning if needed
Review Medications
-
Discuss side effects with your doctor
-
Never self-adjust dosages
Final Thoughts
Ringing in the ears is more than just an annoyance - it can be a signal from your body. While it is often linked to benign causes like stress or temporary hearing strain, persistent tinnitus should never be ignored.
Listening to your body and seeking timely medical advice can help identify the cause, prevent progression, and protect your hearing and overall health.
If something doesn’t feel right, trust that instinct. Early attention makes a real difference.![Tổng hợp] Cách chữa ù tai đơn giản và hiệu quả](https://hongngochospital.vn/wp-content/uploads/2022/03/Cach-chua-u-tai-1.jpg)
News in the same category

3 morning symptoms of people with undiagnosed can.cer
Common routines you ignore every day that may raise your risk of colon cancer
7 Powerful Exercises to Relieve Heel Pain and Treat Plantar Fasciitis Naturally

Important News for Everyone Who Loves a Daytime Nap
Man Says Goodbye To His Wife As They Took Her Off Life Support, But Then She Utters 5 Words
The Vitamin & Mineral Deficiencies That May Be Behind Leg and Bone Pain

What it says about your relationship when your partner sleeps with their back to you
Surprising Causes Of Hives Revealed — What May Be Triggering Your Skin Reaction
4 foods to eat on an empty stomach in the morning to cleanse the gut, boost digestion, and lower cancer risk

7 Ways How To Deal With A Cheating Husband

People who nap during the day should definitely read this

How your daily eating habits could expose you to liver fluke infection
Science backs it up: 3 fruits that fight fatty liver, regulate sugar and cholesterol
21-year-old male student with severe kidney and heart fai.lure: The “culprit” is a familiar drink, not al.cohol

7 Signs of Mini Stroke in The Elderly

It’s More Than Stress! Doctors Say This Symptom Shouldn’t Be Ignored
8 signs of kidney failure that if ignored may require lifelong dialysis
Using a phone while going to the bathroom is a har.mful habit
They may look harmless now, but if ignored, these signs could slowly lead to c.an.cer
News Post

Bull thistle (Cirsium vulgare): A wild plant with surprising benefits

Stuffed Lemon Cookies

3 morning symptoms of people with undiagnosed can.cer

Common routines you ignore every day that may raise your risk of colon cancer

7 Powerful Exercises to Relieve Heel Pain and Treat Plantar Fasciitis Naturally

This Button on Your Car Key Is Something 90% of Owners Have Never Used — Yet It Could Save Your Life in an Emergency

Important News for Everyone Who Loves a Daytime Nap

Man Says Goodbye To His Wife As They Took Her Off Life Support, But Then She Utters 5 Words

The Vitamin & Mineral Deficiencies That May Be Behind Leg and Bone Pain

What it says about your relationship when your partner sleeps with their back to you

Surprising Causes Of Hives Revealed — What May Be Triggering Your Skin Reaction

4 foods to eat on an empty stomach in the morning to cleanse the gut, boost digestion, and lower cancer risk

7 Ways How To Deal With A Cheating Husband

People who nap during the day should definitely read this

Say Goodbye to Joint and Foot Pain with a Relaxing Rosemary Bath

How your daily eating habits could expose you to liver fluke infection

Science backs it up: 3 fruits that fight fatty liver, regulate sugar and cholesterol

There's actually a rule, and now I finally understand the reason

Ever Wonder Why Japanese People Wear Socks to Bed All Year Round? Here’s the Surprising Reason
