
Always Pooping Right After Eating? A Doctor Explains the Surprising Reason

Why You Always Need to Poop Right After You Eat: A Doctor Explains
For many people, the urge to rush to the bathroom immediately after a meal is a familiar experience. While it can feel alarming, doctors say this reaction is often more normal than you might think. In most cases, it’s simply your body’s natural digestive reflex at work — but for some, it may signal an underlying sensitivity in the gut. Understanding what this urge really means can help you know when to relax and when to pay closer attention.
The Gastrocolic Reflex: Your Body’s Natural Trigger
The most common reason you feel the need to poop right after eating is something called the gastrocolic reflex. This is a built-in response that happens when the stomach stretches as it fills with food. That stretch sends a signal to the colon, telling it to contract and make room for new digestive contents.
A key point doctors emphasize:
The food you just ate is not the food you immediately poop out.
Digestion takes hours. The reflex simply pushes out what was already in the colon.
For most people, this process is mild and barely noticeable. But for others, the signal is much stronger — and that’s when the bathroom urge becomes urgent.
Why Some People Feel the Urge More Intensely
Individuals with IBS (Irritable Bowel Syndrome) or a naturally sensitive digestive system tend to have a more reactive gastrocolic reflex. Their gut responds more dramatically to stomach stretching, causing:
-
Sudden bowel movements after eating
-
Cramping
-
Urgency
-
Loose stools
Even healthy foods can trigger strong reactions if the gut is more sensitive.
Foods That Make the Reflex Stronger
Some foods are more likely to stimulate digestion and trigger the reflex, especially in people with IBS, including:
-
High-fat meals
-
Spicy foods
-
Artificial sweeteners
-
Large or heavy meals
-
Foods high in FODMAPs (fermentable carbohydrates)
How to Calm an Overactive Gut
The article recommends practical steps to reduce the urgency after eating, particularly for those with IBS or chronic digestive sensitivity:
1. Follow a Low-FODMAP Diet
This diet limits certain sugars that ferment quickly in the gut, reducing bloating and urgency. Many people with IBS report significant relief through this approach.
2. Choose Gut-Friendly Foods
Some foods can soothe or support the digestive tract, such as:
-
Bananas
-
Ginger
-
Aloe vera juice
-
Yogurt with probiotics
-
Easily digestible fruits and vegetables
These can help the gut move more smoothly and comfortably.
3. Support Your Digestion With Supplements
Depending on individual needs, the article mentions options such as:
-
Digestive enzymes
-
Soluble fiber (e.g., psyllium husk)
-
Magnesium (helps regulate bowel movements)
-
Probiotics or prebiotic fiber
These supplements may strengthen the digestive system over time and reduce post-meal urgency.

When the Bathroom Rush Is Not Normal
Although the post-meal urge is often harmless, a doctor should be consulted if you experience:
-
Persistent diarrhea
-
Severe cramping after meals
-
Unintentional weight loss
-
Blood in the stool
-
Pain that interferes with daily life
These may indicate an underlying condition that needs medical attention.
Final Thoughts
Needing to poop immediately after eating can feel inconvenient or embarrassing, but in many cases, it’s simply your body’s gastrocolic reflex doing its job. For those with IBS or heightened gut sensitivity, the reflex can be stronger — but with the right diet and digestive support, symptoms often improve dramatically.
Listening to your body and recognizing patterns can help you understand what triggers your gut and how to keep your digestion calm, balanced, and healthy.
News in the same category


How 27 minutes of daily meditation for 8 weeks can reshape the brain and reduce stress
Do you sleep on your side? Here's the powerful effect one simple change can have on your body

The 4 most "to.x.ic" vegetables in the world silently "destroy the liver",
8 Can.cer-Fighting Foods That Destroy Abnormal Cells — Yet Most People Overlook Them

Eat tomatoes every day, 1 year later the health check results are surprising
What those strange skin patterns might really mean

Eating These 4 Foods on an Empty Stomach Can Cleanse Your Gut, Improve Digestion, and Lower Can.cer Risk

Eating 1 type of vegetable regularly, 60-year-old woman with can:cer has had no recurrence for 10 years

3 types of drinks that "suck out the bones" of your body every day

More than 2,800 people suffered brain dam.age and high blo.od pressure from eating the same type of meat every day

The whole family has can:cer and illness if you haven't given up these 6 habits that everyone thinks are clean and economical!

Many children hospitalized for stroke: A warning bell from subjectivity
EARLY RECOGNITION OF MENINGITIS SYMPTOMS

The More You Drink, the More Your Bones Suffer: 3 Hidden “Calcium Thieves” That Quietly Weaken Your Skeleton
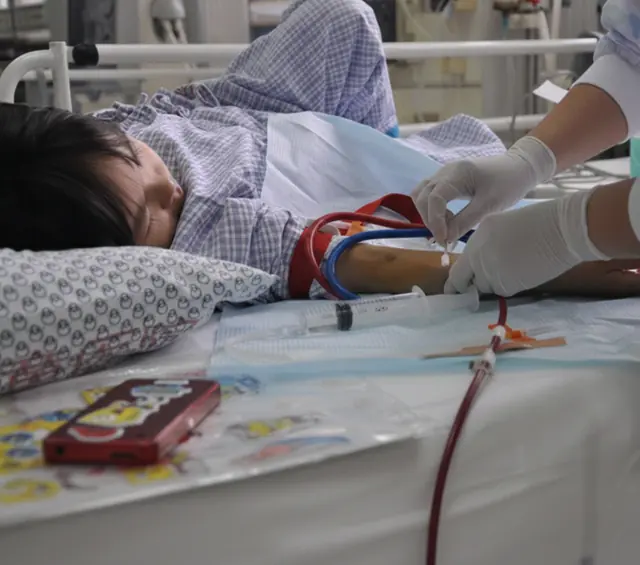
An 8-year-old girl di.es from kid.ney can.cer, father breaks down in tears: “It’s all my fault!”
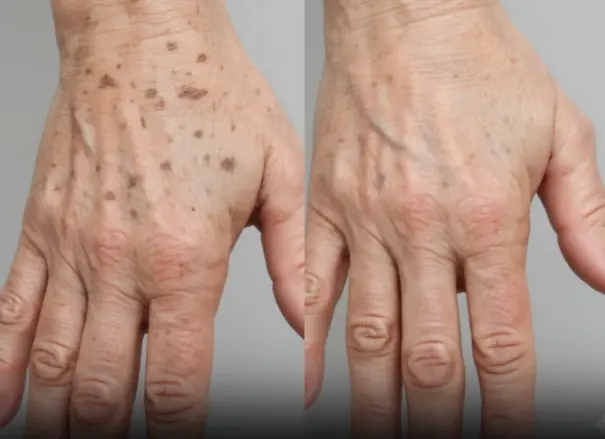
Did you know that if you get spots on your hands it means you have
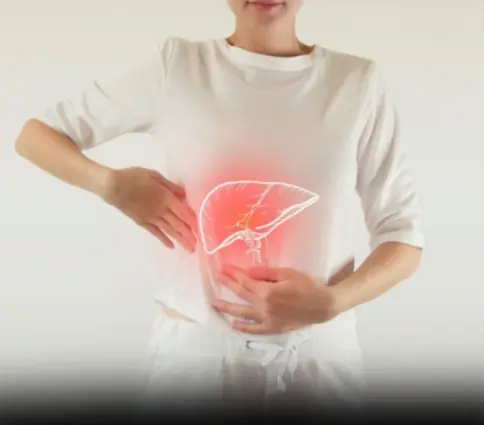
Science backs it up: 3 fruits that fight fatty liver, regulate sugar and cholesterol

Depressing find at the bottom of the Mariana Trench is a warning to the world
News Post

A family of 3 got pancreatic can.cer because of eating this type of meat for breakfast

When buying an apartment, don't touch these 4 floors no matter how cheap: It's uncomfortable to live in and the value will depreciate quickly

How 27 minutes of daily meditation for 8 weeks can reshape the brain and reduce stress

4 people should not drink black bean water, the more you drink the more sick you will be

Do you sleep on your side? Here's the powerful effect one simple change can have on your body

The 4 most "to.x.ic" vegetables in the world silently "destroy the liver",

8 Can.cer-Fighting Foods That Destroy Abnormal Cells — Yet Most People Overlook Them

Eat tomatoes every day, 1 year later the health check results are surprising

What those strange skin patterns might really mean

Top 4 longevity foods in China, sweet potatoes ranked third, number 1 position many people do not expect

Eating These 4 Foods on an Empty Stomach Can Cleanse Your Gut, Improve Digestion, and Lower Can.cer Risk

Avoid ginger if you have these 5 health problems..

Eating 1 type of vegetable regularly, 60-year-old woman with can:cer has had no recurrence for 10 years

Coconut Pineapple Banana Bread

3 types of drinks that "suck out the bones" of your body every day

3 types of spices if you know how to eat them raw, even can:cer will have to... FEAR it

56 year old woman eats lard every day, 1.5 years later the doctor looked at the results and exclaimed 👇

More than 2,800 people suffered brain dam.age and high blo.od pressure from eating the same type of meat every day
