
EARLY RECOGNITION OF MENINGITIS SYMPTOMS
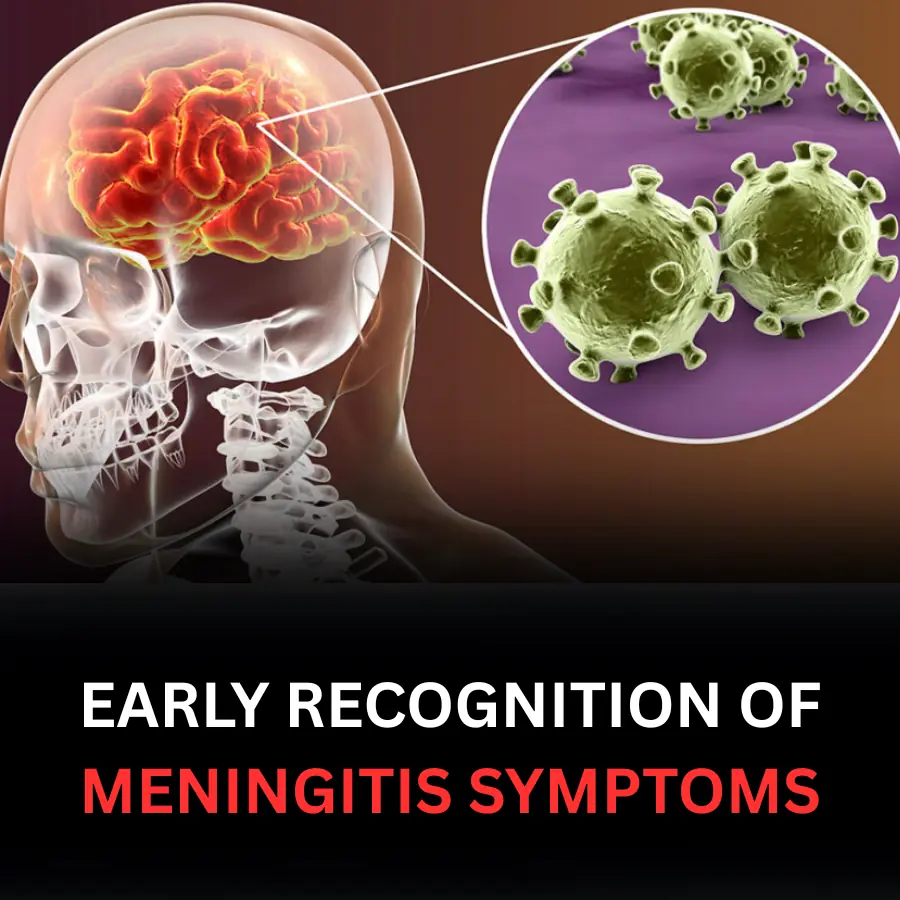
Meningitis can strike anyone at any time and may cause severe, life-threatening consequences if not detected and treated promptly.
Severe headache and acute liver failure caused by fungal and viral meningitis
Patient L.V.H., 42 years old (Thai Nguyen), was admitted to the National Hospital for Tropical Diseases with intense headache, jaundice, ascites from cirrhosis, markedly elevated liver enzymes, acute liver failure, and pneumonia. Cerebrospinal fluid testing confirmed meningitis caused by Cryptococcus fungus, along with EBV and CMV viral infections, and a flare-up of latent hepatitis B.
With a very high risk of mortality, doctors immediately initiated combined treatment including antifungal medications, antiviral therapy for hepatitis B, antibiotics, and lumbar drainage to reduce intracranial pressure. After two months, the patient’s fever subsided, jaundice improved, liver function began to recover, and overall condition stabilized.
What causes meningitis?
Meningitis is inflammation of the meninges — the protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord. It is most commonly caused by infections such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites, but can also result from trauma, chemicals, or autoimmune diseases.
The disease can occur at any age, though infants and the elderly are at higher risk.
Early recognition of symptoms is crucial because meningitis progresses rapidly. Prompt treatment significantly reduces the risk of complications and death.
Some types of meningitis, such as meningococcal bacterial meningitis, are contagious. Early detection allows isolation and prevents community spread.
Even with treatment, meningitis can leave serious long-term complications such as hearing loss, epilepsy, and cognitive impairment. This makes early diagnosis and treatment essential.
Symptoms of meningitis
Symptoms vary depending on the cause, age, and overall health, but common signs include:
– High fever, often accompanied by severe headache centered in the forehead and back of the head.
– Neck stiffness: difficulty bending the head forward due to tight neck muscles, with persistent pain.
– Nausea and vomiting unrelated to eating, caused by increased intracranial pressure.
– Altered consciousness: drowsiness, confusion, unconsciousness, or seizures, indicating severe neurological involvement.
– Skin rash or petechiae: especially in meningococcal infections; this is a medical emergency.
– Sensitivity to light and sound: eye pain under bright light, ear pain with loud noises.
Other possible symptoms include muscle or joint pain, rapid breathing, shortness of breath, and impaired eye movement.
Symptoms in children
In infants and young children, signs may be subtle and harder to recognize. Parents should watch for:
– Persistent crying, irritability, difficult to soothe
– Poor feeding, vomiting
– Bulging fontanelle (in infants)
– Seizures
– Skin rash
Anyone showing signs suggestive of meningitis should seek medical care immediately.
How to prevent meningitis
– Do not share personal items such as cups, water bottles, straws, toothbrushes, lip balm, or cigarettes.
– Keep distance from individuals with respiratory infections.
– Cover your mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing, then wash hands thoroughly.
– Maintain a healthy lifestyle: balanced diet, regular exercise, and adequate sleep to strengthen immunity.
– Ensure vaccinations are up to date according to public health recommendations — this is the most effective preventive measure.
News in the same category


The More You Drink, the More Your Bones Suffer: 3 Hidden “Calcium Thieves” That Quietly Weaken Your Skeleton
An 8-year-old girl di.es from kid.ney can.cer, father breaks down in tears: “It’s all my fault!”
Did you know that if you get spots on your hands it means you have
Science backs it up: 3 fruits that fight fatty liver, regulate sugar and cholesterol

Depressing find at the bottom of the Mariana Trench is a warning to the world
What really happens to your kidneys when you drink coconut water

10 signs you're not drinking enough water
Why Are My Veins Suddenly Bulging and Visible?
How to destroy your liver: 10 worst habits for fatty liver (hepatic steatosis)
See your doctor immediately if you notice these signs in your kidneys
8 Early Warning Signs Of Ovarian Cancer You Shouldn’t Ignore

7 benefits of corn silk and how to use it you may not know
6 Best Remedies To Clear Out Your Arteries
Revealing the Human Heart: A Stunning Look at Its Circulatory System Without Muscle or Fat

5 essential foods that can help strengthen your immune system every day

No matter how small your house is, you must grow this plant in your house

Sweet potatoes are good in every way, but there are 2 times when you should not eat them
News Post

Many children hospitalized for stroke: A warning bell from subjectivity

5 Types of Foods You Should Avoid Buying at the Supermarket

The More You Drink, the More Your Bones Suffer: 3 Hidden “Calcium Thieves” That Quietly Weaken Your Skeleton

Don’t use your air fryer if you don’t know this super-fast cleaning hack!

An 8-year-old girl di.es from kid.ney can.cer, father breaks down in tears: “It’s all my fault!”

Why do smart homemakers keep toilet paper in the refrigerator?

Try These 5 Cleaning Tricks That Make It Shine Like New With Almost No Effort

Did you know that if you get spots on your hands it means you have

Science backs it up: 3 fruits that fight fatty liver, regulate sugar and cholesterol

Depressing find at the bottom of the Mariana Trench is a warning to the world
What Your Belly Is Trying to Tell You

What really happens to your kidneys when you drink coconut water

10 signs you're not drinking enough water

Why Are My Veins Suddenly Bulging and Visible?

How to destroy your liver: 10 worst habits for fatty liver (hepatic steatosis)

See your doctor immediately if you notice these signs in your kidneys

8 Early Warning Signs Of Ovarian Cancer You Shouldn’t Ignore

7 benefits of corn silk and how to use it you may not know
