Catching Nasopharyngeal Cancer in Its Early Stages May Offer a 72% Survival Rate
Nasopharyngeal Cancer
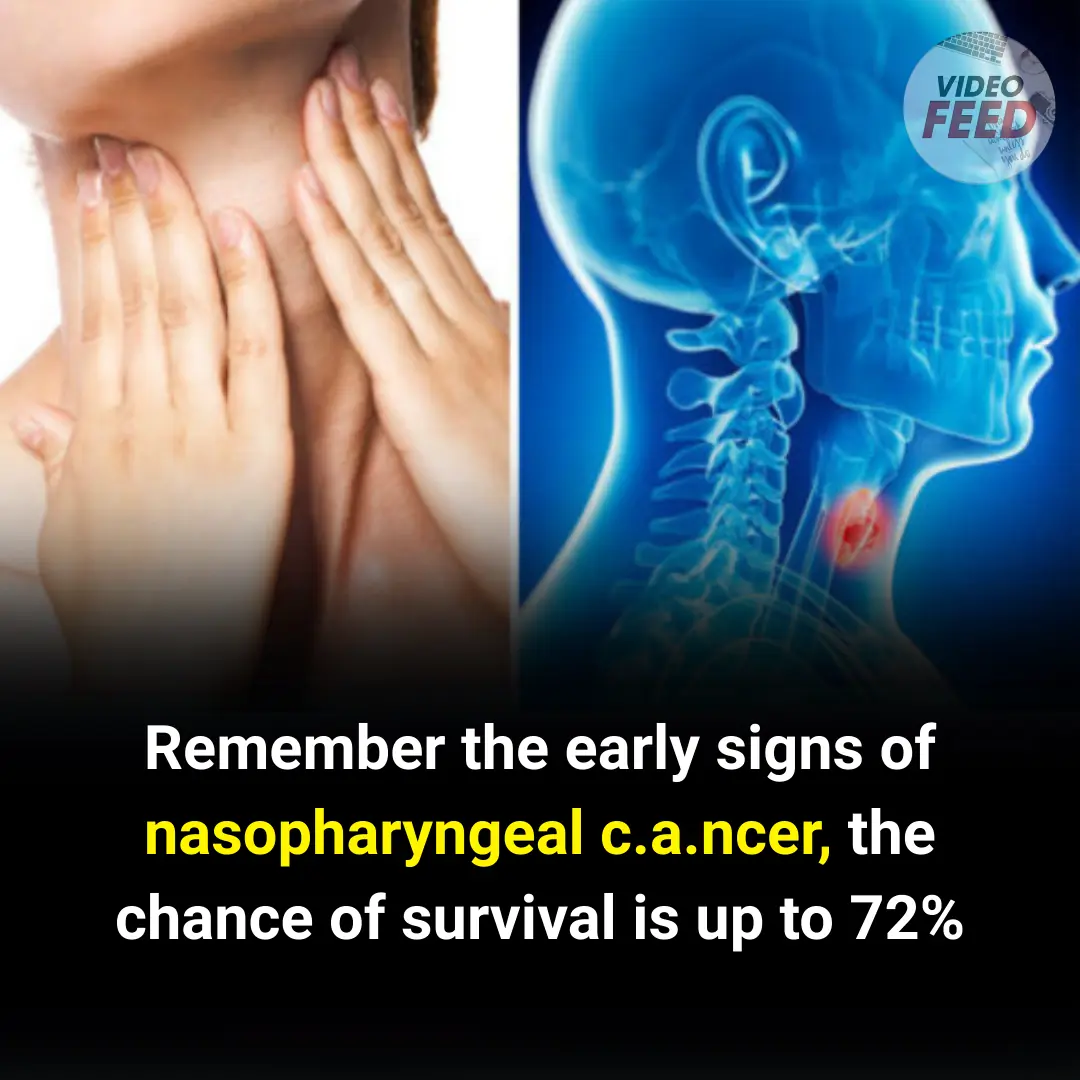
Nasopharyngeal cancer is a rare type of head and neck cancer that occurs in the nasopharynx — the upper part of the throat behind the nose.
The nasopharynx sits in a “precarious” position at the base of the skull, just above the roof of the mouth. The nasal passages connect to the nasopharynx. When you breathe, air passes through the nose, down to the throat and nasopharynx, and then into the lungs.
Nasopharyngeal cancer is also called nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC).
Causes of Nasopharyngeal Cancer
Scientists are not certain about the exact causes of nasopharyngeal cancer. However, it is strongly linked to the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV). Although EBV infection is very common, not everyone infected with EBV will develop nasopharyngeal cancer.
Risk factors may include a diet high in salted meat and fish. Tobacco and alcohol are also considered potential contributors, although their link to nasopharyngeal cancer is less clear. Some researchers believe that chemicals in tobacco and alcohol can damage DNA in cells.
Who Is at Risk?
According to the American Cancer Society, fewer than 1 in 100,000 Americans are diagnosed with this cancer. However, nasopharyngeal cancer is much more common in southern China and Southeast Asia.
You may be at higher risk if you:
-
Frequently eat salted meat and fish
-
Have a family history of nasopharyngeal cancer
-
Carry certain genes linked to cancer development
-
Are infected with EBV
-
Smoke
-
Drink alcohol
-
Are exposed to wood dust or formaldehyde
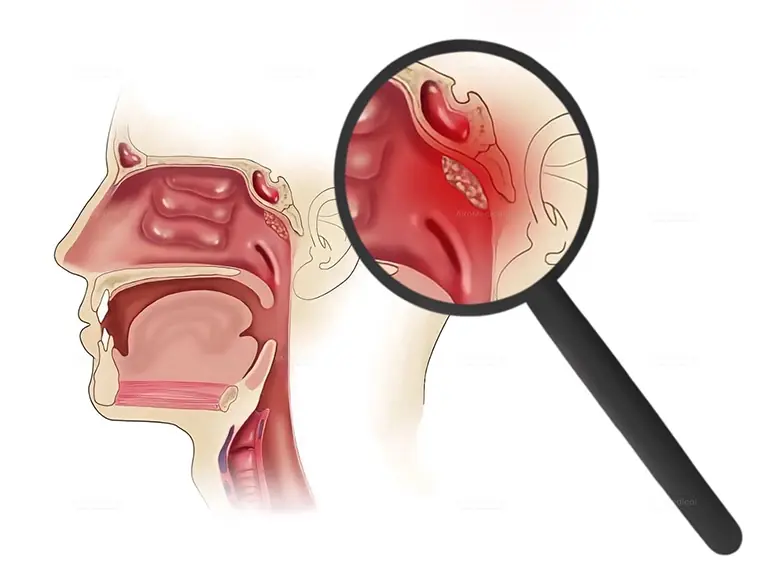
Symptoms of Nasopharyngeal Cancer
-
Lump in the nose or neck
-
Blood in saliva
-
Sore throat
-
Difficulty breathing or speaking
-
Nosebleeds
-
Nasal congestion
-
Hearing loss
-
Frequent ear infections
-
Headaches
Note: These symptoms can also be caused by other, less serious conditions. If you experience any of them, consult a healthcare professional. Only a doctor can determine whether it is nasopharyngeal cancer.
Diagnosis
-
Physical exam and medical history: A doctor will ask about symptoms, personal and family medical history, and perform a general exam to check for signs such as swollen lymph nodes in the neck or other abnormalities.
-
Biopsy: Tissue or cell samples are examined under a microscope for signs of cancer. Samples are usually taken during a nasal endoscopy.
-
Imaging tests: These may include CT scans, MRI, PET scans, or X-rays.
Staging and Prognosis
If diagnosed with nasopharyngeal cancer, additional tests will be done to see how far the cancer has spread. This is called staging.
Nasopharyngeal cancer is staged from Stage 1 (earliest) to Stage 4 (most advanced).
Five-year survival rates vary by stage, according to a U.S. study in 2010:
-
Stage 1: 72%
-
Stage 2: 64%
-
Stage 3: 62%
-
Stage 4: 38%
Treatment Options
Treatment and prognosis depend on factors such as stage, type of cancer, tumor size, patient age, and overall health.
Three standard treatments are used:
-
Radiation therapy: Uses high-energy beams, such as X-rays or protons, to kill cancer cells.
-
Chemotherapy: Uses chemical drugs to destroy cancer cells. Chemotherapy may be given as pills, intravenously, or both. It can be used before, during, or after radiation therapy.
-
Surgery: Surgery is not commonly used for nasopharyngeal cancer, but doctors may perform it to remove affected lymph nodes in the neck.
Can It Be Prevented?
In many cases, nasopharyngeal cancer cannot be fully prevented. However, you can reduce your risk by:
-
Avoiding salted fish and meat
-
Not smoking
-
Avoiding alcohol
News in the same category

7 Foods That Can Turn He.art Medications into a “De.adly Poi.son”

Doctor Reveals 5 Dangerous Mistakes You Must Avoid Right After Eating
"7 Silent Habits That Wreck Your Bones and Joints — Quit Them Now or Face Pain in Old Age

Night Sweats Explained: 7 Surprising Facts
Warning: 10 Overlooked Symptoms That Could Signal Blood Cancer

4 Abnormal Signs in the Abdomen That May Seem “Minor” but Could Indicate Can.cer

Surprising Everyday Foods That Quietly Work Wonders for Your Liver — And Why You Should Add Them to Your Diet

Despite its health benefits, star fruit is strictly off-limits for these groups of people
This condition can trigger a sudden transformation in the fingers, leaving them ghostly white or bluish
Night Clues: 5 Rare Symptoms Pointing to Kidney Damage
Don’t Overlook These 6 Warning Signs of Stage 1 Colon Cancer

These 3 Common Fish Are Actually the Best for Your Health

4 Foods That Help Prevent Vag.inal Infections:

4 Foods to Eat on an Empty Sto.mach in the Morning That Work Like a “Trash Scanner” for the Body

6 Foods That Balance Hormones and Stop Hair Loss — A Secret Few Women Know!
Woman Shocked by Doctor’s Diagnosis After Visiting Hospital for Severe Itching
Cervical Cancer: 8 Hidden Warning Signs Just Uncovered

If your breath carries these 4 unusual odors, it could signal hidden illness — don’t ignore the warning signs
News Post

A 33-Year-Old Woman Ate Lettuce at Every Meal—Three Months Later

7 Foods That Can Turn He.art Medications into a “De.adly Poi.son”

Storing Leftover Rice the Japanese Way

Seafood Shop Owner Warns: 4 Types of Shrimp You Should Never Buy

The hidden function of the small hole in a nail clipper

These 5 Secrets Are the Real “Saviors” for Keeping It Fresh!

Doctor Reveals 5 Dangerous Mistakes You Must Avoid Right After Eating

"7 Silent Habits That Wreck Your Bones and Joints — Quit Them Now or Face Pain in Old Age

Avoid These Plants If You Don’t Want Snakes Near Your House

Night Sweats Explained: 7 Surprising Facts

What the lines on bath towels actually mean?

Farmers put ice on melons before harvest – the reason behind it will surprise everyone

6 Proven Ways to Get Rid of Termites From Wooden Furniture

Warning: 10 Overlooked Symptoms That Could Signal Blood Cancer

Should You Pick Na.vel Oranges With a Big or Small “Na.vel”?

4 Abnormal Signs in the Abdomen That May Seem “Minor” but Could Indicate Can.cer

3 super easy garlic storage hacks

The More You Save, the Sicker You Get: 6 Dangerous Kitchen Habits to Stop Immediately
