
Coffee Isn’t Always Healthy: 12 People Who Should Avoid It

Coffee is generally considered healthy. It may reduce the risk of prostate cancer, lower the risk of heart failure, and even decrease the chance of hearing loss. Drinking coffee might also help with weight loss.
However, for some people, coffee can actually cause more negative side effects than benefits. Here are the types of people who should avoid drinking coffee.
12 Types of People Who Should Avoid Coffee
1. People with Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
Caffeine can increase bowel motility, including the risk of diarrhea—a key symptom of IBS. If you have IBS, it is advisable to limit or avoid caffeinated beverages.
2. People with Glaucoma
Recent research suggests that coffee can increase intraocular pressure in people with glaucoma. It is generally recommended to limit or avoid coffee, although further studies are needed.
3. People with Overactive Bladder
Everyone knows it’s best to avoid coffee before a long trip, especially if bathroom breaks are limited. Caffeine can increase both urinary frequency and urgency. If you don’t drink coffee regularly, you may be even more sensitive to these effects.
4. People with Certain Heart Conditions, Such as Arrhythmias
Caffeine from coffee can temporarily raise blood pressure and heart rate. Anyone with preexisting heart conditions should consult their doctor about whether coffee is safe and how much can be consumed.
5. Pregnant Women
Pregnant women are advised to limit caffeine to 200 mg per day (about two cups of coffee) to reduce the risk of miscarriage, preterm labor, and low birth weight. However, a 2020 review in the British Journal of Medicine concluded that there is no completely safe caffeine level during pregnancy. Pregnant women should discuss their caffeine intake with their doctor.
6. Breastfeeding Women
Because caffeine is a stimulant and a diuretic, breastfeeding mothers may risk dehydration. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists recommends minimizing caffeine intake as much as possible during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
7. People with Sleep Disorders
It may be tempting to have a cup (or more) of coffee after a poor night’s sleep, but this habit can prolong cycles of poor sleep and fatigue. Even if you don’t think an afternoon coffee affects your sleep, it can impact sleep quality. It is recommended to avoid caffeine at least 6 hours before bedtime.
8. People with Anxiety or Panic Disorders
Caffeine is a stimulant and can worsen anxiety in some individuals. If you frequently experience anxiety or panic attacks, consider reducing or avoiding caffeinated coffee.
9. People with Diarrhea
Caffeine increases bowel motility, which is not helpful if you are experiencing diarrhea. Decaffeinated coffee may be less problematic, though hot liquids in general can stimulate the intestines.
10. People with Epilepsy
While research is limited, recent findings suggest that high coffee consumption may be associated with increased seizure frequency. More research is needed, but it’s wise to consult a neurologist about safe caffeine intake if you have epilepsy.
11. Children Under 12
Caffeine can make anyone jittery, but in children, even small amounts can cause more noticeable or serious side effects. Too much caffeine in children can lead to increased heart rate, anxiety, difficulty concentrating, and stomach pain. Another consideration, especially for toddlers, is that coffee may suppress hunger cues, potentially affecting growth and nutrition. Finally, coffee is highly acidic, which can damage tooth enamel and increase the risk of cavities.
12. People with Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
Caffeine can relax the lower esophageal sphincter, the valve between the esophagus and stomach. If you have GERD, consider switching to decaffeinated coffee or avoiding coffee altogether.
News in the same category


A breakthrough that could stop cancer before it spreads — scientists may have found the missing key

Broccoli or Cauliflower: Which Vegetable Offers Greater Health Benefits?
Doctors Warn: Ignoring “Mild” Conditions Can Have Serious Consequences

A Tragic Case Raises Alarms About Nighttime Habits Many People Ignore

This common kitchen root may help keep blood clots away — many people eat it daily without realizing its power

At 31, After Three Strokes: The Price of a “No Consequences, No Fear” Lifestyle Many Young People Live By
Big belly doesn't always mean fa.t: How to distinguish between belly fat and liver disease
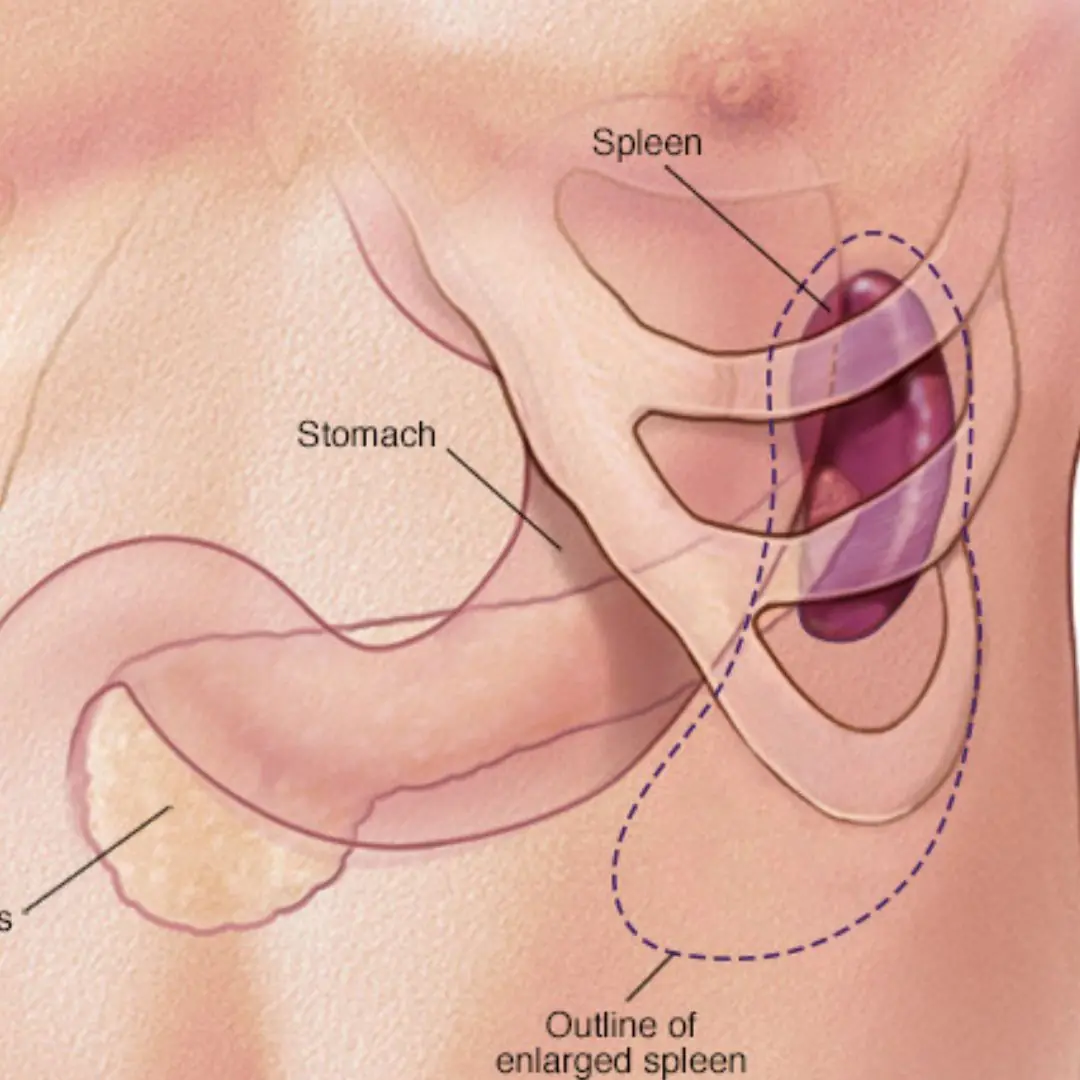
Is Your Spleen Trying to Tell You Something? Watch for These Symptoms

Turmeric with Honey Is Very Beneficial, but There Are 5 Groups of People for Whom It Can Be Harmful
Your legs are screaming ‘HELP!:’ 5 warning signs from your liver
8 Bathroom Signs That Could Signal a Serious Problem

Diabetes warning signs often appear in your feet - here are 10 to look out for

Japan announces 5 foods to eat daily: Eggs only rank 5th, while the true "king of nutrition" is this dish

5 types of vegetables contain "a nest of hidden worms"
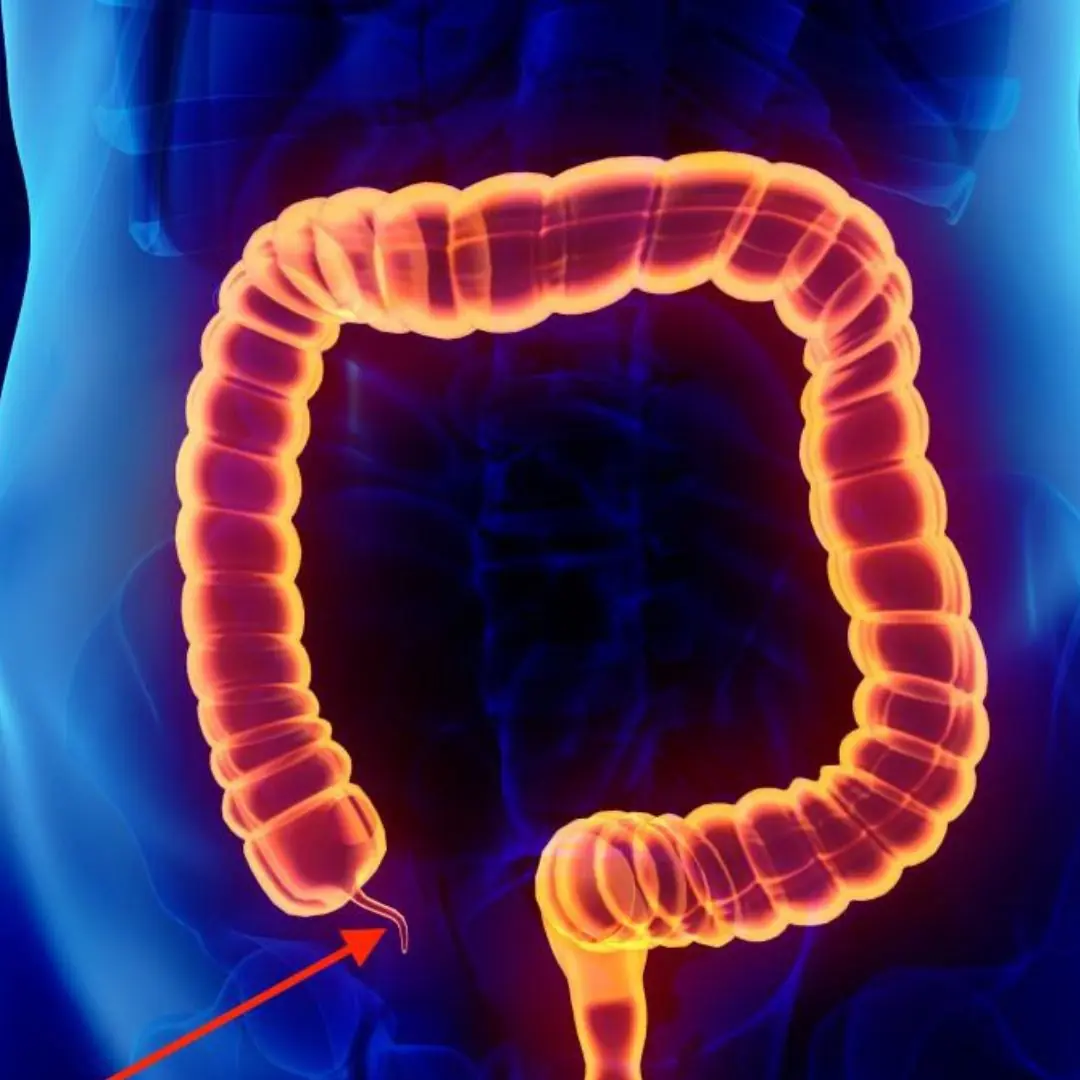
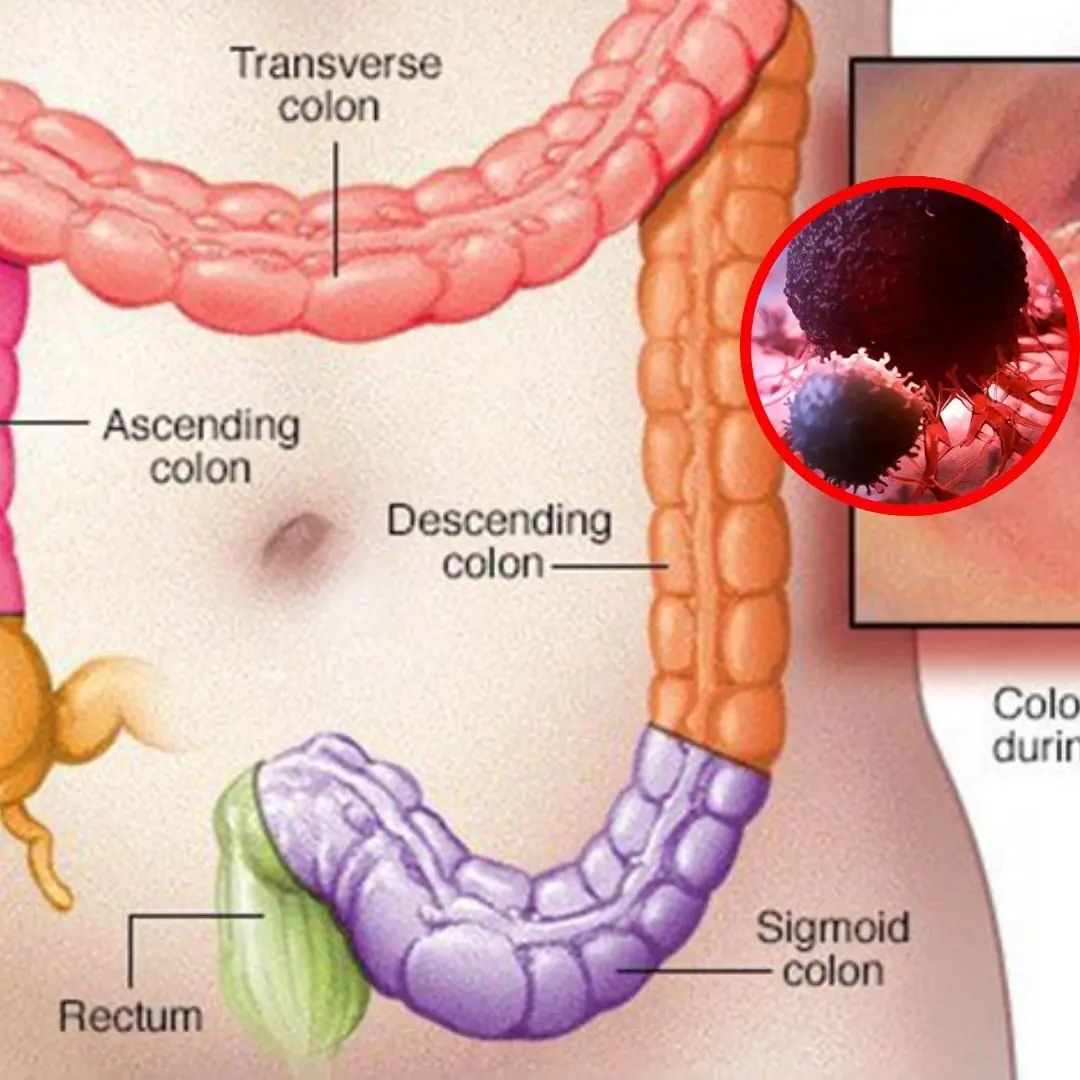
5 Signs of Appendicitis — Don’t Ignore These Symptoms!
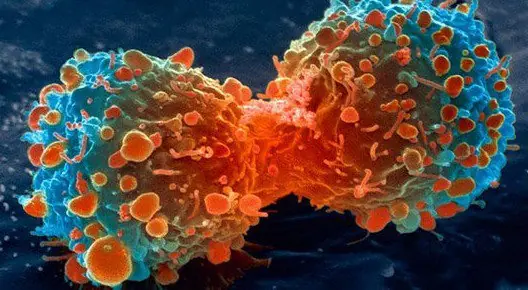
Three Principles to Prevent Can,cer Cells — Everyone Should Act Now to Say No to the Disease
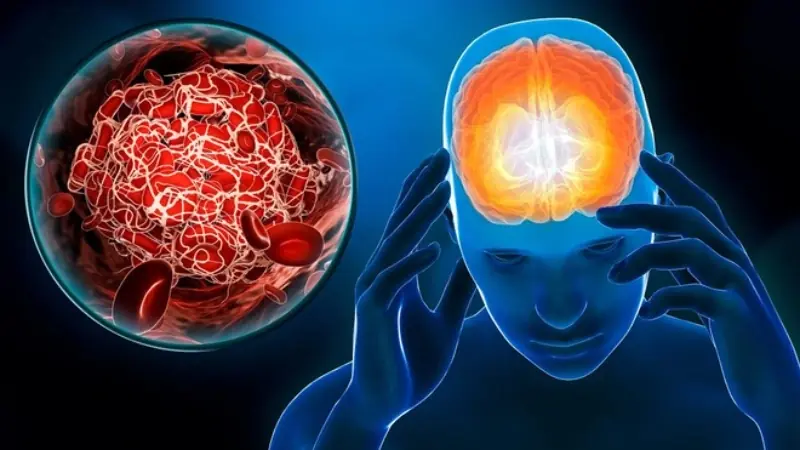
Stroke Warning: Signs That Can Appear Up to One Week in Advance — Do Not Ignore
Drinking These 4 Common Beverages Could Be Harming Your Kid.neys
News Post
If You Notice Even One of These 7 Signs, Get Checked for Stomach Can:cer Immediately

Man Di.es After Eating Eggs: Doctors Warn Against a Common but Dangerous Eating Habit

Diagnosed with can.cer, lived a century: What this Japanese doctor did differently

Not all expired food is trash — these 6 items may still be safe to eat

A breakthrough that could stop cancer before it spreads — scientists may have found the missing key

Broccoli or Cauliflower: Which Vegetable Offers Greater Health Benefits?

Doctors Warn: Ignoring “Mild” Conditions Can Have Serious Consequences

A Tragic Case Raises Alarms About Nighttime Habits Many People Ignore

This common kitchen root may help keep blood clots away — many people eat it daily without realizing its power

Rainbow-Shimmering Beef: Should You Eat It or Throw It Away?

At 31, After Three Strokes: The Price of a “No Consequences, No Fear” Lifestyle Many Young People Live By

Big belly doesn't always mean fa.t: How to distinguish between belly fat and liver disease

Is Your Spleen Trying to Tell You Something? Watch for These Symptoms

Turmeric with Honey Is Very Beneficial, but There Are 5 Groups of People for Whom It Can Be Harmful

Your legs are screaming ‘HELP!:’ 5 warning signs from your liver

8 Bathroom Signs That Could Signal a Serious Problem

Diabetes warning signs often appear in your feet - here are 10 to look out for

Japan announces 5 foods to eat daily: Eggs only rank 5th, while the true "king of nutrition" is this dish
