Don't Mistake Early Sleep as the 'Key' to Health: The Surprising Truth About Sleep
Don't Mistake Early Sleep as the 'Key' to Health: The Surprising Truth About Sleep
Sleep plays a crucial role in protecting and enhancing both physical and mental health. However, the belief that "going to bed early and waking up early" is always beneficial isn't entirely accurate.

Mr. Li's Story: A Sleep Habit Dilemma Mr. Li, a 60-year-old man from Guangzhou, has always prioritized his health. With a habit of going to bed early and waking up early, he believed this practice kept him healthier than his peers. However, recent social media posts left him confused after reading claims like "Going to bed early might lead to early death." This conflicting information left him unsure of what to believe.
Should Seniors Rethink Their Sleep Schedule? Does going to bed early actually affect lifespan?
Traditionally, many believe that "sleeping early is good for health." Traditional Chinese Medicine also advises, "Go to bed early and wake up with the sun." Yet, a recent study published in the Journal of Sleep Medicine suggests otherwise. Researchers tracked over 112,000 people across 21 countries for more than nine years. The results revealed that going to bed before 10 PM was associated with a 29% increased risk of major cardiovascular events compared to those who slept between 10 PM and midnight.
However, this study isn't definitive. Firstly, it's an epidemiological study, meaning it identifies trends but doesn't prove causation. Secondly, a significant proportion of the early sleepers in the study were from less developed countries, where limited healthcare services might contribute to shorter lifespans.
Early to Bed, Early to Rise: Healthier Than Late Sleepers?
The debate around sleeping early versus late continues. One common question is why seniors who go to bed early seem more prone to heart attacks. This phenomenon may be linked to cold early mornings, especially in winter, which can raise blood pressure and constrict blood vessels during outdoor activities, increasing heart attack risks.
So, which is better: sleeping early or late? The key isn't the exact bedtime but maintaining a consistent and sufficient sleep schedule. If you feel alert and productive during the day, your routine is likely fine.
Experts suggest that the ideal bedtime is between 10 PM and 11 PM for optimal heart health. Sleep duration also matters: the World Health Organization (WHO) recommends adults sleep 7-9 hours nightly. Older adults, due to physiological changes, may need more rest:
-
Ages 50-70: 7-8 hours
-
Ages 70-80: 7-9 hours
-
Over 80: 9-10 hours
5 Sleep Habits That Could Harm Your Health
Sleep is essential for recovery and well-being, but poor habits can lead to health complications. Here are five practices to avoid:
-
Sleeping on a Full Stomach Going to bed right after a large meal forces your stomach and intestines to work overtime, potentially disrupting sleep. Avoid eating heavy meals 1-2 hours before bedtime and opt for easily digestible foods.
-
Drinking Alcohol or Stimulants Before Bed Alcohol doesn't improve sleep quality. In fact, it can cause fatigue upon waking. For individuals with breathing issues, alcohol may pose additional risks.
-
Sleeping with Lights On Nighttime light exposure can negatively impact the nervous, cardiovascular, and endocrine systems, potentially increasing the risk of hypertension, diabetes, memory loss, and obesity.
-
Sleeping on Your Stomach Stomach sleeping compresses the chest, reducing lung capacity and making breathing more difficult. It can also impair circulation and cause facial puffiness due to restricted blood flow.
-
Sleeping While Angry Going to bed with unresolved anger triggers stress, which interferes with the brain's ability to relax. This may result in difficulty falling asleep, early awakenings, and nightmares, while also disrupting hormone balance.
Conclusion: Sleep isn't solely about sleeping early; it's about consistency, duration, and healthy habits. Listen to your body's signals and prioritize a stable, restful routine for better long-term health.
News in the same category

4 Finger Changes You Shouldn’t Ignore — Possible Signs of Lung Cancer
Middle-Aged People, Stop Doing These 7 Things-Even in the Cold Winter-Before It's Too Late!
How Sleeping on Your Left Side Supports Brain, Digestive, and Lymphatic Health
Your feet are a "bl.o.od sugar meter" Beware of diabetes if you frequent experience these 5 strange symptoms
Causes and symptoms of an umb:ilical hernia
7 indicators that your kidneys are functioning well - check

12 Benefits You’ll See After Eating Banana and Avocado Every Morning
Swollen Lymph Nodes in the Ne.ck - Here's When You Need to Worry

5 foods you should never keep overnight, if left over, throw it away
Early Warning Signs That C.a.ncer Is Growing In Your Body
The liver is an important detoxification and metabolic organ of the body.

People Sho:cked to Learn Reason Public Toilet Doors Don’t Touch The Floor
You shouldn't ignore these signs

Eggplant holds the crown among vegetables — but if you fall into one of these 4 groups, stay away from it
If You Keep Noticing These 5 Strange Symptoms, Diabetes Might Be the Reason

5 unusual bowel-related symptoms you should never ignore

Doctors Reveal What These Bruises on Your Body Could Indicate
Two Early Warning Signs of Kidney Damage: Morning Urine Color That Should Never Be Ignored

Just 30 Seconds at Home: A Simple Test That May Help You Notice Early Warning Signs of Can,cer
News Post

Pumpkin Crunch Parfaits

Calling all sweet potato fans!

4 Finger Changes You Shouldn’t Ignore — Possible Signs of Lung Cancer

Middle-Aged People, Stop Doing These 7 Things-Even in the Cold Winter-Before It's Too Late!

How Sleeping on Your Left Side Supports Brain, Digestive, and Lymphatic Health

Ever Wondered Why Hotels Put a Cloth Across the Bed? Here’s the Answer

Your feet are a "bl.o.od sugar meter" Beware of diabetes if you frequent experience these 5 strange symptoms

Causes and symptoms of an umb:ilical hernia

7 indicators that your kidneys are functioning well - check

12 Benefits You’ll See After Eating Banana and Avocado Every Morning

Swollen Lymph Nodes in the Ne.ck - Here's When You Need to Worry

5 foods you should never keep overnight, if left over, throw it away

Early Warning Signs That C.a.ncer Is Growing In Your Body

Steamed Cockles with Spicy Lime Chili Dipping Sauce

Spicy Stir-Fried Squid with Basil
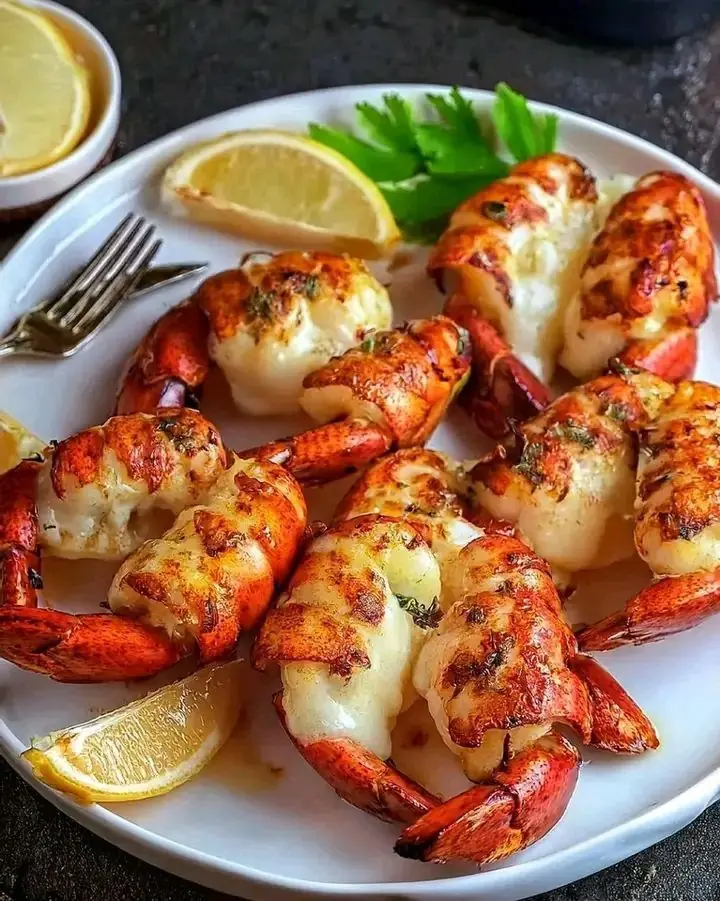

Baked Stuffed Lobster Tails with Garlic Butter
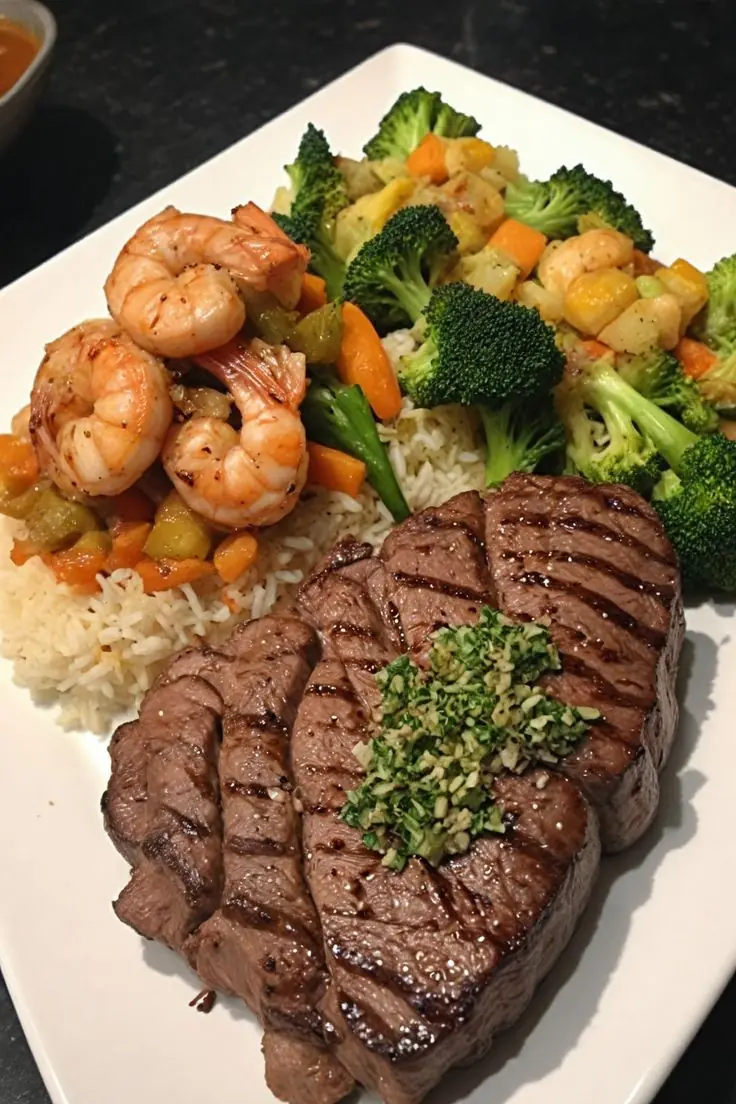

Grilled Steak & Shrimp with Rice and Mixed Vegetables
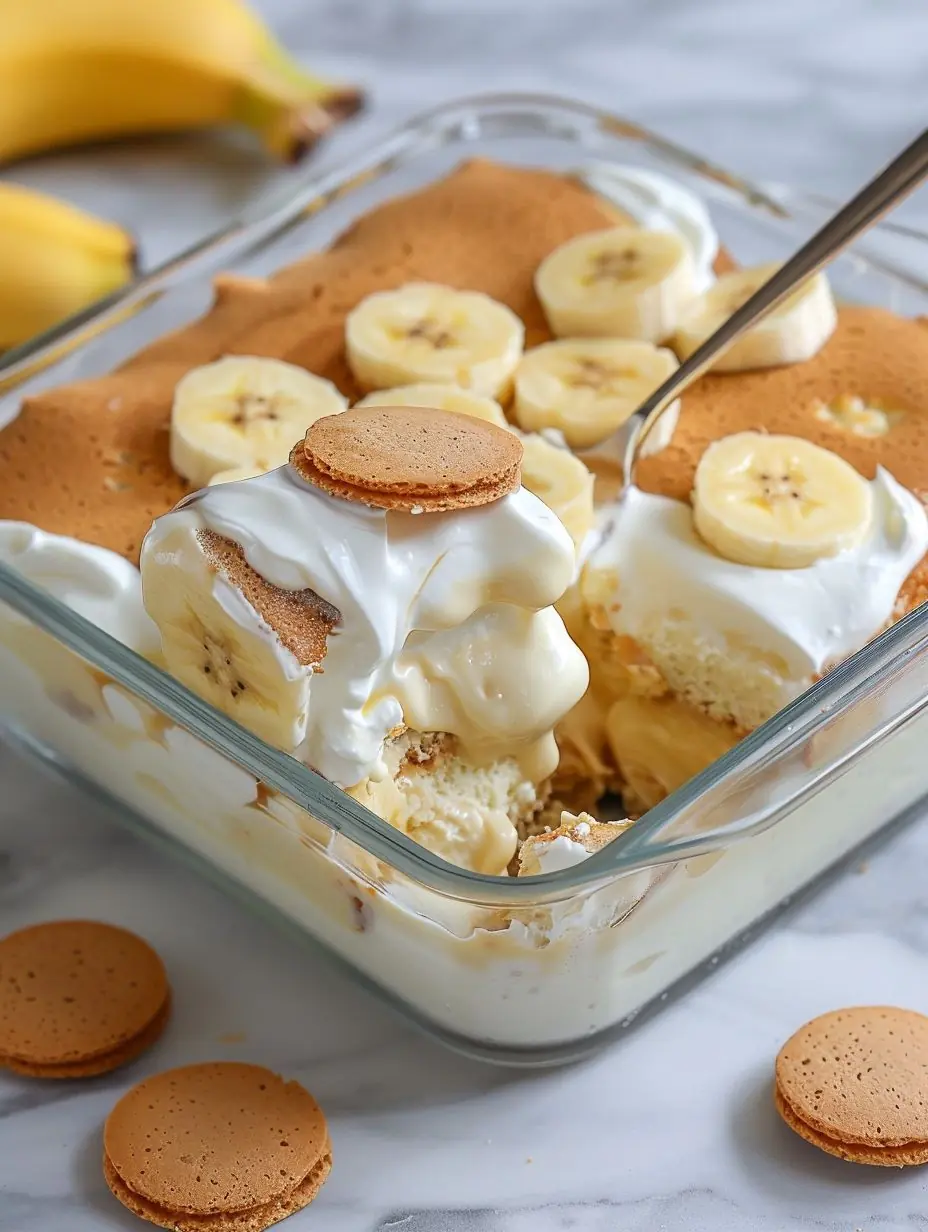

Classic Banana Pudding (No-Bake Layered Dessert)
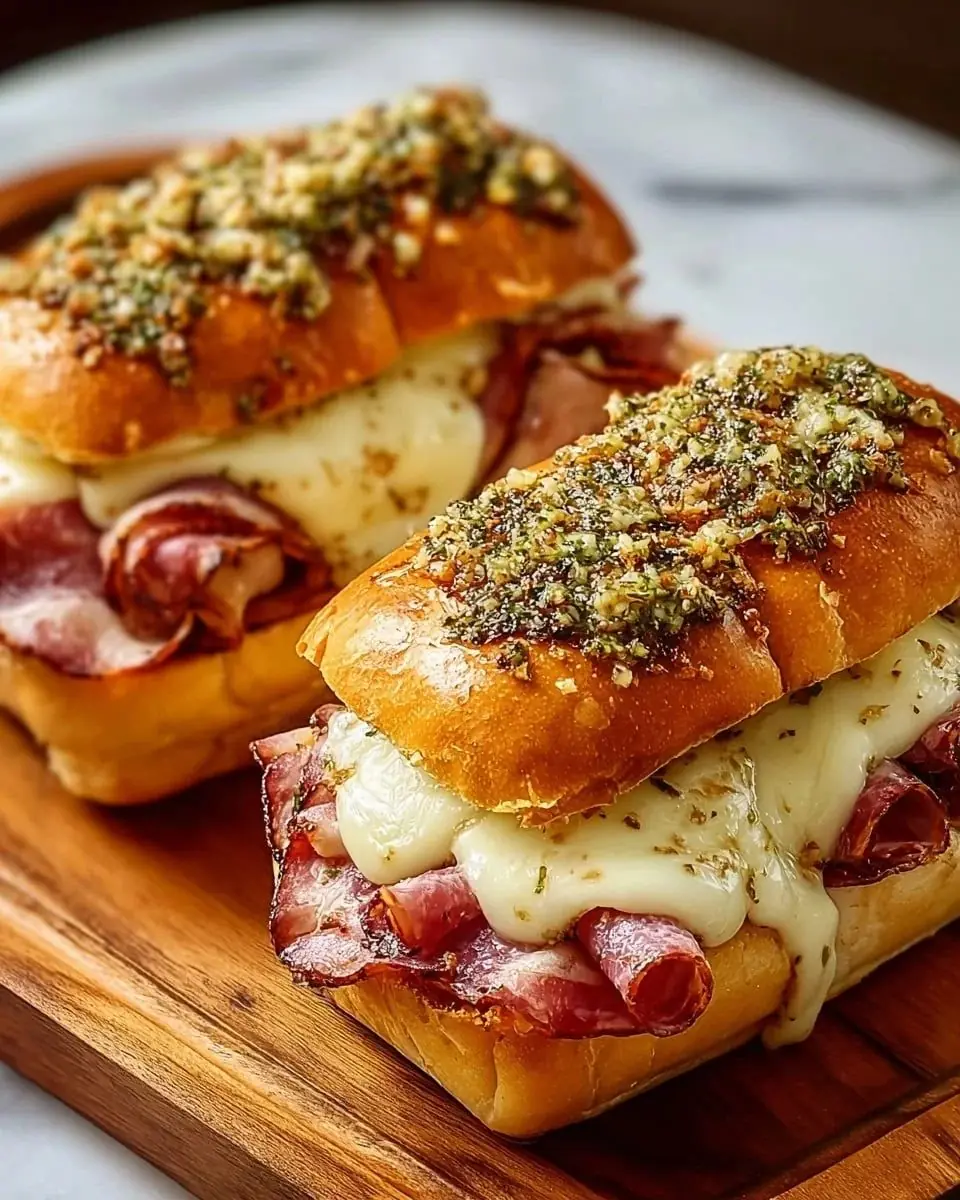

Italian Deli Sandwich with Melted Cheese & Herb Butter
