
Examination shows milky serum, a warning sign of stroke risk
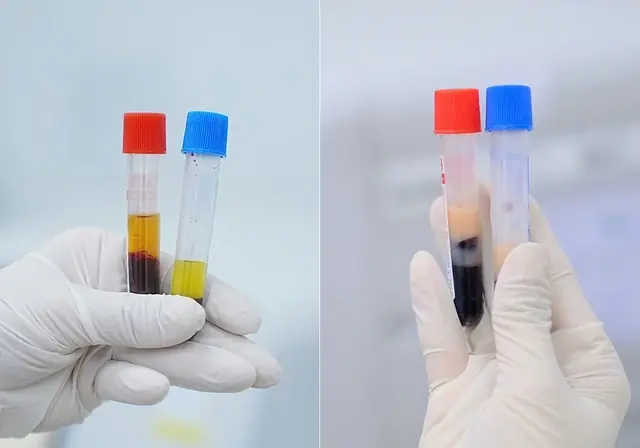
Milky-White Serum: A Warning Sign of Stroke Risk
Introduction
Many people feel surprised and worried when their doctor informs them that their blood serum appears cloudy or milky during a health checkup. This condition not only affects test results but is also an important sign warning of many serious health problems, especially the risk of stroke and other cardiovascular diseases. So why does the serum become cloudy? What does it indicate about your health? And most importantly, how can you prevent the dangerous complications related to this? This article will help you better understand this phenomenon and the necessary measures to protect your health.
What Is Serum? Why Can Serum Become Cloudy?
Serum is the clear, pale yellow fluid portion of blood that remains after removing blood cells and clotting components. Normally, serum is transparent or slightly yellowish. However, when the serum appears cloudy or milky, this indicates a phenomenon called lipemia.
What Is Lipemia?
Lipemia is a condition where serum contains excessively high amounts of fats, mainly triglycerides, making the serum appear cloudy, white, or milky. Triglycerides are a type of fat in the blood that store energy and participate in many metabolic processes. However, when triglyceride levels exceed normal limits, it causes serious health problems.
Causes of Milky-White Serum
Common causes of lipemia due to elevated triglycerides include:
-
Unhealthy diet: Consuming excessive fats, cholesterol-rich foods, sweets, and processed foods can increase triglyceride levels.
-
Obesity and overweight: Excess body fat increases triglyceride production and reduces their clearance from the blood.
-
Diabetes: Especially type 2 diabetes, which disrupts lipid metabolism, causing elevated triglycerides.
-
Lipid metabolism disorders: Some genetic or acquired diseases cause lipid imbalance.
-
Certain medications: Such as contraceptives, corticosteroids, which may raise triglyceride levels.
-
Alcohol consumption: Alcohol increases triglyceride production in the liver.
-
Hypothyroidism: Slows lipid metabolism, leading to triglyceride elevation.
-
Some liver or kidney diseases: Affect lipid metabolism and clearance.
How Does Milky Serum Relate to Stroke Risk?
1. High Triglycerides and Atherosclerosis
When triglycerides are too high, they contribute to the buildup of fatty plaques on artery walls — known as atherosclerosis. These plaques narrow the arteries, reducing blood flow to vital organs such as the brain and heart.
2. Risk of Blood Vessel Blockage
Plaques can rupture, causing blood clots to form. If these clots block a brain artery, they cause ischemic stroke — one of the leading causes of death and disability worldwide.
3. Blood Viscosity and Circulation Disorders
Lipemia increases blood viscosity, making blood thicker and harder to circulate, raising the risk of clot formation inside blood vessels, which leads to cardiovascular complications and stroke.
4. Impact on Overall Health
Besides stroke risk, elevated triglycerides are associated with higher risks of other heart diseases such as heart attack, heart failure, and circulatory disorders.
Symptoms and Warning Signs
Lipemia often has no obvious symptoms, so many people only detect it via blood tests. However, when triglycerides become very high, patients may experience:
-
Headaches, dizziness
-
Chest pain or tightness
-
Fatigue, shortness of breath
-
Yellowish fatty deposits on the skin (xanthomas)
-
Abdominal pain, nausea (in cases of pancreatitis caused by high triglycerides)
Therefore, regular lipid blood testing is essential for early detection and timely treatment.
Prevention and Treatment of Lipemia Due to High Triglycerides
1. Lifestyle Changes
-
Diet: Limit saturated fats, cholesterol, and sugar. Increase intake of vegetables, fruits, whole grains, fish, and omega-3 rich foods.
-
Exercise: Regular physical activity improves lipid metabolism and helps maintain a healthy weight.
-
Weight control: Losing excess weight effectively lowers triglycerides.
-
Limit alcohol: Alcohol raises triglycerides, so it should be avoided or minimized.
-
Quit smoking: Smoking damages blood vessels and increases cardiovascular risk.
2. Medical Treatment
-
Lipid-lowering drugs: If lifestyle changes are insufficient, doctors prescribe medications such as statins, fibrates, or niacin to control triglycerides.
-
Treat underlying diseases: Proper management of diabetes, hypothyroidism, or other related illnesses.
-
Regular monitoring: Periodic lipid testing to assess treatment efficacy and adjust therapy.
When Should You See a Doctor?
You should consult a doctor if:
-
Blood tests show milky serum or high triglycerides.
-
You have a family history of cardiovascular or lipid disorders.
-
You have risk factors such as diabetes, obesity, or high blood pressure.
-
You experience symptoms like chest pain, dizziness, or shortness of breath.
Conclusion
Milky-white serum in blood tests is not just an abnormal phenomenon but a warning sign of serious hypertriglyceridemia — a major cause of atherosclerosis and stroke. Early recognition and implementing preventive measures, lifestyle changes, and proper medical treatment can help reduce the risk of dangerous complications, protect cardiovascular health, and improve quality of life.
News in the same category


6 familiar dishes that are extremely dangerous if left overnight
Doctor Urges 4 Actions to Protect Your Body’s "Blo.od Filter"

Can overly hot baths harm your heart and circulation?
7 signs of brain c.a.ncer that are easily confused with other diseases

4 Things to Avoid After 5 PM to Lower Your Risk of Stro.ke
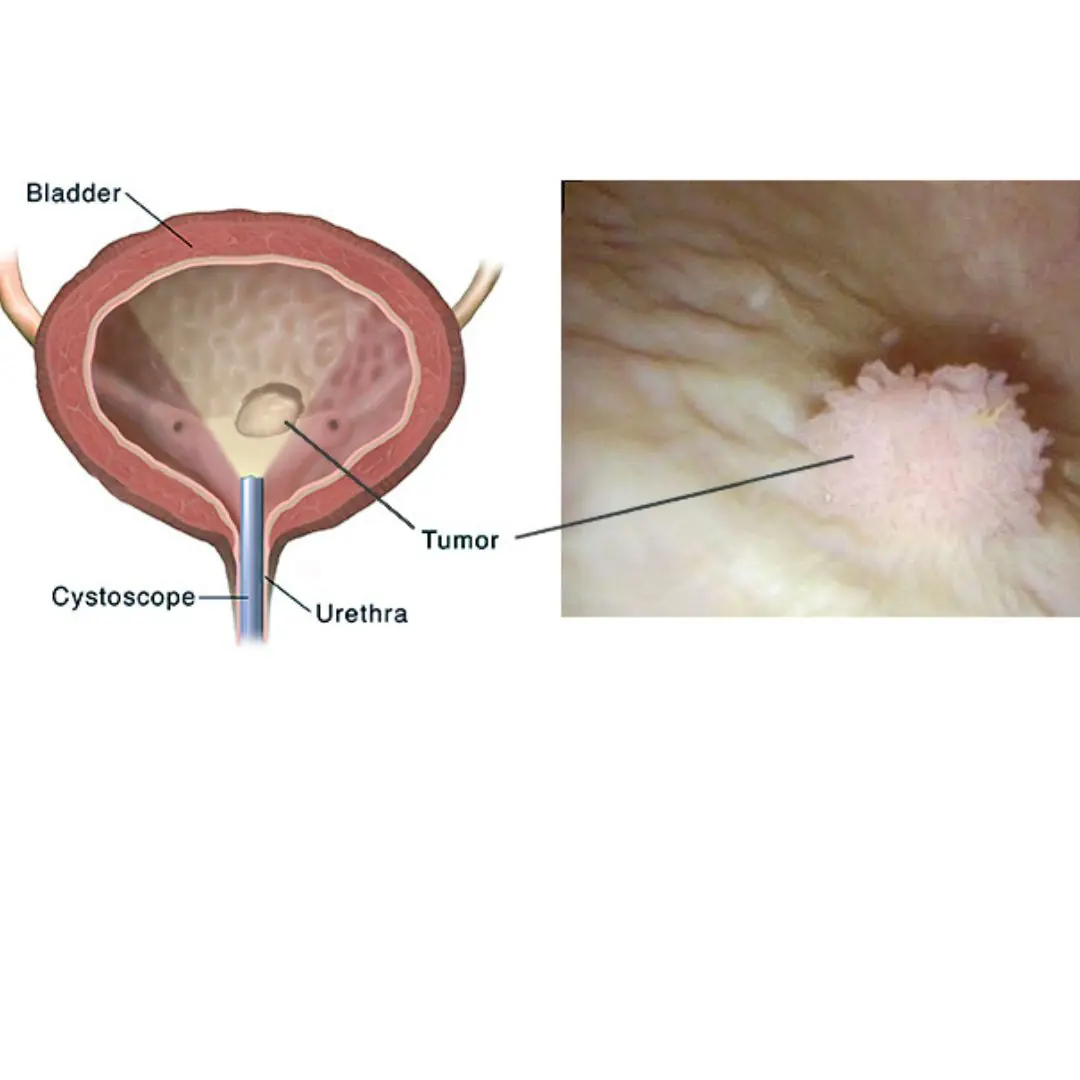
Bladder Ca.ncer: Symptoms You Shouldn’t Ignore

The Surprising Benefits of Donating Bl.o.od

5 types of vegetables and fruits help cool the liver and effectively lower liver enzymes

Woman Sudden Kidney Failure After Meal: Doctor Says “This Vegetable Is Poisonous… You Shouldn’t Eat It”

3 Critical Mistakes You Must Never Make with a Stro.ke Victim — Regret Won’t Undo the Damage

Shocking Truth: Black Garlic Isn’t for Everyone — 5 Types of People Who Should Avoid or Limit It Immediately

5 Early Warning Signs Your Body May Be Signaling Can.cer — See a Doctor Before It’s Too Late

Who should not drink soy milk? 6 things to remember
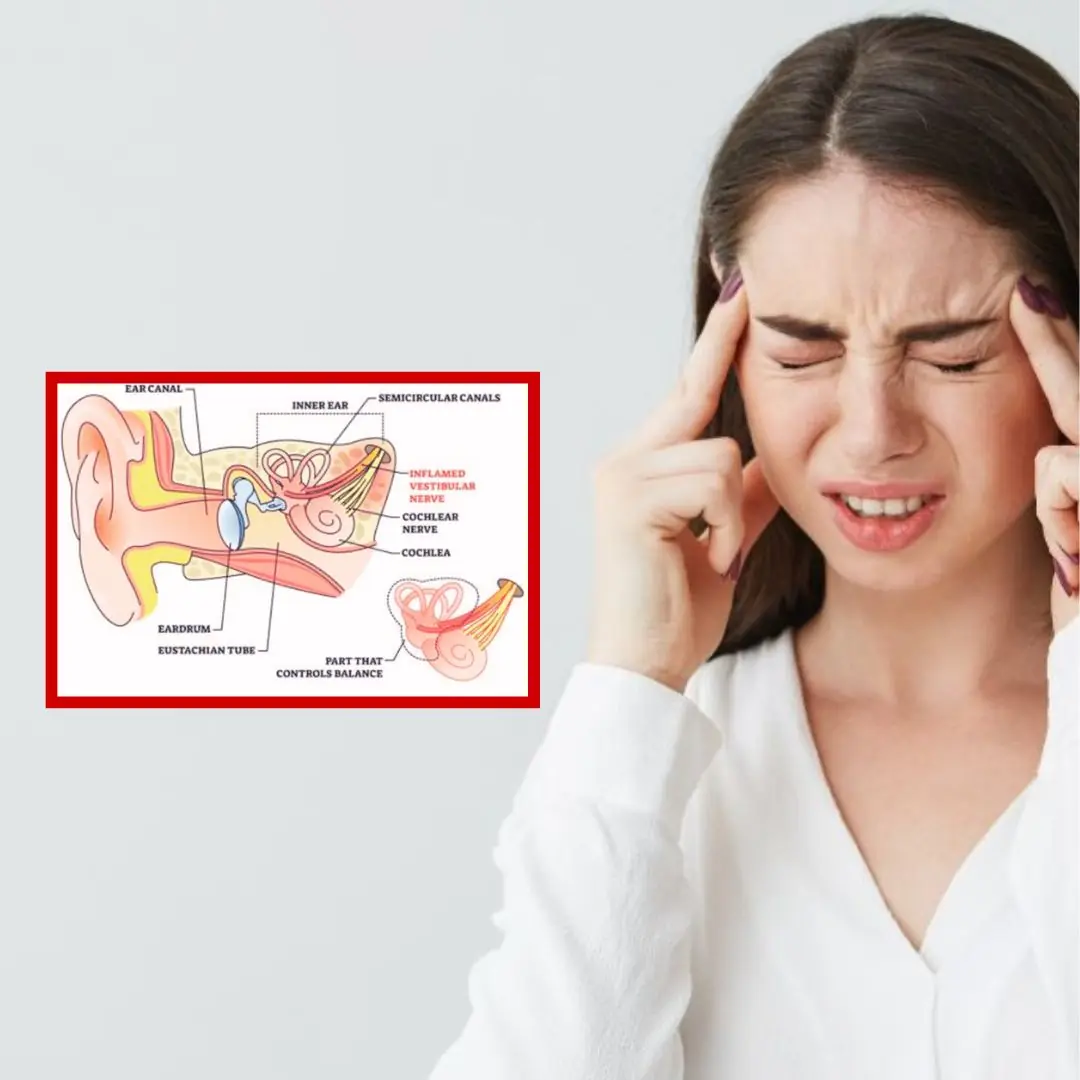
Understanding Vestibular Disorders: Causes, Symptoms, and How They're Treated
Symptoms of end stage kidney can,cer

4 best vegetables to help prevent canc.er

This fruit is extremely high in starch but helps reduce blood sugar and prevent 5 types of can.cer

These 3 “Frugal” Habits Are Actually Selling Out Your Health

Types of cooking oils that are good for the heart
News Post

4 Vegetables You Should Never Eat Raw — They Could Do More Harm Than Good!

6 familiar dishes that are extremely dangerous if left overnight

The Most Nutritious Part of the Chicken—“Pricier than Gold” Yet Often Thrown Away by Home Cooks

Doctor Urges 4 Actions to Protect Your Body’s "Blo.od Filter"

6 Smart Tips for Choosing Quality Honey Sellers Don’t Want You to Know

Can overly hot baths harm your heart and circulation?

7 signs of brain c.a.ncer that are easily confused with other diseases

4 Things to Avoid After 5 PM to Lower Your Risk of Stro.ke

Doctors Warn: This Common Way of Eating Boiled Eggs Can Clog Your Arteries

Blanch Bones First or Simmer Directly?

2 Common Vegetables That Can Harbor Parasites

The 'Vitamin C King' of the Vegetable World

Avoid Swimming If You Spot 'Square Waves'

3 Green Vegetables Called the “King” of Sto.mach Protection

Why You Should Not Bring Seeds on a Plane: A Detailed Explanation

Bladder Ca.ncer: Symptoms You Shouldn’t Ignore
4 Healing Drinks to Prevent and Dissolve Kidney Stones

10 Powerful Reasons a Simple Smile Can Change Your Life

The Surprising Benefits of Donating Bl.o.od
