
Frequent Mouth Ulcers in Winter: Don’t Ignore Them, as They May Signal Serious Health Issues
Frequent Mouth Ulcers in Winter: Don’t Ignore Them, as They May Signal Serious Health Issues
Mouth ulcers are usually benign, but in some cases they can be symptoms of underlying medical conditions.
Mouth ulcers are small, painful sores that develop inside the mouth and are quite common. Although they are often harmless, they can significantly affect eating, speaking, and daily comfort. When mouth ulcers persist or become severe, they may indicate underlying health problems such as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) or autoimmune disorders. Gentle oral care, a balanced diet, and effective stress management are key to preventing and easing symptoms.
Moreover, understanding the causes and contributing factors is essential for reducing discomfort and protecting both oral health and overall well-being.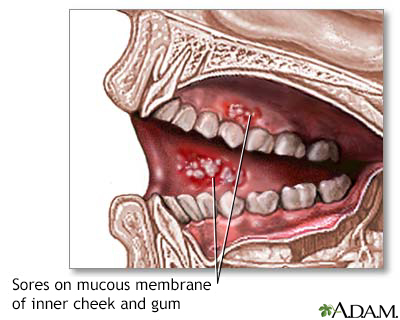
Causes of Mouth Ulcers
Mouth ulcers can occur after even minor injuries to the oral tissues. These injuries may result from accidentally biting the inside of the mouth, dental procedures, or sports-related trauma. Irritation from orthodontic appliances, brushing too hard, or using toothpaste and mouthwash containing sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS) can also trigger ulcers.
Reactions to acidic foods and drinks—such as citrus fruits, pineapple, strawberries, coffee, or chocolate—may worsen existing ulcers. In addition, stress and lack of sleep can increase susceptibility to mouth ulcers.
Deficiencies in certain essential nutrients can weaken oral tissues, leading to frequent ulcers. Adequate intake of folic acid (vitamin B9), vitamin B12, zinc, and iron is important, as deficiencies in these nutrients increase the risk of mouth ulcers. A healthy diet or appropriate supplementation can significantly reduce their severity or frequency.
Serious Health Conditions Linked to Mouth Ulcers
While most mouth ulcers are uncomplicated and benign, some may be signs of underlying health conditions, including:
-
Digestive disorders
-
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), including ulcerative colitis
-
Metabolic disorders such as diabetes, which can cause recurrent mouth ulcers
-
Viral infections such as HIV
-
Autoimmune diseases, including lupus, oral lichen planus, and Behçet’s disease—a rare condition characterized by inflammation of blood vessels
Who Is at Higher Risk?
Certain groups are more prone to mouth ulcers. Women tend to experience them more often due to hormonal changes related to the menstrual cycle or pregnancy. Children and adolescents are also more susceptible, possibly due to developing immune systems and lifestyle factors. A family history of mouth ulcers increases the risk, suggesting a genetic component. Awareness of these risk factors allows for earlier prevention and treatment.
Prevention and Treatment of Mouth Ulcers
Preventing mouth ulcers involves lifestyle and dietary adjustments, along with stress control, good oral hygiene, adequate hydration, and avoidance of irritating foods or sharp dental surfaces.
-
Practice gentle oral hygiene
-
Avoid products containing SLS
-
Manage stress effectively
-
Maintain a balanced, nutrient-rich diet
Identifying food sensitivities and limiting acidic or irritating foods can also help prevent ulcers. People who experience recurrent or worsening mouth ulcers should seek medical evaluation to determine whether there is an underlying health condition and to receive appropriate treatment.
Although mouth ulcers are common, they can serve as warning signs of overall health issues. The best way to manage discomfort is to recognize and avoid triggers, maintain proper oral care, and address any nutritional deficiencies.
News in the same category


A Serious Reminder: 3 Types of Fruit That Can.cer Cells “Love” — Doctors Avoid Them, Yet Many People Eat Them Daily
Here are some possible reasons you might be getting these bruises
A Heart Attack Can Warn You 3 Months Early These 5 Signs Are Often Ignored

Popular low-calorie sweetener linked to liver disease: new study

The “Miracle Food” Against Can.cer and Aging — Surprisingly Found at Every Market

Doctors Warn: If You’re One of These 5 People, Stay Away From Jackfruit
7 Can.cer Warning Signs That Can Appear When You Wake Up
Six Alarming Symptoms That May Indicate Advanced-Stage Can.cer

Doctors Warn: Three Types of People Who Should Never Drink Coffee

One Month Before A Heart At.tack, Your Body Will Warn You Of These 7 Signs
Young and at Risk: Str.ok.e Strikes 19-Year-Old After Headache — 5 Symptoms You Shouldn’t Ignore
20 Early Warning Signs That Can.cer May Be Developing in Your Body
Waking up to these 7 signs may mean your body is silently feeding can.cer cells.

From “Poor Man’s Vegetable” to “King of Herbs”: The Leafy Green as Nutritious as Meat

Many people are still unaware of this vegetable

If your kidneys aren't working properly, the body shows these 10 signs

Loofah: “The Poor Man’s Ginseng” — Nutritious but Not Compatible with These 3 Foods
Woman Sudden Kidney Failure After Meal: Doctor Says “This Vegetable Is Pois.onous… You Shouldn’t Eat It”
News Post

Banana Blossom – A Cheap Dish with Benefits That Even Doctors Find Surprising

A Serious Reminder: 3 Types of Fruit That Can.cer Cells “Love” — Doctors Avoid Them, Yet Many People Eat Them Daily

Here are some possible reasons you might be getting these bruises

A Heart Attack Can Warn You 3 Months Early These 5 Signs Are Often Ignored

Popular low-calorie sweetener linked to liver disease: new study

The “Miracle Food” Against Can.cer and Aging — Surprisingly Found at Every Market

Doctors Warn: If You’re One of These 5 People, Stay Away From Jackfruit

7 Can.cer Warning Signs That Can Appear When You Wake Up

Six Alarming Symptoms That May Indicate Advanced-Stage Can.cer

Doctors Warn: Three Types of People Who Should Never Drink Coffee

Drinking Polyscias fruticosa Leaf Tea Daily: A Simple Habit Linked to Notable Health Benefits

One Month Before A Heart At.tack, Your Body Will Warn You Of These 7 Signs

Young and at Risk: Str.ok.e Strikes 19-Year-Old After Headache — 5 Symptoms You Shouldn’t Ignore

20 Early Warning Signs That Can.cer May Be Developing in Your Body

Waking up to these 7 signs may mean your body is silently feeding can.cer cells.

From “Poor Man’s Vegetable” to “King of Herbs”: The Leafy Green as Nutritious as Meat

Many people are still unaware of this vegetable

If your kidneys aren't working properly, the body shows these 10 signs
