
Have you set the temperature correctly?

Many individuals unknowingly set their refrigerator’s temperature incorrectly, which can cause vegetables to lose freshness and wilt prematurely. The optimal temperature range for most refrigerators is between 37°F (3°C) and 40°F (4°C). Temperatures that are too high will cause produce to spoil quickly, while temperatures that are too low may freeze and damage the vegetables. Proper temperature control is essential for maintaining crispness and extending the shelf life of fruits and vegetables.
Common Mistakes When Storing Fruits and Vegetables in the Refrigerator
Improper storage of fruits and vegetables in the fridge can negatively impact your health. Here are some frequent errors to avoid:
1. Mixing Different Fruits and Vegetables Together
Failing to separate fruits and vegetables can lead to spoilage spreading from one item to another and nutrient loss. Some fruits like mangoes, bananas, pears, tomatoes, and plums produce ethylene gas, which accelerates ripening and causes nearby produce to spoil faster. Store these separately in different bags to maintain freshness.
2. Putting Wet Produce Directly into the Fridge
Many think storing damp vegetables and fruits preserves freshness, but moisture actually encourages bacterial growth and speeds up wilting. It’s best to dry produce thoroughly before refrigerating.
3. Keeping Produce in the Fridge for Too Long
People often stockpile large amounts of food during holidays and forget to consume them promptly. Different vegetables have varying shelf lives - lettuce can last about 10 days, while mushrooms, cabbage, and asparagus should be eaten within 2-3 days. Monitor storage times carefully to prevent spoilage and contamination.
4. Not Washing Produce Before Refrigeration
Leaving dirt or fertilizer residues on fruits and vegetables can introduce bacteria that spread inside the fridge. Always clean produce before storing.
5. Storing Raw and Cooked Foods Together
Cooked and raw foods should be stored separately to avoid cross-contamination, which can cause foodborne illnesses and reduce nutrient quality.
6. Incorrect Refrigerator Temperature Setting
Maintain the fridge temperature between 34-40°F (1-4°C) to keep produce fresh. Higher temperatures encourage bacterial growth, while temperatures below freezing can damage food texture and nutrients.
7. Overfilling the Refrigerator
Overcrowding the fridge restricts airflow, leading to uneven cooling and quicker spoilage. Keep the fridge organized and avoid overloading.
8. Improper Use of Plastic Bags
Refrigerators generally maintain 65% humidity, but most vegetables require 80-95% humidity to stay fresh. Store leafy greens and skinless vegetables in plastic bags to preserve moisture. However, avoid bagging certain items like tomatoes and mushrooms, as plastic traps moisture that causes them to spoil faster.
9. Cutting Fruits and Vegetables Before Storage
Cutting produce before storing may seem convenient but reduces nutrient content and can trigger the release of harmful compounds. It’s best to store fruits and vegetables whole and only trim or wash before use.
By following these guidelines, you can significantly extend the freshness and quality of your refrigerated produce while protecting your health.
News in the same category


Eating These 5 Foods for Breakfast Is Like Shortening Your Lifespan — But Many People Still Love Them

5 Foods That Stay Edible for a Whole Month at Room Temperature — But Spoil Quickly in the Fridge!

Putting plastic bags in the refrigerator causes can.cer? After hearing the truth, many people immediately ran to do 1 thing

The Peels of These 3 Fruits Are Actually 'Pesticide-Free Vegetables': Cook 3 Delicious Dishes That Also Beautify Your Skin and Aid in Weight Loss

One Person Boils Water, the Whole Family Gets Cancer

5 Foods That Seem Edible but Are Actually Harmful — Tell Your Parents to Throw Them Out

4 Familiar Vegetables That Naturally Detox the Liver and Are Great for the Whole Family

A Fruit That’s 300 Times Sweeter Than Cane Sugar, Doesn’t Raise Blood Sugar Levels, and May Help Prevent Cancer

One Person Boils Water, the Whole Family Gets Can.cer? 3 Water-Boiling Habits That Secretly Pois.on Your Loved Ones

One person boils water, the whole family gets cancer? 3 water boiling habits that "poison" the whole family that many people don't know about

4 Pretty but To.xic Cups: I Sadly Realized My Home Had Them All

Doctors Reveal the Commonly Overlooked Body Part You MUST Clean Daily — Ignoring It Could Be Life-Threa.tening

2 cooking mistakes that "lead" to all kinds of cancer: Almost everyone makes them at least once in their life

Leaving These 5 Things in Your Bedroom Will Make You “Regret It” in the Middle of the Night!

Three Common Fruits Contain “Toxins” You Need to Be Especially Careful About When Eating

Man Dies After Days of Diarrhea—Doctor Issues Urgent Warning About 3 Common Leftovers

The Collagen-Boosting Power of a Humble Green: Nature’s Secret to Glowing Skin
News Post

The Gospel According To Joan

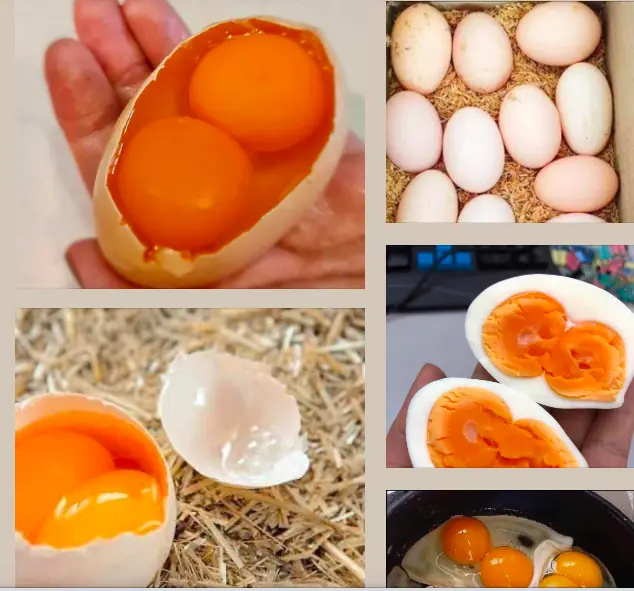
Are These Mutant Eggs Safe to Eat? The Truth About Double Yolks and Rainbow Shells
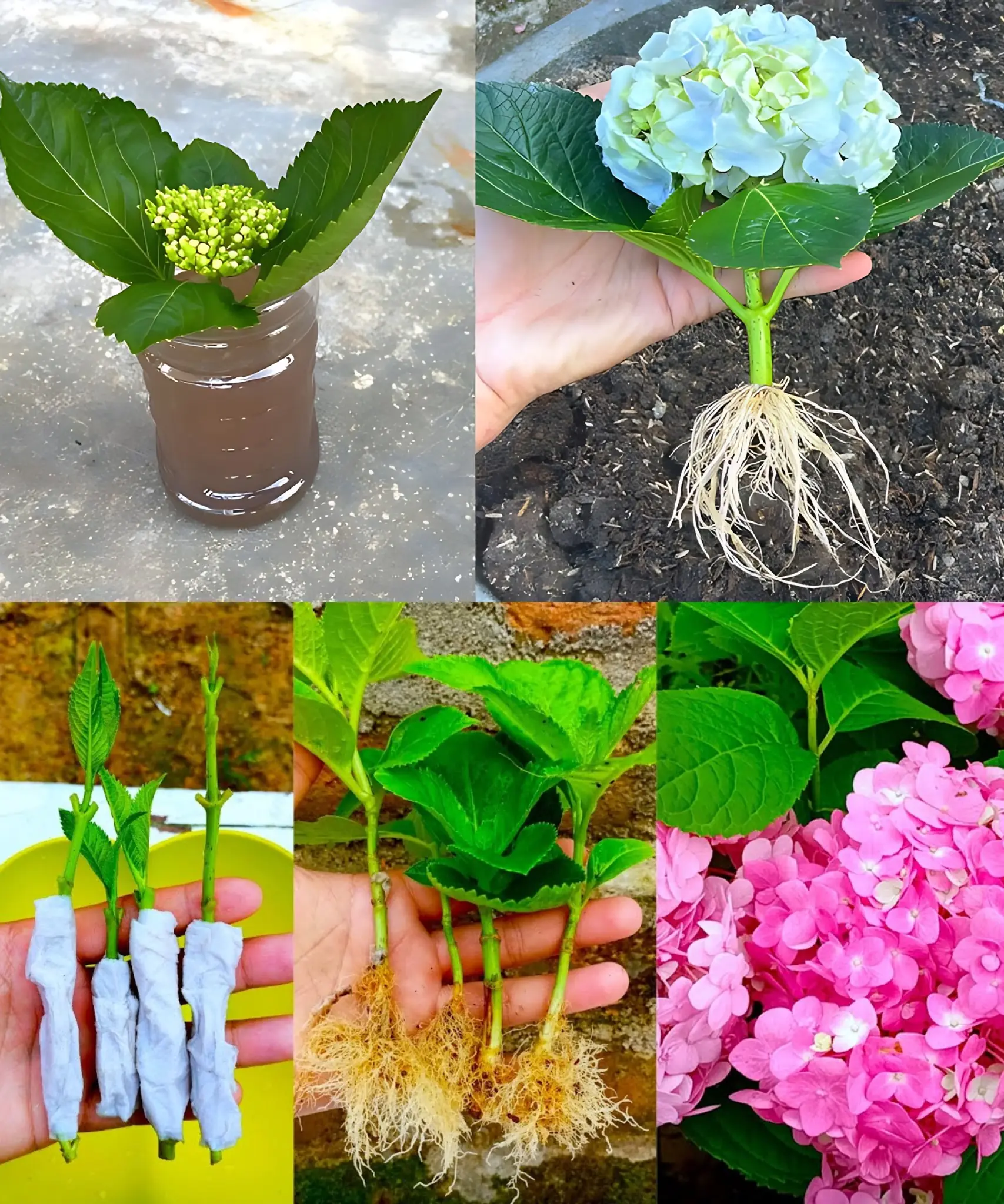

Growing hydrangeas from cuttings

One Thing Most Stro.ke Victims Have in Common: Are You Living at Risk of Cerebral Infarction?

Suddenly Suffering a Stroke After Waking Up, the Woman Regrets a 'Critical' Mistake She Made Six Months Ago

Eating These 5 Foods for Breakfast Is Like Shortening Your Lifespan — But Many People Still Love Them

5 Foods That Stay Edible for a Whole Month at Room Temperature — But Spoil Quickly in the Fridge!

Waking Up at This Hour Every Day May Signal Lu.ng Damage — See a Doctor Immediately if You Also Have These 6 Symptoms

Many doctors recommend using two pillows when sleeping for better sleep health!
Eat 4 foods on an empty stomach in the morning to help clean the intestines, improve digestion, and prevent canc.er

Putting plastic bags in the refrigerator causes can.cer? After hearing the truth, many people immediately ran to do 1 thing

Top foods to absolutely avoid at night if you don't want to affect your health

Walking around the market, a smart person can immediately see that these 5 types of vegetables are "soaked in chemicals", especially number 4
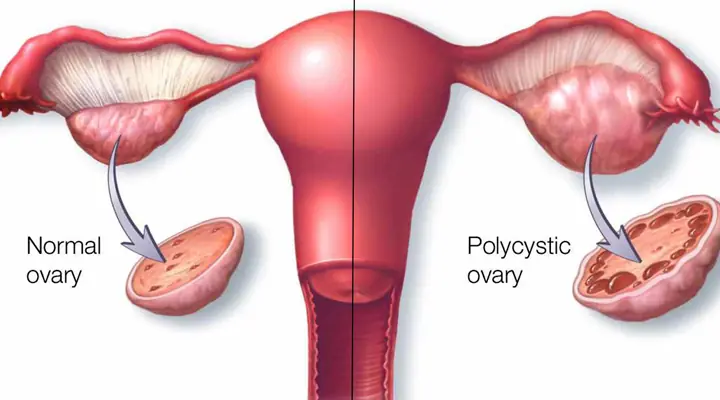
Eat 6 things to help women detoxify their ovaries and prevent gynecological diseases
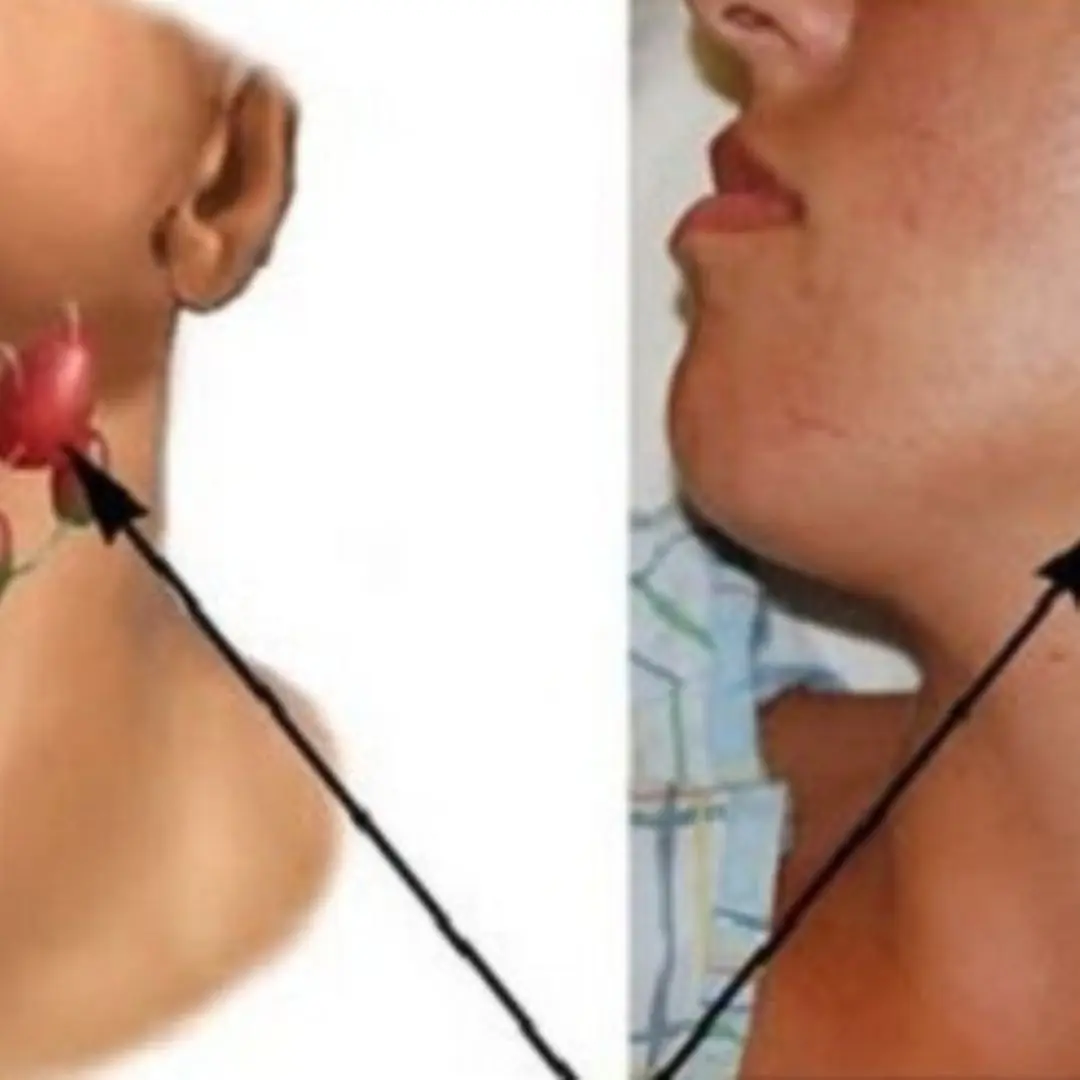
4 warning signs of nasopharyngeal ca.n.c.er that are most easily overlooked
Female patient suffered a perforated small intestine due to a 'lost' thing in her body for 30 years
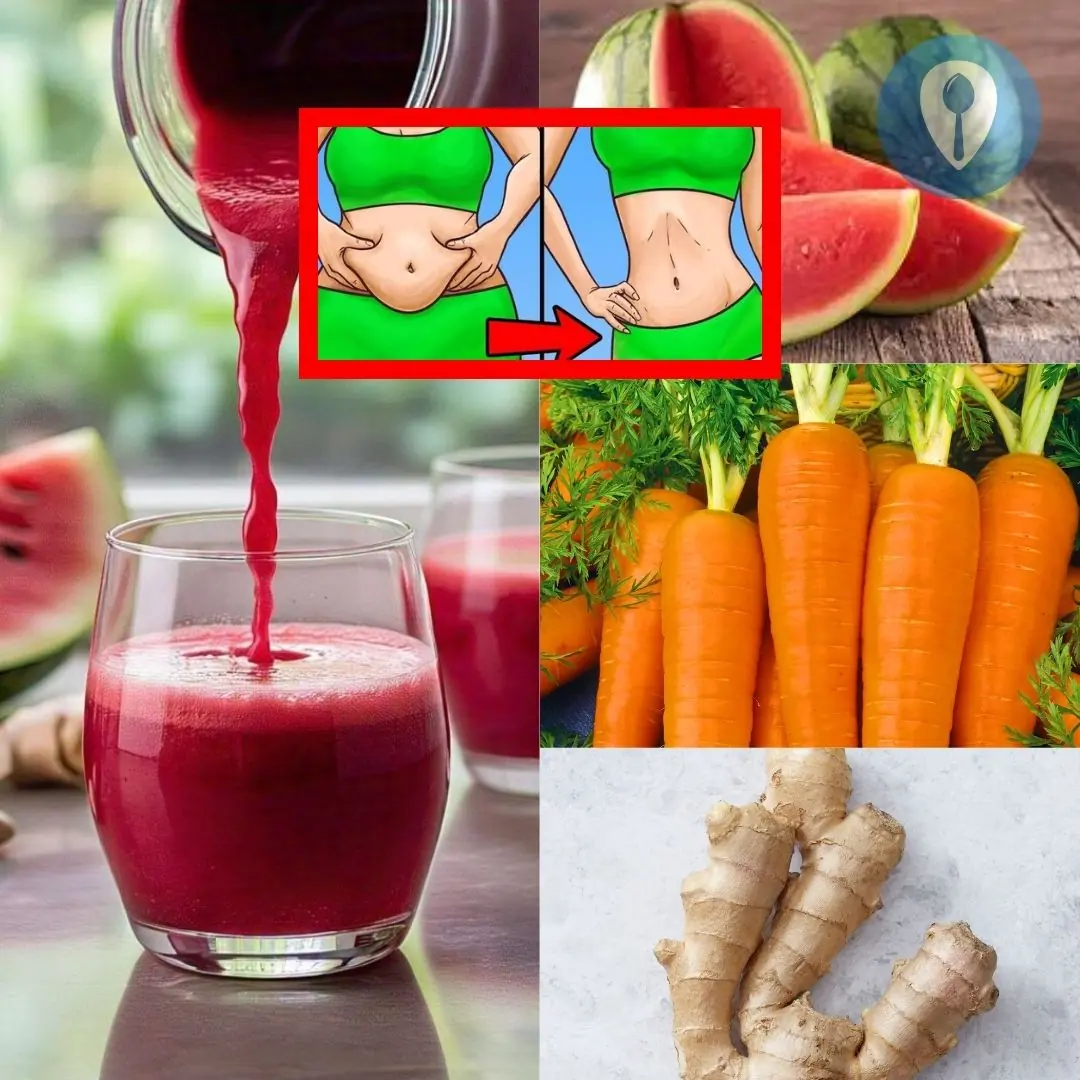

If you are looking for a natural and safe weight loss juice, this recipe from watermelon, carrots, beets and ginger is worth a try

The Peels of These 3 Fruits Are Actually 'Pesticide-Free Vegetables': Cook 3 Delicious Dishes That Also Beautify Your Skin and Aid in Weight Loss

One Person Boils Water, the Whole Family Gets Cancer
