Honey is good but not for everyone

Health Risks You Should Know About Honey: Use with Caution
In modern life, honey has become a popular natural gift thanks to its distinctive flavor and high nutritional value. However, it’s important to remember that honey is not safe for everyone. Infants under 1 year old, people with diabetes, those with allergies, or individuals with sensitive health conditions need to use honey carefully.
Honey contains many vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that boost immunity, aid digestion, and improve skin health. Yet, if used improperly, honey can cause serious health issues.
1. Infants Under 1 Year Should Avoid Honey Completely
For babies under one year, honey can cause severe harm. According to the World Health Organization (WHO) and the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), infants should never be given honey, even in tiny amounts. Honey sometimes contains spores of Clostridium botulinum. Since babies’ digestive systems are not fully developed, they cannot destroy these spores. Once inside the body, the spores produce toxins causing symptoms such as respiratory failure, muscle paralysis, and potentially death. Therefore, parents must strictly avoid feeding honey to infants under 12 months.
2. People with Diabetes Must Monitor Sugar Intake
Honey is high in sugar, mainly fructose and glucose. According to the USDA Nutrient Database, one tablespoon (about 21 grams) of honey contains roughly 17.3 grams of sugar and 64 calories. This sugar load can significantly affect blood glucose levels, posing risks for diabetics. If you have diabetes, consult your doctor before using honey and closely monitor your blood sugar to adjust your diet accordingly.
3. Allergy Sufferers Should Be Careful
If you have allergies to pollen, propolis (bee glue), or have had severe reactions to bee stings, exercise caution with honey. These allergies suggest your immune system may react to honey components. Honey can trigger a release of histamine causing symptoms ranging from mild itching and swelling to severe breathing difficulties and anaphylaxis. When trying honey for the first time, use only a small amount and observe your body’s reaction over 24 hours. Stop using immediately if you experience any adverse effects.
Other Groups Who Should Use Honey with Caution
-
People with Low Blood Pressure: Honey can dilate blood vessels and lower blo.od pressure further.
-
Those with Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): High fructose content may worsen digestive symptoms like bloating and diarrhea.
-
Liver Patients: The liver must work harder to process honey’s sugars, potentially worsening fatty liver disease.
-
Overweight or Weight-Loss Individuals: Although better than refined sugar, honey’s high calorie content can hinder weight management efforts.
-
Post-Surgery Patients: Honey may slow blood clotting; consult your doctor before use.
-
People on Medication: Honey can interact with certain drugs, altering their effectiveness.
Tips for Safe Honey Use
- Even healthy adults should consume honey in moderation. Limit added sugars (including natural sugars like honey, syrups, and fruit juices) to less than 10% of daily caloric intake.
- Choose pure, unprocessed honey and avoid mixing it with boiling water, which destroys beneficial enzymes and nutrients.
- Avoid combining honey with legumes or seafood, as it may cause unwanted biochemical reactions.
How to Choose Quality Honey
Choosing pure, high-quality honey is essential to maximize health benefits and avoid adulterated products that can cause harm. Here are some tips to help you select the best honey:
-
Check the label: Look for honey labeled as “raw,” “organic,” or “unprocessed,” which indicates minimal heating and filtration.
-
Avoid added sugars: Some commercial honey is mixed with sugar syrups or corn syrup; check the ingredient list carefully.
-
Test for crystallization: Natural honey tends to crystallize over time, which is a good sign of purity.
-
Do the water test: Put a spoonful of honey in water. Pure honey tends to settle at the bottom without dissolving quickly.
-
Taste and aroma: Genuine honey has a unique floral aroma and complex flavor that varies by flower source.
Safe Ways to Use Honey in Your Diet
Honey can be a delicious and healthy addition to your meals when used properly. Here are some safe and tasty ideas:
-
Sweeten your tea or herbal infusions: Add honey once your drink has cooled slightly to preserve its nutrients.
-
Use honey as a natural sweetener in baking: Substitute refined sugar with honey but reduce the overall liquid in the recipe to compensate.
-
Mix honey with lemon and warm water: A soothing drink for the throat, but consume in moderation and avoid giving to infants.
-
Create honey-based salad dressings: Combine honey with olive oil, vinegar, and mustard for a tasty and healthy dressing.
-
Top yogurt or oatmeal with honey: Adds natural sweetness along with antioxidants.
Honey as a Topical Treatment
Honey is also widely known for its antibacterial and healing properties when applied to the skin:
-
Use raw honey as a face mask to moisturize and soothe irritated skin.
-
Apply honey to minor cuts or burns to promote faster healing and reduce infection risk.
-
Add honey to homemade lip balms for hydration and protection.
While honey offers numerous health and culinary benefits, always consume and apply it with care, especially if you fall into one of the sensitive groups mentioned earlier. Consult with healthcare providers when necessary and prioritize safety to fully enjoy this sweet gift of nature.
Conclusion
Honey is truly a natural treasure, but it isn’t always safe for everyone. Understanding important precautions and using honey correctly allows you to enjoy its benefits while avoiding unnecessary risks. Be a wise consumer and listen to your bo.dy to make the best decisions for your health!

News in the same category


Mother Collapses: "I Thought These Two Things Were Can.cer-Preventing Superfoods"

5 bad habits that increase the risk of stroke at night

15 years without can.cer recurrence: Japanese doctor shares 5 simple secrets to keep malignant cells from "daring to return"
Insomnia, when to see a doctor?

30-year-old couple both have stomach can:cer due to dishwashing habit that many people also have

Top Natural Drinks That Safely Rejuvenate Your Skin From Within

You’ve Been Throwing Away the Most Medicinal Part of the Mango Tree

Meet the Miracle Plantain!

8 vegetables full of pa.rasites that people don't know about

No Matter How Hot It Gets, Avoid These Dange.rous Habits

Family of 4 brothers all have stomach can.cer, doctor shakes head: 2 "fatal" common points that many people have
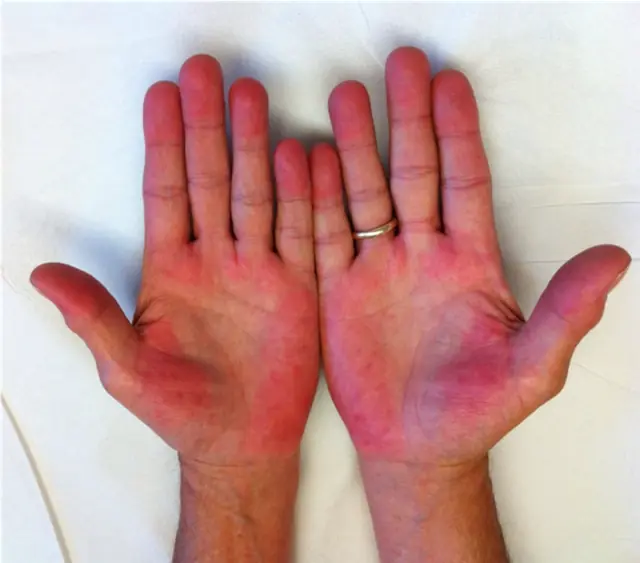
Check Your Skin for Liver Problems: If You See These 3 Colors—Red, Black, or Yellow—See a Doctor Before It’s Too Late!
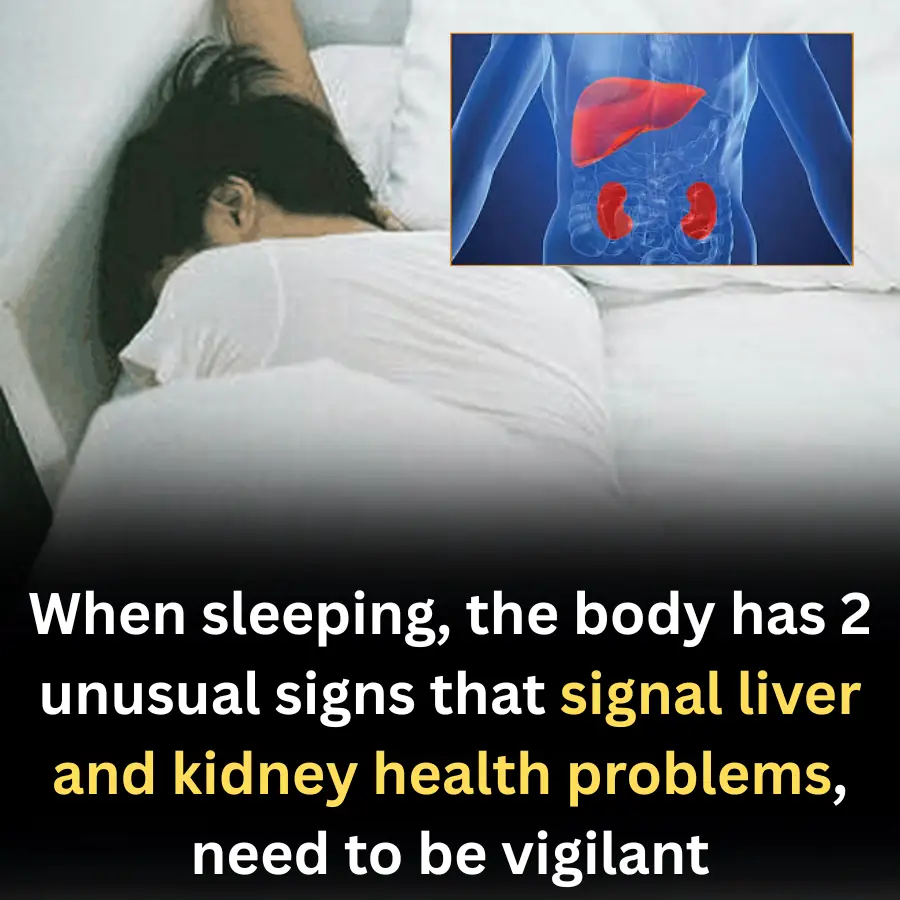
When sleeping, the body has 2 unusual signs that signal liver and kidney health problems, need to be vigilant

Chicken is a valuable and healthy food, but if used incorrectly it can lead to many serious health problems
Tetanus Infection – Early Warning Signs

26-year-old man di.es suddenly from heatstroke, doctor points out 4 dangerous warning signs of the body in hot weather
Man Di.es Suddenly During Morning Exercise – Doctor Warns: Avoid These 3 Common Mistakes When Working Out Early

Be careful with these foods that contain a lot of para.sites
News Post

Waking Up With Numb Hands? Here's What Your Body's Trying to Tell You

The Power of Yeast: A Natural Booster for Growing Tomatoes, Peppers, and Cucumbers

Thought You Had to Simmer Pork for Hours to Make It Tender?

Mother Collapses: "I Thought These Two Things Were Can.cer-Preventing Superfoods"

The 8 Biggest Tomato Growing Mistakes, According to Experts

How to Grow Beets This Fall for a Hearty Autumn Harvest

5 bad habits that increase the risk of stroke at night
Should you brush your teeth before or after breakfast

15 years without can.cer recurrence: Japanese doctor shares 5 simple secrets to keep malignant cells from "daring to return"

5 diseases that cause stomach pain after eating

6 factors that silently increase the risk of myocardial infarction

Insomnia, when to see a doctor?

30-year-old couple both have stomach can:cer due to dishwashing habit that many people also have

More Than Just Leaves: The Hidden Healing Power of Fish Mint Roots

Don’t Dismiss This “Rustic” Dish – It’s a Stomach Healer and a Breakfast Hero!

Deciphering Orchid Roots: Reasons They Extend Beyond Pots and Recommended Actions

How to Multiply Your Sansevieria Quickly: From One Plant to a Thriving Collection

Top Natural Drinks That Safely Rejuvenate Your Skin From Within

How to handle when the refrigerator is leaking water
