
6 factors that silently increase the risk of myocardial infarction

6 Silent Factors That Increase the Risk of Heart Attack
Heart attack, also known as myocardial infarction, is one of the leading causes of death worldwide. While factors like high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and diabetes are clear causes, there are other silent factors that we may not always pay attention to, yet they contribute to the risk of heart disease, including heart attack.
1. Chronic Stress
Long-term stress can lead to the production of hormones such as cortisol and adrenaline, which increase blood pressure and heart rate. This puts pressure on blood vessels, causing them to narrow and increasing the risk of blockages, leading to a heart attack. Prolonged stress can also trigger unhealthy habits like poor eating and smoking, which further increase the risk of heart disease.
2. Unbalanced Diet
An improper diet, especially one rich in processed foods, saturated fats, and refined sugars, can increase LDL (bad cholesterol) and decrease HDL (good cholesterol), contributing to plaque buildup in the arteries. This leads to blocked blood vessels and increases the risk of heart disease, including heart attacks.
3. Smoking
Smoking is one of the biggest risk factors for heart disease. Nicotine and chemicals in cigarettes reduce the elasticity of blood vessels, promote atherosclerosis, and increase blood pressure. Smoking also causes inflammation and damage to blood vessel walls, increasing the likelihood of blood clots and, consequently, heart attacks.
4. Sleep Deprivation and Sleep Disorders
Not getting enough sleep or poor-quality sleep can raise blood pressure, increase stress levels, and cause metabolic issues like insulin resistance. These issues increase the risk of heart disease. Sleep disorders, such as sleep apnea, also contribute to cardiovascular problems.
5. Lack of Physical Activity
A sedentary lifestyle is a major risk factor for heart disease. Physical inactivity weakens cardiovascular health, increases bad cholesterol levels, raises blood pressure, and makes it harder to control weight. This contributes to the risk of heart attacks. Regular exercise helps maintain heart health and reduces these risk factors.
6. Chronic Inflammation
Chronic inflammation can be a sign of many health problems, including heart disease. When the body is inflamed, blood vessels can be damaged, allowing plaque to build up in the arteries, leading to atherosclerosis. Chronic inflammation can be caused by factors such as arthritis, long-term infections, or even prolonged stress.
Conclusion:
While factors like genetics and underlying health conditions are important in increasing the risk of heart attack, silent factors such as stress, poor diet, smoking, lack of sleep, inactivity, and chronic inflammation also play a significant role. To reduce the risk of heart disease, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, managing stress, and getting regular check-ups are essential.
News in the same category

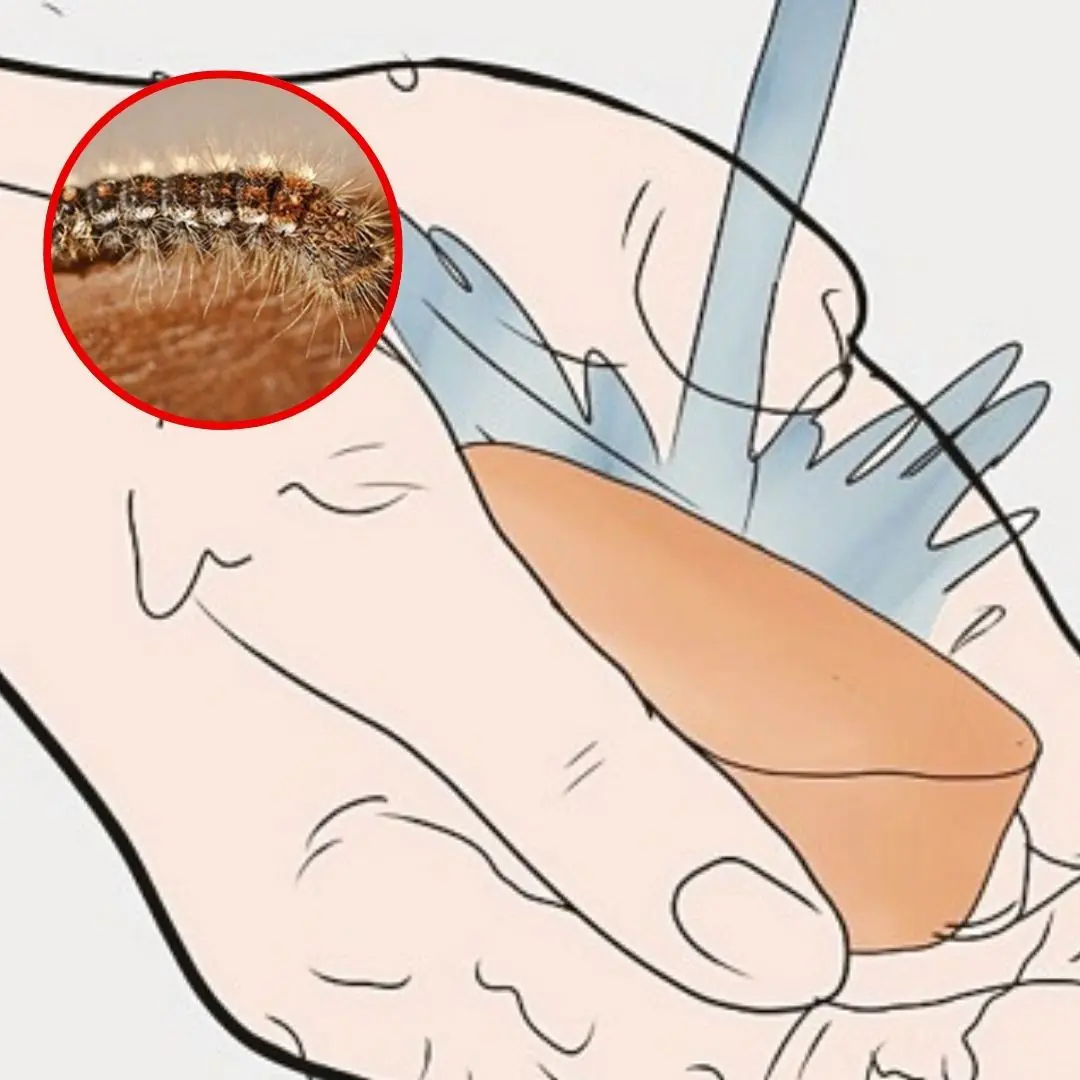
Caterpillar on you: 5 simple steps to treat at home
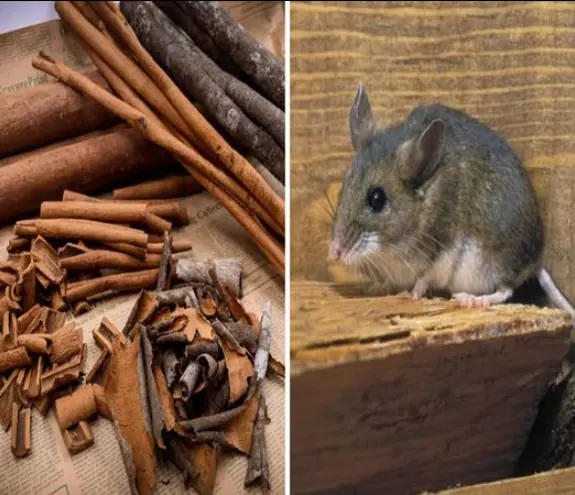

Put them in your home and mice will run away

Drinking Coffee at These Two Times Is Like “Poiso.ning Your Body”
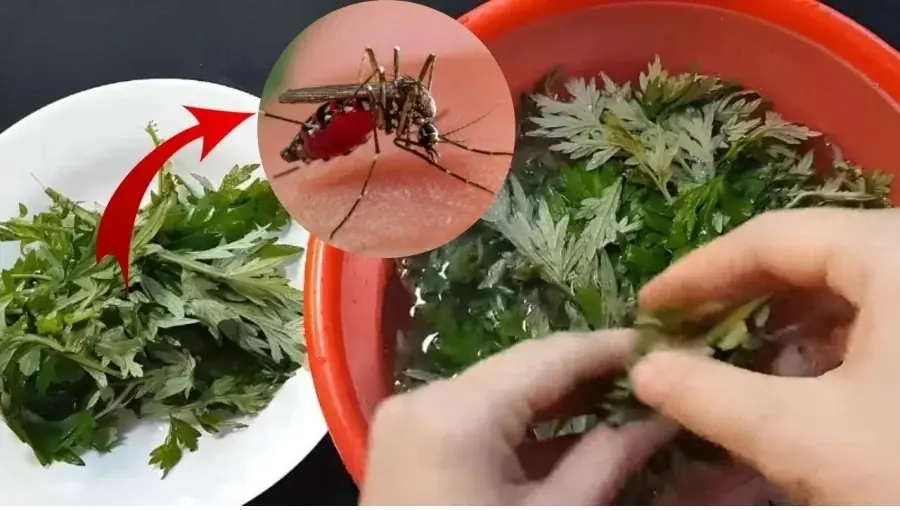

No Need for Sprays or Mosquito Nets: Just Place This Herb in Your Room and Mosquitoes Will Flee
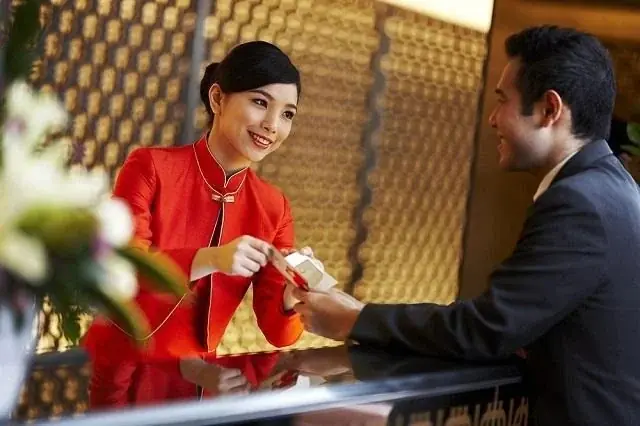

Hotel Check-In: Say These 3 Sentences to the Front Desk for Instant Perks!
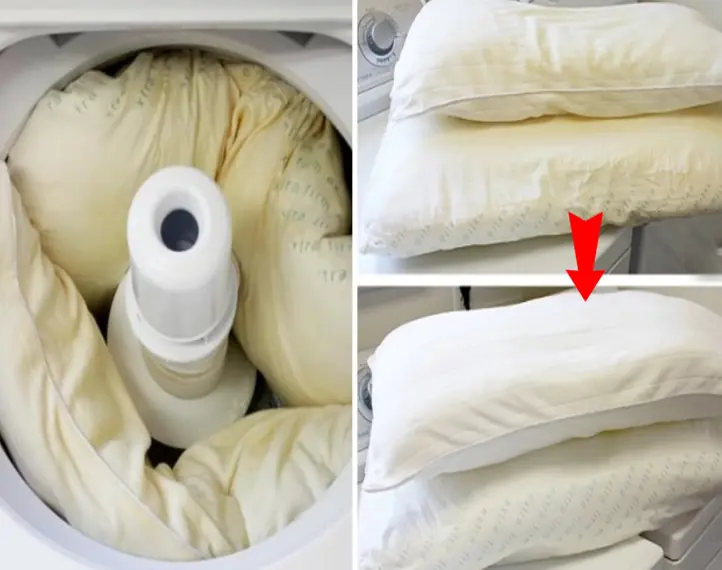

Tips for cleaning yellow pillow cores with tiny mold spots
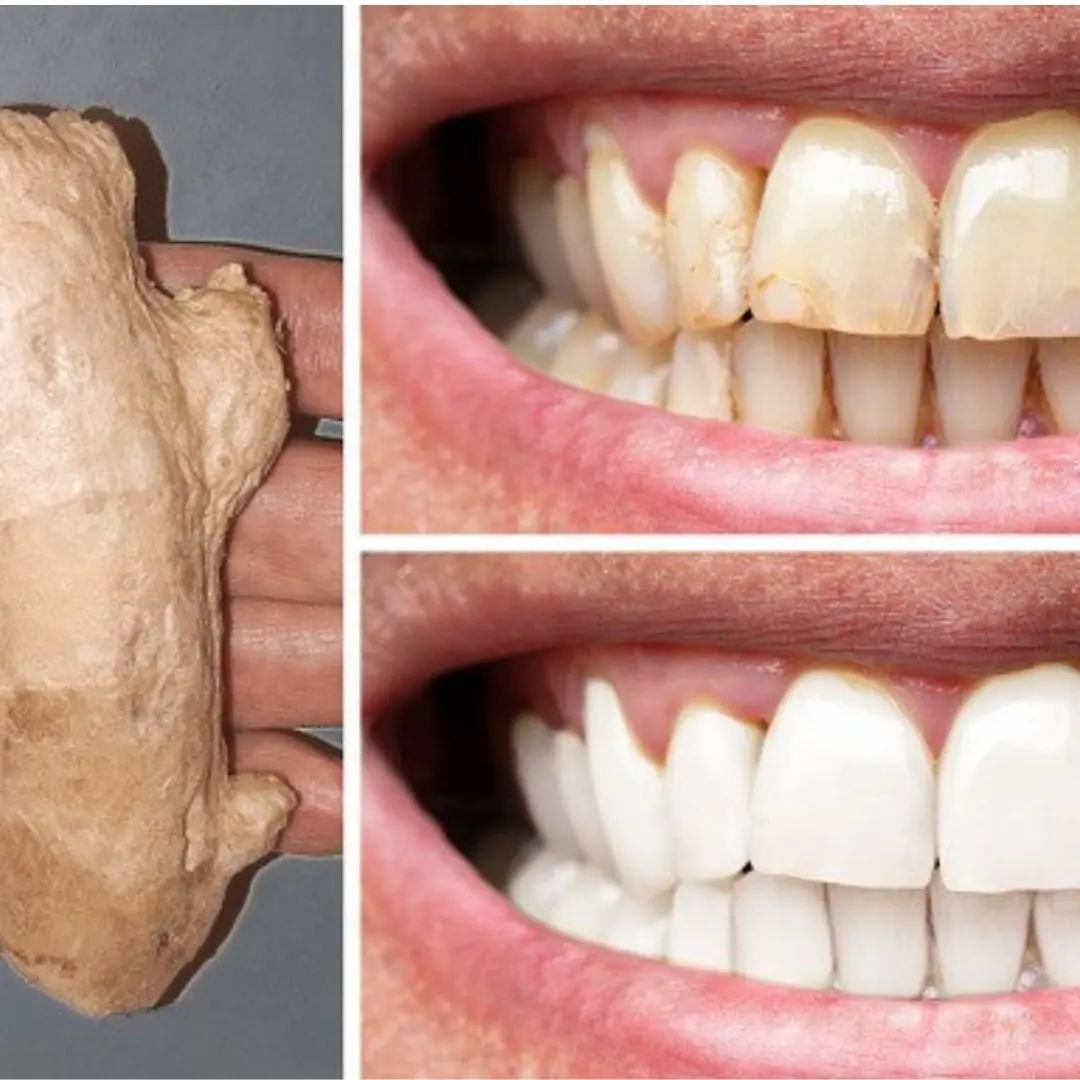
7 Natural Tips to Improve Teeth Whiteness at Home
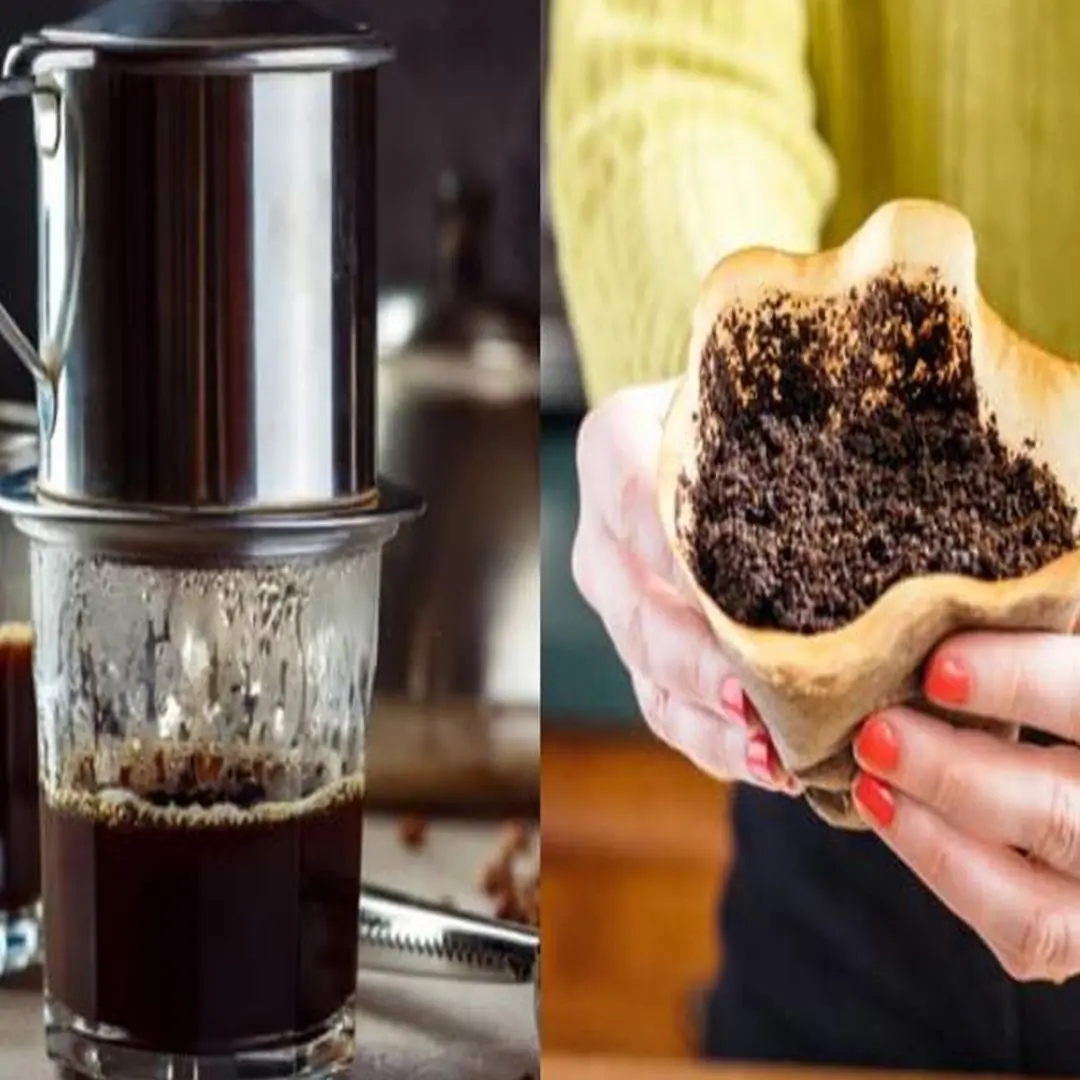

Throwing away coffee grounds is like throwing away money. Uses of coffee grounds that every home needs

Thought You Had to Simmer Pork for Hours to Make It Tender?

How to handle when the refrigerator is leaking water

Tips to fix washing machine making loud noise when spinning

Plants that effectively repel mice

Tips to solve all household problems with 2 old toothbrushes

Tips to clean burnt pan in 3 minutes

Check your eyes now! If you have one of these 4 characteristics, you may have diabetes.
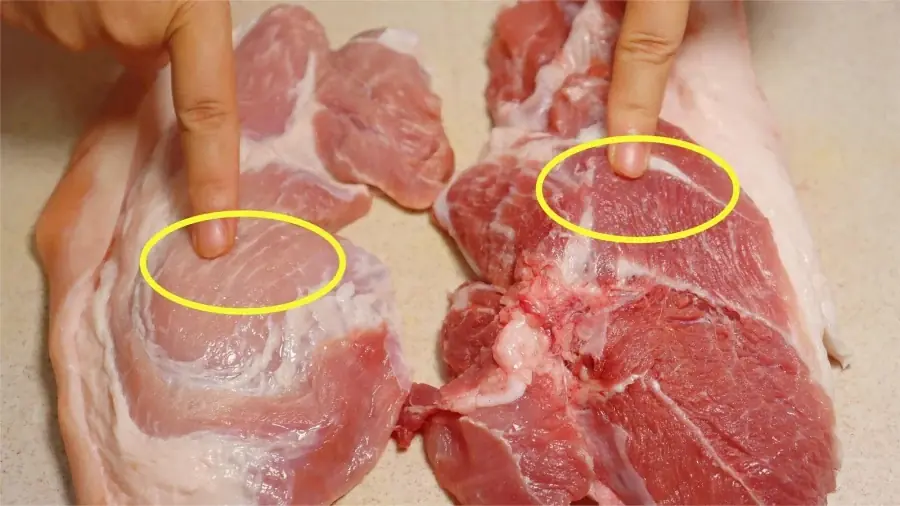
How to Identify Safe, Clean Pork in Just 1 Minute – Anyone Can Do It

Why should you put a lemon at the head of your bed?
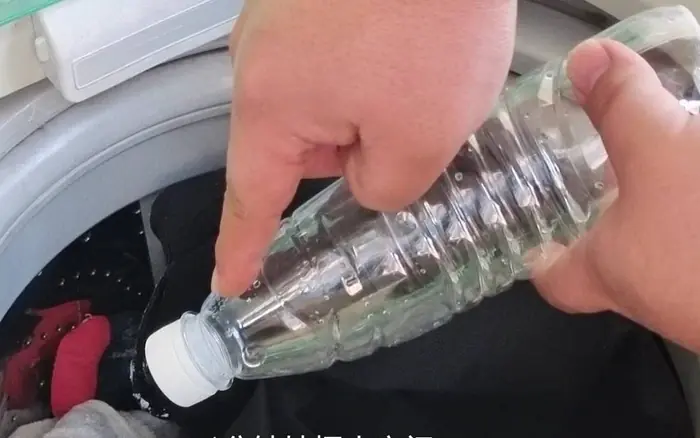

Tips to prevent clothes from tangling and wrinkling in the washing machine
News Post
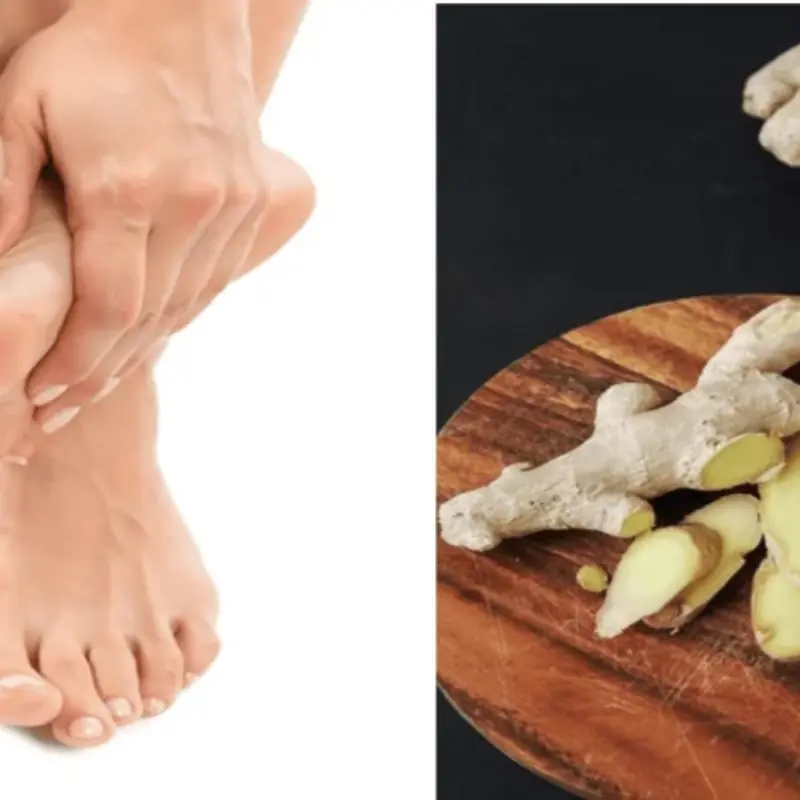

Rub Ginger on the Soles of Your Feet Before Bed, and You’ll Experience Its “Miraculous” Health Benefits
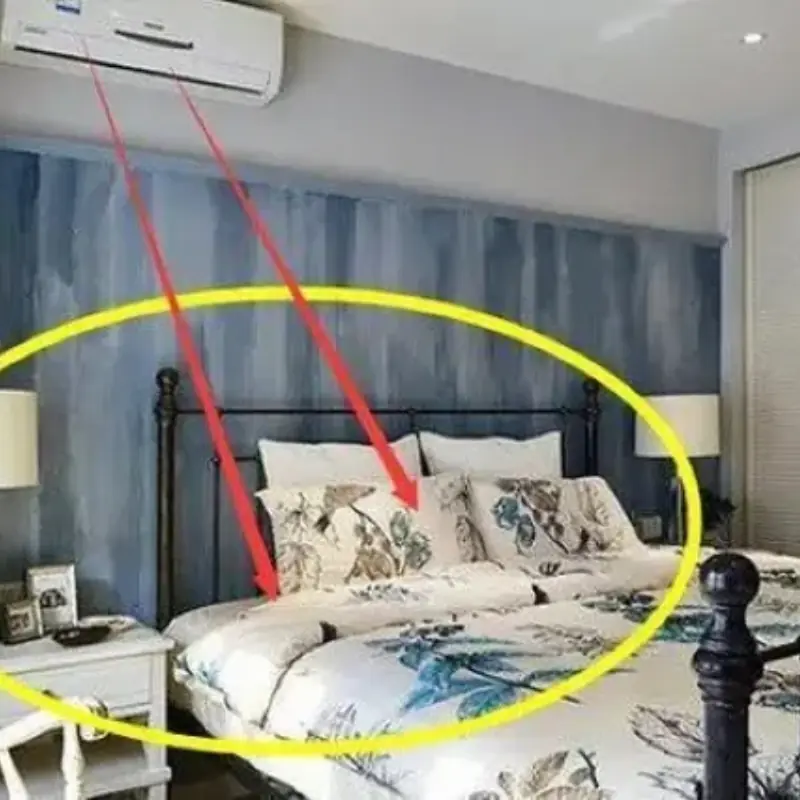

When Installing an Air Conditioner, Avoid These 4 Spots to Protect Your Family’s Health
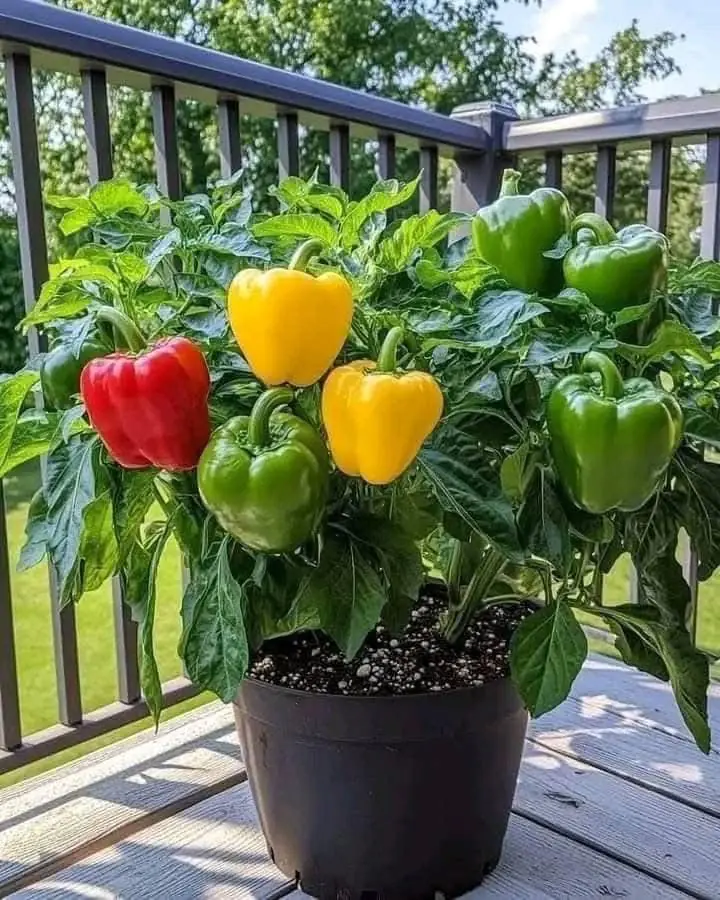

10 Tips for Growing a Big Pepper Harvest
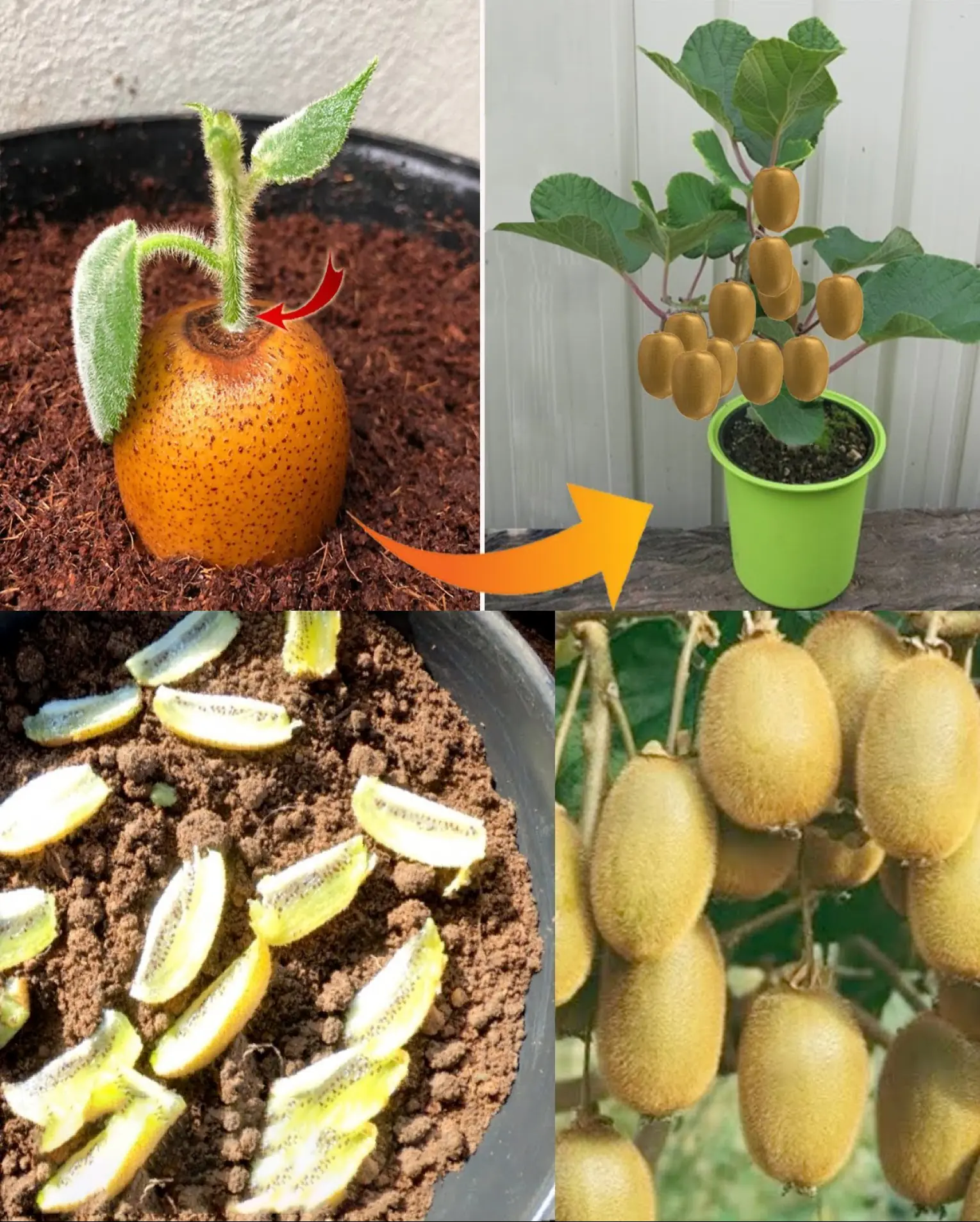

How to Grow Kiwi in Containers at Home

What happens to your body if you drink orange juice every day?
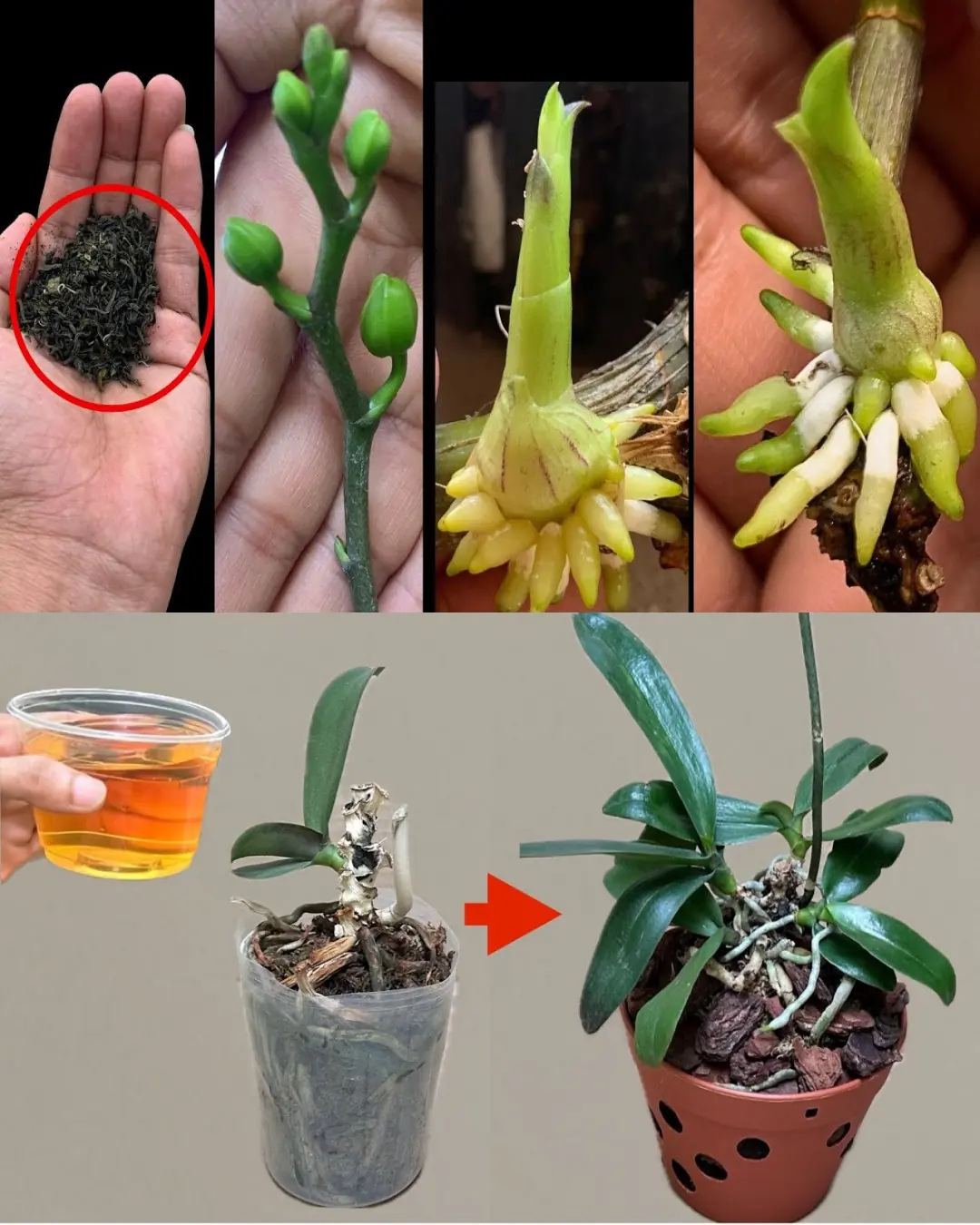

Revitalizing Orchids Using Tea: A Comprehensive Guide with Handy Tips

4 effective ways to ensure your home is free of cockroaches
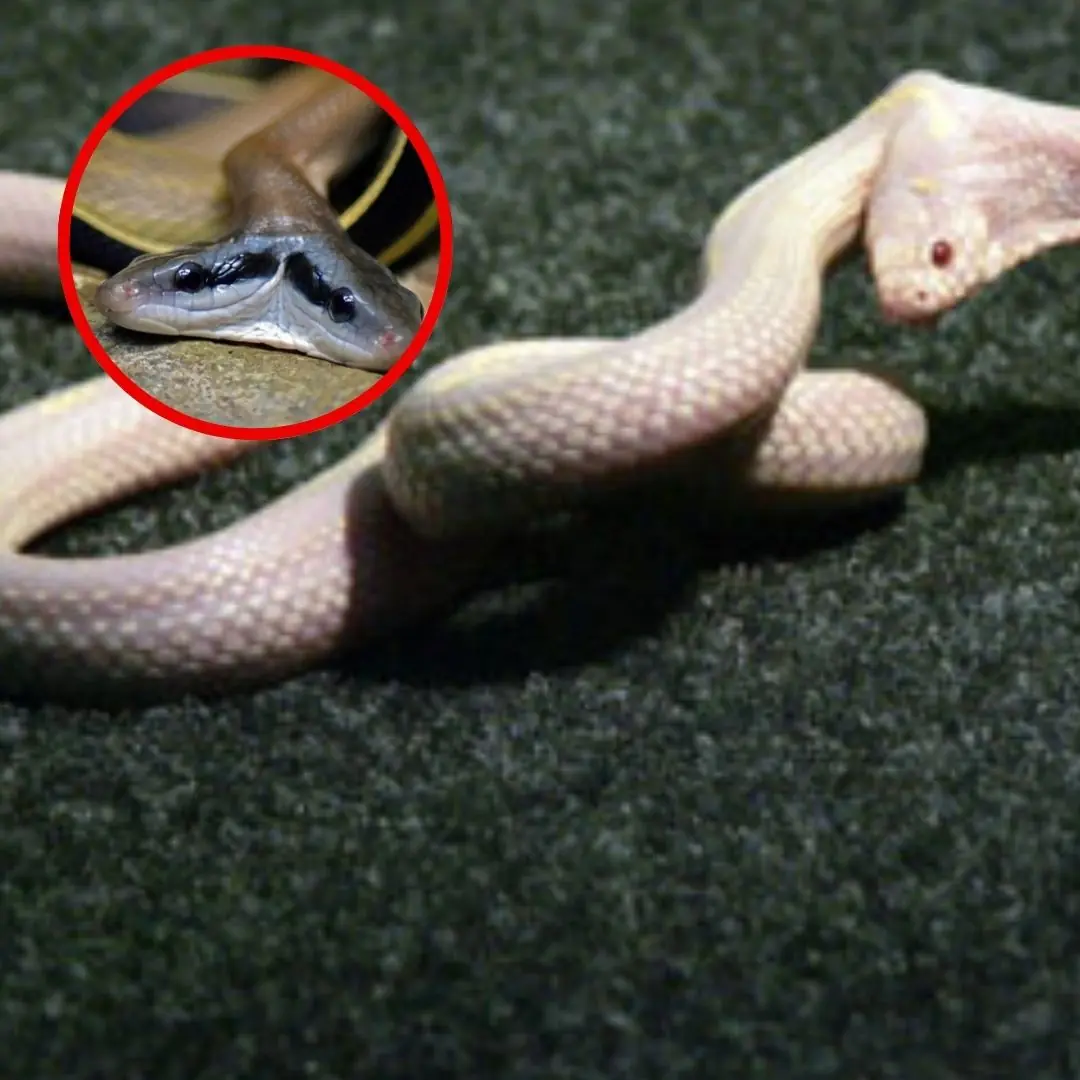

Are two-headed snakes real? Why does this phenomenon occur?

A cup of hot water can offer many health benefits

Caterpillar on you: 5 simple steps to treat at home
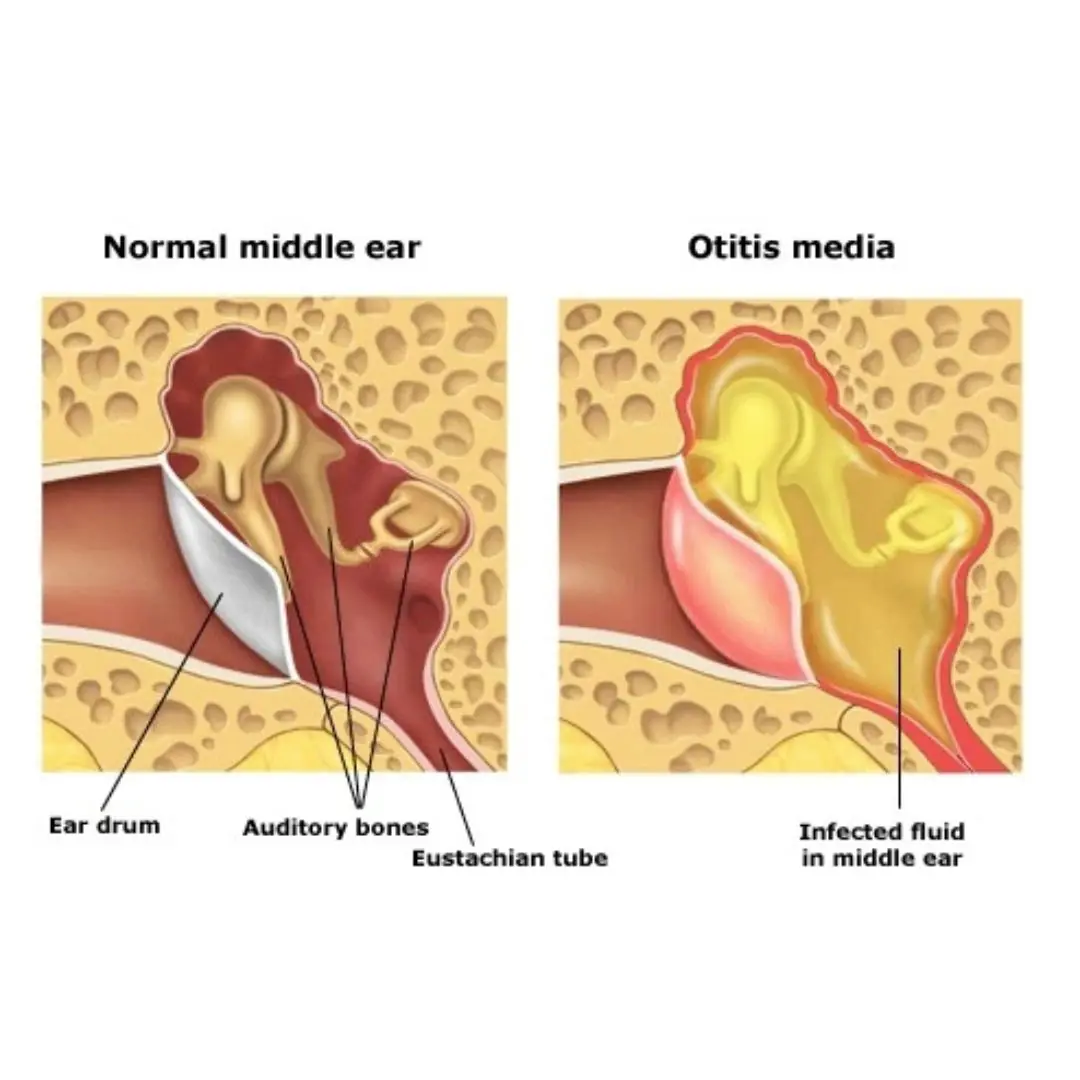
Otitis media – the “hidden culprit” causing vestibular disorders that many people ignore

Don't drink water before bed but still urinate at night, beware of these 3 diseases
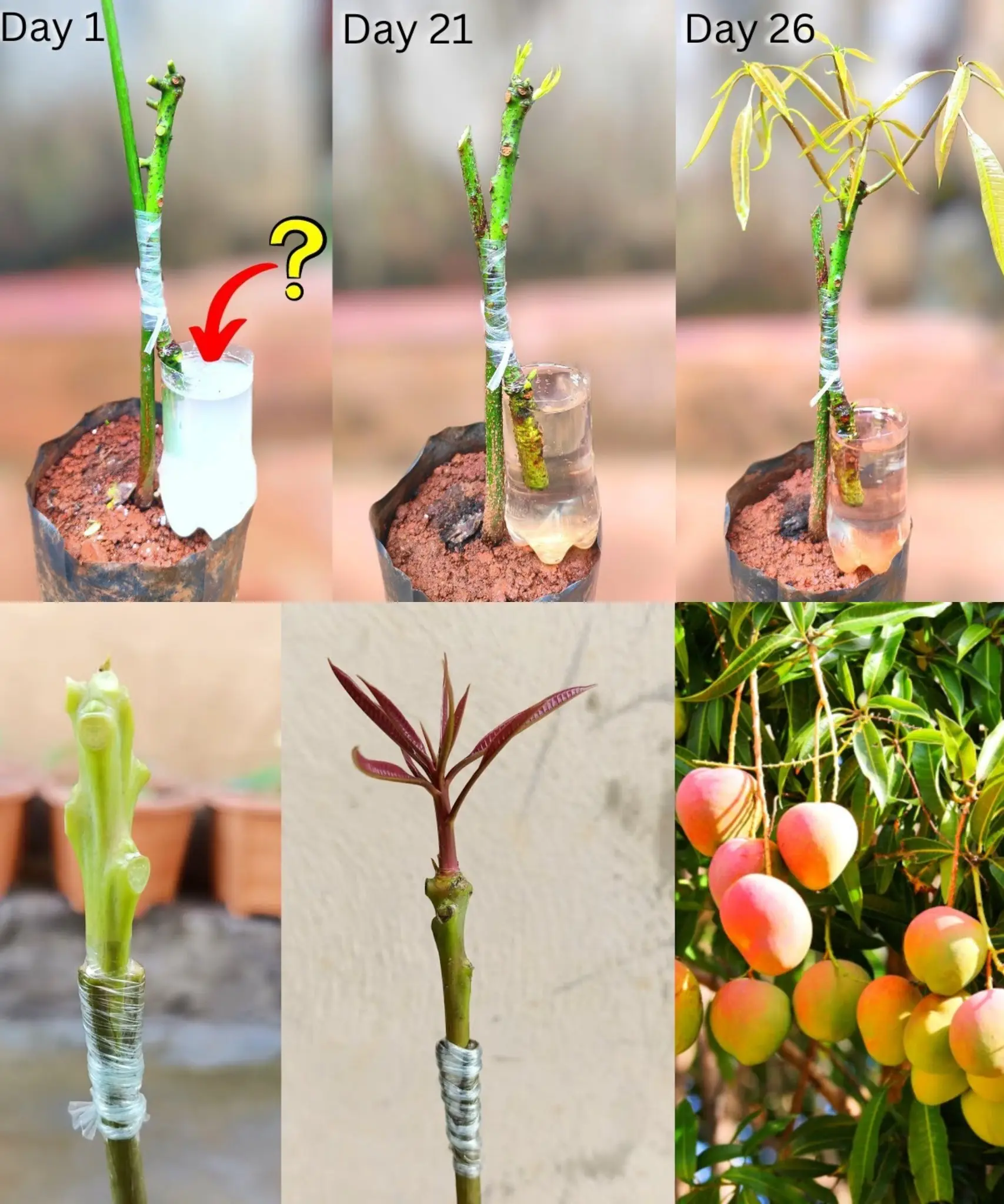

How to Plant a Mango Seed and Successfully Grow
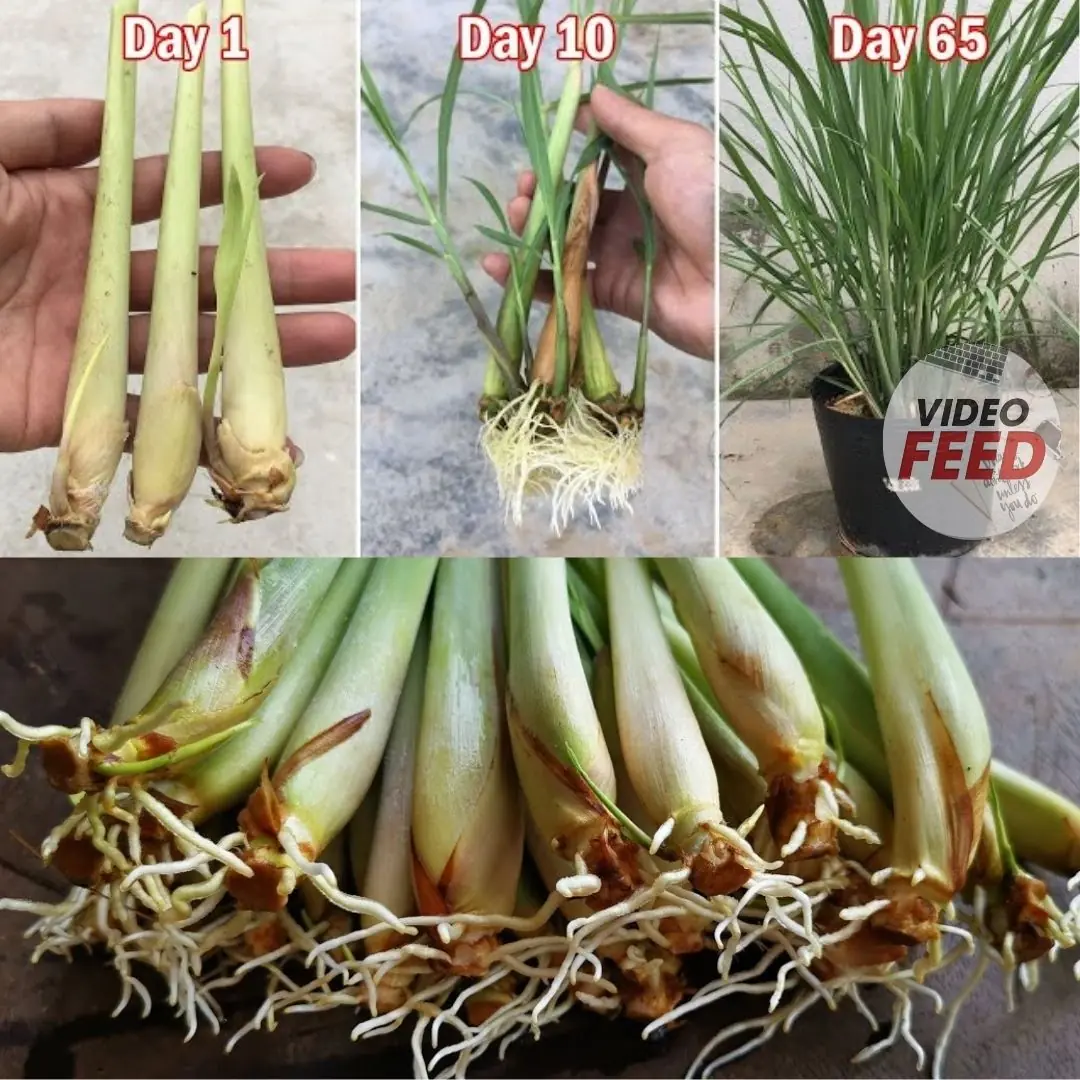

Secrets to growing lemongrass at home – easy to do, suitable for beginners

4 changes in fingers that could be signs of lung can.cer

Grow Your Own Asparagus Plants

Put them in your home and mice will run away

How to Grow a Pineapple at Home: Simple and Fast

For the Sake of Your Family’s Health, I Strongly Urge You to Get Rid of These 10 Items
