Pay Attention: 6 Foot Signs Linked to Serious Conditions
Diabetic neuropathy complications are one of the most common chronic complications of diabetes and also a major cause of diabetic foot disease.
Tetanus is an extremely dangerous bacterial infection that causes severe pain and has a high mortality rate. What is the most effective method for preventing infection? Let’s explore in the article below.
Tetanus is a highly dangerous bacterial infection caused by a powerful neurotoxin called tetanospasmin, produced by the bacterium Clostridium tetani. This bacterium typically thrives in wounds under anaerobic conditions. Tetanus is characterized by painful muscle stiffness that usually starts in the jaw muscles, facial muscles, and neck muscles before progressing to affect the whole body.
Clostridium tetani bacteria
Tetanus bacteria commonly live and grow in soil, animal feces, and anaerobic environments—these are the main sources of infection. Tetanus is not a contagious disease. The bacteria do not spread from person to person but can infect through open wounds that come into direct contact with contaminated environments. The bacteria enter the body through deep wounds contaminated with dirty soil, human or animal feces, crushed wounds, or unsterile injections.
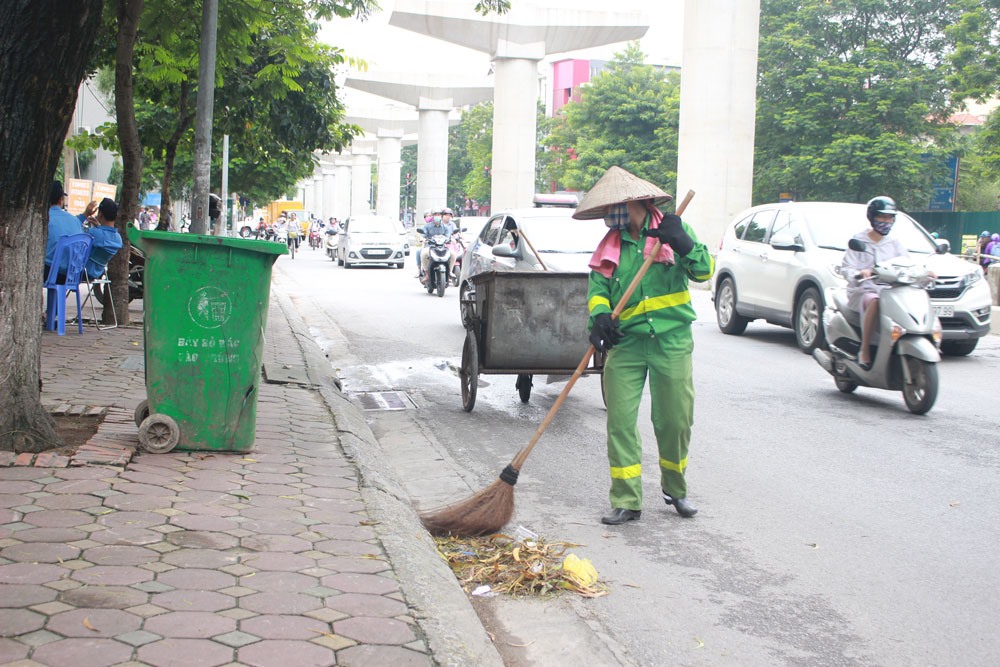

High-risk groups for tetanus infection include:
– Gardeners
– Environmental sanitation workers
– Poultry and livestock farm workers
– Construction workers
– Soldiers and youth volunteers
People at high risk of tetanus infection
In addition to the above causes, tetanus bacteria can also enter the body through surgical wounds, abortion procedures, or childbirth. Neonatal tetanus is commonly seen in newborns, usually appearing around two weeks after birth, with symptoms like refusal to breastfeed and full-body muscle stiffness. If not treated promptly, the risk of death is high.
The incubation period is from the time of injury to the first symptom of tetanus, typically jaw stiffness, occurring within 3 to 21 days. The length of the incubation period depends on the location and severity of the wound and the individual's health. On average, symptoms appear around day 7. The shorter the incubation period (under 7 days), the more severe the disease.
The onset stage begins when jaw stiffness first appears and lasts until the first seizure or throat and larynx spasms appear, usually within 1 to 7 days. A shorter onset (less than 48 hours) indicates a more severe illness.
Common symptoms during this stage include:
– Jaw fatigue
– Difficulty speaking
– Feeling of obstruction while swallowing
– Difficulty chewing
– Difficulty opening the mouth (lockjaw or trismus—a hallmark symptom)
Other muscle stiffness symptoms may include:
– Facial and jaw muscle stiffness causing a “forced grin” appearance
– Neck muscle stiffness causing the neck to tilt backward, with prominent sternocleidomastoid muscles
– Back muscle stiffness causing arching or straightening of the back
– Abdominal muscle stiffness, with noticeable firm abdominal muscles
– Chest and intercostal muscle stiffness
– Upper limb stiffness (arms remain bent)
– Lower limb stiffness (legs remain extended)
– Muscle stiffness triggered by stimuli, accompanied by sweating, restlessness, and high fever
This stage typically lasts for about 3 weeks, with symptoms including:
– Continuous full-body muscle stiffness, severe pain, and an arched back posture known as opisthotonos
– Laryngeal spasms causing cyanosis, difficulty breathing, and potentially respiratory failure or cardiac arrest
– Pharyngeal spasms causing swallowing difficulty and choking
– Sphincter spasms causing urinary and bowel retention
– Full-body seizures: the patient remains conscious, clenches fists, arches the back, bends arms, and extends legs; spasms can lead to respiratory and cardiac arrest
– Autonomic dysfunction: pale skin, profuse sweating, excessive salivation, high fever (39–40°C), unstable blood pressure, and cardiac arrest
A patient experiencing seizures being treated in a hospital
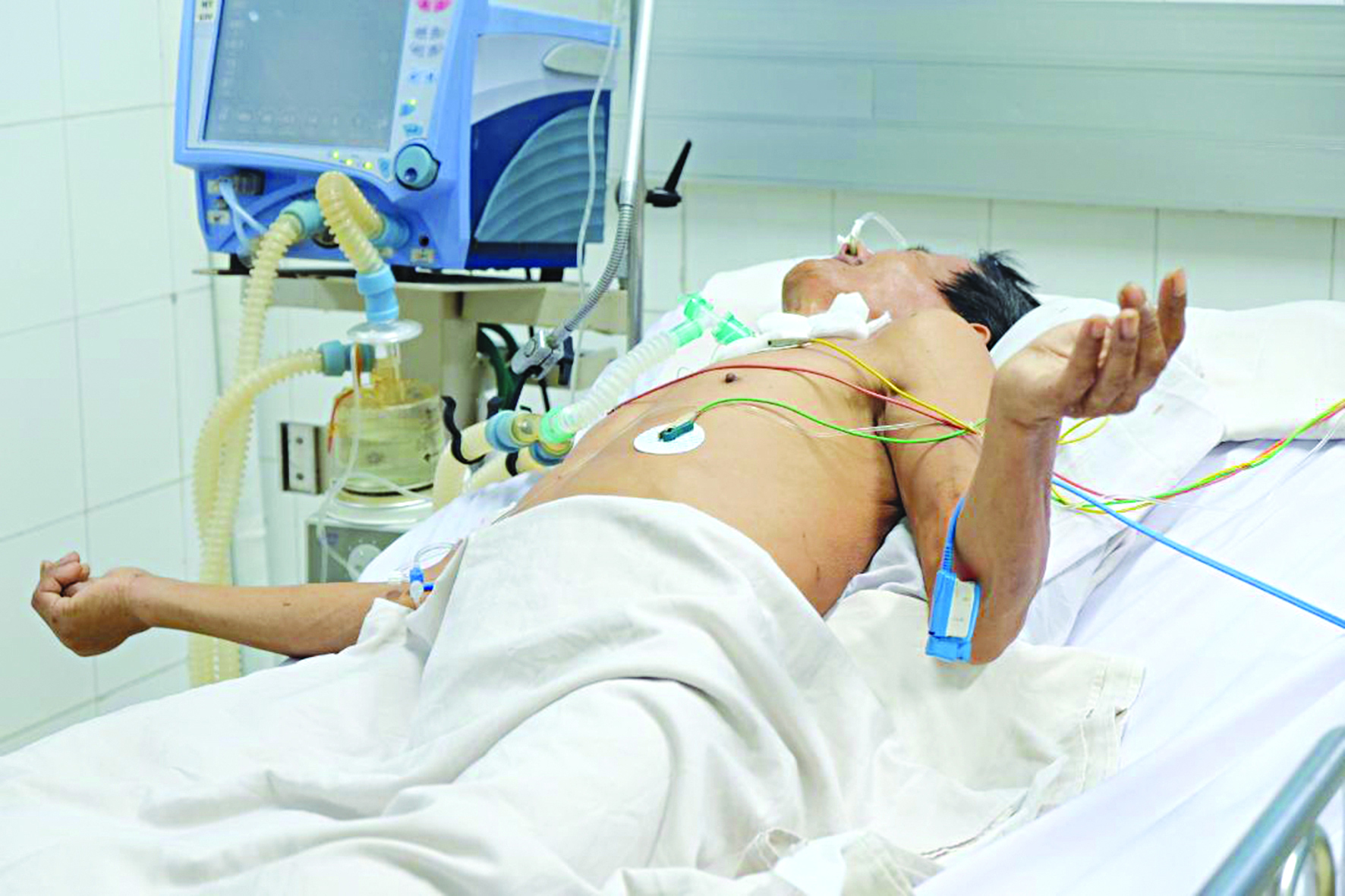
The recovery stage begins when the seizures reduce in severity and frequency, the mouth begins to open again, and the swallowing reflex returns. This period can last from several weeks to several months, depending on the severity of the disease.
If not detected and treated in time, tetanus can lead to serious complications with a guarded prognosis:
– Bone fractures: severe muscle spasms or seizures can cause bone fractures in extreme cases
– Pneumonia: respiratory infections from aspirated stomach contents can develop into pneumonia
– Seizures: if the infection spreads to the brain, epilepsy-like symptoms may appear
– Pulmonary embolism: blood clots in the lungs can disrupt respiratory and circulatory function; treatment may require oxygen and anticoagulants
– Severe kidney failure: intense muscle spasms can damage muscle tissue, releasing protein into the urine and potentially leading to kidney failure
– Cardiovascular complications: patients may experience erratic blood pressure, sudden drops, arrhythmia, or cardiac arrest
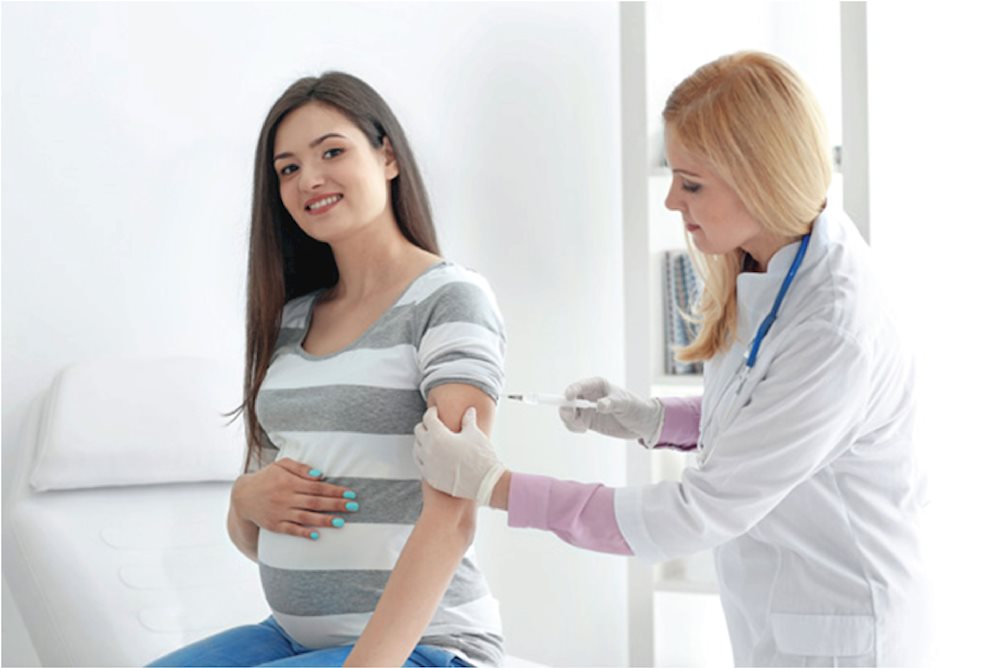
Experts agree that vaccination against tetanus is the most effective prevention method. Vaccination ensures temporary immunity from infection. The following groups are especially recommended to receive tetanus vaccines:
– Pregnant women and newborns: Vaccination during pregnancy is critical to protect both mother and baby, as neonatal tetanus has a mortality rate of up to 90%.
– Farmers: Due to frequent contact with soil and animal waste, farmers are at high risk of tetanus infection through open wounds.
– Factory workers: Workers often operate in less sanitary conditions, increasing their risk of infection. Vaccination helps greatly reduce this risk.
Vaccination against tetanus for pregnant women
Tetanus is a dangerous disease if contracted. However, with proper preventive care, you can build long-term immunity and worry less about open wound injuries.

Diabetic neuropathy complications are one of the most common chronic complications of diabetes and also a major cause of diabetic foot disease.
Bathing is a habit that helps clean the body and relax, but we should not always bathe immediately.

The Myth About Fruits Feeding Cancer Cells: A Critical Look at the Claims
Some unhealthy habits during intimacy may be a hidden cause of cervical cancer in women.
A hidden disease may grow silently — and one habit worsens it.
Garlic has long become an indispensable spice in the family kitchen.
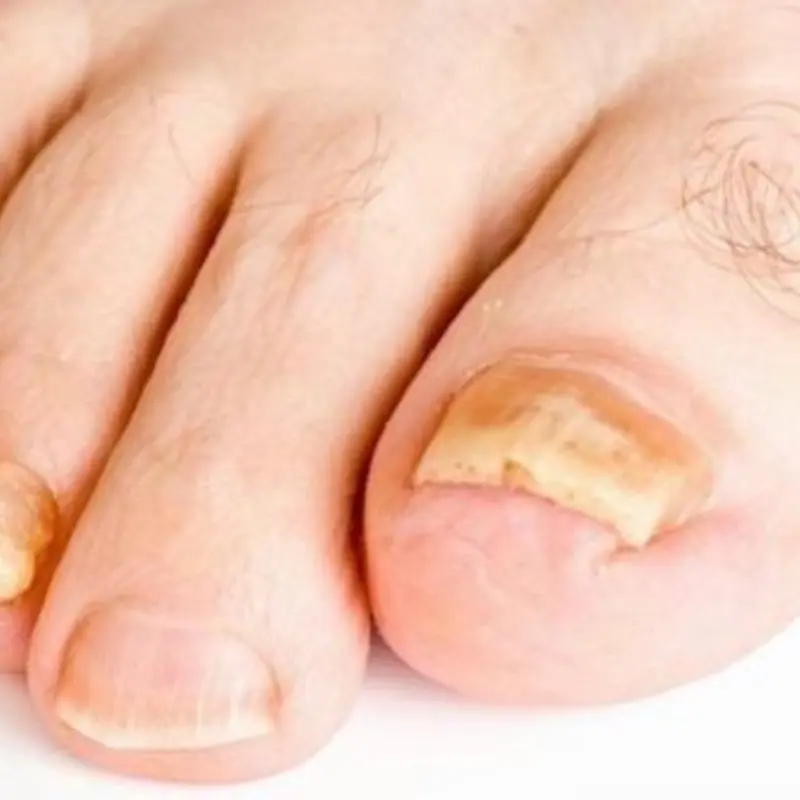
Two small changes in your feet may reveal serious hidden health risks.
Despite having a full night’s rest, many people still get up feeling sleepy and lacking energy.
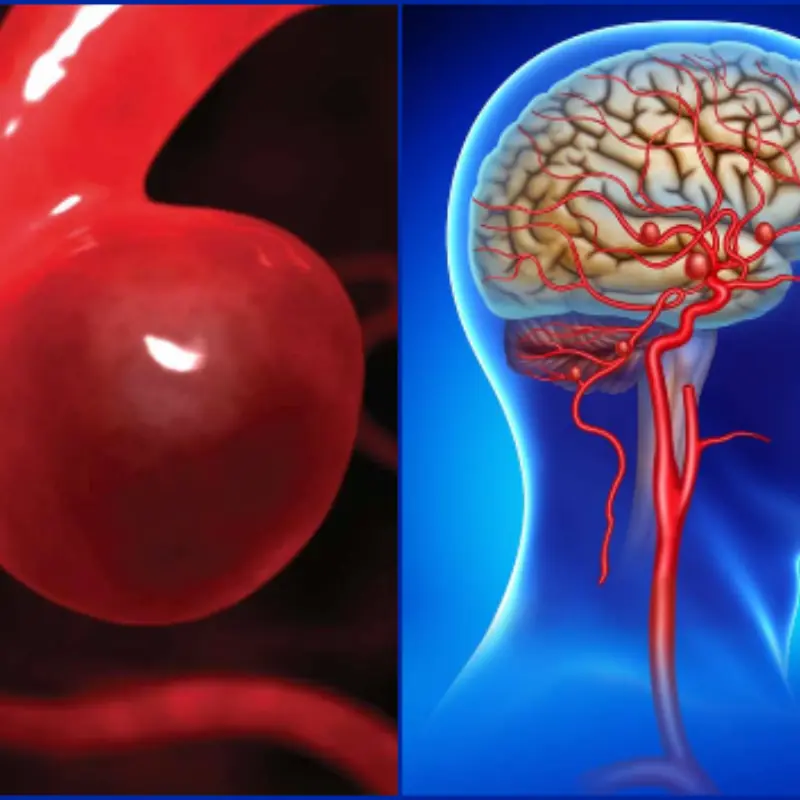
Hidden aneurysm signs can appear suddenly and turn life-threatening.
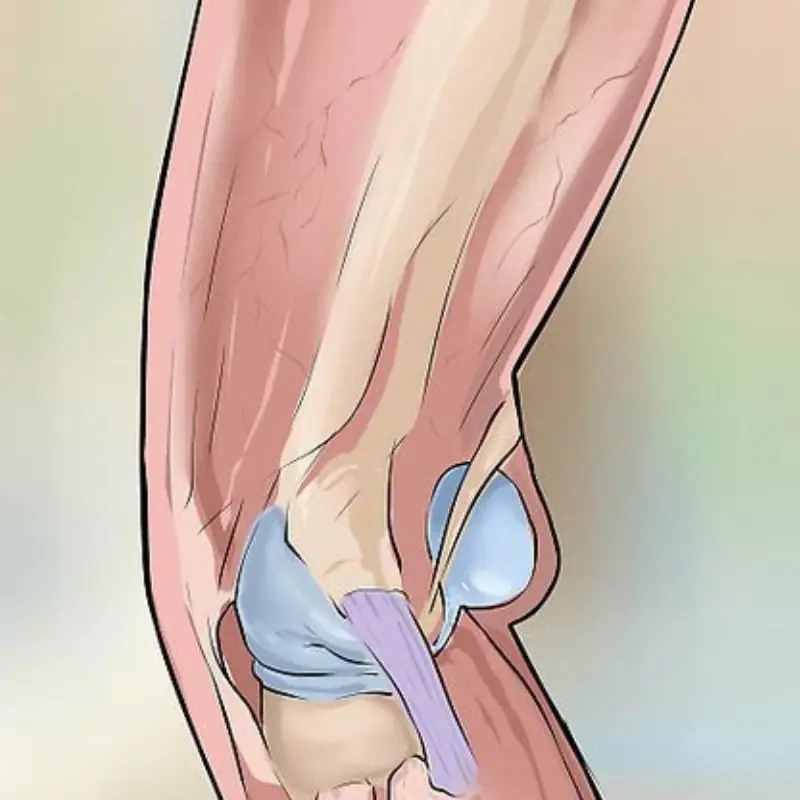
Pain behind the knee may signal hidden health risks—don’t ignore it.

Pay attention to these signs!
Almost no one knows about it, and it's more useful than you think
9 subtle warning signs of brain clots that may appear before a stroke
Doctors warn after woman develops sudden kidney failure post-dinner.
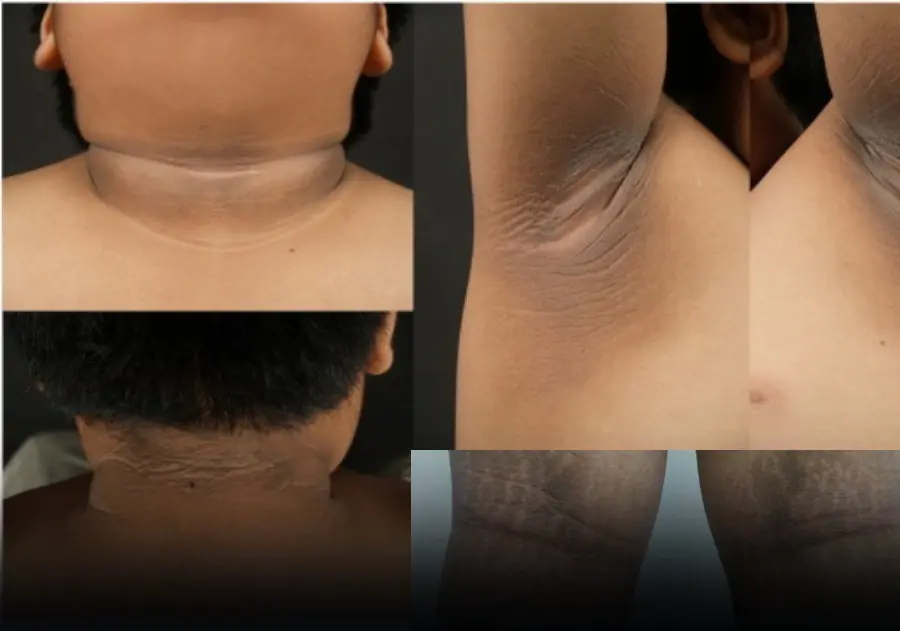
It commonly occurs in healthy people, but in some cases it can be a sign of an underlying disease.

Why You Should Drink Water on an Empty Stomach Immediately After Waking Up
Your eyes can reveal more than you think — even hidden signs of diabetes that often go unnoticed
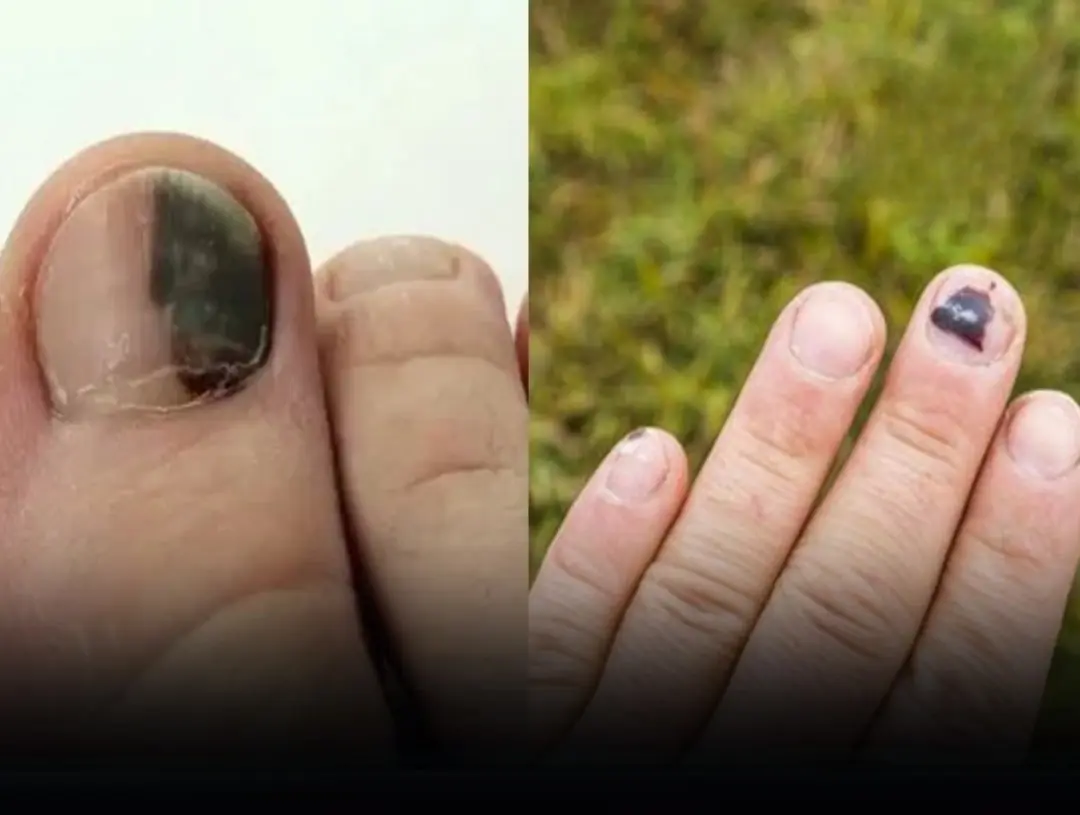
3 Subtle Limb Changes You Should Never Ignore
One spoon a day — and these 8 surprising benefits will transform your body
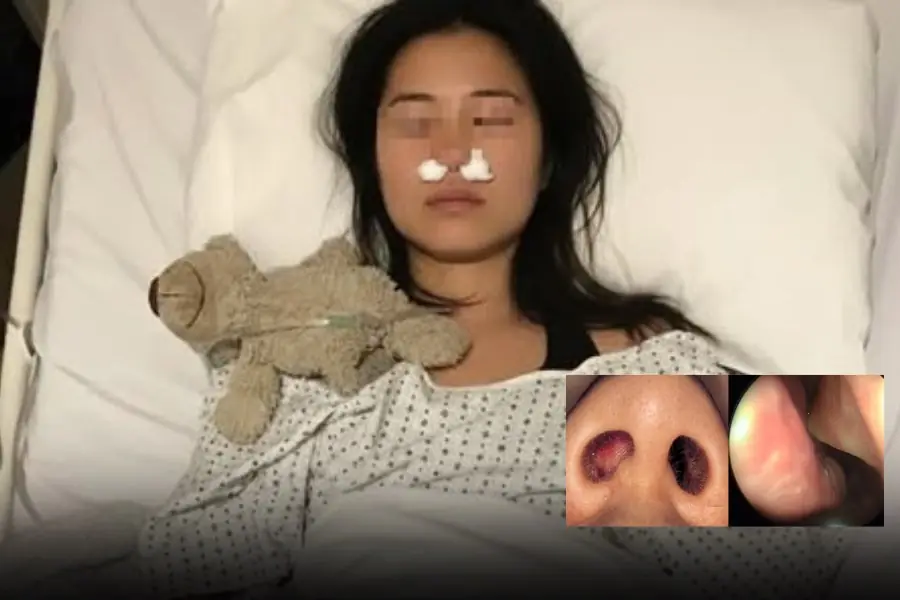
She grew a cluster of fungi in her nose — all because of a habit nearly everyone does daily

Diabetic neuropathy complications are one of the most common chronic complications of diabetes and also a major cause of diabetic foot disease.

Bathing is a habit that helps clean the body and relax, but we should not always bathe immediately.

The Myth About Fruits Feeding Cancer Cells: A Critical Look at the Claims

Some unhealthy habits during intimacy may be a hidden cause of cervical cancer in women.

A hidden disease may grow silently — and one habit worsens it.

Garlic has long become an indispensable spice in the family kitchen.

Two small changes in your feet may reveal serious hidden health risks.

Despite having a full night’s rest, many people still get up feeling sleepy and lacking energy.

Hidden aneurysm signs can appear suddenly and turn life-threatening.

Pain behind the knee may signal hidden health risks—don’t ignore it.

He Ordered in German to Humiliate the Waitress—But She Spoke Seven Languages

My Husband Started Taking Our Dog on Three-Hour “Walks” Every Night—Until I Checked Daisy’s GPS Colla

Pay attention to these signs!

I Let Them Think I Was a Freeloader—Until Thanksgiving Changed Everything

Twelve Julys of “The Islands”—And the Phone Call That Changed Everything

Almost no one knows about it, and it's more useful than you think

A millionaire’s unexpected discovery: how love, truth, and a child’s laughter changed everything

9 subtle warning signs of brain clots that may appear before a stroke

Penthouse Illusions: The Swipe That Ended Their Fantasy

Doctors warn after woman develops sudden kidney failure post-dinner.