
5 diseases that cause stomach pain after eating

5 Health Conditions That Cause Stomach Pain After Eating
Stomach pain after eating is a common symptom that can sometimes be a normal physiological response. However, if it happens frequently, lasts a long time, or is accompanied by other unusual symptoms, it could be a sign of underlying digestive disorders. Here are 5 health conditions to watch out for:
1. Gastric and Duodenal Ulcers
This is one of the most common causes of stomach pain after eating. Excess stomach acid released during or after meals can irritate ulcers on the stomach or duodenal lining, causing a burning pain in the upper abdomen, bloating, acid reflux, and nausea. The pain usually appears 30 minutes to 2 hours after eating.
2. Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
When the lower esophageal sphincter is weak, acid and food from the stomach can flow back into the esophagus, causing a burning pain behind the breastbone, bloating, nausea, acid reflux, and chest pain after eating, especially when lying down or bending over. GERD not only causes discomfort but can also lead to esophageal inflammation or complications if not treated.
3. Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
This is a chronic digestive disorder with no clear organic damage. People with IBS often experience abdominal pain accompanied by changes in bowel habits (diarrhea, constipation, or alternating between both). The pain typically occurs after eating and subsides after bowel movements. Stress, anxiety, and certain foods can worsen the condition.
4. Cholecystitis or Gallstones
After eating, especially fatty foods, the gallbladder contracts to release bile to help digest food. If there is inflammation or a blockage caused by gallstones, it can lead to severe pain in the upper right abdomen or upper middle abdomen, which may radiate to the right shoulder. This condition is often accompanied by nausea, fever, and jaundice, and requires prompt medical attention.
5. Acute or Chronic Pancreatitis
The pancreas helps digest fats and proteins. When it becomes inflamed, digestive enzymes are not secreted properly, leading to stomach pain after eating, especially after consuming fatty foods. The pain often occurs in the middle or left side of the abdomen and may radiate to the back. It is also associated with nausea, diarrhea, and weight loss.
When Should You See a Doctor?
If you experience recurring stomach pain after eating, persistent pain, or additional symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, weight loss, diarrhea, fever, or blood in stools, you should consult a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis. Early detection and treatment are important to prevent complications.
News in the same category
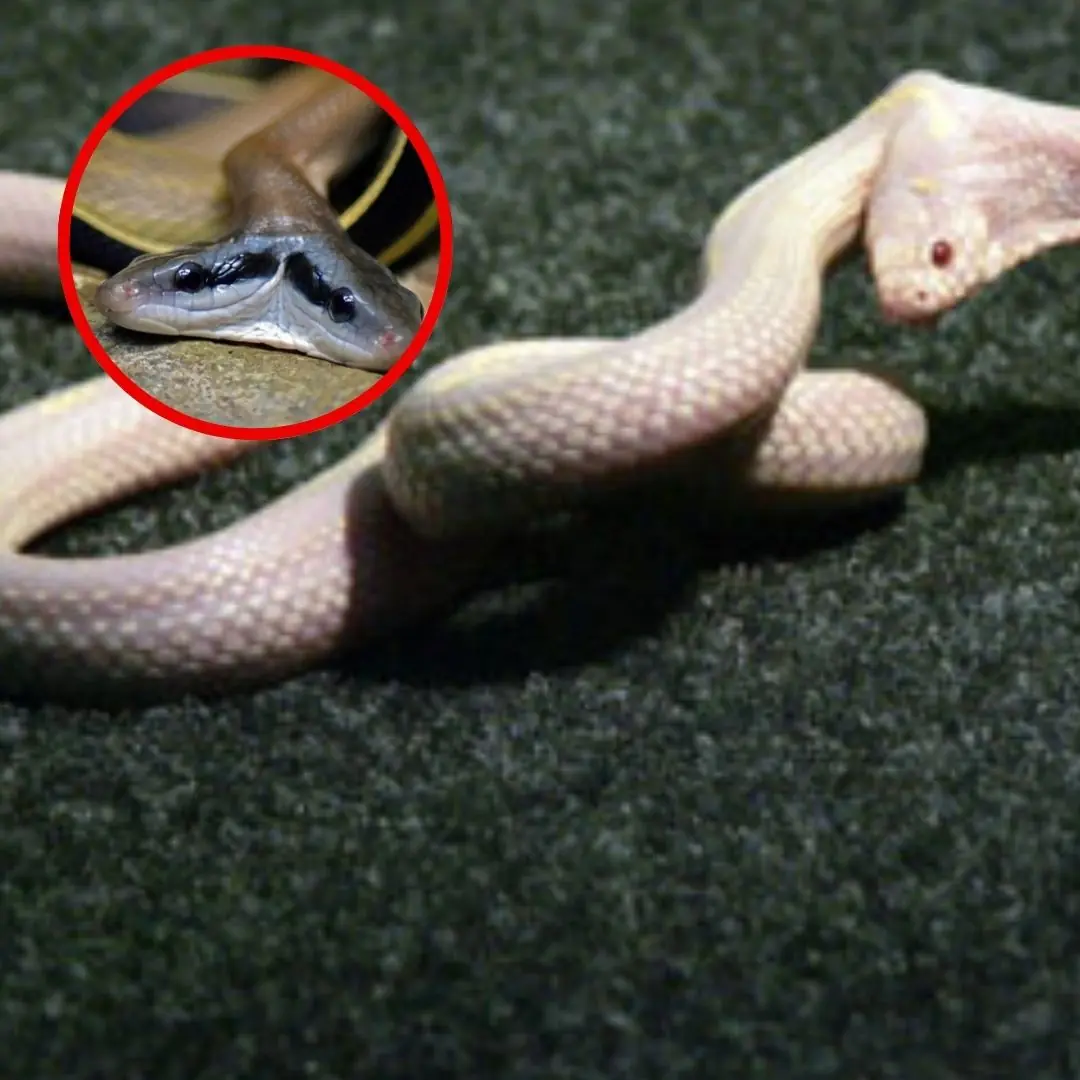


Are two-headed snakes real? Why does this phenomenon occur?

For the Sake of Your Family’s Health, I Strongly Urge You to Get Rid of These 10 Items
Should you brush your teeth before or after breakfast

More Than Just Leaves: The Hidden Healing Power of Fish Mint Roots

Don’t Dismiss This “Rustic” Dish – It’s a Stomach Healer and a Breakfast Hero!

Should you plug the phone in first or the charger first?

The “Dark Secret” of Thermos Bottles: Most People Use Them Without Knowing the Risks

"King of herbs" is good for the heart and breaks down kidney stones
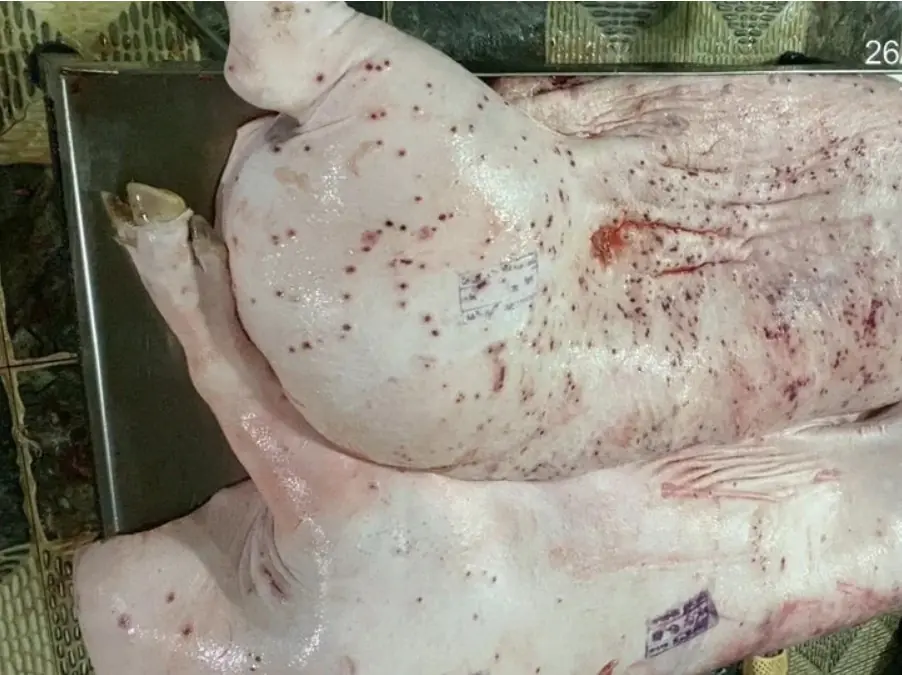
Sick pork can be used as fish feed, just "cook it and it's done": What do experts say?

Should you drink water that has been left overnight and uncovered?

What the small hole on a kn.ife is for?

Think Salmon Is the King of Omega-3? Think Again—This Humble Supermarket Fish Takes the Crown

Even if the Noodle Seller Denies It, This 5-Second Trick Will Reveal If Borax Is in Your Noodles

5 foods that are better off stored outside the fridge

Unexplained Phenomenon: Strange Signals Suspected Aliens Are Trying to Contact Earth?

Dirty Grout Between Bathroom Tiles? These 5 Simple Methods Will Restore the Shine With Minimal Effort

No More Watery or Dry Meat – Use This Drop Method to Defrost Fast and Keep It Fresh

Why smart people always do that?
News Post

Rub Ginger on the Soles of Your Feet Before Bed, and You’ll Experience Its “Miraculous” Health Benefits

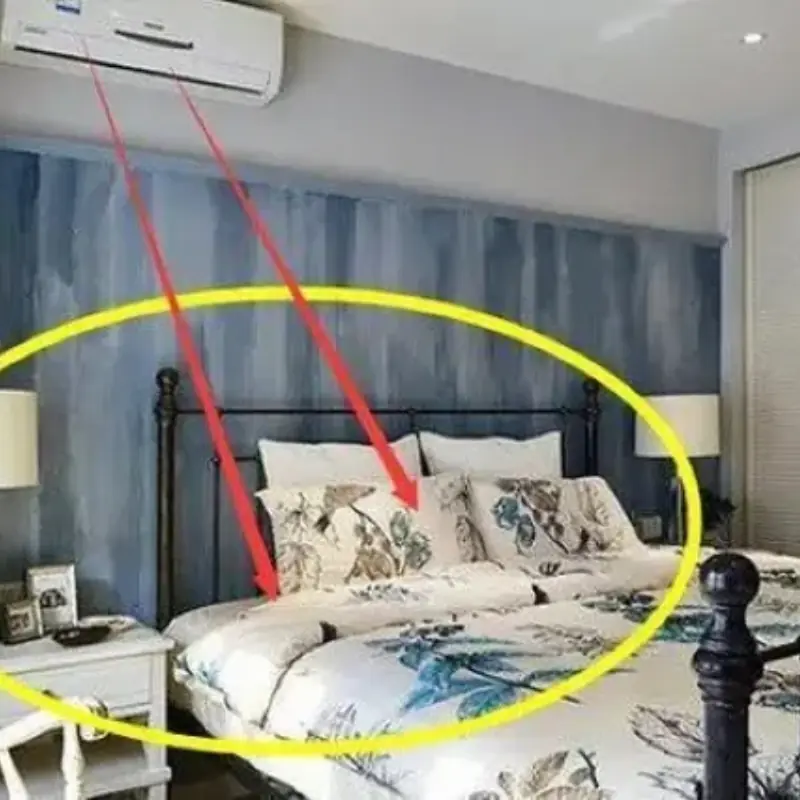
When Installing an Air Conditioner, Avoid These 4 Spots to Protect Your Family’s Health

10 Tips for Growing a Big Pepper Harvest
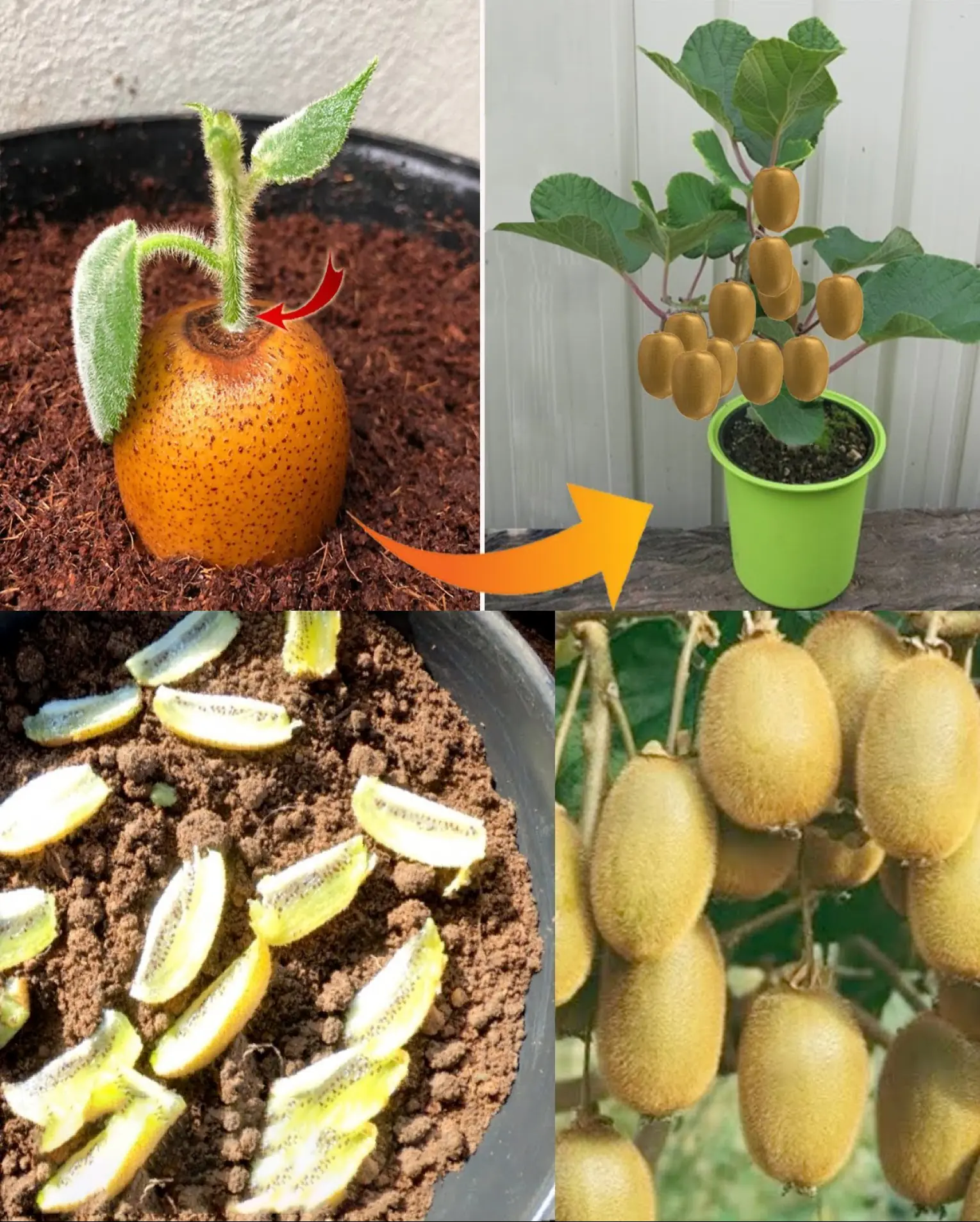

How to Grow Kiwi in Containers at Home
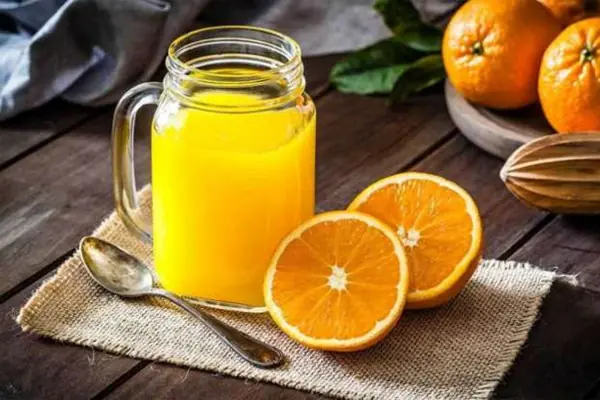

What happens to your body if you drink orange juice every day?
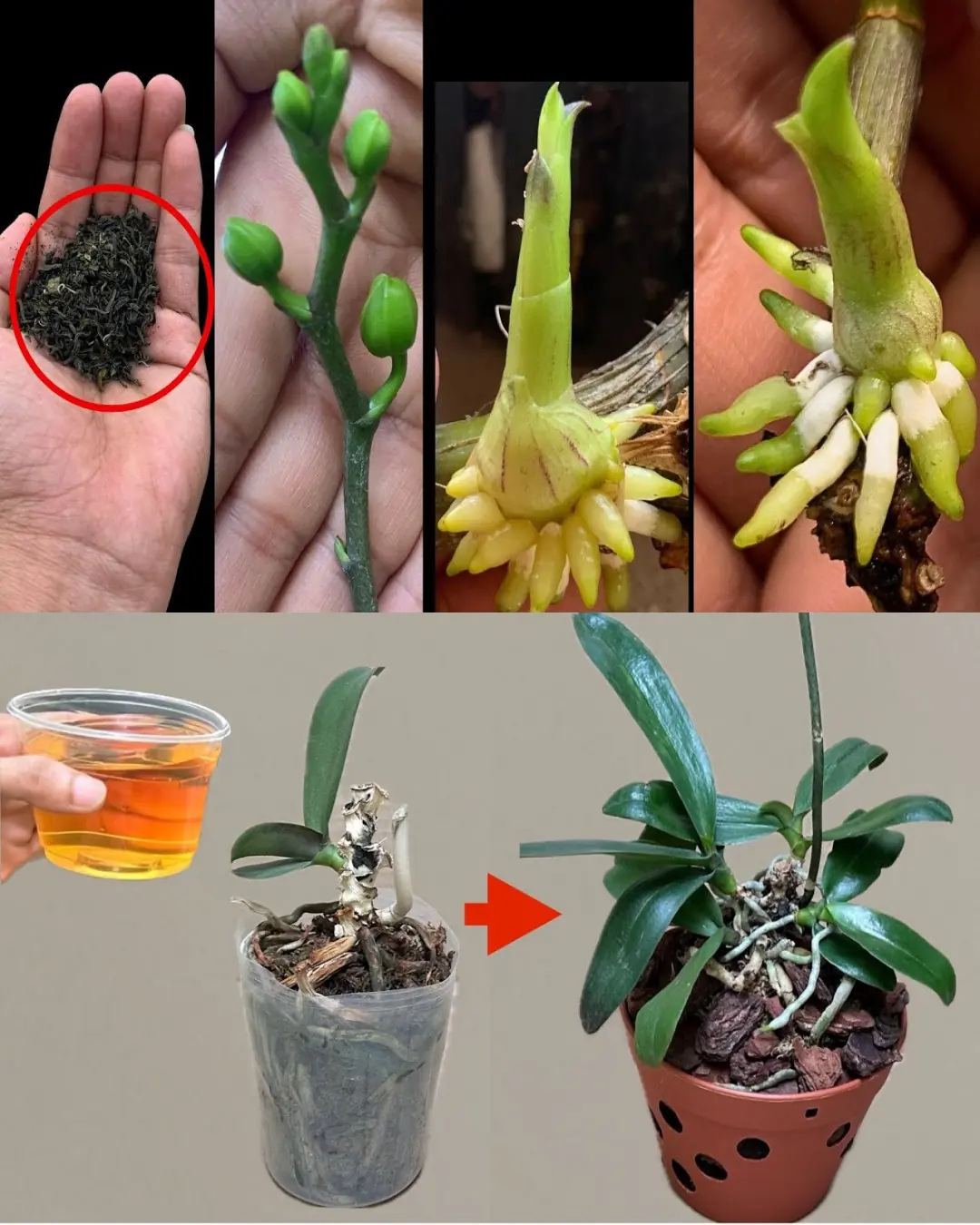

Revitalizing Orchids Using Tea: A Comprehensive Guide with Handy Tips

4 effective ways to ensure your home is free of cockroaches

Are two-headed snakes real? Why does this phenomenon occur?

A cup of hot water can offer many health benefits
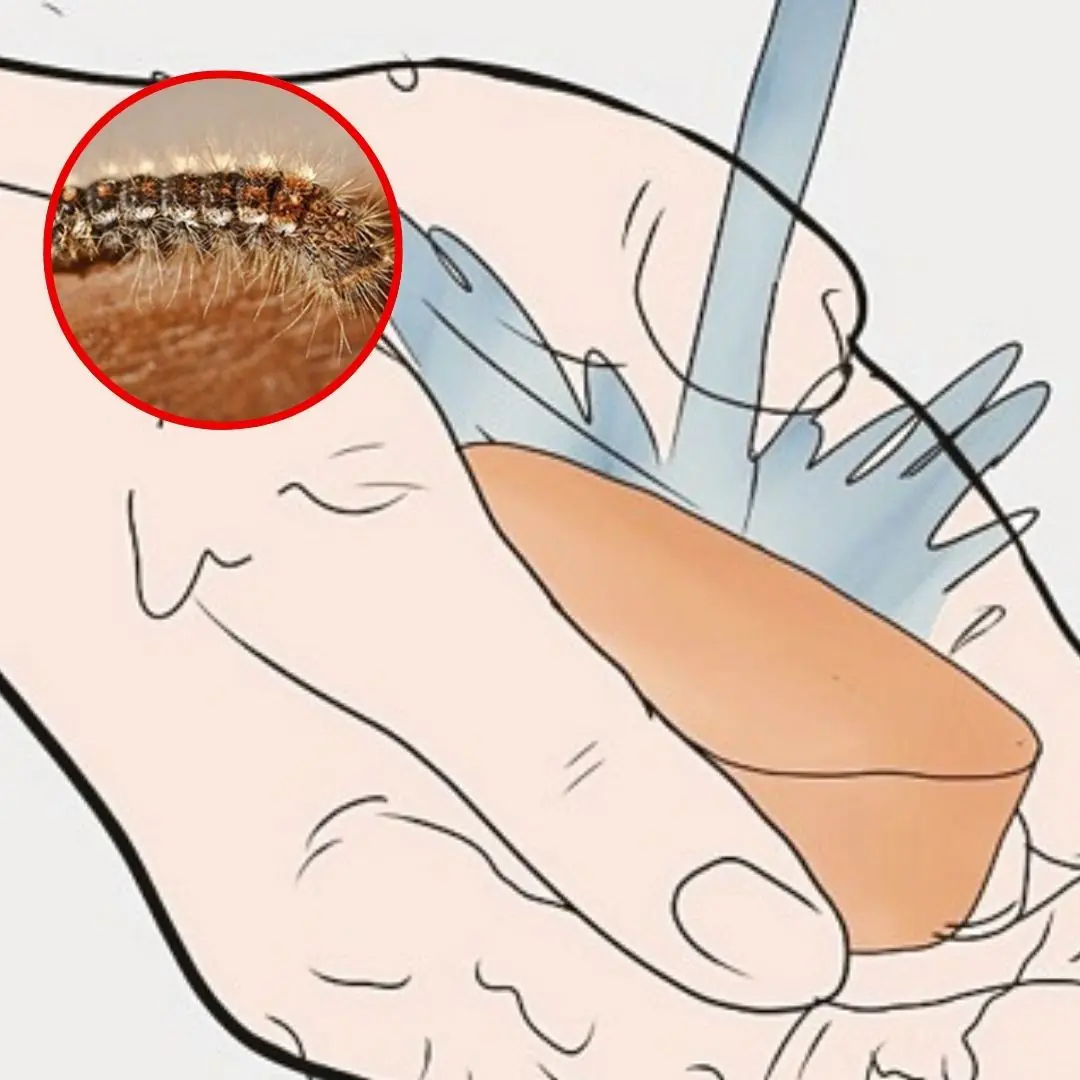
Caterpillar on you: 5 simple steps to treat at home
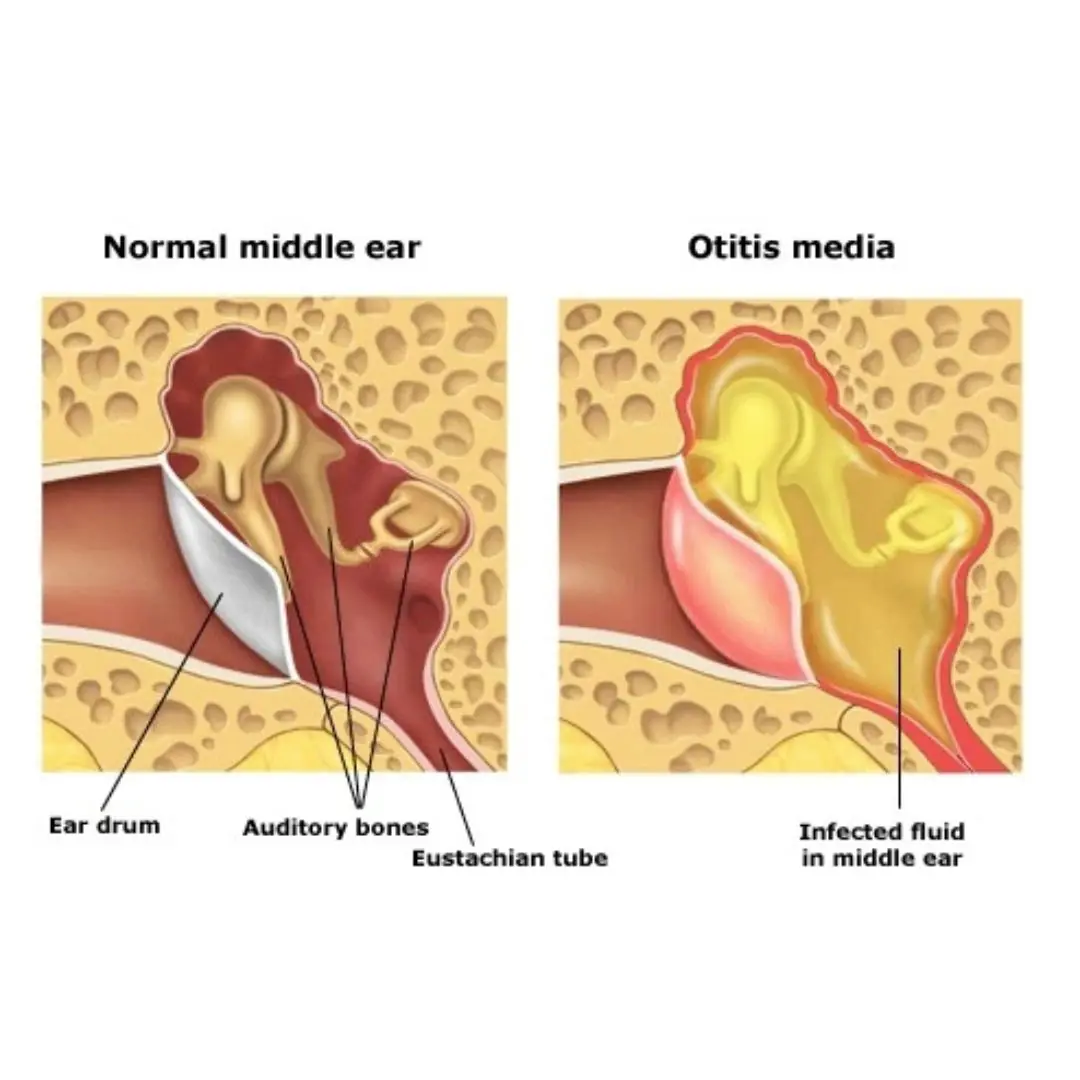
Otitis media – the “hidden culprit” causing vestibular disorders that many people ignore

Don't drink water before bed but still urinate at night, beware of these 3 diseases
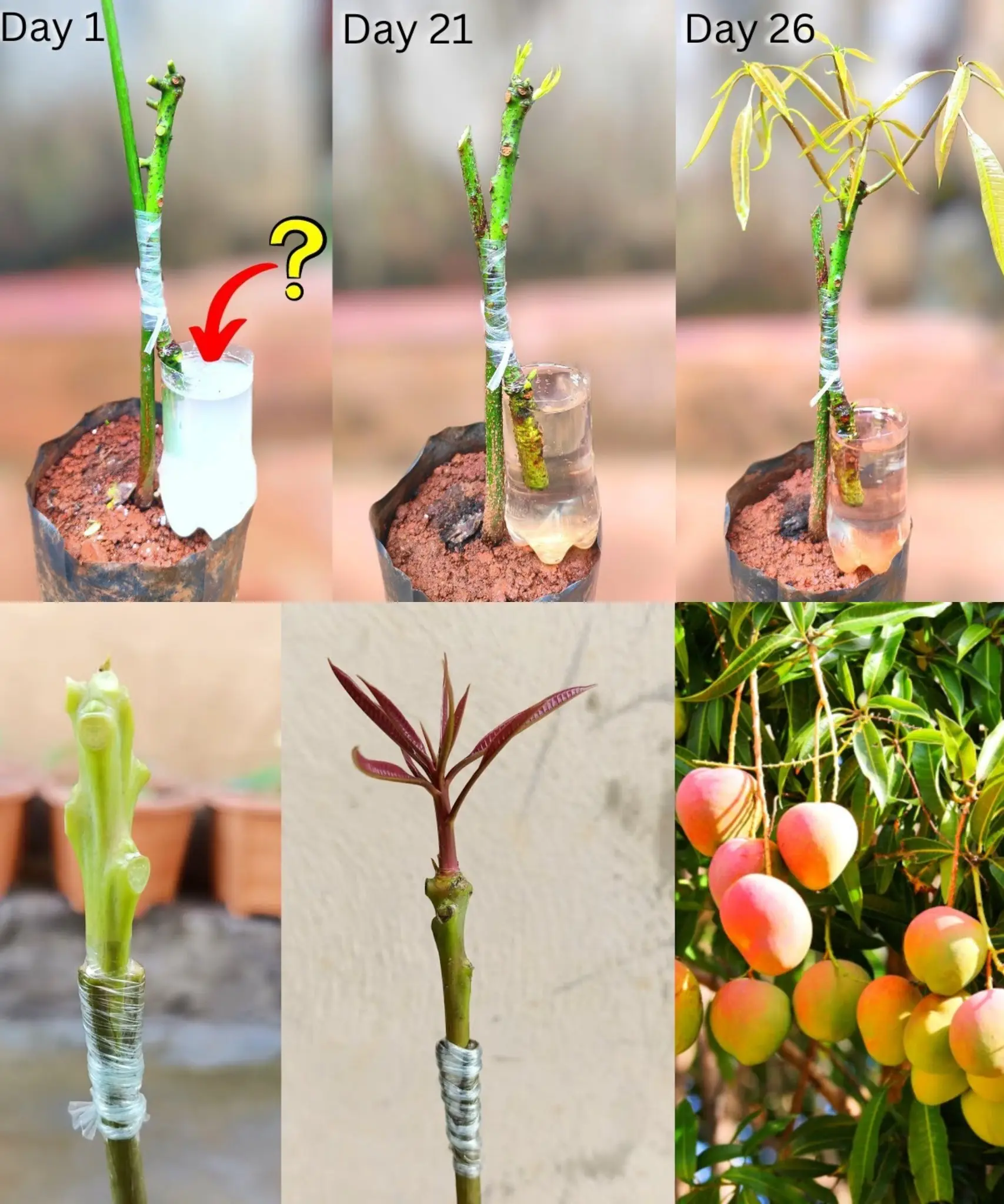

How to Plant a Mango Seed and Successfully Grow
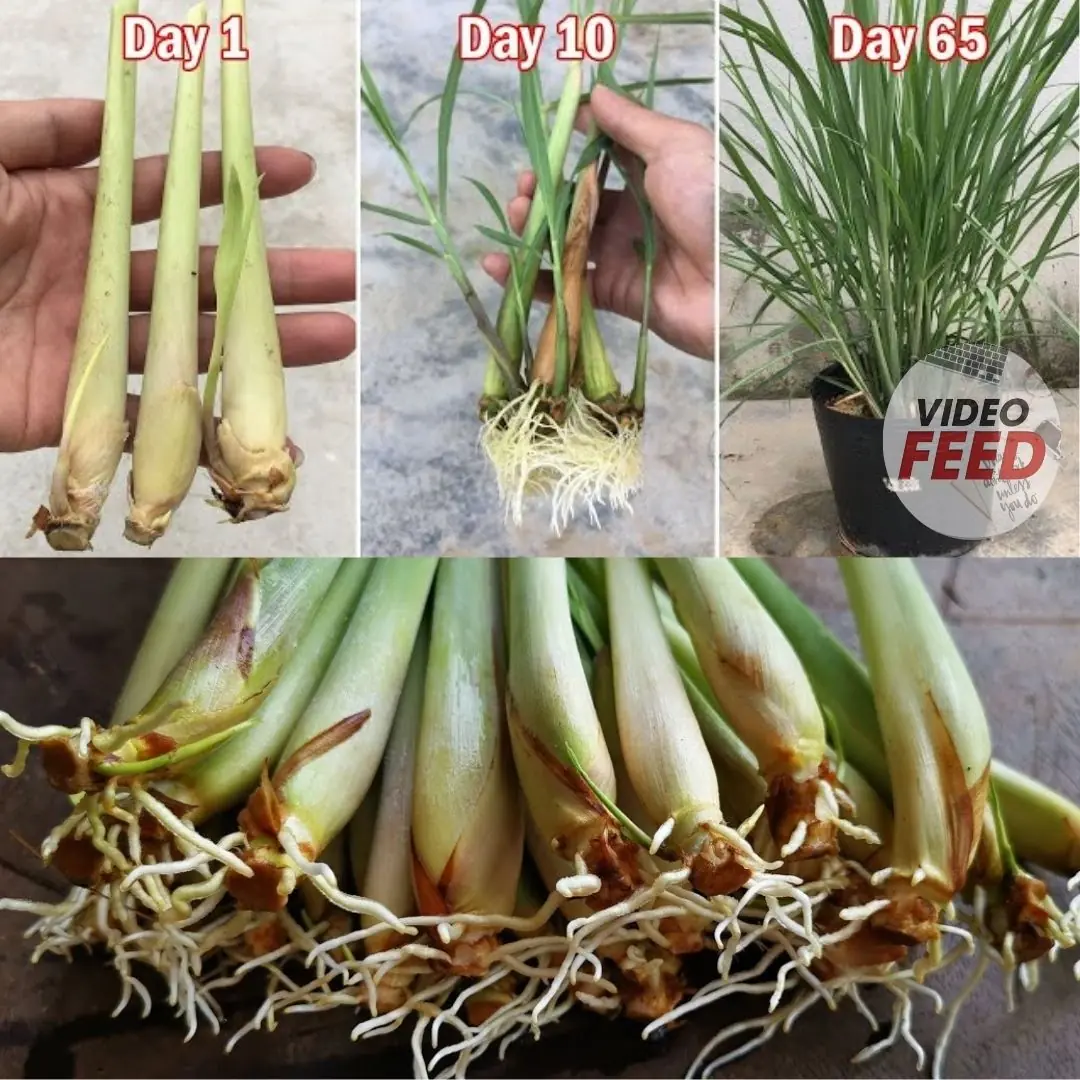

Secrets to growing lemongrass at home – easy to do, suitable for beginners

4 changes in fingers that could be signs of lung can.cer

Grow Your Own Asparagus Plants

Put them in your home and mice will run away

How to Grow a Pineapple at Home: Simple and Fast

For the Sake of Your Family’s Health, I Strongly Urge You to Get Rid of These 10 Items
