Heart Health Alert: 7 Silent Warning Signs You Should Never Ignore
Heart Health Alert: 7 Silent Warning Signs You Should Never Ignore
Is Moldy Food Still Edible If You Just Cut Off the Mold? Warning Signs Not Everyone Recognizes
Summer is the season when food safety deserves extra attention. Do you know how to properly handle moldy food?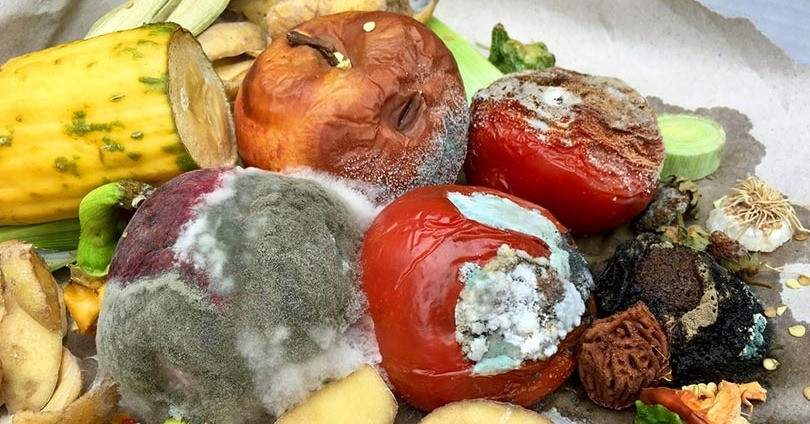
As soon as summer begins, temperatures can soar above 30°C, making fruits and vegetables prone to spoilage and mold after just a few days. Mold is a clear sign that food has deteriorated and, if not handled correctly, can pose serious health risks.
Food spoilage is the result of physical and chemical changes caused by environmental factors, which degrade quality, alter color, flavor, and reduce nutritional value. The main culprits are bacteria, mold, and natural enzymes in the food itself. In favorable conditions such as high temperature and humidity, these microorganisms thrive and break down proteins, fats, and starches — accelerating spoilage.
Beyond making food unappetizing, spoilage can also lead to the production of dangerous toxins. Consuming spoiled food may result in symptoms like nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, and in severe cases, food poisoning and even death. Proper food storage is essential for health protection and disease prevention.
Recognizing Spoiled Food by Smell and Taste
Spoiled food usually emits an unpleasant odor due to biological decomposition. Fats in cooking oil, butter, lard, baked goods, and oily seeds can oxidize, causing rancid smells, bitter tastes, and changes in texture and color.
Protein-rich foods like meat, fish, eggs, seafood, and tofu produce foul odors when decomposing due to compounds such as amines, sulfides, and aldehydes.
Carbohydrate-rich foods — cereals, fruits, vegetables, and sugars — tend to taste sour or smell slightly alcoholic due to fermentation, which produces organic acids and alcohol. Common signs include rotting fruit, sour baked goods, or moldy rice.
Foods like bread, steamed buns, and rice stored in warm and humid environments are prone to mold, often emitting a musty smell and potentially containing aflatoxin — a dangerous toxin harmful to health.
Dry seafood like shrimp, fish, and squid, if stored for too long, may develop a strong ammonia odor and turn pink. This indicates protein breakdown and the formation of toxic amines and nitrosamines — cancer-causing substances.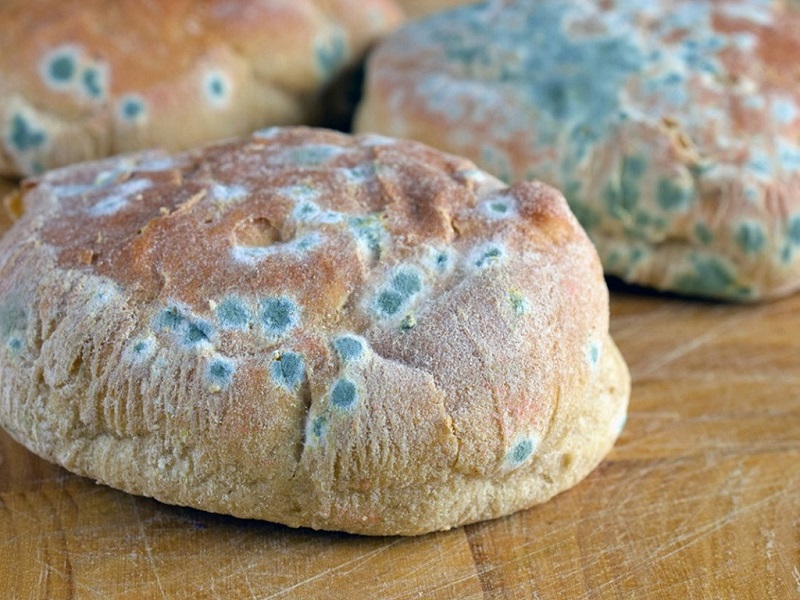
The Real Culprit Behind Mold
Mold thrives in warm and humid conditions, damaging food, clothes, and furniture. It forms thread-like structures that spread like spiderwebs and can grow even on non-nutritive surfaces if there is organic dust present.
Besides spoilage, mold also produces harmful toxins like aflatoxin (linked to liver cancer, often found in moldy grains and nuts) and patulin (found in moldy fruits, harmful to the digestive and nervous systems). Consuming mold-contaminated food poses serious health risks.
Many people try to salvage moldy food by cutting off the moldy part or reheating it, but this isn’t safe. Mold spores can spread throughout the food, and the toxins they produce are invisible and often odorless. Toxins like aflatoxin are heat-resistant and only destroyed at around 280°C, while regular cooking temperatures are around 100°C. The safest choice is to throw moldy food away.
In addition, mold can cause plant diseases and trigger allergies or illnesses in humans such as asthma, rhinitis, and dermatitis. It’s best to avoid contact with moldy food altogether.
Food That Should Be Discarded Immediately
Sprouted potatoes contain solanine, which is toxic.
Moldy sugarcane can produce neurotoxic mold.
Old spices may lose benefits and pose health risks.
Moldy peanuts and corn often carry aflatoxin and can cause cancer.
Spoiled seafood produces toxins that cause food poisoning.
Unhygienic fermented foods may lead to botulism.
Partially spoiled fruit usually means the whole fruit is contaminated.
Sweet potatoes with black spots can cause poisoning.
Rotten ginger may contain safrole, a liver toxin and potential carcinogen.
Tips to Prevent Food Spoilage
Buy smart: Choose ingredients based on your household’s needs. Check the production and expiration dates.
Store properly: Keep food in dry, cool, well-ventilated places. Store grains in airtight containers and vegetables in the refrigerator.
Clean regularly: Disinfect storage areas, inspect food frequently, and discard any moldy items.
Choose reputable brands: This reduces the risk of contamination from mold toxins.

Heart Health Alert: 7 Silent Warning Signs You Should Never Ignore
If You’re Getting Bruises Without Injury, Here’s What Your Body Might Be Telling You

5 Types of People Who Should Limit Eating Eggs — And the Reasons Why
Doctors Explain Why Your Throat Feels Mucusy and Sticky
Waking Up With These 4 Symptoms? Doctors Say It Could Be a Sign of Advancing Lung Cancer

7 Subtle Symptoms Many Women Ignore — But They Could Be Warning Signs of a Stroke
If Your Heel Hurts When You Wake Up or After Standing for a Long Time
In everyday routines, women tend to be highly mindful of personal hygiene, particularly intimate care
One Month Before a Heart Attack, Your Body May Warn You With These 7 Signs
Wives’ bre.ast can.cer risk linked to husbands’ unhealthy habits

Stretch Your Ring Finger With Your Thumb for a Few Seconds — You’ll Love the Reason
Learn how people-pleasing affects your health and triggers autoimmune disorders—details in the comments below!.....

Boiled eggs in the morning may offer surprising health benefits.

9 Silent Warning Signs of a Brain Blo:od Clot
11 Warning Signs You Shouldn’t Ignore
Do These 6 Simple Things Before It Gets Worse

3 Foods You Should Never Eat Together with Eggs for Better Health

Why Pumpkin Seeds Are So Good for You: 11 Proven Benefits

If you often experience bloating or constipation, you don’t necessarily have to rely on laxatives.

Heart Health Alert: 7 Silent Warning Signs You Should Never Ignore

If You’re Getting Bruises Without Injury, Here’s What Your Body Might Be Telling You

5 Types of People Who Should Limit Eating Eggs — And the Reasons Why

Doctors Explain Why Your Throat Feels Mucusy and Sticky

The Best Methods to Get Rid of the Wax Coating on Apples

Waking Up With These 4 Symptoms? Doctors Say It Could Be a Sign of Advancing Lung Cancer

This common food found in many homes may carry hidden health risks if eaten too often.

7 Subtle Symptoms Many Women Ignore — But They Could Be Warning Signs of a Stroke

If Your Heel Hurts When You Wake Up or After Standing for a Long Time

Make Your Tiles Look Brand New with These Free Home Cleaning Tips

In everyday routines, women tend to be highly mindful of personal hygiene, particularly intimate care

One Month Before a Heart Attack, Your Body May Warn You With These 7 Signs

Wives’ bre.ast can.cer risk linked to husbands’ unhealthy habits

Stretch Your Ring Finger With Your Thumb for a Few Seconds — You’ll Love the Reason

Learn how people-pleasing affects your health and triggers autoimmune disorders—details in the comments below!.....

Boiled eggs in the morning may offer surprising health benefits.

9 Silent Warning Signs of a Brain Blo:od Clot

11 Warning Signs You Shouldn’t Ignore

Do These 6 Simple Things Before It Gets Worse

3 Foods You Should Never Eat Together with Eggs for Better Health